Email Security Appliance Round-Robins to the Next SMTP Route If a Destination Mail Server is Still Responsive
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how the Email Security Appliance (ESA) behaves when a destination host configured in the SMTP routes responds with a 4.x.x SMTP code.
Background Information
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) routes allow you to redirect email that is specified for one domain to a different mail exchange (MX) host. A domain that receives email can have multiple destination hosts, each assigned a priority number, similar to an MX record. Destinations with identical priorities are treated in a 'round-robin' fashion where if one or more of the destination hosts does not respond, the messages are delivered to the next functional host.
Problem
A functional exchange server destination host can respond with a 4.x.x SMTP response that indicates the server cannot accept email due to insufficent system resources. Here is an example of a 4.3.1 insufficent system resource message:
4.3.1 - Mail system full ('452', [4.3.1 Insufficent system resources'])
Solution
If a destination host responds with a 4.x.x SMTP response code, no action is required. The ESA automatically acts on the response and delivers the message to the next configured destination host in 'round-robin' fashion.
Example Scenario
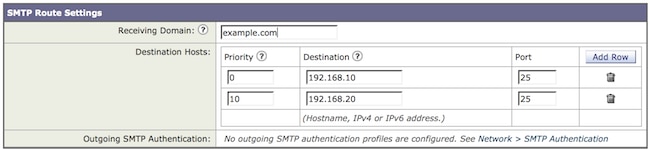
SMTP Routes
Here is an example of a domain configured with two destination hosts:
ESA Mail Log
Here is an example of an ESA mail log that shows a 4.3.1 SMTP response received from the first configured destination host after which the message is delivered to the second destination host:
Wed Jul 2 09:15:07 2014 Info: New SMTP DCID 299 interface 192.168.1.1 address
192.168.1.10 port 25
Wed Jul 2 09:15:07 2014 Info: Connection Error: DCID 299 domain: example.com
IP: 192.168.1.10 port: 25 details: 431-?example.com ESMTP\nMail system full'
interface: 192.168.1.10 reason: unexpected SMTP response
Wed Jul 2 09:15:07 2014 Info: New SMTP DCID 300 interface 192.168.1.1 address
192.168.1.20 port 25
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
08-Jul-2014 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback