Introduction
This document describes how to configure the spam quarantine on the ESA or SMA and associated features : external authentication with LDAP and spam quarantine notification.
Procedure
Configure Local Spam Quarantine on the ESA
- On the ESA, choose Monitor > Spam Quarantine.
- In the Spam Quarantine Settings section, check the Enable Spam Quarantine check box and set the desired quarantine settings.

- Choose Security Services > Spam Quarantine.
- Ensure the Enable External Spam Quarantine check box is unchecked, unless you plan to use External Spam Quarantine (see section below).

- Submit and commit changes.
Enable Quarantine Ports and Specify a Quarantine URL at the Interface
- Choose Network > IP Interfaces.
- Click the interface name of the interface you will use in order to access the quarantine.
In the spam quarantine section, check the check boxes and specify default ports or change as required:
- Spam Quarantine HTTP
- Spam Quarantine HTTPS

- Check the This is the default interface for Spam Quarantine check box.
- Under "URL Displayed in Notifications", by default the appliance uses the system hostname (cli: sethostname) unless otherwise specified in the second radio button option and text field.
This example specifies the default hostname setting.

You can specify a custom URL in order to access your Spam Quarantine.

Note: If you configure the quarantine for external access, you will need an external IP address configured on the interface or an external IP that is Network Address Translated to an internal IP.
If you do not use a hostname you can keep the Hostname radio button checked, but still access the quarantine by IP address only. For example, https://10.10.10.10:83.
- Submit and commit changes.
- Validate.
If you specify a hostname for the spam quarantine, ensure the hostname is resolvable via internal Domain Name System (DNS) or external DNS. DNS will resolve the hostname to your IP address.
If you do not get a result, check with your Network Administrator and continue to access the Quarantine by IP address like the previous example until the host shows up in DNS.
> nslookup quarantine.mydomain.com
Navigate to your URL configured previously in a web browser in order to validate that you can access the quarantine:
https://quarantine.mydomain.com:83
https://10.10.10.10:83
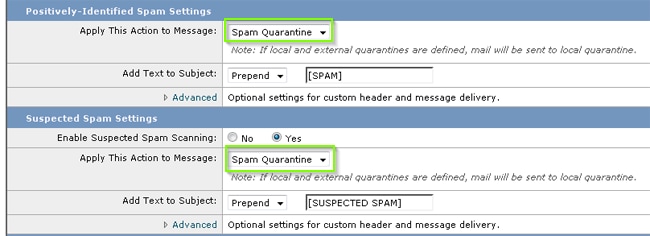
Configure the ESA to Move Positive Spam and/or Suspect Spam to Spam Quarantine
In order to quarantine your Suspect Spam and/or Positively Identified Spam messages, complete these steps:
- On the ESA, click Mail Policies > Incoming Mail Policies and then the anti-spam column for the Default Policy.
- Change the action of either the Positively Identified Spam or Suspect Spam to send to the Spam Quarantine."
- Repeat the process for any other ESAs you might have configured for External Spam Quarantine. If you made this change at the cluster level you will not have to repeat it as the change will be propogated to the other appliances in the cluster.
- Submit and commit changes.
- At this point, mail that would have otherwise been delivered or dropped will get quarantined.
Configure External Spam Quarantine on the SMA
The steps to configure External Spam Quarantine on the SMA are the same as the previous section with a few exceptions:
- On each of your ESAs, you will need to disable the local quarantine. Choose Monitor > Quarantines.
- On your ESA, choose Security Services > Spam Quarantine and click Enable External Spam Quarantine.
- Point the ESA to the IP address of your SMA and specify the port you would like to use. The default is Port 6025.

- Ensure Port 6025 is open from the ESA to the SMA. This port is for delivery of quarantined messages from ESA > SMA.
This can be validated by with a telnet test from the CLI on the ESA on port 6025. If a connection opens and stays open you should be set.
tarheel.rtp> telnet 14.2.30.116 6025
Trying 14.2.30.116...
Connected to steelers.rtp.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 steelers.rtp ESMTP
- Ensure you have configured the IP/hostname to access the spam quarantine, such as in "Enable Quarantine Ports and Specify a Quarantine URL at the Interface".
- Verify that messages arrive to the spam quarantine from your ESAs. If the spam quarantine does not show any messages, there might be an issue with connectivity from ESA > SMA on port 6025 (see previous steps).
Configure Spam Quarantine Notification
- On the ESA, choose Monitor > Spam Quarantine.
- On the SMA you would navigate to the Spam Quarantine settings in order to perform the same steps.
- Click Spam Quarantine.
- Check the Enable Spam Notification check box.

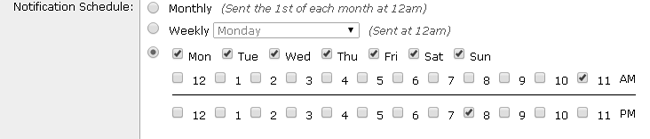
- Choose your notification Schedule.
- Submit and commit changes.
Configure End-User Spam Quarantine Access via Spam Quarantine End-User Authentication Query
- On the SMA or ESA, choose System Administration > LDAP.
- Open your LDAP Server Profile.
- In order to verify you are able to authenticate with an Active Directory account, check your Spam Quarantine End-User Authentication Query is enabled.
- Check the Designate as Active Query check box.

- Click Test in order to test the query.
Match Positive means that the authentication was successful:

- Submit and commit changes.
- On the ESA, choose Monitor > Spam Quarantine.
On the SMA, navigate to the Spam Quarantine settings in order to perform the same steps.
- Click Spam Quarantine.
- Check the Enable End-User Quarantine Access check box.
- Choose LDAP from the End-User Authentication drop-down list.

- Submit and commit changes.
- Validate that External Authentication is on ESA/SMA.
- Navigate to your URL configured previously in a web browser in order to validate that you can access the quarantine:
https://quarantine.mydomain.com:83
https://10.10.10.10:83
- Log in with your LDAP account. If this fails, check the External authentication LDAP profile and enable End-User Quarantine Access (see previous steps).
Configure Administrative User Access to the Spam Quarantine
Use the procedure in this section in order to allow administrative users with these roles to manage messages in the Spam Quarantine: Operator, Read-Only Operator, Help Desk, or Guestroles, and custom user roles that include access to the Spam Quarantine.
Administrator-level users, which include the default admin user and Email Administrator users, can always access the Spam Quarantine and do not need to be associated with the Spam Quarantine feature using this procedure.
Note: Non-Administrator-level users can access messages in the Spam Quarantine, but they cannot edit the quarantine settings. Administrator-level users can access messages and edit the settings.
In order to enable administrative users who do not have full Administrator privileges to manage messages in the Spam Quarantine, complete these steps:
- Make sure you have created users and assigned them a user role with access to the Spam Quarantine.
- On the Security Management appliance, choose Management Appliance > Centralized Services > Spam Quarantine.
- Click Enable or Edit Settings in the Spam Quarantine Settings section.
- In the Administrative Users area of the Spam Quarantine Settings section, click the selection link for Local Users, Externally Authenticated Users, or Custom User Roles.
- Choose the users to whom you want to grant access to view and manage messages in the Spam Quarantine.
- Click OK.
- Repeat if needed for each of the other types of Administrative Users listed in the section (Local Users, Externally Authenticated Users, or Custom User Roles).
- Submit and commit your changes.















 Feedback
Feedback