FlexVPN Dynamic Configuration with Local AAA Attribute Lists
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This configuration example demonstrates how to use local Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) attribute list in order to perform dynamic and potentially advanced configuration without the use of external Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server.
This is desired in certain scenarios, especially when rapid deployment or test is required. Such deployments are typically proof-of-concept labs, new deployment testing, or troubleshooting.
Dynamic configuration is important on the concentrator/hub side where different policies or attributes should be applied on a per-user, per-customer, per-session basis.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on, but not limited to, these software and hardware versions. This list does not outline the minimum requirements, but reflects the state of the device throughout the test phase of this feature.
Hardware
-
Aggregation Services Routers (ASR) - ASR 1001 - called "bsns-asr1001-4"
-
Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 (ISR G2) - 3925e - called "bsns-3925e-1"
-
Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 (ISR G2) - 3945e - called "bsns-3945e-1"
Software
-
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8 - 15.3(1)S
-
Cisco IOS® Software Release 15.2(4)M1 and 15.2(4)M2
Licenses
-
ASR routers have the adventerprise and ipsec feature licenses enabled.
-
ISR G2 routers have the ipbasek9, securityk9, and hseck9 feature licenses enabled.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Topology
The topology used in this exercise is basic. A hub router (ASR) and two spoke routers (ISR) are utilized, which simulate clients.
Configurations
The configurations in this document are intended to show a basic setup, with smart defaults as much as possible. For Cisco recommendations on cryptography, visit the Next Generation Encryption page on cisco.com.
Spoke Configuration
As mentioned previously, most of the actions in this documentation are performed on the hub. Spoke configuration is here for reference. In this configuration, notice that only change is identity between Client1 and Client2 (displayed in bold).
aaa new-model aaa authorization network default local aaa session-id common crypto ikev2 keyring Flex_key peer Spokes address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 pre-shared-key local cisco pre-shared-key remote cisco !! crypto ikev2 profile Flex_IKEv2 match identity remote address 0.0.0.0 identity local email Client1@cisco.com authentication remote pre-share authentication local pre-share keyring local Flex_key aaa authorization group psk list default default virtual-template 1 crypto logging session crypto ipsec profile default set ikev2-profile Flex_IKEv2 interface Tunnel1 ip address negotiated ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp network-id 2 ip nhrp shortcut virtual-template 1 ip nhrp redirect ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source GigabitEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 172.25.1.1 tunnel path-mtu-discovery tunnel protection ipsec profile default interface Virtual-Template1 type tunnel ip unnumbered Tunnel1 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp network-id 2 ip nhrp shortcut virtual-template 1 ip nhrp redirect ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel path-mtu-discovery tunnel protection ipsec profile default
Hub Configuration
The hub configuration is divided into two parts:
-
Basic connectivity configuration, which outlines the configuration needed for basic connectivity.
-
Extended configuration, which outlines the configuration changes needed in order to demonstrate how an administrator can use the AAA attribute list to perform per-user or per-session configuration changes.
Basic Connectivity Configuration
This configuration is for reference only and is not meant to be optimal, only functional.
The greatest limitation of this configuration is usage of pre-shared key (PSK) as the authentication method. Cisco recommends the use of certificates whenever applicable.
aaa new-model aaa authorization network default local aaa session-id common crypto ikev2 authorization policy default pool FlexSpokes route set interface crypto ikev2 keyring Flex_key peer Spokes address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 pre-shared-key local cisco pre-shared-key remote cisco !! peer Client1 identity email Client1@cisco.com pre-shared-key cisco !! peer Client2 identity email Client2@cisco.com pre-shared-key cisco crypto ikev2 profile Flex_IKEv2 match fvrf any match identity remote address 0.0.0.0 match identity remote email domain cisco.com authentication remote pre-share authentication local pre-share keyring local Flex_key aaa authorization group psk list default default virtual-template 1 no crypto ikev2 http-url cert crypto logging session crypto ipsec profile default set ikev2-profile Flex_IKEv2 interface Virtual-Template1 type tunnel vrf forwarding IVRF ip unnumbered Loopback100 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp network-id 2 ip nhrp redirect ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel path-mtu-discovery tunnel vrf INTERNET tunnel protection ipsec profile default
Extended Configuration
There are a few things needed to assign AAA attributes to a particular session. This example shows complete work for client1; then it shows how to add another client/user.
Extended Hub Configuration for Client1
-
Define a AAA attribute list.
aaa attribute list Client1 attribute type interface-config "ip mtu 1300" protocol ip attribute type interface-config "service-policy output TEST" protocol ip
Note: Remember that the entity assigned via attributes must exist locally. In this case, policy-map was previously configured.
policy-map TEST class class-default shape average 60000
-
Assign AAA attribute list to an authorization policy.
crypto ikev2 authorization policy Client1 pool FlexSpokes aaa attribute list Client1 route set interface
-
Ensure that this new policy used by the clients that connect. In this case, extract the username portion of the identity sent by the clients. The clients should use an email address of ClientX@cisco.com (X is 1 or 2, dependent on the client). The mangler splits the email address into username and domain portion and uses only one of them (username in this case) to choose the name of authorization policy.
crypto ikev2 name-mangler GET_NAME email username crypto ikev2 profile Flex_IKEv2 aaa authorization group psk list default name-mangler GET_NAME
When client1 is operational, client2 can be added relatively easy.
Extended Hub Configuration for Client2
Ensure a policy and a separate set of attributes, if needed, exist.
aaa attribute list Client2 attribute type interface-config "ip tcp adjust-mss 1200" protocol ip attribute type interface-config "ip access-group 133 in" protocol ip crypto ikev2 authorization policy Client2 pool FlexSpokes aaa attribute list Client2 route set interface
In this example, an updated maximum segment size (MSS) setting and an inbound access-list to operate for this client is applied. Other settings can be easily chosen. A typical setting is to assign different virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) for different clients. As mentioned earlier, any entity assigned to the attribute list, such as access-list 133 in this scenario, must already exist in the configuration.
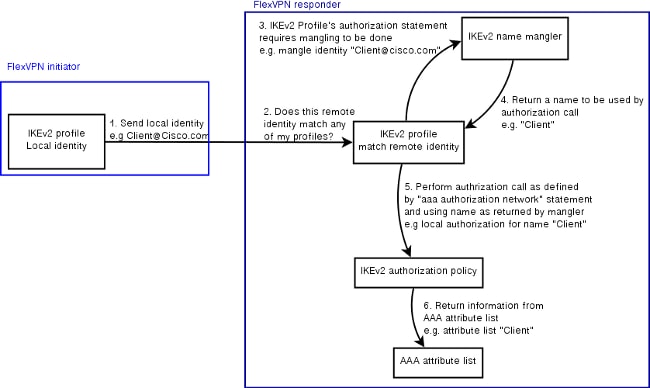
Process Overview
This figure outlines the order of operation when AAA authorization is processed via the Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) profile and contains information specific to this configuration example.
Verification
This section shows how to verify that the settings previously assigned have been applied to the clients.
Client1
Here are the commands that verify that the maximum transmission units (MTU) settings, as well as the service policy have been applied.
bsns-asr1001-4#show cef int virtual-access 1 (...) Hardware idb is Virtual-Access1 Fast switching type 14, interface type 21 IP CEF switching enabled IP CEF switching turbo vector IP Null turbo vector VPN Forwarding table "IVRF" IP prefix lookup IPv4 mtrie 8-8-8-8 optimized Tunnel VPN Forwarding table "INTERNET" (tableid 2) Input fast flags 0x0, Output fast flags 0x4000 ifindex 16(16) Slot unknown (4294967295) Slot unit 1 VC -1 IP MTU 1300 Real output interface is GigabitEthernet0/0/0 bsns-asr1001-4#show policy-map interface virtual-access1 Virtual-Access1 Service-policy output: TEST Class-map: class-default (match-any) 5 packets, 620 bytes 5 minute offered rate 0000 bps, drop rate 0000 bps Match: any Queueing queue limit 64 packets (queue depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0 (pkts output/bytes output) 5/910 shape (average) cir 60000, bc 240, be 240 target shape rate 60000
Client2
Here are the commands that verify that the MSS settings have been pushed and that the access-list 133 has also been applied as an inbound filter on the equivalent virtual access interface.
bsns-asr1001-4#show cef int virtual-access 2 Virtual-Access2 is up (if_number 18) Corresponding hwidb fast_if_number 18 Corresponding hwidb firstsw->if_number 18 Internet address is 0.0.0.0/0 Unnumbered interface. Using address of Loopback100 (192.168.1.1) ICMP redirects are never sent Per packet load-sharing is disabled IP unicast RPF check is disabled Input features: Access List, TCP Adjust MSS (...) bsns-asr1001-4#show ip interface virtual-access2 Virtual-Access2 is up, line protocol is up Interface is unnumbered. Using address of Loopback100 (192.168.1.1) Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255 MTU is 1400 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 133, default is not set (...)
Debug
There are two major blocks to debug. This is useful when you need to open a TAC case and get things on track quicker.
Debug IKEv2
Begin with this major debug command:
debug crypto ikev2 [internal|packet]
Then enter these commands:
show crypto ikev2 sa show crypto ipsec sa peer a.b.c.d
Debug AAA Attribute Assignment
If you would like to debug AAA assignment of attributes, these debugs can be helpful.
debug aaa authorization debug aaa attr debug aaa proto local
Conclusion
This document demonstrates how to use the AAA attribute list in order to allow added flexibility in FlexVPN deployments where the RADIUS server might not be available or is not desired. The AAA attribute list offers added configuration options on a per-session, per-group basis, if it is required.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Mar-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback