Cisco Sx250 Series Smart Switches Product Specifications
Available Languages
Introduction

The Cisco Sx250 Series Smart Switches are designed to be easy to configure, manage, and troubleshoot, allowing you to focus on your business priorities. These switches are equipped with a new generation of highly-integrated, cost-effective packet processors targeted for Carrier Ethernet and Small-Medium Enterprise (SME) applications with full wire-speed performance Fast Ethernet (FE) or Gigabit Ethernet (GE) ports, and GE Combo platforms.
The web-based utility allows you to deploy and manage your network efficiently. Setting up and troubleshooting can be done easily with easy-to-use tools such as Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), FindIT, and Cisco Smartports, which let your network automatically detect and configure all connected Cisco devices.
This article shows the product specifications of the Sx250 Smart Switches.
Note: If you want to know about the features and functions of the Sx250 Smart Switches, click here.
Applicable Devices
- SF250 Series
- SG250 Series
Software Version
- 2.2.5.68
Sx250 Series Product Specifications
Performance
| Feature |
Description |
||
| Switching capacity and forwarding rate All switches are wire-speed and non-blocking |
Model |
Capacity in Millions of Packets per Second (mpps) (64-byte packets) |
Switching Capacity in Gigabits per Second (Gbps) |
| SF250-48 |
13.10 |
17.6 |
|
| SF250- 48HP |
13.10 |
17.6 |
|
| SG250-10P |
14.88 |
20.0 |
|
| SG250- 26 |
38.69 |
52.0 |
|
| SG250-26HP |
38.69 |
52.0 |
|
| SG250-26P |
38.69 |
52.0 |
|
Layer 2 Switching
| Feature |
Description |
| Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) |
Standard 802.1d spanning tree support Fast convergence using 802.1w (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol [RSTP]), enabled by default Multiple spanning tree instances using 802.1s (MSTP); 8 instances are supported |
| Port grouping/link aggregation |
Support for IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) Up to 4 groups Up to 8 ports per group with 16 candidate ports for each (dynamic) 802.3ad LAG |
| VLAN |
Support for up to 256 active VLANs simultaneously Port-based and 802.1Q tag-based VLANs Management VLAN |
| Voice VLAN |
Voice traffic is automatically assigned to a voice-specific VLAN and treated with appropriate levels of QoS. Auto voice capabilities deliver networkwide zero-touch deployment of voice endpoints and call control devices. |
| IGMP (versions 1, 2, and 3) snooping |
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) limits bandwidth-intensive multicast traffic to only the requesters; supports 4K multicast groups (source-specific multicasting is also supported). |
| HOL blocking |
Head-of-line (HOL) blocking. |
Security
| Feature |
Description |
| SSL |
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encrypts all HTTPS traffic, allowing secure access to the web-based utility in the switch. |
| IEEE 802.1X (authenticator role) |
RADIUS authentication, MD5 hash, single/multiple host mode, and single/multiple sessions. |
| Secure Sensitive Data (SSD) |
A mechanism to manage sensitive data (such as passwords, keys, and so on) securely on the switch, populating this data to other devices, and secure autoconfig. Access to view the sensitive data as plaintext or encrypted is provided according to the user-configured access level and the access method of the user. |
| Port security |
Ability to lock source MAC addresses to ports and limit the number of learned MAC addresses. |
| RADIUS |
Supports RADIUS authentication for management access. Switch functions as a client. |
| Storm control |
Broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast. |
| DoS prevention |
Denial-of-service (DoS) attack prevention. |
Quality of Service
| Feature |
Description |
| Priority levels |
4 hardware queues |
| Scheduling |
Strict priority and weighted round-robin (WRR) |
| Class of service |
Port based; 802.1p VLAN priority based; IPv4/v6 IP precedence/ToS/DSCP based; DiffServ; trusted QoS Queue assignment based on differentiated services code point (DSCP) and class of service (802.1p/CoS) |
| Rate limiting |
Ingress policer, per VLAN, per port |
Standards
| Feature |
Description |
| Standards |
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet, IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet, IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol, IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.3x Flow Control, IEEE 802.3 ad LACP, IEEE 802.1D (STP), IEEE 802.1Q/p VLAN, IEEE 802.1w RSTP, IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP, IEEE 802.1X Port Access Authentication, IEEE 802.3af, IEEE 802.3at, RFC 768, RFC 783, RFC 791, RFC 792, RFC 793, RFC 813, RFC 879, RFC 896, RFC 826, RFC 854, RFC 855, RFC 856, RFC 858, RFC 894, RFC 919, RFC 920, RFC 922, RFC 950, RFC 951, RFC 1042, RFC 1071, RFC 1123, RFC 1141, RFC 1155, RFC 1157, RFC 1213, RFC 1215, RFC 1286, RFC 1350, RFC 1442, RFC 1451, RFC 1493, RFC 1533, RFC 1541, RFC 1542, RFC 1573, RFC 1624, RFC 1643, RFC 1700, RFC 1757, RFC 1867, RFC 1907, RFC 2011, RFC 2012, RFC 2013, RFC 2030, RFC 2131, RFC 2132, RFC 2233, RFC 2576, RFC 2616, RFC 2618, RFC 2665, RFC 2666, RFC 2674, RFC 2737, RFC 2819, RFC 2863, RFC 3164, RFC 3411, RFC 3412, RFC 3413, RFC 3414, RFC 3415, RFC 3416, RFC 4330 |
IPv6
| Feature |
Description |
| IPv6 |
Ipv6 host mode Ipv6 over Ethernet Dual Ipv6/Ipv4 stack Ipv6 neighbor and router discovery (ND) Ipv6 stateless address auto configuration Path maximum transmission unit (MTU) discovery Duplicate address detection (DAD) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) version 6 Ipv6 over Ipv4 network with Intrasite Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) support USGv6 and Ipv6 Gold Logo certified |
| Ipv6 QoS |
Prioritize Ipv6 packets in hardware |
| Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD v1/2) snooping |
Deliver Ipv6 multicast packets only to the required receivers |
| Ipv6 applications |
Web/SSL, Ping, Traceroute, Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS), Syslog, DNS client, DHCP Client, DHCP Autoconfig |
| Ipv6 RFC supported |
RFC 4443 (which obsoletes RFC 2463): ICMPv6 RFC 4291 (which obsoletes RFC 3513): Ipv6 address architecture RFC 4291: IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture RFC 2460: Ipv6 Specification RFC 4861 (which obsoletes RFC 2461): Neighbor Discovery for Ipv6 RFC 4862 (which obsoletes RFC 2462): Ipv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration RFC 1981: Path MTU Discovery RFC 4007: Ipv6 Scoped Address Architecture RFC 3484: Default address selection mechanism RFC 5214 (which obsoletes RFC 4214): ISATAP tunneling RFC 4293; MIB Ipv6: Textual Conventions and General Group RFC 3595: Textual Conventions for Ipv6 Flow Label |
Management
| Feature |
Description |
|
| Web-based Utility |
Built-in switch configuration utility for easy browser-based device configuration (HTTP/HTTPS). Supports configuration, system dashboard, system maintenance, and monitoring. |
|
| SNMP |
SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3 with support for traps, and SNMP v3 User-based Security Model (USM) |
|
| Standard MIBs |
lldp-MIB lldpextdot1-MIB lldpextdot3-MIB lldpextmed-MIB rfc2674-MIB rfc2575-MIB rfc2573-MIB rfc2233-MIB rfc2013-MIB rfc2012-MIB rfc2011-MIB RFC-1212 RFC-1215 SNMPv2-CONF SNMPv2-TC p-bridge-MIB q-bridge-MIB rfc1389-MIB rfc1493-MIB rfc1611-MIB rfc1612-MIB rfc1850-MIB rfc1907-MIB rfc2571-MIB rfc2572-MIB rfc2574-MIB rfc2576-MIB rfc2613-MIB |
rfc2665-MIB rfc2668-MIB rfc2737-MIB rfc2925-MIB rfc3621-MIB rfc4668-MIB rfc4670-MIB trunk-MIB tunnel-MIB udp-MIB draft-ietf-bridge-8021x-MIB draft-ietf-bridge-rstpmib-04-MIB draft-ietf-hubmib-etherif-mib-v3-00-MIB draft-ietf-syslog-device-MIB ianaaddrfamnumbers-MIB ianaifty-MIB ianaprot-MIB inet-address-MIB ip-forward-MIB ip-MIB RFC1155-SMI RFC1213-MIB SNMPv2-MIB SNMPv2-SMI SNMPv2-TM RMON-MIB rfc1724-MIB dcb-raj-DCBX-MIB-1108-MIB rfc1213-MIB rfc1757-MIB |
| Private MIBs |
CISCOSB-lldp-MIB CISCOSB-brgmulticast-MIB CISCOSB-bridgemibobjects-MIB CISCOSB-bonjour-MIB CISCOSB-dhcpcl-MIB CISCOSB-MIB CISCOSB-wrandomtaildrop-MIB CISCOSB-traceroute-MIB CISCOSB-telnet-MIB CISCOSB-stormctrl-MIB CISCOSBssh-MIB CISCOSB-socket-MIB CISCOSB-sntp-MIB CISCOSB-smon-MIB CISCOSB-phy-MIB CISCOSB-multisessionterminal-MIB CISCOSB-mri-MIB CISCOSB-jumboframes-MIB CISCOSB-gvrp-MIB CISCOSB-endofmib-MIB CISCOSB-dot1x-MIB CISCOSB-deviceparams-MIB CISCOSB-cli-MIB CISCOSB-cdb-MIB CISCOSB-brgmacswitch-MIB CISCOSB-3sw2swtables-MIB CISCOSB-smartPorts-MIB CISCOSB-tbi-MIB CISCOSB-macbaseprio-MIB CISCOSB-env_mib-MIB CISCOSB-policy-MIB CISCOSB-sensor-MIB CISCOSB-aaa-MIB CISCOSB-application-MIB CISCOSB-bridgesecurity-MIB CISCOSB-copy-MIB CISCOSB-CpuCounters-MIB CISCOSB-Custom1BonjourService-MIB CISCOSB-dhcp-MIB CISCOSB-dlf-MIB CISCOSB-dnscl-MIB CISCOSB-embweb-MIB CISCOSB-fft-MIB CISCOSB-file-MIB CISCOSB-greeneth-MIB CISCOSB-greeneth-MIB CISCOSB-interfaces-MIB CISCOSB-interfaces_recovery-MIB |
CISCOSB-ip-MIB CISCOSB-iprouter-MIB CISCOSB-ipv6-MIB CISCOSB-mnginf-MIB CISCOSB-lcli-MIB CISCOSB-localization-MIB CISCOSB-mcmngr-MIB CISCOSB-mng-MIB CISCOSB-physdescription-MIB CISCOSB-PoE-MIB CISCOSB-protectedport-MIB CISCOSB-rmon-MIB CISCOSB-rs232-MIB CISCOSB-SecuritySuite-MIB CISCOSB-snmp-MIB CISCOSB-specialbpdu-MIB CISCOSB-banner-MIB CISCOSB-syslog-MIB CISCOSB-TcpSession-MIB CISCOSB-traps-MIB CISCOSB-trunk-MIB CISCOSB-tuning-MIB CISCOSB-tunnel-MIB CISCOSB-udp-MIB CISCOSB-vlan-MIB CISCOSB-ipstdacl-MIB CISCOSB-eee-MIB CISCOSB-ssl-MIB CISCOSB-digitalkeymanage-MIB CISCOSB-qosclimib-MIB CISCOSB-digitalkeymanage-MIB CISCOSB-tbp-MIB CISCOSMB-MIB CISCOSB-secsd-MIB CISCOSB-draft-ietf-entmib-sensor-MIB CISCOSB-draft-ietf-syslog-device-MIB CISCOSB-rfc2925-MIB CISCO-SMI-MIB CISCOSB-DebugCapabilities-MIB CISCOSB-CDP-MIB CISCOSB-vlanVoice-MIB CISCOSB-EVENTS-MIB CISCOSB-sysmng-MIB CISCOSB-sct-MIB CISCO-TC-MIB CISCO-VTP-MIB CISCO-CDP-MIB |
| Remote monitoring (RMON) |
Embedded RMON software agent supports 4 RMON groups (history, statistics, alarms, and events) for enhanced traffic management, monitoring, and analysis |
|
| Ipv4 and Ipv6 dual stack |
Coexistence of both protocol stacks to ease migration |
|
| Firmware upgrade |
Web browser upgrade (HTTP/HTTPS) and TFTP and SCP |
|
| Port mirroring |
Traffic on a port can be mirrored to another port for analysis with a network analyzer or RMON probe. Up to 4 source ports can be mirrored to one destination port. |
|
| VLAN mirroring |
Traffic from a VLAN can be mirrored to a port for analysis with a network analyzer or RMON probe. Up to 4 source VLANs can be mirrored to one destination port. |
|
| Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) (options 12, 66, 67, 129, and 150) |
DHCP options facilitate tighter control from a central point (DHCP server), to obtain IP address, autoconfiguration (with configuration file download), DHCP Relay, and host name. |
|
| Autoconfiguration |
Enables mass deployment with protection of sensitive data. |
|
| Text-editable configs |
Config files can be edited with a text editor and downloaded to another switch, facilitating easier mass deployment. |
|
| Smartports |
Simplified configuration of QoS and security capabilities. |
|
| Auto Smartports |
Automatically applies the intelligence delivered through the Smartports roles to the port based on the devices discovered over Cisco Discovery Protocol or LLDP-MED. This facilitates zero-touch deployments. |
|
| Cloud services |
Support for Cisco Active Advisor |
|
| Localization |
Localization of the web-based utility and documentation into multiple languages |
|
| Login banner |
Configurable multiple banners for web as well as CLI |
|
| Other management |
Traceroute; single IP management; HTTP/HTTPS; RADIUS; port mirroring; TFTP upgrade; DHCP client; Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP); cable diagnostics; Ping; syslog; automatic time settings from Management Station. |
|
Green (Power Efficiency)
| Feature |
Description |
| Energy detect |
Automatically turns power off on RJ-45 port when detecting link down. Active mode is resumed without loss of any packets when the switch detects the link is up. |
| Cable length detection |
Adjusts the signal strength based on the cable length. Reduces the power consumption for shorter cables. |
| EEE compliant (802.3az) |
Supports IEEE 802.3az on all copper Gigabit Ethernet ports. |
| Disable port LEDs |
LEDs can be manually turned off to save on energy. |
| General |
|
| Jumbo frames |
Frame sizes up to 9K bytes. The default MTU is 2K bytes. |
| MAC table |
8K addresses. |
Discovery
| Feature |
Description |
| Bonjour |
The switch advertises itself using the Bonjour protocol. |
| Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) (802.1ab) with LLDP-MED extensions |
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) allows the switch to advertise its identification, configuration, and capabilities to neighboring devices that store the data in a MIB. LLDP-MED is an enhancement to LLDP that adds the extensions needed for IP phones. |
| Cisco Discovery Protocol |
The switch advertises itself using the Cisco Discovery Protocol. It also learns the connected device and its characteristics using Cisco Discovery Protocol. |
| Auto Smartports |
Automatically applies the intelligence delivered through the Smartports roles to the port based on the devices discovered over Cisco Discovery Protocol or LLDP-MED. This capability facilitates zero-touch deployments. |
802.3at PoE+ and 802.3af PoE delivered over any of the RJ-45 ports within the listed power budgets
The following switches support 802.3at PoE+, 802.3af, and Cisco pre-standard (legacy) PoE. There is a maximum power of 30.0 W to any 10/100 or Gigabit Ethernet port until the PoE budget for the switch is reached. The total power available for PoE per switch is as follows:
| Model |
Power Dedicated to PoE |
Number of Ports That Support PoE |
| SF250-48HP |
195 W |
48 |
| SG250-10P |
62 W |
8 |
| SG250-26HP |
100 W |
24 |
| SG250-26P |
195 W |
24 |
PoE powered device (PD) and PoE pass-through
Besides AC power, compact switch models can work as PoE powered device (PD) and be powered by PoE switches connected to the uplink ports. The switch can also pass through the power to downstream PoE end devices if required.
Maximum of 60 W can be drawn per uplink port if the peer PoE switch supports 60 W PoE. When multiple uplink ports are connected to PoE switches, the power drawn from these ports is combined.
When AC power is connected and functioning correctly, it is preferred over PoE power. The PoE power can function as a backup to the AC power source or be used as the sole power source for the switch.
| Model |
Power Option |
Available PoE Power (W) |
Can Switch Be Powered with Uplinks? |
| SG250-10P |
1 PoE uplink 2 PoE uplink 1 PoE+ uplink 2 PoE+ uplink 1 60W PoE uplink 2 60W PoE uplink AC Power |
0W 0W 0W 22W 22W 50W 62W |
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes |
Power Consumption
| Model |
Green Power (mode) |
System Power Consumption |
Power Consumption (with PoE) |
Heat Dissipation (BTU/hr) |
| SF250-48 |
EEE, Energy Detect |
110V=23.4W 220V=24.2W |
N/A |
82.57 |
| SF250-48HP |
EEE, Energy Detect |
110V=43.1W 220V=44.3W |
110V=265.2W 220V=255.8W |
904.90 |
| SG250-10P |
EEE, Energy Detect, Short Reach |
110V=13.25W 220V=13.42W |
110V=85.19W 220V=84.17W |
290.68 |
| SG250-26 |
EEE, Energy Detect, Short Reach |
110V=18.1W 220V=18.9W |
N/A |
64.49 |
| SG250-26HP |
EEE, Energy Detect, Short Reach |
110V=23.5W 220V=24.4W |
110V=135.2W 220V=133.9W |
461.32 |
| SG250-26P |
EEE, Energy Detect, Short Reach |
110V=34.2W 220V=37.2W |
110V=262W 220V=254.5W |
893.98 |
Physical Interfaces
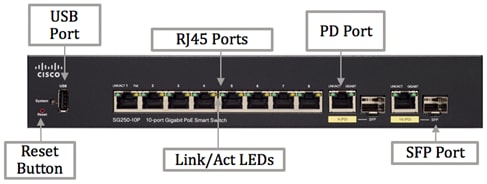
Ports
| Model Name |
Total System Ports |
RJ-45 Ports |
Combo Ports (RJ-45 + SFP) |
| SF250-48 |
48 Fast Ethernet + 2 Gigabit Ethernet |
48 Fast Ethernet |
2 Gigabit Ethernet combo + 2 SFP |
| SF250-48HP |
48 Fast Ethernet + 2 Gigabit Ethernet |
48 Fast Ethernet |
2 Gigabit Ethernet combo + 2 SFP |
| SG250-10P |
10 Gigabit Ethernet |
8 Gigabit Ethernet |
2 Gigabit Ethernet combo |
| SG250-26 |
26 Gigabit Ethernet |
24 Gigabit Ethernet |
2 Gigabit Ethernet combo |
| SG250-26HP |
26 Gigabit Ethernet |
24 Gigabit Ethernet |
2 Gigabit Ethernet combo |
| SG250-26P |
26 Gigabit Ethernet |
24 Gigabit Ethernet |
2 Gigabit Ethernet combo |
Buttons
| Feature |
Description |
| USB Slot |
USB Type-A slot at the front panel of the switch for easy file and image management |
| Buttons |
Reset button |
| Cabling Type |
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) Category 5 or better for 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX; UTP Category 5e or better for 1000BASE-T |
| LEDs |
System, Link/Act, PoE, Speed |
| Flash |
256 MB |
| CPU |
800 MHz ARM |
| CPU Memory |
512 MB |
Packet Buffer
All numbers are aggregate across all ports because the buffers are dynamically shared:
| Model Name |
Packet Buffer |
| SF250-48 |
24 Mb |
| SF250-48HP |
24 Mb |
| SG250-10P |
12 Mb |
| SG250-26 |
12 Mb |
| SG250-26HP |
12 Mb |
| SG250-26P |
12 Mb |
| Feature |
Description |
|||
| Supported SFP/SFP+ modules |
SKU |
Media |
Speed |
Maximum Distance |
| MGBBX1 |
Single-mode fiber |
100 Mbps |
10 km |
|
| MGBSX1 |
Multimode fiber |
100 Mbps |
500 m |
|
| MGBLH1 |
Single-mode fiber |
100 Mbps |
40 km |
|
| MGBLX1 |
Single-mode fiber |
100 Mbps |
10 km |
|
| MGBT1 |
UTP cat 5e |
100 Mbps |
100 m |
|
Environmental
| Feature |
Description |
|
| Unit dimensions (W x H x D) |
Model Name |
Unit Dimensions |
| SF250-48 |
440 x 44 x 257 mm (17.3 x 1.45 x 10.12 in) |
|
| SF250-48HP |
440 x 44 x 350 mm (17.3 x 1.45 x 13.78 in) |
|
| SG250-10P |
280 x 44 x 170 mm (11.0 x 1.45 x 6.69 in) |
|
| SG250-26 |
440 x 44 x 202 mm (17.3 x 1.45 x 7.95 in) |
|
| SG250-26HP |
440 x 44 x 257 mm (17.3 x 1.45 x 10.12 in) |
|
| SG250-26P |
440 x 44 x 257 mm (17.3 x 1.45 x 10.12 in) |
|
| Unit weight |
Model Name |
Unit Weight |
| SF250-48 |
3.57 kg (7.87 lb) |
|
| SF250-48HP |
4.93 kg (10.87 lb) |
|
| SG250-10P |
1.2 kg (2.65 lb) |
|
| SG250-26 |
2.72 kg (6.0 lb) |
|
| SG250-26HP |
3.37 kg (7.43 lb) |
|
| SG250-26P |
3.81 kg (8.40 lb) |
|
| Power |
100–240V 50–60 Hz, internal, universal – SF250-48, SF250-48HP, SG250-26, SG250-26HP, SG250-26P 100–240V 50–60 Hz, external – SG250-10P |
|
| Certification |
UL (UL 60950), CSA (CSA 22.2), CE mark, FCC Part 15 (CFR 47) Class A |
|
| Operating temperature |
SF250-48, SF250-48HP, SG250-10P, SG250-26, SG250-26HP, SG250-26P 32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C) |
|
| Storage temperature |
-4° to 158°F (-20° to 70°C) |
|
| Operating humidity |
10% to 90%, relative, noncondensing |
|
| Storage humidity |
10% to 90%, relative, noncondensing |
|
| Feature |
Description |
|||
| Acoustic noise and mean time between failures (MTBF) |
Model Name |
Fan (Number) |
Acoustic Noise |
MTBF at 50°C (Hours) |
| SF250-48 |
No fan |
N/A |
256,281.25 |
|
| SF250-48HP |
2 |
0°C to 30°C: 38.0dB 50°C: 52.7dB |
286,555.77 |
|
| SG250-10P |
No fan |
N/A |
205,647.00 |
|
| SG250-26 |
No fan |
N/A |
343,592.66 |
|
| SG250-26HP |
1 |
0°C to 30°C: 37.5dB 50°C: 49.7dB |
333,792.21 |
|
| SG250-26P |
2 |
0°C to 30°C: 36.0dB 50°C: 53.7dB |
430,341.06 |
|
| Warranty |
Limited lifetime |
|||
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback