Configuring the PIX Firewall and VPN Clients Using PPTP, MPPE and IPSec
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
In this sample configuration, four different kinds of clients connect and encrypt traffic with the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall as tunnel endpoint:
-
Users that run Cisco Secure VPN Client 1.1 on Microsoft Windows 95/98/NT
-
Users that run the Cisco Secure VPN 3000 Client 2.5.x on Windows 95/98/NT
-
Users that run native Windows 98/2000/XP Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) clients
-
Users that run the Cisco VPN Client 3.x/4.x on Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP
In this example, a single pool for IPsec and PPTP is configured. However, the pools can also be made separate.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
PIX Software Release 6.3.3
-
Cisco Secure VPN Client 1.1
-
Cisco VPN 3000 Client version 2.5
-
Cisco VPN Client 3.x and 4.x
-
Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows 98 clients
Note: This was tested on PIX Software Release 6.3.3 but should work on release 5.2.x and 5.3.1. PIX Software Release 6.x is required for the Cisco VPN Client 3.x and 4.x. (Support for the Cisco VPN 3000 Client 2.5 is added in PIX Software Release 5.2.x. The configuration also works for PIX Software Release 5.1.x, except for the Cisco VPN 3000 Client part.) IPsec and PPTP/Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) should be made to work separately first. If they do not work separately, they do not work together.
Note: PIX 7.0 uses the inspect rpc command to handle RPC packets. The inspect sunrpc command enables or disables application inspection for the Sun RPC protocol. Sun RPC services can run on any port on the system. When a client attempts to access an RPC service on a server, it must find out which port that particular service runs on. It does this by querying the portmapper process on the well-known port number 111. The client sends the RPC program number of the service, and gets back the port number. From this point on, the client program sends its RPC queries to that new port.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
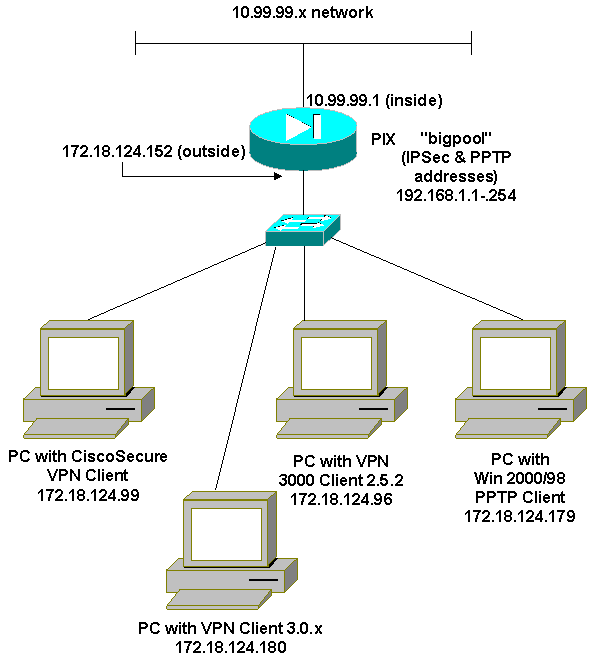
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in this diagram.
Configurations
This document uses these configurations.
| Cisco Secure PIX Firewall |
|---|
PIX Version 6.3(3) interface ethernet0 auto interface ethernet1 100full nameif ethernet0 outside security0 nameif ethernet1 inside security100 enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted hostname goss-515A fixup protocol ftp 21 fixup protocol h323 h225 1720 fixup protocol h323 ras 1718-1719 fixup protocol http 80 fixup protocol ils 389 fixup protocol rsh 514 fixup protocol rtsp 554 fixup protocol sip 5060 fixup protocol sip udp 5060 fixup protocol skinny 2000 fixup protocol smtp 25 fixup protocol sqlnet 1521 names access-list 101 permit ip 10.99.99.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 pager lines 24 mtu outside 1500 mtu inside 1500 ip address outside 172.18.124.152 255.255.255.0 ip address inside 10.99.99.1 255.255.255.0 ip audit info action alarm ip audit attack action alarm ip local pool bigpool 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 pdm history enable arp timeout 14400 nat (inside) 0 access-list 101 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 rpc 0:10:00 h225 1:00:00 timeout h323 0:05:00 mgcp 0:05:00 sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+ aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius aaa-server LOCAL protocol local no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server community public no snmp-server enable traps floodguard enable sysopt connection permit-ipsec sysopt connection permit-pptp crypto ipsec transform-set myset esp-des esp-md5-hmac crypto dynamic-map dynmap 10 set transform-set myset crypto map mymap 10 ipsec-isakmp dynamic dynmap crypto map mymap client configuration address initiate crypto map mymap client configuration address respond crypto map mymap interface outside isakmp enable outside !--- Cisco Secure_VPNClient_key. isakmp key ******** address 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 isakmp identity address isakmp client configuration address-pool local bigpool outside !--- ISAKMP Policy for Cisco VPN Client 2.5 or !--- Cisco Secure VPN Client 1.1. isakmp policy 10 authentication pre-share isakmp policy 10 encryption des isakmp policy 10 hash md5 !--- The 1.1 and 2.5 VPN Clients use Diffie-Hellman (D-H) !--- group 1 policy (PIX default). isakmp policy 10 group 1 isakmp policy 10 lifetime 86400 !--- ISAKMP Policy for VPN Client 3.0 and 4.0. isakmp policy 20 authentication pre-share isakmp policy 20 encryption des isakmp policy 20 hash md5 !--- The 3.0/4.0 VPN Clients use D-H group 2 policy !--- and PIX 6.0 code. isakmp policy 20 group 2 isakmp policy 20 lifetime 86400 vpngroup vpn3000-all address-pool bigpool vpngroup vpn3000-all dns-server 10.99.99.99 vpngroup vpn3000-all wins-server 10.99.99.99 vpngroup vpn3000-all default-domain password vpngroup vpn3000-all idle-time 1800 !--- VPN 3000 group_name and group_password. vpngroup vpn3000-all password ******** telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 vpdn group 1 accept dialin pptp vpdn group 1 ppp authentication pap vpdn group 1 ppp authentication chap vpdn group 1 ppp authentication mschap vpdn group 1 ppp encryption mppe auto vpdn group 1 client configuration address local bigpool vpdn group 1 pptp echo 60 vpdn group 1 client authentication local !--- PPTP username and password. vpdn username cisco password ********* vpdn enable outside terminal width 80 Cryptochecksum:d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e : end goss-515A# |
| Cisco Secure VPN Client 1.1 |
|---|
1- TACconn
My Identity
Connection security: Secure
Remote Party Identity and addressing
ID Type: IP subnet
10.99.99.0
255.255.255.0
Port all Protocol all
Connect using secure tunnel
ID Type: IP address
172.18.124.152
Pre-shared Key=CiscoSecure_VPNClient_key
Authentication (Phase 1)
Proposal 1
Authentication method: pre-shared key
Encryp Alg: DES
Hash Alg: MD5
SA life: Unspecified
Key Group: DH 1
Key exchange (Phase 2)
Proposal 1
Encapsulation ESP
Encrypt Alg: DES
Hash Alg: MD5
Encap: tunnel
SA life: Unspecified
no AH
2- Other Connections
Connection security: Non-secure
Local Network Interface
Name: Any
IP Addr: Any
Port: All |
Cisco VPN 3000 Client 2.5.x or Cisco VPN Client 3.x and 4.x
Select Options > Properties > Authentication. Group-name and group password match the group_name and group_password on the PIX as in:
vpngroup vpn3000-all password ******** Host-name = 172.18.124.152
Windows 98/2000/XP PPTP Client Setup
You can contact the vendor who makes the PPTP client. Refer to How to Configure the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall to Use PPTP for information on how to set this up.
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Commands
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
PIX IPsec Debug
-
debug crypto ipsec—Displays the IPsec negotiations of phase 2.
-
debug crypto isakmp—Displays the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) negotiations of phase 1.
-
debug crypto engine—Displays the traffic that is encrypted.
PIX PPTP Debug
-
debug ppp io—Displays the packet information for the PPTP PPP virtual interface.
-
debug ppp error—Displays PPTP PPP virtual interface error messages.
-
debug vpdn error—Displays PPTP protocol error messages.
-
debug vpdn packets—Displays PPTP packet information about PPTP traffic.
-
debug vpdn events—Displays PPTP tunnel event change information.
-
debug ppp uauth—Displays the PPTP PPP virtual interface AAA user authentication debugging messages.
Microsoft Related Issues
-
How to Keep RAS Connections Active After Logging Off
 —When you log off from a Windows Remote Access Service (RAS) client, any RAS connections are automatically disconnected. In order to remain connected after you log off, enable the KeepRasConnections key in the registry on the RAS client.
—When you log off from a Windows Remote Access Service (RAS) client, any RAS connections are automatically disconnected. In order to remain connected after you log off, enable the KeepRasConnections key in the registry on the RAS client. -
User Is Not Alerted When Logging On with Cached Credentials
 —Symptoms - When you attempt to log on to a domain from a Windows-based workstation or member server and a domain controller cannot be located, no error message is displayed. Instead, you are logged on to the local computer using cached credentials.
—Symptoms - When you attempt to log on to a domain from a Windows-based workstation or member server and a domain controller cannot be located, no error message is displayed. Instead, you are logged on to the local computer using cached credentials. -
How to Write an LMHOSTS File for Domain Validation and Other Name Resolution Issues
 —There can be instances when you experience name resolution issues on your TCP/IP network and you need to use Lmhosts files to resolve NetBIOS names. This article discusses the proper method of creating an Lmhosts file to aid in name resolution and domain validation.
—There can be instances when you experience name resolution issues on your TCP/IP network and you need to use Lmhosts files to resolve NetBIOS names. This article discusses the proper method of creating an Lmhosts file to aid in name resolution and domain validation.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-Oct-2008 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback