ASA: Send Network Traffic from the ASA to the AIP SSM Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for how to send network traffic that passes through the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) to the Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Module (AIP-SSM) (IPS) module. Configuration examples are provided with the command line interface (CLI).
Refer to ASA: Send Network Traffic from the ASA to the CSC-SSM Configuration Example in order to send network traffic from the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) to the Content Security and Control Security Services Module (CSC-SSM).
Refer to Assigning Virtual Sensors to a Security Context (AIP SSM Only) for more information on how to send network traffic that passes through the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) in multiple context mode to the Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Module (AIP-SSM) (IPS) module.
Note: Network traffic that traverses the ASA includes internal users who access the Internet or Internet users who access resources protected by ASA in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) or inside network. Network traffic sent to and from the ASA is not sent to the IPS module for inspection. An example of traffic not sent to the IPS module includes pinging (ICMP) the ASA interfaces or Telnetting to the ASA.
Note: Modular Policy Framework used by the ASA in order to classify traffic for inspection does not support IPv6. So if you divert the IPv6 traffic to the AIP SSM through ASA, it is not supported.
Note: For more information on initial Configuration of AIP-SSM, refer to Initial Configuration of the AIP-SSM Sensor.
Prerequisites
Requirements
This document assumes that the audience has a basic understanding of how to configure Cisco ASA software version 8.x and IPS software version 6.x.
-
Necessary configuration components for ASA 8.x include interfaces, access-lists, network address translation (NAT), and routing.
-
Necessary configuration components for AIP-SSM (IPS software 6.x) include network setup, allowed hosts, interface configuration, signature definitions, and event action rules.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
ASA 5510 with software version 8.0.2
-
AIP-SSM-10 with IPS software version 6.1.2
Note: This configuration example is compatible with any Cisco ASA 5500 Series Firewall with OS 7.x and later and the AIP-SSM module with IPS 5.x and later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
The IP addressing schemes used in this configuration are not legally routable on the Internet. They are RFC 1918 ![]() addresses which have been used in a lab environment.
addresses which have been used in a lab environment.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
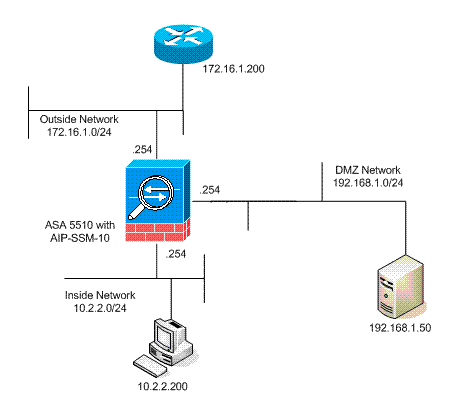
Initial Configurations
This document uses these configurations. Both the ASA and AIP-SSM start with a default configuration but have specific changes made for testing purposes. Additions are noted in the configuration.
| ASA 5510 |
|---|
ciscoasa#show running-config : Saved : ASA Version 8.0(2) ! hostname ciscoasa enable password 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted names ! !--- IP addressing is added to the default configuration. interface Ethernet0/0 nameif outside security-level 0 ip address 172.16.1.254 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 nameif inside security-level 100 ip address 10.2.2.254 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/2 nameif dmz security-level 50 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ! interface Management0/0 nameif management security-level 0 ip address 172.22.1.160 255.255.255.0 management-only ! passwd 9jNfZuG3TC5tCVH0 encrypted ftp mode passive !--- Access lists are added in order to allow test !--- traffic (ICMP and Telnet). access-list acl_outside_in extended permit icmp any host 172.16.1.50 access-list acl_inside_in extended permit ip 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 any access-list acl_dmz_in extended permit icmp 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 any pager lines 24 !--- Logging is enabled. logging enable logging buffered debugging mtu outside 1500 mtu inside 1500 mtu dmz 1500 mtu management 1500 asdm image disk0:/asdm-613.bin no asdm history enable arp timeout 14400 !--- Translation rules are added. global (outside) 1 172.16.1.100 global (dmz) 1 192.168.1.100 nat (inside) 1 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 static (dmz,outside) 172.16.1.50 192.168.1.50 netmask 255.255.255.255 static (inside,dmz) 10.2.2.200 10.2.2.200 netmask 255.255.255.255 !--- Access lists are applied to the interfaces. access-group acl_outside_in in interface outside access-group acl_inside_in in interface inside access-group acl_dmz_in in interface dmz timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02 timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00 timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute http server enable http 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 dmz no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 ! class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters message-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy !--- Out-of-the-box default configuration includes !--- policy-map global_policy. class inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map inspect ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect netbios inspect rsh inspect rtsp inspect skinny inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect sunrpc inspect tftp inspect sip inspect xdmcp ! service-policy global_policy global !--- Out-of-the-box default configuration includes !--- the service-policy global_policy applied globally. prompt hostname context . : end |
| AIP SSM (IPS) |
|---|
AIP-SSM#show configuration ! ------------------------------ ! Version 6.1(2) ! Current configuration last modified Mon Mar 23 21:46:47 2009 ! ------------------------------ service interface exit ! ------------------------------ service analysis-engine virtual-sensor vs0 physical-interface GigabitEthernet0/1 exit exit ! ------------------------------ service authentication exit ! ------------------------------ service event-action-rules rules0 !--- The variables are defined. variables DMZ address 192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255 variables IN address 10.2.2.0-10.2.2.255 exit ! ------------------------------ service host network-settings !--- The management IP address is set. host-ip 172.22.1.169/24,172.22.1.1 host-name AIP-SSM telnet-option disabled access-list x.x.0.0/16 !--- The access list IP address is removed from the configuration !--- because the specific IP address is not relevant to this document. exit time-zone-settings offset -360 standard-time-zone-name GMT-06:00 exit summertime-option recurring offset 60 summertime-zone-name UTC start-summertime month april week-of-month first day-of-week sunday time-of-day 02:00:00 exit end-summertime month october week-of-month last day-of-week sunday time-of-day 02:00:00 exit exit exit ! ------------------------------ service logger exit ! ------------------------------ service network-access exit ! ------------------------------ service notification exit ! ------------------------------ service signature-definition sig0 !--- The signature is modified from the default setting for testing purposes. signatures 2000 0 alert-severity high engine atomic-ip event-action produce-alert|produce-verbose-alert exit alert-frequency summary-mode fire-all summary-key AxBx exit exit status enabled true exit exit !--- The signature is modified from the default setting for testing purposes. signatures 2004 0 alert-severity high engine atomic-ip event-action produce-alert|produce-verbose-alert exit alert-frequency summary-mode fire-all summary-key AxBx exit exit status enabled true exit exit !--- The custom signature is added for testing purposes. signatures 60000 0 alert-severity high sig-fidelity-rating 75 sig-description sig-name Telnet Command Authorization Failure sig-string-info Command authorization failed sig-comment signature triggers string command authorization failed exit engine atomic-ip specify-l4-protocol yes l4-protocol tcp no tcp-flags no tcp-mask exit specify-payload-inspection yes regex-string Command authorization failed exit exit exit exit exit ! ------------------------------ service ssh-known-hosts exit ! ------------------------------ service trusted-certificates exit ! ------------------------------ service web-server enable-tls true exit AIP-SSM# |
Note: If you are unable access the AIP-SSM module with https, then complete these steps:
-
Configure a management IP address for the module. And you can configure the network access list, in which you specify the IPs/IP networks that are allowed to connect to the management IP.
-
Make sure that you have connected the external Ethernet interface of the AIP module. Management access to the AIP module is possible through this interface only.
Refer to Initializing AIP-SSM for more information.
Inspect All Traffic with the AIP-SSM in inline or promiscous mode
The network administrators and company senior management often indicate that everything needs to be monitored. This configuration meets the requirement to monitor everything. In addition to monitoring everything, two decisions need to be made about how the ASA and AIP-SSM interact.
-
Is the AIP-SSM module to function or be deployed in promiscuous or inline mode?
-
Promiscuous mode means that a copy of the data is sent to the AIP-SSM while the ASA forwards the original data on to the destination. The AIP-SSM in promiscuous mode can be considered to be an intrusion detection system (IDS). In this mode, the trigger packet (the packet that causes the alarm) can still reach the destination. Shunning can take place and stop additional packets from reaching the destination, however the trigger packet is not stopped.
-
Inline mode means that the ASA forwards the data to the AIP-SSM for inspection. If the data passes AIP-SSM inspection, the data returns to the ASA in order to continue being processed and sent to the destination. The AIP-SSM in inline mode can be considered to be an intrusion prevention system (IPS). Unlike promiscuous mode, inline mode (IPS) can actually stop the trigger packet from reaching the destination.
-
-
In the event that the ASA is not able to communicate with the AIP-SSM, how should the ASA handle to-be-inspected traffic? Examples of instances when the ASA is not able to communicate with AIP-SSM include AIP-SSM reloads or if the module fails and needs replacement. In this case the ASA can fail-open or fail-closed.
-
Fail-open allows the ASA to continue to pass to-be-inspected traffic to the final destination if the AIP-SSM cannot be reached.
-
Fail-closed blocks to-be-inspected traffic when the ASA cannot communicate with the AIP-SSM.
Note: The to-be-inspected traffic is defined with the use of an access-list. In this example output, the access-list permits all IP traffic from any source to any destination. Therefore, to-be-inspected traffic can be anything that passes through the ASA.
-
ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips permit ip any any ciscoasa(config)#class-map ips_class_map ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match access-list traffic_for_ips !--- The match any command can be used in place of !--- the match access-list [access-list name] command. !--- In this example, access-list traffic_for_ips permits !--- all traffic. The match any command also !--- permits all traffic. You can use either configuration. !--- When you define an access-list, it can ease troubleshooting. ciscoasa(config)#policy-map global_policy !--- Note that policy-map global_policy is a part of the !--- default configuration. In addition, policy-map global_policy !--- is applied globally with the service-policy command. ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class ips_class_map ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#ips inline fail-open !--- Two decisions need to be made. !--- First, does the AIP-SSM function !--- in inline or promiscuous mode? !--- Second, does the ASA fail-open or fail-closed? ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#ips promiscous fail-open !--- If AIP-SSM is in promiscous mode, issue !--- the no ips promiscous fail-open command !--- in order to negate the command and then use !--- the ips inline fail-open command.
Inspect All Traffic with the AIP-SSM using ASDM
Complete these steps in order to inspect all traffic with AIP-SSM that uses ASDM:.
-
Choose Configuration > IPS > Sensor Setup > Startup Wizard in ASDM home page to start the configuration, as shown:
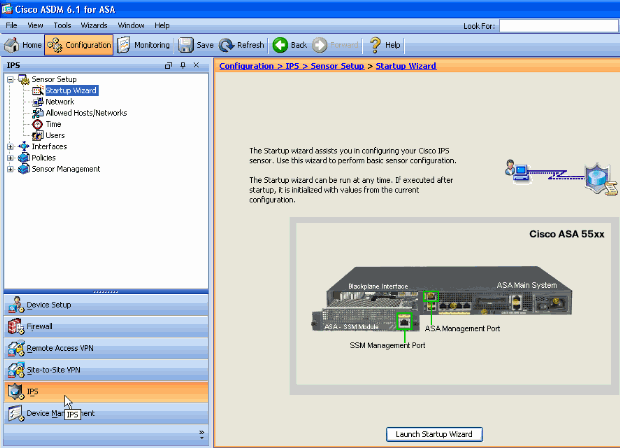
-
Click Launch Startup Wizard.
-
Click Next in the new window that comes up after you launch the startup wizard.
-
In the new window, provide the Host Name, IP Address, Subnet Mask and the Default Gateway address for the AIP-SSM module in the respective space provided under the Network settings section. Then click Add in order to add the access-lists to allow all traffic with AIP-SSM.
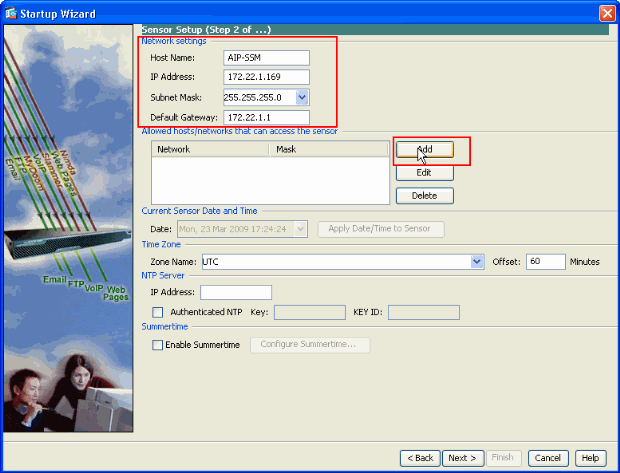
-
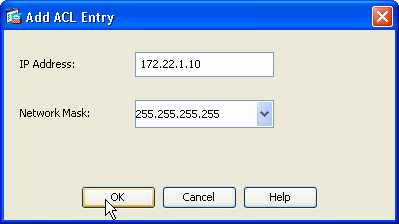
In the Add ACL Entry window provide the IP Address and the Network Mask details of the hosts/networks to be allowed to access the sensor. Click OK.
Note: The Host/Network IP address should belong to the Management Network address Range.
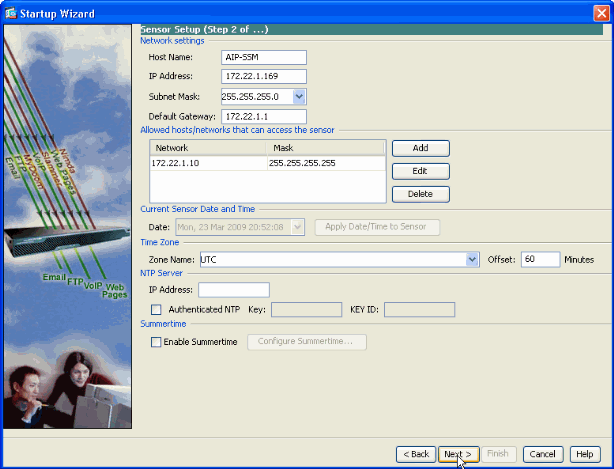
-
Click Next after you provide the details in the respective spaces provided.
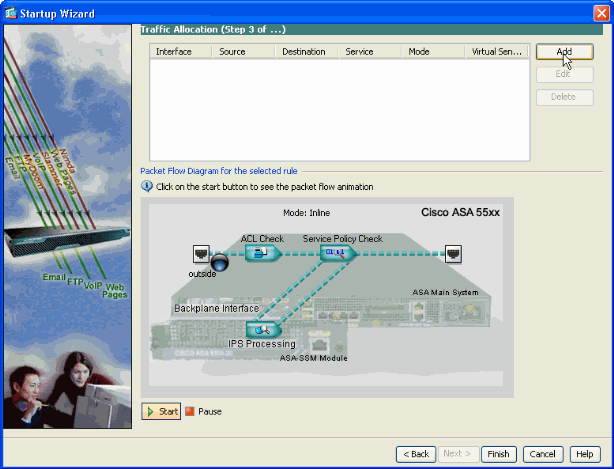
-
Click Add in order to configure the traffic allocation details.
-
Provide the source and the destination network address and also the type of service, for example, IP is used here. In this example, any is used for source and destination as you inspect all traffic with AIP-SSM. Then click OK.
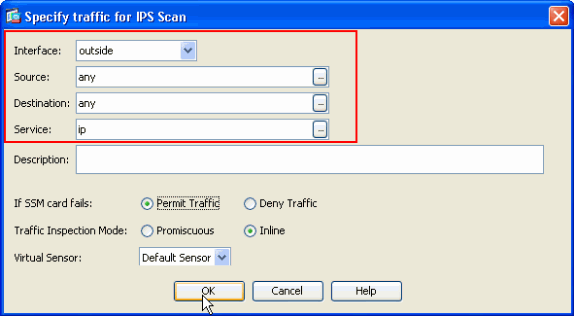
-
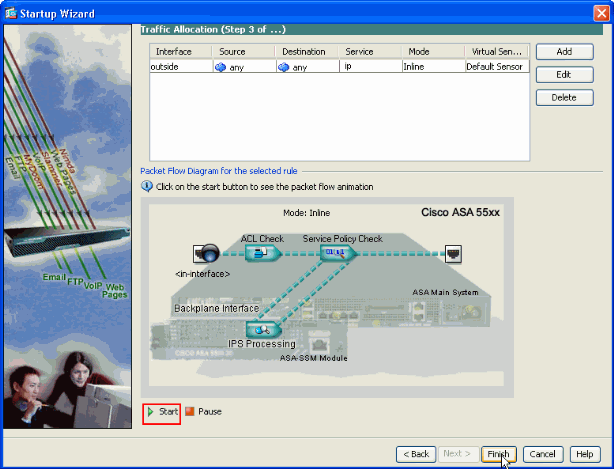
Configured Traffic Allocation rules are shown in this window and you can add as many rules as needed if you complete the same procedure as explained in steps 7 and 8. Then click Finish and this completes the ASDM Configuration procedure.
Note: You can view the packet flow animation if you click on Start.
Inspect Specific Traffic with the AIP-SSM
In the event that the network administrator wants to have the AIP-SSM monitor as a subset of all traffic, the ASA has two independant variables that can be modified. First, the access-list can be written to include or exclude the necessary traffic. In addition to the modification of access-lists, a service-policy can be applied to an interface or globally in order to change the traffic inspected by the AIP-SSM.
With reference to the network diagram in this document, the network administrator wants the AIP-SSM to inspect all traffic between the outside network and DMZ network.
ciscoasa#configure terminal ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips deny ip 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips permit ip any 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips deny ip 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips permit ip 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 any ciscoasa(config)#class-map ips_class_map ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match access-list traffic_for_ips ciscoasa(config)#policy-map interface_policy ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class ips_class_map ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#ips inline fail-open ciscoasa(config)#service-policy interface_policy interface dmz !--- The access-list denies traffic from the inside network to the DMZ network !--- and traffic to the inside network from the DMZ network. !--- In addition, the service-policy command is applied to the DMZ interface.
Next, the network administrator wants the AIP-SSM to monitor traffic initiated from the inside network to the outside network. Inside network to DMZ network is not monitored.
Note: This particular section requires an intermediate understanding of statefulness, TCP, UDP, ICMP, connection, and connectionless communications.
ciscoasa#configure terminal ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips deny ip 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 ciscoasa(config)#access-list traffic_for_ips permit ip 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 any ciscoasa(config)#class-map ips_class_map ciscoasa(config-cmap)#match access-list traffic_for_ips ciscoasa(config)#policy-map interface_policy ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class ips_class_map ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#ips inline fail-open ciscoasa(config)#service-policy interface_policy interface inside
The access-list denies traffic initiated on the inside network destined for the DMZ network. The second access-list line permits or sends traffic initiated on the inside network destined for the outside network to the AIP-SSM. At this point the statefulness of the ASA comes into play. For example, an internal user initiates a TCP connection (Telnet) to a device on the outside network (router). The user successfully connects to the router and logs in. The user then issues a router command that is not authorized. The router responds with Command authorizaton failed. The data packet that contains the Command authorization failed string has a source of the outside router and a destination of the inside user. The source (outside) and destination (inside) do not match the access-lists previously defined in this document. The ASA keeps track of stateful connections, because of this, the data packet that returns (outside to inside) is sent to the AIP-SSM for inspection. Custom signature 60000 0, which is configured on the AIP-SSM, alarms.
Note: By default, the ASA does not keep state for ICMP traffic. In the previous sample configuration, the internal user pings (ICMP echo request) the outside router. The router responds with ICMP echo-reply. The AIP-SSM inspects the echo request packet but not the echo-reply packet. If ICMP inspection is enabled on the ASA, both the echo request and echo-reply packets are inspected by the AIP-SSM.
Exclude specific network traffic from AIP-SSM scanning
The given generalized example provides a view on exempting specific traffic to be scanned by AIP-SSM. In order to perform this, you need to create an access-list that contains the traffic flow that is to be excluded from AIP-SSM scanning in deny statement. In this example, IPS is the name of the access-list that define the traffic flow to be scanned by AIP-SSM. Traffic between <source> and <destination> are excluded from scanning; all other traffic is inspected.
access-list IPS deny IP <source> <destination> access-list IPS permit ip any any ! class-map my_ips_class match access-list IPS ! ! policy-map my-ids-policy class my-ips-class ips inline fail-open
Verify
Verify that alert events are recorded in the AIP-SSM.
Log into the AIP-SSM with the administrator user account. The show events alert command generates this output.
Note: The output varies based on signature settings, type of traffic sent to the AIP-SSM, and network load.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT in order to view an analysis of show command output.
show events alert
evIdsAlert: eventId=1156198930427770356 severity=high vendor=Cisco
originator:
hostId: AIP-SSM
appName: sensorApp
appInstanceId: 345
time: 2009/03/23 22:52:57 2006/08/24 17:52:57 UTC
signature: description=Telnet Command Authorization Failure id=60000 version=custom
subsigId: 0
sigDetails: Command authorization failed
interfaceGroup:
vlan: 0
participants:
attacker:
addr: locality=OUT 172.16.1.200
port: 23
target:
addr: locality=IN 10.2.2.200
port: 33189
riskRatingValue: 75
interface: ge0_1
protocol: tcp
evIdsAlert: eventId=1156205750427770078 severity=high vendor=Cisco
originator:
hostId: AIP-SSM
appName: sensorApp
appInstanceId: 345
time: 2009/03/23 23:46:08 2009/03/23 18:46:08 UTC
signature: description=ICMP Echo Request id=2004 version=S1
subsigId: 0
interfaceGroup:
vlan: 0
participants:
attacker:
addr: locality=OUT 172.16.1.200
target:
addr: locality=DMZ 192.168.1.50
triggerPacket:
000000 00 16 C7 9F 74 8C 00 15 2B 95 F9 5E 08 00 45 00 ....t...+..^..E.
000010 00 3C 2A 57 00 00 FF 01 21 B7 AC 10 01 C8 C0 A8 .<*W....!.......
000020 01 32 08 00 F5 DA 11 24 00 00 00 01 02 03 04 05 .2.....$........
000030 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 10 11 12 13 14 15 ................
000040 16 17 18 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F ..........
riskRatingValue: 100
interface: ge0_1
protocol: icmp
evIdsAlert: eventId=1156205750427770079 severity=high vendor=Cisco
originator:
hostId: AIP-SSM
appName: sensorApp
appInstanceId: 345
time: 2009/03/23 23:46:08 2009/03/23 18:46:08 UTC
signature: description=ICMP Echo Reply id=2000 version=S1
subsigId: 0
interfaceGroup:
vlan: 0
participants:
attacker:
addr: locality=DMZ 192.168.1.50
target:
addr: locality=OUT 172.16.1.200
triggerPacket:
000000 00 16 C7 9F 74 8E 00 03 E3 02 6A 21 08 00 45 00 ....t.....j!..E.
000010 00 3C 2A 57 00 00 FF 01 36 4F AC 10 01 32 AC 10 .<*W....6O...2..
000020 01 C8 00 00 FD DA 11 24 00 00 00 01 02 03 04 05 .......$........
000030 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 10 11 12 13 14 15 ................
000040 16 17 18 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F ..........
riskRatingValue: 100
interface: ge0_1
protocol: icmp
In the sample configurations, several IPS signatures are tuned to alarm on test traffic. Signature 2000 and 2004 are modified. Custom signature 60000 is added. In a lab environment or a network where little data passes through the ASA, it can be necessary to modify signatures in order to trigger events. If the ASA and AIP-SSM are deployed in an environment that passes a large amount of traffic, the default signature settings are likely to generate an event.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT in order to view an analysis of show command output.
Issue these show commands from the ASA.
-
show module—Shows information about the SSM on the ASA as well as system information.
ciscoasa#show module Mod Card Type Model Serial No. --- -------------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------- 0 ASA 5510 Adaptive Security Appliance ASA5510 JMX0935K040 1 ASA 5500 Series Security Services Module-10 ASA-SSM-10 JAB09440271 Mod MAC Address Range Hw Version Fw Version Sw Version --- --------------------------------- ------------ ------------ --------------- 0 0012.d948.e912 to 0012.d948.e916 1.0 1.0(10)0 8.0(2) 1 0013.c480.cc18 to 0013.c480.cc18 1.0 1.0(10)0 6.1(2)E3 Mod SSM Application Name Status SSM Application Version --- ------------------------------ ---------------- -------------------------- 1 IPS Up 6.1(2)E3 Mod Status Data Plane Status Compatibility --- ------------------ --------------------- ------------- 0 Up Sys Not Applicable 1 Up Up !--- Each of the areas highlighted indicate that !--- the ASA recognizes the AIP-SSM and the AIP-SSM status is up.
-
show run
ciscoasa#show run !--- Output is suppressed. access-list traffic_for_ips extended permit ip any any ... class-map ips_class_map match access-list traffic_for_ips ... policy-map global_policy ... class ips_class_map ips inline fail-open ... service-policy global_policy global !--- Each of these lines are needed !--- in order to send data to the AIP-SSM.
-
show access-list—Shows the counters for an access-list.
ciscoasa#show access-list traffic_for_ips access-list traffic_for_ips; 1 elements access-list traffic_for_ips line 1 extended permit ip any any (hitcnt=2) 0x9bea7286 !--- Confirms the access-list displays a hit count greater than zero.
Before you install and use the AIP-SSM, does network traffic pass through the ASA as expected? If not, it can be necessary to troubleshoot the network and ASA access policy rules.
Problems with Failover
-
If you have two ASAs in a failover configuration and each has an AIP-SSM, you must manually replicate the configuration of the AIP-SSMs. Only the configuration of the ASA is replicated by the failover mechanism. The AIP-SSM is not included in the failover. Refer to PIX/ASA 7.x Active/Standby Failover Configuration Example for more information on Failover problems.
-
The AIP-SSM does not participate in stateful failover if stateful failover is configured on the ASA failover pair.
Error Messages
The IPS Module (AIP-SSM) produces error messages as shown and not firing events.
07Aug2007 18:59:50.468 0.757 interface[367] Cid/W errWarning Inline data bypass has started. 07Aug2007 18:59:59.619 9.151 mainApp[418] cplane/E Error during socket read 07Aug2007 19:03:13.219 193.600 nac[373] Cid/W errWarning New host ip [192.168.101.76] 07Aug2007 19:06:13.979 180.760 sensorApp[417] Cid/W errWarning unspecifiedWarning:There are no interfaces assigned to any virtual sensors. This can result in some packets not being monitored. 07Aug2007 19:08:42.713 148.734 mainApp[394] cplane/E Error - accept() call returned -1 07Aug2007 19:08:42.740 0.027 interface[367] Cid/W errWarning Inline data bypass has started.
The cause for this error message is that the IPS virtual sensor was not assigned to the backplane interface of the ASA. The ASA is setup in the correct manner in order to send traffic to the SSM module, but you need to assign the virtual sensor to the backplane interface that the ASA creates in order for the SSM to scan the traffic.
errorMessage: IpLogProcessor::addIpLog: Ran out of file descriptors name=errWarn errorMessage: IpLog 1701858066 terminated early due to lack of file handles. name=ErrLimitExceeded
These messages are indicative of IP LOGGING being enabled, which in turn hogged up all the system resources. Cisco recommends to disable IP LOGGING as it should only be used for troubleshooting/investigative purposes only.
Note: The errWarning Inline data bypass has started error message is expected behavior as the sensor momentarily restarts the analysis engine after the signature update, which is a necessary part of the signature update process.
Syslog Support
The AIP-SSM does not support syslog as an alert format.
The default method to receive alert information from the AIP-SSM is through Security Device Event Exchange (SDEE). Another option is to configure individual signatures in order to generate a SNMP trap as an action to take when they are triggered.
AIP-SSM Reboot
The AIP-SSM module does not respond properly.
If the AIP-SSM module does not respond properly, then reboot the AIP-SSM module without rebooting the ASA. Use the hw-module module 1 reload command in order to reboot the AIP-SSM module and do not reboot ASA.
AIP-SSM Email Alert
Can AIP-SSM send email alerts to users?
No, it is not supported.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Aug-2006 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)









 Feedback
Feedback