Configure IGMP Snooping on CBS220 Series Switches
Available Languages
Objective
The objective of this document is to show you how to configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping on the Cisco Business 220 Series Switches.
Applicable Devices | Software Version
- CBS220 series (DataSheet) | 2.0.0.17
Introduction
Multicast is the network layer technique used to transmit data packets from one host to selected hosts in the network. At the lower layer, the switch broadcasts the multicast traffic on all ports, even if only one host needs to receive it. Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping is used to forward Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) multicast traffic to the desired host.
When IGMP is enabled, it detects the IGMP messages exchanged between the IPv4 router and the multicast hosts attached to the interfaces. It then maintains a table that restricts IPv4 multicast traffic and forwards them dynamically to the parts that need to receive them.
The following configurations are prerequisites for configuring IGMP:
- Configure Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
- Enable Bridge Multicast Filtering (steps shown in the next section)
Enable IGMP Snooping and Multicast Action
In order for IGMP Snooping to work, Bridge Multicast filtering must be enabled. The IGMP Snooping must be enabled globally and for each relevant VLAN on the IGMP Snooping page.
Step 1
Log in to the web configuration utility and choose Multicast > Properties.

Step 2
Make sure IGMP Snooping is enabled. Select the procedure for Unknown Multicast Action. The options are Drop, Flood, or Forward to Router Port.
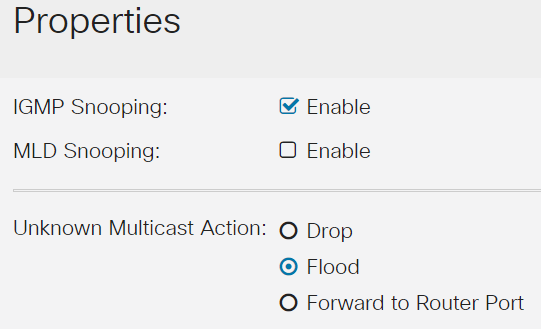
Step 3
Click Apply.
Configure IGMP Snooping
Step 1
Log in to the web-based utility and choose Multicast > IGMP Snooping.

Step 2
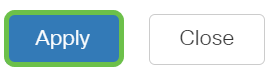
Select the radio button for the IGMP version you would want to use. Your options are IGMPv2 or IGMPv3.
Report suppression is enabled by default. If you disable this feature, all IGMP reports will be forwarded to Multicast routers.
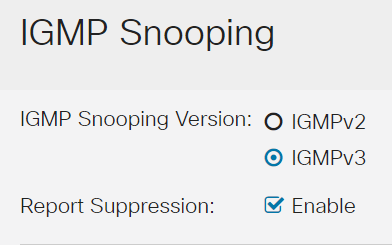
Step 3
Select a VLAN and click the edit icon.
Step 4
Check the Enable check box for IGMP Snooping Status. This will enable IGMP snooping on the VLAN. The device monitors network traffic to determine which hosts have asked to be sent Multicast traffic.

Step 5 (Optional)
To allow the multicast router to automatically learn the connected ports, check the Enable check box for MRouter Ports Auto Learn.
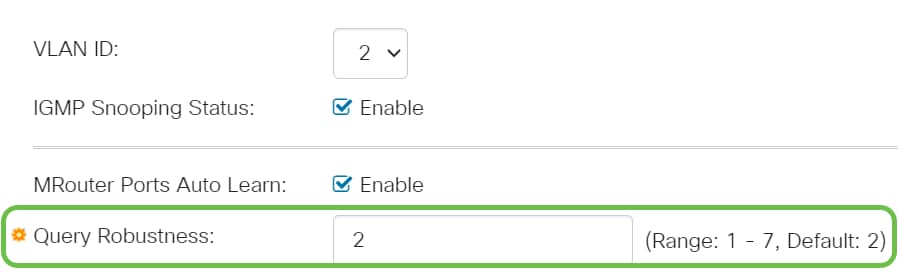
Step 6
Query Robustness - Enter the robustness variable to be used if this switch is the elected querier.
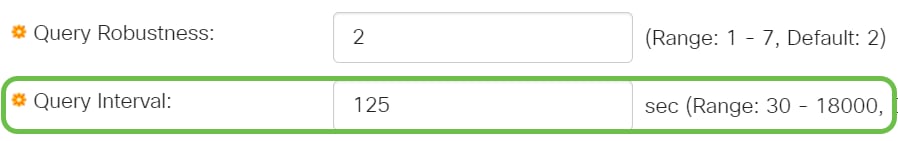
Step 7
Query Interval - Enter the interval between the general queries to be used if this switch is the elected querier.
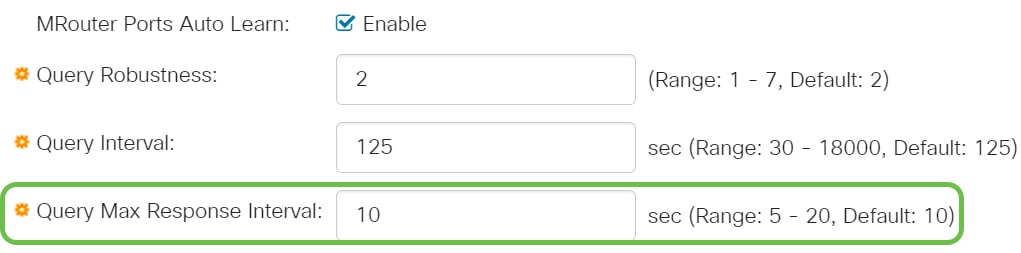
Step 8
Query Max Response Interval - Enter the delay used to calculate the maximum response code inserted into the periodic general queries.
Step 9
Last Member Query Counter – The number of IGMP group-specific queries sent before the device assumes that there are no more members for the group if the device is the elected querier.

Step 10
Last Member Query Interval - Enter the maximum response delay to be used if the switch cannot read the maximum response time value from group-specific queries sent by the elected querier.
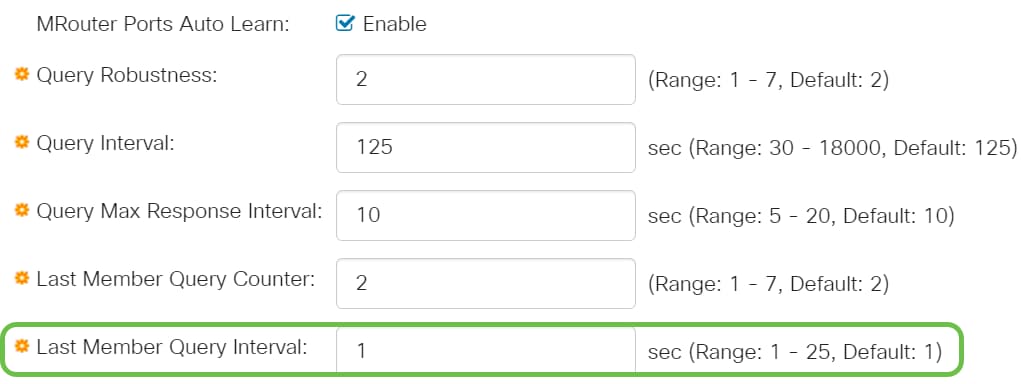
Step 11
Immediate Leave - Select to enable the switch to remove an interface that sends a leave message from the forwarding table without first sending out MAC-based general queries to the interface. When Immediate Leave an IGMP Leave Group message is received from a host, the system removes the host port from the table entry. After it relays the IGMP queries from the Multicast router, it deletes entries periodically if it doesn’t receive any IGMP membership reports from the Multicast clients. When enabled, this feature reduces the time it takes to block unnecessary IGMP traffic sent to a device port.
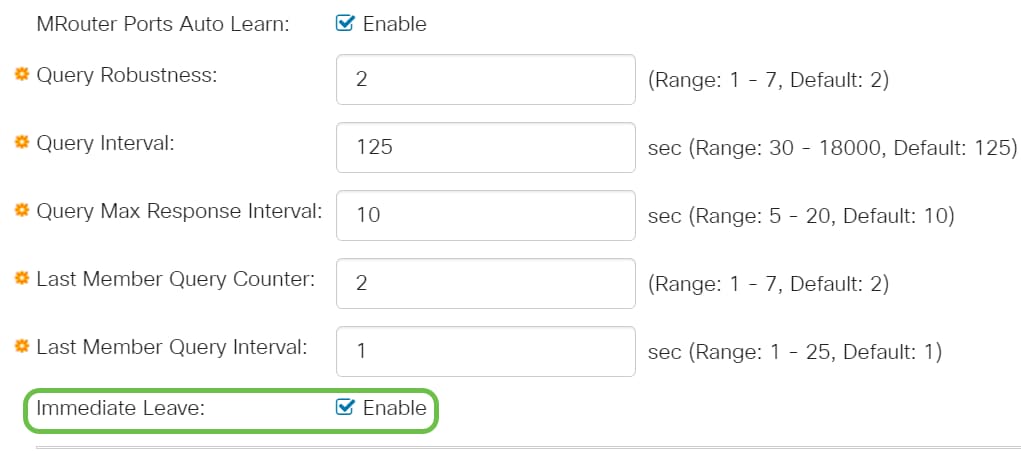
Step 12 (Optional)
IGMP Querier Status - Select to enable this feature. This feature is required if there’s no Multicast router.
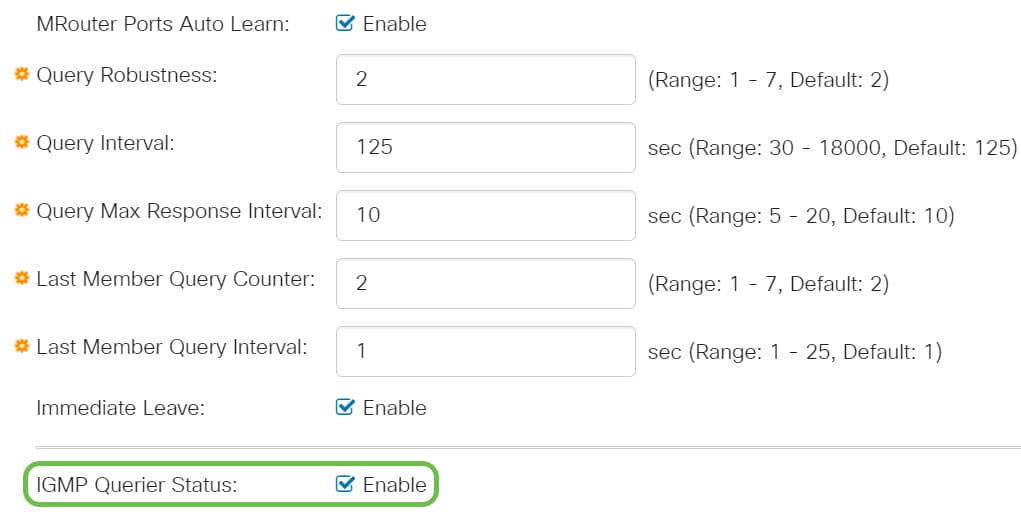
Step 13
IGMP Querier Version - Select the IGMP version to be used if the device becomes the elected querier. Select IGMPv3 if there are switches and/or Multicast routers in the VLAN that perform source-specific IP Multicast forwarding. Otherwise, select IGMPv2.
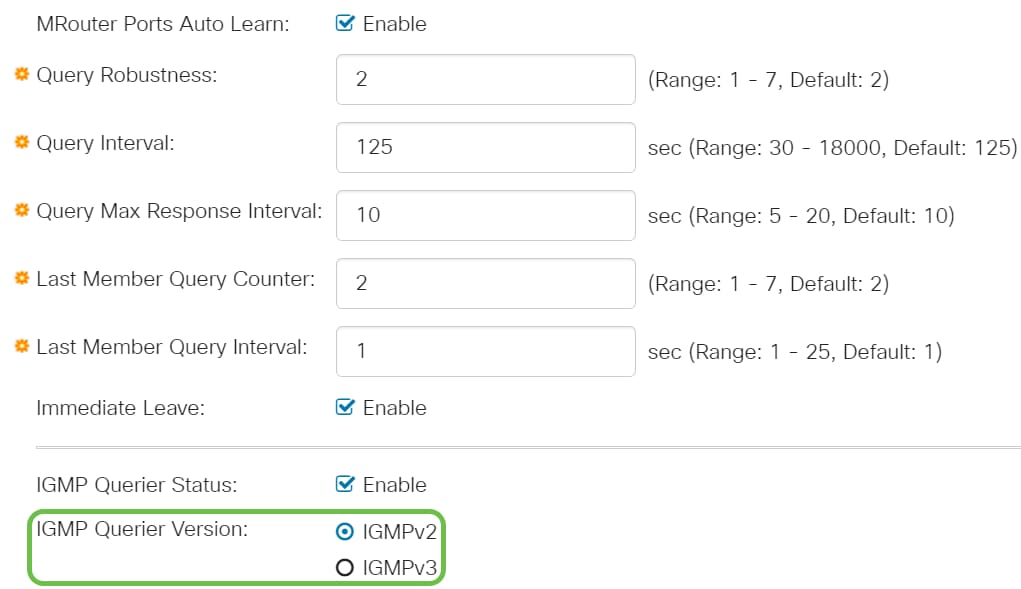
Step 14
Click Apply. The Running Configuration file is updated.

Step 15
To save this configuration from the running configuration to the startup configuration, click the save icon in the top right corner of your screen.
Conclusion
It’s as simple as that, you have now configured IGMP Snooping.
For more configurations, refer to the Cisco Business 220 Series Switches Administration Guide.
If you want to see more articles on CBS220 switches, check out the 220 Series support page.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback