UCS IPv6 Management Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure the Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) management end-points with IPv6 addresses.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Cisco UCS Manager (UCSM )
- Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC)
- Familiarity with IPv6
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Cisco UCS B Series
- Cisco UCSM Version 2.2(3a)
- Cisco UCS M3 Series Blade Servers
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
IPv6 management support on the UCS was introduced in UCS Version 2.2. Both the 6100 and 6200 Series Fabric Interconnects (FIs) can have an IPv6 address for the management port apart from their IPv4 addresses. In addition to this, the CIMC address for the M3 servers can have IPv6 addresses. This is available when you choose the Inband access method.
IPv6 can be used by external clients in order to access UCS services such as:
- HTTP/HTTPS
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- Telnet
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Cisco Interaction Manager (CIM)
- Web Service Management (WS-Management)
- Flash Policy Server
With the UCS as a client, IPv6 can be used in order to access various categories of services such as:
- Network Services – Domain Name System (DNS), SNMP, and Network Time Protocol (NTP)
- Authentication services – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), TACACS, and RADIUS
- File transfer services – SSH, FTP, SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), and TFTP
- Other services – Syslog, Callhome, Network File System (NFS) client, and vCenter agent
Configure
This section describes how to configure the Cisco UCSM end-points with IPv6 addresses
FI Configuration
During initial setup, you can configure the management interface with either an IPv4 or an IPv6 address. If it is configured with an IPv6 address, then you must manually add an IPv4 address for the management interface after the initial setup via the UCSM CLI or GUI.
This example shows the steps that are completed in order to configure an IPv6 address for the management port during initial setup:
Enter the configuration method. (console/gui) ? console
Enter the setup mode; setup newly or restore from backup. (setup/restore) ? setup
You have chosen to setup a new Fabric interconnect. Continue? (y/n): y
Enforce strong password? (y/n) [y]: n
Enter the password for "admin":
Confirm the password for "admin":
Is this Fabric interconnect part of a cluster(select 'no' for standalone)?
(yes/no) [n]: n
Fabric interconnect will be in stand alone mode
Enter the system name: ucs-ipv6
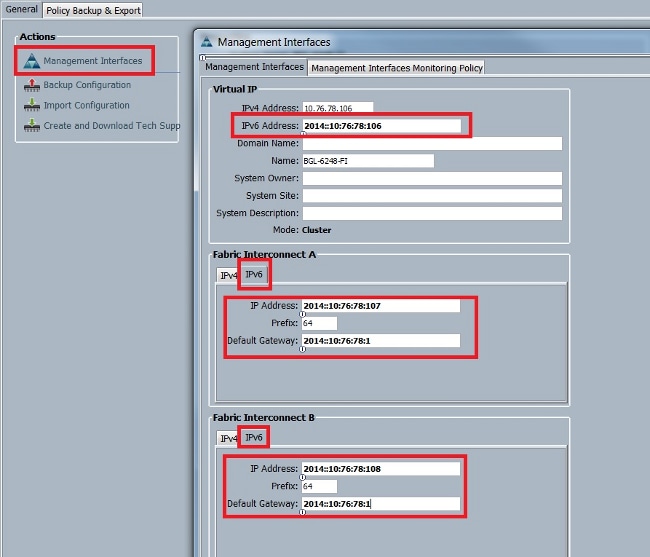
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IP address : 2014::10:76:78:107
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IPv6 prefix : 64
IPv6 address of the default gateway : 2014::10:76:78:1
IPv6 addresses can be added to a setup that has only IPv4 addresses, and the current IPv6 addresses can be changed as well. These options are available from both the UCSM GUI and the CLI.
This example shows the steps that are completed from the UCSM GUI:
This example shows the steps that are completed from the UCSM CLI:
FI-A# scope fabric-interconnect a
FI-A /fabric-interconnect # scope ipv6-config
FI-A /fabric-interconnect/ipv6-config # set out-of-band ipv6 2014::10:76:78:107
FI-A /fabric-interconnect/ipv6-config* # set out-of-band ipv6-gw 2014::10:76:78:1
FI-A /fabric-interconnect/ipv6-config* # set out-of-band ipv6-prefix 64
FI-A* # scope fabric-interconnect b
FI-A /fabric-interconnect* # scope ipv6-config
FI-A /fabric-interconnect/ipv6-config* # set out-of-band ipv6 2014::10:76:78:108
FI-A /fabric-interconnect/ipv6-config* # set out-of-band ipv6-gw 2014::10:76:78:1
FI-A /fabric-interconnect/ipv6-config* # set out-of-band ipv6-prefix 64
FI-A* # scope system
FI-A /system* # set virtual-ip ipv6 2014::10:76:78:106
FI-A* # commit-buffer
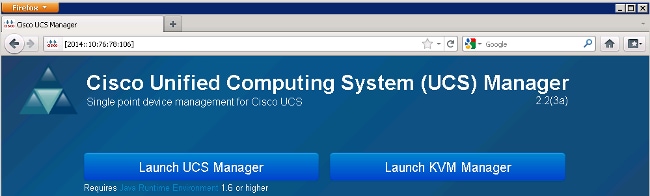
Access the UCSM Via IPv6
You can access the UCSM GUI and the CLI with the use of the assigned IPv6 addresses:
CIMC Over IPv6
This section describes the Inband management of the CIMC.
Prior to UCS Version 2.2, the CIMC access was through the Out of Band management port of the UCS FI. The CIMC can have two different IP addresses up until UCS Version 2.2:
- An IPv4 address that is assigned from the Equipment tab – This address sticks to the server hardware itself and does not change, irrespective of the service profile association.
- An IPv4 address that is assigned from the Servers tab – This address sticks to the service profile and moves with the service profile.
UCS Version 2.2 also enabled Inband access of the CIMC for M3 servers. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses can be used for Inband access, so the CIMC can have up to six different addresses from UCS Version 2.2:
| Out of Band | Inband | |
| Equipment | IPv4 | IPv4, IPv6 |
| Servers | IPv4 | IPv4, IPv6 |
This example describes the steps that are completed in order to configure Inband IPv6 addresses for the CIMC via the Equipment tab of the UCSM GUI:
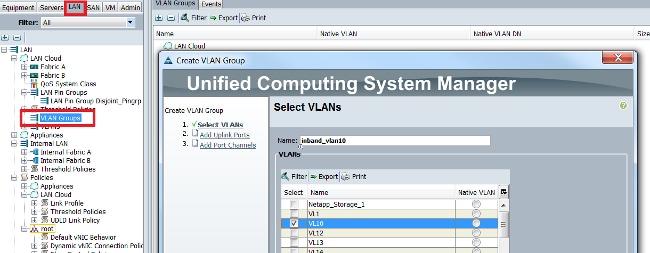
- Navigate to LAN > VLAN Groups and create a VLAN group with the list of VLANs that will be used for Inband management:
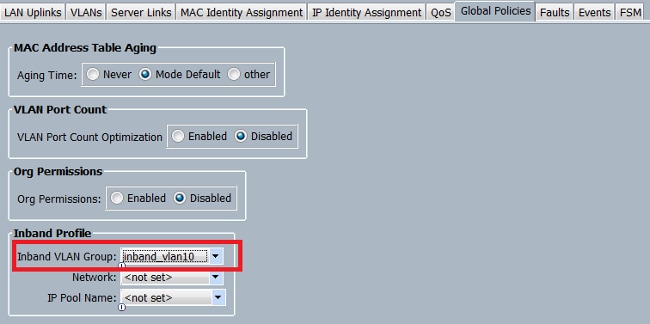
- Navigate to LAN > Global Policies > Inband Profile and select the VLAN group in order to associate it to the Inband Profile:
- Navigate to the server from the Equipment tab, click Inventory > CIMC > Change Inband Management IP, associate a VLAN from the group to the CIMC, and assign an IPv6 address:
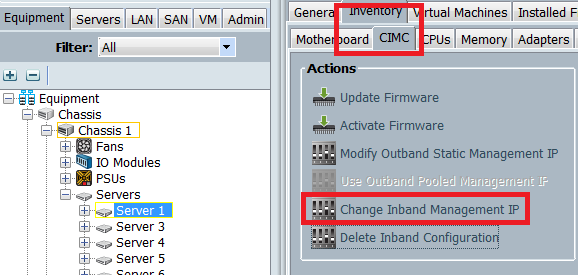
- Choose a VLAN from the Network drop down list, click Inband IPv6, and assign an IPv6 address. The next image shows the static assignment method.
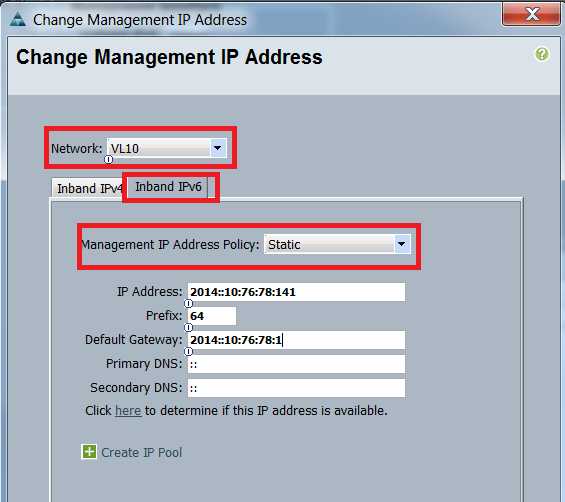
The same procedure is used when you assign the IPv6 address from the Servers tab. The next example shows the steps that are completed in order to configure an Inband IPv6 address for the CIMC from the Equipment tab via the UCSM CLI:
FI-A# scope server 1/1
FI-A /chassis/server # scope cimc
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc # create mgmt-iface in-band
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface* # create mgmt-vlan
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface/mgmt-vlan* # set network-name VL10
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface/mgmt-vlan* # create ext-static-ip6
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface/mgmt-vlan/ext-static-ip6* # set addr
2014::10:76:78:141
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface/mgmt-vlan/ext-static-ip6* # set prefix 64
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface/mgmt-vlan/ext-static-ip6* # set default-gw
2014::10:76:78:1
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc/mgmt-iface/mgmt-vlan/ext-static-ip6* # commit-buffer
Launch the KVM Console and Other Services
The CIMC address is used for services such as Keyboard, Video, and Mouse (KVM), vMedia, Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI), and Serial over LAN (SoL). These services are available for both the Inband and Out of Band addresses.
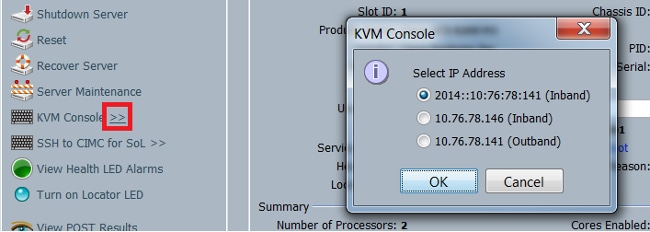
When you launch the KVM console, click the >> symbol next to the KVM Console option in order to view the various addresses available for access to the KVM console:
The same option is available from the KVM launcher:

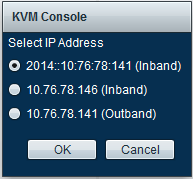
The addresses that are assigned to the Service Profile take precedence over the addresses that are assigned to the server hardware via the Equipment tab.
The IPv6 address is the default address that is chosen for a launch of the KVM console, so when you click on the KVM console, it uses this address. The KVM launch fails if this IPv6 address is not reachable. In order to choose the other addresses, click the >> symbol next to the KVM Console option, as mentioned above.
The UCS Version 2.2 introduced direct KVM access as well. However, this feature is available only for Out of Band management. The IPv6 addresses cannot be used here, as Out of Band uses only IPv4 addresses.
Verify
This section describes how to verify that your configuration works properly.
Verify the IPv6 Address Assignment for the FIs
This example shows how to verify the IPv6 address assignment for the FIs from the UCSM GUI:

This example shows how to verify the IPv6 address assignment for the FIs from the UCSM CLI:
FI-A(local-mgmt)# show mgmt-ip-debug ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 54:7F:EE:65:81:A1
inet addr:10.76.78.107 Bcast:10.76.78.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: 2014::10:76:78:106/64 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: 2014::10:76:78:107/64 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: fe80::567f:eeff:fe65:81a1/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:24775380 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:14343153 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
FI-B(local-mgmt)# show mgmt-ip-debug ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 54:7F:EE:6F:71:81
inet addr:10.76.78.108 Bcast:10.76.78.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: 2014::10:76:78:108/64 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: fe80::567f:eeff:fe6f:7181/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:18646548 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:238825 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:3206162748 (2.9 GiB) TX bytes:56366913 (53.7 MiB)
Test Basic Network Connectivity
This example shows how to perform basic network connectivity tests from the UCSM CLI:
FI-A(local-mgmt)# ping6 2014::10:76:78:216
PING 2014::10:76:78:216(2014::10:76:78:216) from 2014::10:76:78:106 eth0:
56 data bytes
64 bytes from 2014::10:76:78:216: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.92 ms
64 bytes from 2014::10:76:78:216: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.262 ms
64 bytes from 2014::10:76:78:216: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.260 ms
64 bytes from 2014::10:76:78:216: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.222 ms
64 bytes from 2014::10:76:78:216: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.196 ms
64 bytes from 2014::10:76:78:216: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.231 ms
FI-A(local-mgmt)# traceroute6 2014::10:76:78:216
traceroute to 2014::10:76:78:216 (2014::10:76:78:216) from
2014::10:76:78:106, 30 hops max, 16 byte packets
1 2014::10:76:78:216 (2014::10:76:78:216) 0.244 ms * 0.253 ms
Verify the IPv6 Address Assignment for the CIMC
This example shows how to verify the IPv6 addresses that are assigned to the CIMC from the UCSM GUI:

This example shows how to verify the IPv6 addresses that are assigned to the CIMC from the UCSM CLI:
FI-A# scope server 1/1
FI-A /chassis/server # scope cimc
FI-A /chassis/server/cimc # show mgmt-iface in-band detail expand
External Management Interface:
Mode: In Band
Ip V4 State: None
Ip V6 State: Static
Is Derived from Inband Profile: No
External Management Virtual LAN:
Network Name: VL10
Id: 10
External Management Static IPv6:
IP Address: 2014::10:76:78:146
Default Gateway: 2014::10:76:78:1
Prefix: 64
Primary DNS IP: ::
Secondary DNS IP: ::
Trace the CIMC Inband Connection Path for Blade Servers
The next example shows how to trace the path for the CIMC Inband connection for the blade servers. The CIMC Inband interface should be mapped to the last Host Interfaces (HIF) port on the IOM that corresponds. The IO Module (IOM) is chosen based on the managing instance of the server.
From the UCSM GUI, navigate to Equipment > Server > General > Connection Details:

You can also verify via the UCSM CLI as well:
FI-A# scope server 1/1
FI-A /chassis/server # show detail
Server:
Slot: 1
<snip>
Conn Path: A,B
Conn Status: A,B
Managing Instance: A
As shown, Eth1/1/33 is pinned to the uplink port Eth1/19, which is used for the Inband connection.
FI-A(nxos)# show fex 1 detail
Fex Port State Fabric Port
Eth1/1/1 Up Eth1/17
Eth1/1/2 Up Eth1/17
Eth1/1/3 Up Eth1/17
Eth1/1/4 Up Eth1/17
Eth1/1/5 Down None
Eth1/1/6 Down None
Eth1/1/7 Down None
Eth1/1/8 Down None
Eth1/1/9 Up Eth1/19
Eth1/1/10 Down None
Eth1/1/11 Down None
Eth1/1/12 Down None
Eth1/1/13 Up Eth1/20
Eth1/1/14 Down None
Eth1/1/15 Down None
Eth1/1/16 Down None
Eth1/1/17 Up Eth1/17
Eth1/1/18 Down None
Eth1/1/19 Down None
Eth1/1/20 Down None
Eth1/1/21 Up Eth1/18
Eth1/1/22 Up Eth1/18
Eth1/1/23 Up Eth1/18
Eth1/1/24 Up Eth1/18
Eth1/1/25 Down None
Eth1/1/26 Down None
Eth1/1/27 Down None
Eth1/1/28 Down None
Eth1/1/29 Down Eth1/20
Eth1/1/30 Down Eth1/20
Eth1/1/31 Down Eth1/20
Eth1/1/32 Down Eth1/20
Eth1/1/33 Up Eth1/19
The running configuration now adds the Inband VLAN, which is VLAN 10 in this example.
FI-A(nxos)# show run int eth1/1/33
interface Ethernet1/1/33
no pinning server sticky
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 4044
switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,4044
no shutdown
FI-A(nxos)# show mac address-table vlan 10
Legend:
* - primary entry, G - Gateway MAC, (R) - Routed MAC, O - Overlay MAC
age - seconds since last seen,+ - primary entry using vPC Peer-Link
VLAN MAC Address Type age Secure NTFY Ports/SWID.SSID.LID
---------+-----------------+--------+---------+------+----+------------------
* 10 e02f.6d9a.9e71 dynamic 0 F F Eth1/1/33
Trace the CIMC Inband Connection Path for Rack Servers
This example shows how to trace the CIMC Inband connection path for the rack servers. The CIMC interface should be mapped to a Vethernet interface, which is mapped to the Fabric Extender (FEX) port to which the server is connected. If the server connects to two different FEX modules in an High Availability (HA) setup, the managing instance must be checked in order to determine the path.
From the UCSM GUI, navigate to Equipment > Rack-mounts > Server > General > Connection Details:

You can also verify via the UCSM CLI as well:
FI-A# scope server 1
FI-A /server # show detail
Server:
Conn Path: A,B
Conn Status: A,B
Managing Instance: B
As shown, Eth2/1/4 on the FEX is connected to the rack server.
FI-B(nxos)# show fex 2 detail
Fex Port State Fabric Port
Eth2/1/1 Down None
Eth2/1/2 Down None
Eth2/1/3 Down None
Eth2/1/4 Up Po1154
Eth2/1/5 Down None
Eth2/1/6 Down None
Eth2/1/7 Down None
Eth2/1/8 Down None
Eth2/1/9 Down None
Eth2/1/10 Down None
Eth2/1/11 Down None
Eth2/1/12 Down None
Eth2/1/13 Down None
Eth2/1/14 Down None
Eth2/1/15 Down None
Eth2/1/16 Down None
Eth2/1/17 Down None
Eth2/1/18 Down None
Eth2/1/19 Down None
Eth2/1/20 Down None
Eth2/1/21 Down None
Eth2/1/22 Down None
Eth2/1/23 Down None
Eth2/1/24 Down None
Eth2/1/25 Down None
Eth2/1/26 Down None
Eth2/1/27 Down None
Eth2/1/28 Down None
Eth2/1/29 Down None
Eth2/1/30 Down None
Eth2/1/31 Down None
Eth2/1/32 Down None
These Vethernet interfaces are mapped to Eth2/1/4:
FI-B(nxos)# show vifs interface ethernet 2/1/4
Interface MAX-VIFS VIFS
-------------- -------- ------------------------------------
Eth2/1/4 60 Veth689, Veth32769,
FI-B(nxos)# show run int veth32769
interface Vethernet32769
inherit port-profile ucsm_internal_rackserver_portprofile
no pinning server sticky
bind interface Ethernet2/1/4 channel 65535
As shown, Veth32769 is pinned to uplink port Eth1/17.
FI-B(nxos)# show pinning border-interfaces
--------------------+---------+-----------------------------
Border Interface Status SIFs
--------------------+---------+-----------------------------
Eth1/17 Active sup-eth2 Veth32769
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section describes some FAQs and answers.
Can I use IPv6 Private Unicast addresses for the management port?
No. Only Global Unicast addresses are supported.
Does UCS support Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC)?
No. Only static address assignment is supported for the FI management port.
Can I use IPv6 for iSCSI initiators when I use iSCSI boot?
No. IPv6 is not supported for Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) initiator at this time.
What happens when the UCSM is downgraded from UCS Version 2.2 or later to UCS Version 2.1 or earlier?
If the management ports of the FI or if the CIMC has an IPv6 address or an Inband configuration, then the downgrade fails with an error message.
What happens when the FI is downgraded from UCS Version 2.2 or later to UCS Version 2.1 or earlier?
If the UCSM currently uses Version 2.2 or later, the FI downgrade completes successfully. The IPv6 configuration on the FI should continue to work.
What happens when the CIMC uses UCS Version 2.1 or earlier?
If the UCSM uses Version 2.2 or later, the Inband or IPv6 configuration for the CIMC is allowed. However, this is not recognized and the CIMC continues to use the Out of Band IPv4 address.
What happens when the CIMC is downgraded from UCS Version 2.2 or later to UCS Version 2.1 or earlier?
If the CIMC has an Inband or IPv6 configuration, the downgrade fails with an error message.
Are there any reserved prefixes that cannot be used for IPv6 addresses?
Yes. Reserved prefix values are 0 and 128. Only 1 through 127 can be used.
Are there any reserved VLANs that cannot be used for Inband management?
Yes. VLANs 1, 2, and 3 cannot be used along with the regular list of reserved VLANs (3968 to 4047).
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
06-Mar-2015 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)




 Feedback
Feedback