Configure ASR9K TACACS with Cisco Identity Services Engine 2.4
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the configuration of ASR 9000 series Aggregation Services Router (ASR) in order to authenticate and authorize via TACACS+ with Cisco Identity Services Engine 2.4 server.
Background Information
It examples the implementation of the administrative model of task-based authorization that is used in order to control user access in the Cisco IOS® XR software system. The major tasks required to implement task-based authorization involve how to configure user groups and task groups. User groups and task groups are configured through the Cisco IOS® XR software command set used for Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) services. Authentication commands are used to verify the identity of a user or principal. Authorization commands are used to verify that an authenticated user (or principal) is granted permission in order to perform a specific task. Accounting commands are used for logging of sessions and to create an audit trail by recording certain user or system generated actions.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- ASR 9000 Deployment and Basic Configuration
- TACACS+ Protocol
- ISE 2.4 Deployment and Configuration
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- ASR 9000 with Cisco IOS® XR Software, Version 5.3.4
- Cisco ISE 2.4
The information in this document is created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If the network is live, make sure that the potential impact of any configuration change is completely understood.
Configure
Predefined Components on the IOS® XR
There are predefined user groups and task groups in IOS® XR. The administrator can either use these predefined groups or define custom groups as per requirement.
Predefined User Groups
These user groups are predefined on IOS® XR:
| User Group | Privileges |
|---|---|
| cisco-support | Debug and troubleshoot features (usually, used by Cisco Technical Support personnel). |
| netadmin | Configure network protocols such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) (usually used by network administrators). |
| operator | Perform day-to-day monitoring activities, and have limited configuration rights. |
| root-lr | Display and execute all commands within a single RP. |
| root-system | Display and execute all commands for all RPs in the system. |
| sysadmin | Perform system administration tasks for the router, such as maintaining where the core dumps are stored or setting up the Network Time Protocol (NTP) clock. |
| serviceadmin | Perform service administration tasks, such as Session Border Controller (SBC). |
Each predefined user group has certain task groups mapped to them and cannot be modified. Use these commands in order to check the predefined user groups:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9k#sh aaa usergroup ?
| Output Modifiers
root-lr Name of the usergroup
netadmin Name of the usergroup
operator Name of the usergroup
sysadmin Name of the usergroup
retrieval Name of the usergroup
maintenance Name of the usergroup
root-system Name of the usergroup
provisioning Name of the usergroup
read-only-tg Name of the usergroup
serviceadmin Name of the usergroup
cisco-support Name of the usergroup
WORD Name of the usergroup
<cr>
Pre-Defined Task Groups
These predefined task groups are available for administrators to use, typically for initial configuration:
- cisco-support: Cisco support personnel tasks
- netadmin: Network administrator tasks
- operator: Operator day-to-day tasks (for demonstration purposes)
- root-lr: Secure domain router administrator tasks
- root-system: System-wide administrator tasks
- sysadmin: System administrator tasks
- serviceadmin: Service administration tasks
Use these commands in order to check the predefined task groups:
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show aaa taskgroup ?
| Output Modifiers
root-lr Name of the taskgroup
netadmin Name of the taskgroup
operator Name of the taskgroup
sysadmin Name of the taskgroup
root-system Name of the taskgroup
serviceadmin Name of the taskgroup
cisco-support Name of the taskgroup
WORD Name of the taskgroup
<cr>
Use this command in order to check the supported tasks:
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show aaa task supported
Here is the list of supported tasks:
|
Aaa |
Acl |
Admin |
Ancp |
Atm |
basic-services |
Bcdl |
Bfd |
bgp |
|
Boot |
Bundle |
call-home |
Cdp |
Cef |
Cgn |
cisco-support |
config-mgmt |
config-services |
|
Crypto |
Diag |
Disallowed |
Drivers |
Dwdm |
Eem |
Eigrp |
ethernet-services |
ext-access |
|
Fabric |
fault-mgr |
Filesystem |
Firewall |
Fr |
Hdlc |
host-services |
Hsrp |
interface |
|
Inventory |
ip-services |
Ipv4 |
Ipv6 |
Isis |
L2vpn |
Li |
Lisp |
logging |
|
Lpts |
Monitor |
mpls-ldp |
mpls-static |
mpls-te |
Multicast |
Netflow |
Network |
nps |
|
Ospf |
Ouni |
Pbr |
pkg-mgmt |
pos-dpt |
Ppp |
Qos |
Rcmd |
rib |
|
Rip |
root-lr |
root-system |
route-map |
route-policy |
Sbc |
Snmp |
sonet-sdh |
static |
|
Sysmgr |
System |
Transport |
tty-access |
Tunnel |
Universal |
Vlan |
Vpdn |
vrrp |
Each of these mentioned tasks can be given with any of these or all the four permissions:
|
Read |
Specifies a designation that permits only a read operation. |
|
Write |
Specifies a designation that permits a change operation and implicitly allows a read operation. |
|
Execute |
Specifies a designation that permits an access operation; for example, ping and Telnet. |
|
Debug |
Specifies a designation that permits a debug operation. |
User-Defined Task Groups
Administrators can configure custom task groups to meet particular needs. Here is a configuration example:
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config)#taskgroup TAC-Defined-TASK RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task ? debug Specify a debug-type task ID execute Specify a execute-type task ID read Specify a read-type task ID write Specify a read-write-type task ID RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task read aaa RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task write aaa RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task execute aaa RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task debug aaa RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task read acl RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task write acl RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#task execute acl RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tg)#commit RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show aaa taskgroup TAC-Defined-TASK Task group 'TAC-Defined-TASK' Task IDs included directly by this group: Task: aaa : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: acl : READ WRITE EXECUTE Task group 'TAC-Defined-TASK' has the following combined set of task IDs (including all inherited groups): Task: aaa : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: acl : READ WRITE EXECUTE
Describe command can be used to find what task group and permission is needed for a certain command.
Example 1.
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#describe show aaa usergroup Package: ..... User needs ALL of the following taskids: aaa (READ) RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#
In order to allow a user to run the commandshow aaa usergroup, task group: task read aaa should be assigned to the usergroup.
Example 2.
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config)#describe aaa authentication login default group tacacs+ Package: ..... User needs ALL of the following taskids: aaa (READ WRITE) RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config)#
In order to allow a user to run the commandaaa authentication login default group tacacs+from the configuration mode, task group: task read write aaa should be assigned to the usergroup.
Administrators can define the user group that can inherit several task groups. Here is the configuration example:
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show aaa usergroup TAC-Defined Tue Feb 16 00:50:56.799 UTC User group 'TAC-Defined' Inherits from task group 'operator' User group 'TAC-Defined' has the following combined set of task IDs (including all inherited groups): Task: basic-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cdp : READ Task: diag : READ Task: ext-access : READ EXECUTE Task: logging : READ RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#conf t RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config)#usergroup TAC-Defined RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-ug)#taskgroup TAC-Defined-TASK RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-ug)#commit RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show aaa usergroup TAC-Defined Tue Feb 16 00:51:31.494 UTC User group 'TAC-Defined' Inherits from task group 'operator' Inherits from task group 'TAC-Defined-TASK' User group 'TAC-Defined' has the following combined set of task IDs (including all inherited groups): Task: aaa : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: acl : READ WRITE EXECUTE Task: basic-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cdp : READ Task: diag : READ Task: ext-access : READ EXECUTE Task: logging : READ
AAA Configuration on the Router
Configure the TACACS server on the ASR router with the IP address and the shared secret to be used.
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config)#tacacs-server host 10.106.73.233 port 49 RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tacacs-host)#key 0 cisco RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k(config-tacacs-host)#commit ! tacacs-server host 10.127.196.160 port 49 key 7 14141B180F0B !
Configure authentication and authorization in order to use TACACS server configured.
#aaa authentication login default group tacacs+ local #aaa authorization exec default group tacacs+ local
Configure command authorization to use TACACS server configured (optional):
Note: Ensure that the authentication and authorization work as expected, and ensure that the command sets are also configured properly before you enable command authorization. If not configured properly, users might not be able to enter any commands on the device.
#aaa authorization commands default group tacacs+
Configure command accounting in order to use TACACS server configured (optional).
#aaa accounting commands default start-stop group tacacs+ #aaa accounting update newinfo
ISE Server Configuration
Step 1. In order to define the router IP in the AAA clients list on ISE server, navigate to Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices as shown in the image. Shared secret should be the same as the one configured on the ASR Router as shown in the image.
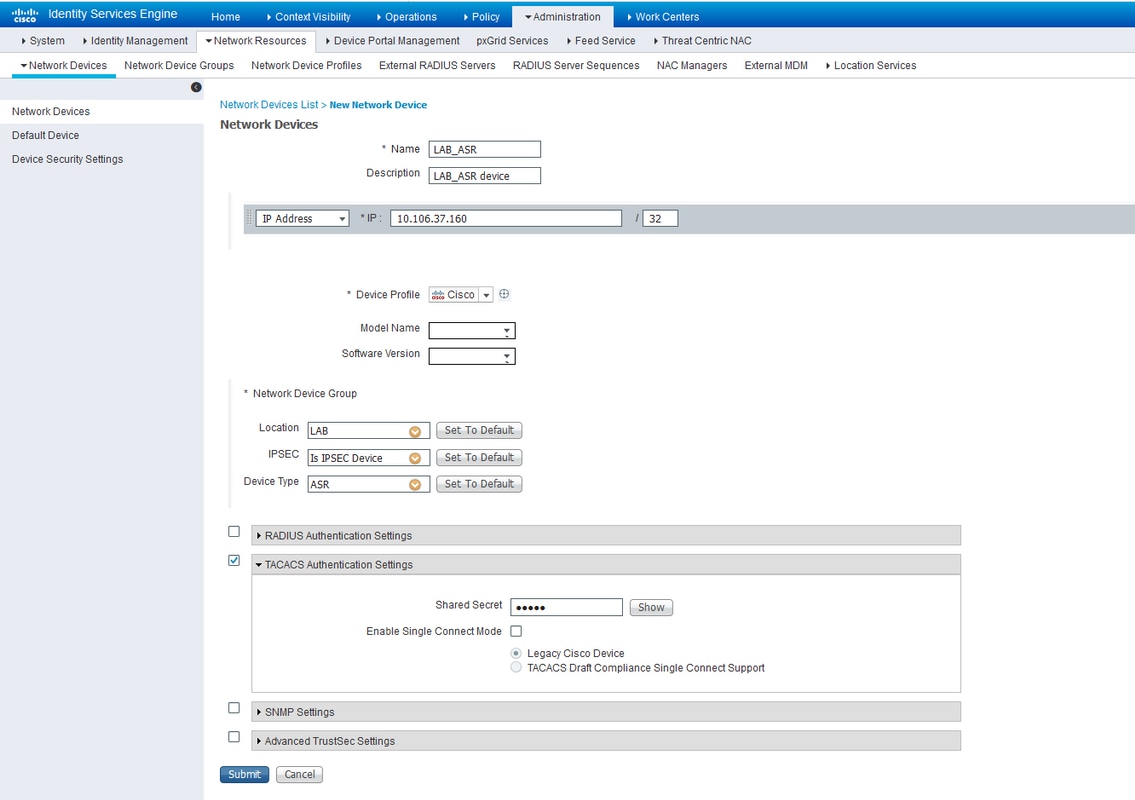 Network Device Configuration
Network Device Configuration
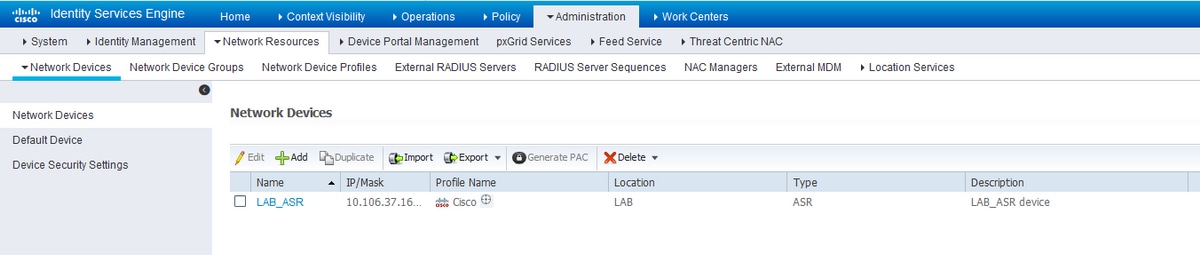 Network Device Configuration
Network Device Configuration
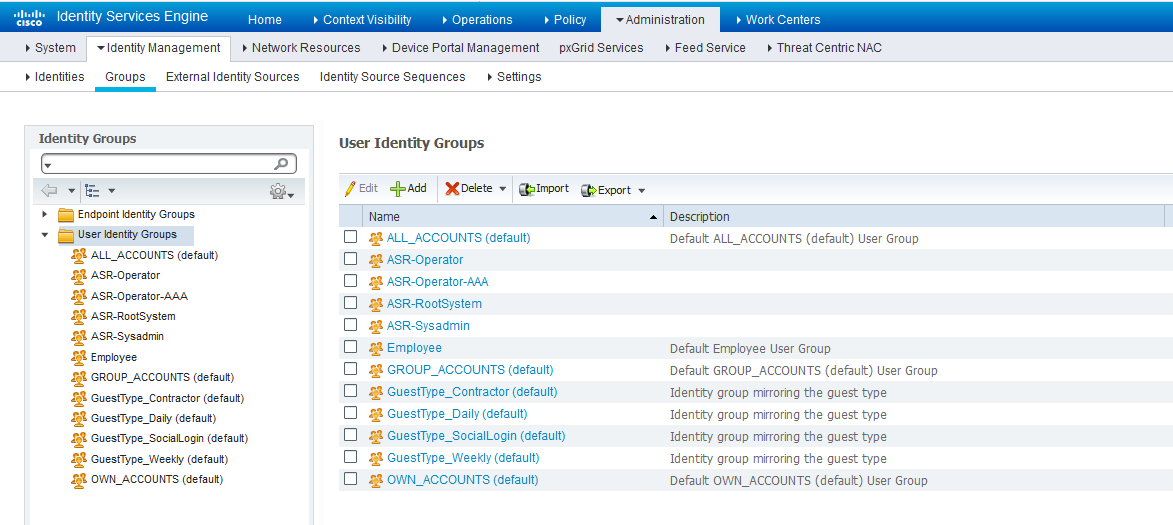
Step 2. Define the user groups as per your requirement, in the example, as shown in this image, you use four groups. You can define the groups under Administration > Identity Management > Groups > User Identity Groups. The groups created in this example are:
- ASR-Operator
- ASR-Operator-AAA
- ASR-RootSystem
- ASR-Sysadmin
 Identity GroupsStep 3. As shown in the image, create the users and map them to the respective user group that was created before.
Identity GroupsStep 3. As shown in the image, create the users and map them to the respective user group that was created before.
 Identities/Users
Identities/Users
Note: In this example, the ISE internal users are used for authentication and authorization. Authentications and authorizations with External Identity Source are out of the scope of this document.
Step 4. Define the Shell Profile to be pushed for the respective users. In order to do so, navigate to Work Centers > Device Administration > Policy Elements > Results > TACACS Profiles. One can configure a new shell profile as shown in the images as well for previous versions of ISE. The shell profiles defined in this example are:
1. ASR_Operator
2. ASR_RootSystem
3. ASR_Sysadmin
4. Operator_with_AAA
 Shell Profiles for TACACS
Shell Profiles for TACACS
One can click on the Add button to enter the fields Type, Name and Value as shown in the images under the Custom Attributes section.
For Operator role:
 ASR Operator shell profileFor root-system role:
ASR Operator shell profileFor root-system role:
 ASR Root System shell profileFor sysadmin role:
ASR Root System shell profileFor sysadmin role:
 ASR Sysadmin shell profileFor operator and AAA role:
ASR Sysadmin shell profileFor operator and AAA role:
 Operator with AAA shell profileStep 5. Configure the Identity Source Sequence to use the Internal Users at Administration > Identity Management > Identity Source Sequences. One can either add a new Identity Source Sequence or edit the available ones.
Operator with AAA shell profileStep 5. Configure the Identity Source Sequence to use the Internal Users at Administration > Identity Management > Identity Source Sequences. One can either add a new Identity Source Sequence or edit the available ones.

Step 6. Configure the authentication policy at Work Centers > Device Administration > Device Admin Policy Sets > [Choose Policy Set] in order to make use of the Identity Store Sequence that contains the internal users. Configure the authorization based on the requirement with the use of the previously created user identity groups and map the respective Shell Profiles, as shown in the image.
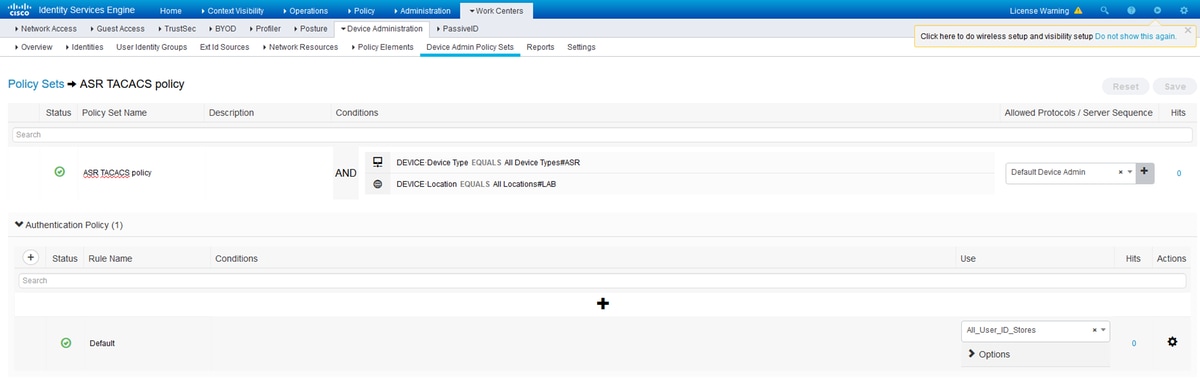 Authentication Policy
Authentication Policy
Authorization policies can be configured in many ways based on the requirement. The rules shown here in the image are based on the device location, type and the specific internal user identity group. The Shell Profiles selected will be pushed at the time of the authorization along with the Command Sets.
 Authorization Policy
Authorization Policy
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Operator
Verify the user group and the task groups assigned whenasrread user logs into the router.
username: ASRread password: RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show user ASRread RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show user group operator RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show user tasks Task: basic-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cdp : READ Task: diag : READ Task: ext-access : READ EXECUTE Task: logging : READ
Operator with AAA
Verify the user group and the task groups assigned whenasraaa user logs into the router.
Note:asraaais the operator task pushed from TACACS server along with the AAA task read, write and execute permissions.
username: asraaa
password:
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#sh user
asraaa
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#sh user group
operator
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#sh user tasks
Task: aaa : READ WRITE EXECUTE
Task: basic-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG
Task: cdp : READ
Task: diag : READ
Task: ext-access : READ EXECUTE
Task: logging : READ
Sysadmin
Verify the user group and the task groups assigned whenasrwrite user logs into the router.
username: asrwrite password: RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#sh user asrwrite RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#sh user group sysadmin RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#sh user tasks Task: aaa : READ Task: acl : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: admin : READ Task: ancp : READ Task: atm : READ Task: basic-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: bcdl : READ Task: bfd : READ Task: bgp : READ Task: boot : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: bundle : READ Task: call-home : READ Task: cdp : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cef : READ Task: cgn : READ Task: config-mgmt : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: config-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: crypto : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: diag : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: drivers : READ Task: dwdm : READ Task: eem : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: eigrp : READ Task: ethernet-services : READ --More-- (output omitted )
Root-System
Verify the user group and the task groups assigned whenasrroot user logs into the router.
username: asrroot password: RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show user asrroot RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ASR9k#show user group root-system RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:ios#show user tasks Task: aaa : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: acl : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: admin : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: ancp : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: atm : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: basic-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: bcdl : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: bfd : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: bgp : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: boot : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: bundle : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: call-home : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cdp : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cef : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: cgn : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: config-mgmt : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: config-services : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: crypto : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: diag : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: drivers : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: dwdm : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: eem : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG Task: eigrp : READ WRITE EXECUTE DEBUG --More-- (output omitted )
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Verify the ISE report from the Operations > TACACS > Live Logs. Click on the magnifying glass symbol in order to see the detailed report.
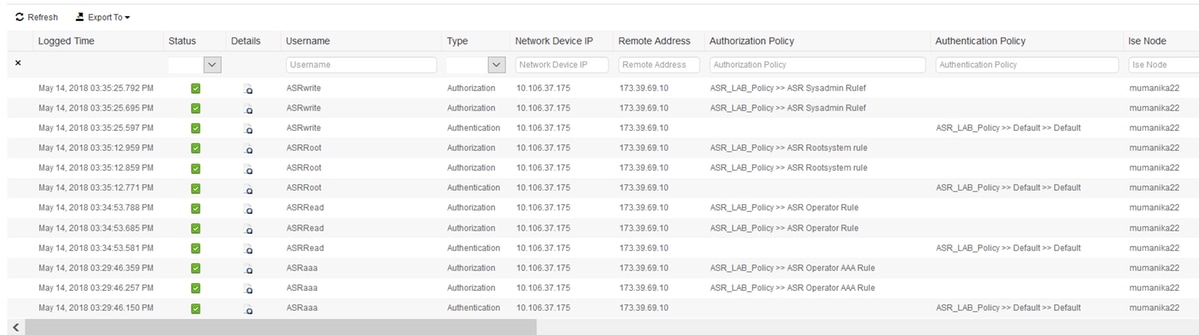
These are a few helpful commands in order to troubleshoot on ASR:
- show user
- show user group
- show user tasks
- show user all
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
23-Jan-2019 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Mukul ManikandanCisco TAC Engineer
- Surendra Reddy KanalaCisco TAC Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback