Configure Port to Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) Settings on a Switch
Available Languages
Objective
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows you to logically segment a Local Area Network (LAN) into different broadcast domains. In scenarios where sensitive data may be broadcast on a network, VLANs can be created to enhance security by designating a broadcast to a specific VLAN. Only users that belong to a VLAN are able to access and manipulate the data on that VLAN. VLANs can also be used to enhance performance by reducing the need to send broadcasts and multicasts to unnecessary destinations.
To forward the packets properly, intermediate VLAN-aware devices that carry VLAN traffic along the path between end nodes must either be manually configured or must dynamically learn the VLANs and their port memberships from Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP).
Untagged port membership between two VLAN-aware devices with no intervening VLAN-aware devices must be on the same VLAN. In other words, the Port VLAN ID (PVID) on the ports between the two devices must be the same if the ports are to send and receive untagged packets to and from the VLAN. Otherwise, traffic might leak from one VLAN to another.
Frames that are VLAN-tagged can pass through other network devices that are VLAN-aware or VLAN-unaware. If a destination end node is VLAN-unaware, but is to receive traffic from a VLAN, then the last VLAN-aware device (if there is one), must send frames of the destination VLAN to the end node untagged.
This article provides instructions on how to use the Port to VLAN page in the web-based utility to display and configure the ports within a specific VLAN in a switch.
Applicable Devices | Software Version
- Sx350 Series | 2.2.5.68 (Download latest)
- SG350X Series | 2.2.5.68 (Download latest)
- Sx550X Series | 2.2.5.68 (Download latest)
Configure VLAN Settings on the Switch
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility and chooseVLAN Management > Port to VLAN.

Step 2. Choose a VLAN ID from the Filter VLAN ID equals to drop-down list.

Note: In this example, VLAN20 is chosen.
Step 3. Choose an interface or Link Aggregation (LAG) from the Interface Type equals to drop-down list then click Go.
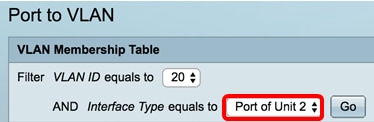
Note: In this example, Port of Unit 2 is chosen.
The port mode for each port or LAG appears with its current port mode (Access or Trunk) configured from the Interface Settings page. Each port or LAG appears with its current registration to the VLAN.

Step 4. Choose an interface to change the registration of an interface to the VLAN then choose a Membership Type from the drop-down list.
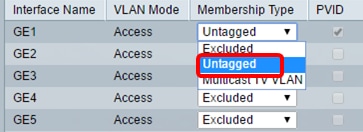
The options are:
- Excluded — The interface is currently not a member of the VLAN. This is the default for all the ports and LAGs when the VLAN is newly created.
- Tagged — The interface is a tagged member of the VLAN. This option is only available if the interface is in Trunk mode.
- Untagged — The interface is an untagged member of the VLAN. Frames of the VLAN are sent untagged to the interface VLAN.
- Multicast TV VLAN — The interface used for Digital TV using Multicast IP. The port joins the VLAN with a VLAN tag of Multicast TV VLAN. This option is only available if the interface is in Access mode. To learn how to configure Access Port Multicast TV VLAN, click here for instructions.
Note: In this example, GE1 interface is changed to Untagged.
Step 5. Scroll down to the bottom of the page then click Apply. The interface is assigned to the VLAN and saved in running configuration file.

Step 6. (Optional) Repeat Steps 2 to 5 to configure port membership of another VLAN by choosing another VLAN ID.
Step 7. (Optional) Click Save to save settings to the startup configuration file.
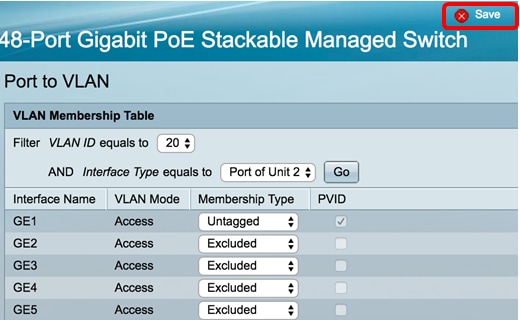
You should now have configured the ports within a specific VLAN in a switch.
Other links you might find valuable: