Configure IP SLA Tracking for IPv4 Static Routes on an SG550XG Switch
Available Languages
Introduction
When using static routing, you may experience a situation where a static route is active, but the destination network is not reachable via the specified next hop. For example, if the static route in question has the lowest metric to the destination network and the status of the outgoing interface to the next hop is Up, however the connectivity is broken somewhere along the path to the destination network. In this case, the device can use the static route although it does not actually provide connectivity to the destination network. The Internet Protocol Service Level Agreement (IP SLA) Object tracking for static routes provides a mechanism to track the connectivity to the destination network via the next hop specified in the static route. If connectivity to the destination network is lost, the route state is set to Down, and if available, a different static route (which is in state Up) can be selected for routing traffic.
Similar to IP SLAs tracking for Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), IP SLAs object tracking for static routes also relies on IP SLAs operations to detect connectivity to destination networks. IP SLAs operation sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets to the address defined by the user (a host on the required destination network), and also defines the next hop to use for the ping operation. IP SLAs operation then monitors success or failure of replies from the host. A track object is used to track operation results and set the status to Up or Down, based on the success or failure of the ICMP destination. The track operation is assigned to a static route. If the track status is down, the static route state is set to Down. If track status is Up, the static route state remains Up.
The following describes the main terms used in this article:
- Operation - Each IP SLAs ICMP Echo operation sends a single ICMP Echo request to a target address at a configured frequency rate. It then waits for a response.
- Track Object State - Each tracking object maintains an operation state. The state is either Up or Down. After object creation, the state is set to Up. The following table specifies the conversion of the IP SLAs operation return code to the object state:
| Operation Return Code |
Track Operation State |
| OK |
Up |
| Error |
Down |
Note: If the IP SLAs operation specified by the track argument is not configured or is its schedule is pending, its state is OK. An application that is bound to a non-existing tracking object will receive the Up state.
- SLA Operation State - This can be either Scheduled, which means the operation begins immediately or Pending, which means it has been created but not activated.
- Timeout value - Specifies the interval time of waiting for the ICMP echo reply message or an ICMP error message.
- Return Code - After an operation has been finished, the operation return code is set according to the following:
- ICMP Echo reply has been received - Return code is set to OK.
- ICMP Error reply has been received - Return code is set to error.
- No any ICMP reply has been received - Return code is set to error.
- Configured Source IP address or Source interface is not accessible - Return code is set to error.
- Tracker - Tracks the results of operations.
- Delay - When the result of an IP SLA operation indicates that the state of the tracking object should change to X from Y, the tracking object performs the following actions:
- The state of the tracking object is not changed and the tracking object starts the delay timer for the interval.
- If during the time that the timer is set, the original state (Y) is received again, the timer is canceled, and the state remains Y.
- If the delay timer is expired, the state of the tracking object is changed to X and the X state is passed to the associated applications.
Objective
This article provides instructions on how to configure the IP SLA tracking settings for IPv4 static routes on your switch. In this scenario, the static route has been preconfigured.
Note: To learn how to configure an IPv4 static route on your switch, click here.
Applicable Devices
- SG550XG Series
Software Version
- 2.3.0.130
Configure IP SLA Tracking for IPv4 Static Routes
Configure ICMP Echo Operations
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility of your switch then choose Advanced in the Display Mode drop-down list.
Note: The available menu options may vary depending on the device model. In this example, SG550XG-24T is used.

Step 2. Choose IP Configuration >SLA > ICMP-Echo Operations.

IP SLA ICMP-Echo operations can be configured in this page. These operations will be executed according to the frequency entered.
Step 3. To add a new operation, click Add.

Step 4. Enter an unused number in the Operation Number field.

Note: In this example, the operation number is 1.
Step 5. In the Operation State area, choose one from the following options:
- Pending - Operation is not activated.
- Scheduled - Operation is activated.

Note: In this example, Scheduled is chosen.
ICMP-Echo Parameters
Step 6. In the Operation Target area, choose how the operation target is defined:
- By IP - Enter the operation IP address of the target.
- By host name - Enter the operation host name of the target.
Note: If the IP SLA operation is for the Static Routes feature, the operation target is the IP address of the host in the remote network defined by the static route.

Note: In this example, By IP is chosen and 192.168.1.1 is the specified destination target.
Step 7. If the source definition is not defined, the operation selects the source IP address nearest to the destination. To define the source definition, select from one of the following options:
- Auto - The source interface is based on Forwarding Table information.
- By address - If this option is chosen, choose a source IP address from the drop-down list.

Note: In this example, By address and 192.168.100.126 are chosen.
Step 8. In the Next Hop IP Address area, choose from the following options:
- None - No next hop address.
- User defined - If this option is chosen, enter the next hop IP address in the provided field.
Note: This parameter should be defined only for IP SLAs operations to be used in the static routes.

Note: In this example, User defined is chosen and 192.168.100.1 is the defined next hop IP address.
Step 9. In the Request Data Size field, enter the request packet data size for an ICMP Echo operation. This data size is the payload portion of the ICMP packet, which makes a 64-byte IP packet. The range is from 28 up to 1472 Bytes and the default is 28 Bytes.

Note: In this example, the default value is used.
Step 10. In the Frequency field, enter the frequency with which the SLA operation is carried out (packets are sent). This value must be larger than the Timeout value. The range is from 10 to 500 seconds and the default value is 10 seconds.

Note: In this example, the default value is used.
Step 11. In the Timeout field, enter the amount of time an IP SLA operation waits for a response to its request packet. It is recommended that the value of the milliseconds argument be based on the sum of the maximum round-trip time (RTT) value for the packets and the processing time of the IP SLAs operation. The range is from 50 to 5000 milliseconds and the default value is 2000 milliseconds.

Note: In this example, the default value is used.
Step 12. Click Apply to save the settings then click Close.

The ICMP-Echo operations status will be displayed as the following:
- State - Displays either Pending or Scheduled, as described in the Overview above.
- Return Code - Displays either OK or Error, as described in the Overview above.

Step 13. (Optional) Repeat steps 3 to 11 to configure another ICMP Echo operation.
You should now have successfully verified the configured routing resources on your switch.
Configure SLA Tracking
Step 1. Choose IP Configuration >SLA > SLA Tracks.
![]()
Step 2. To add a new object, click Add.
![]()
Step 3. Enter an unused number in the Track Number field.
![]()
Note: In this example, the track number is 1.
Step 4. Choose an SLA operation from the Operation Number drop-down list.
![]()
Note: In this example, the previously created operation number 1 is chosen.
Step 5. The Up Delay area specifies a period of time in seconds to delay state changes from Down to Up. To configure the Up Delay settings, choose from the following options:
- None - Change the state of the track immediately.
- Delay Period - Change the state of the track after a specific delay period. If this option is chosen, enter the delay period in the provided field. The range is from one up to 180 seconds.
![]()
Note: In this example, the delay period of 5 seconds is defined.
Step 6. The Down Delay area specifies a period of time in seconds to delay state changes from Up to Down. To configure the Down Delay settings, choose from the following options:
- None - Change the state of the track immediately.
- Delay Period - Change the state of the track after a specific delay period. If this option is chosen, enter the delay period in the provided field. The range is from one up to 180 seconds.
![]()
Note: In this example, the delay period of 2 seconds is defined.
Step 7. Click Apply to save the settings the click Close.
![]()
The status of the configured SLA Track objects are displayed in the SLA Tracker Table:
![]()
- State - Displays one of the following states:
- Down - There is no connectivity to the route (packet returned Error return code).
- Up - There is connectivity to the route (packet returned OK return code).
- Operation Type - Can only display ICMP-Echo.
- Delay Interval Remainder (Sec) - How much of Delay period remains.
Step 8. (Optional) Click the Save button to save the settings to the startup configuration file.
![]()
You should now have successfully configured SLA tracking for an IPv4 static route on your switch.
Display ICMP Echo Statistics
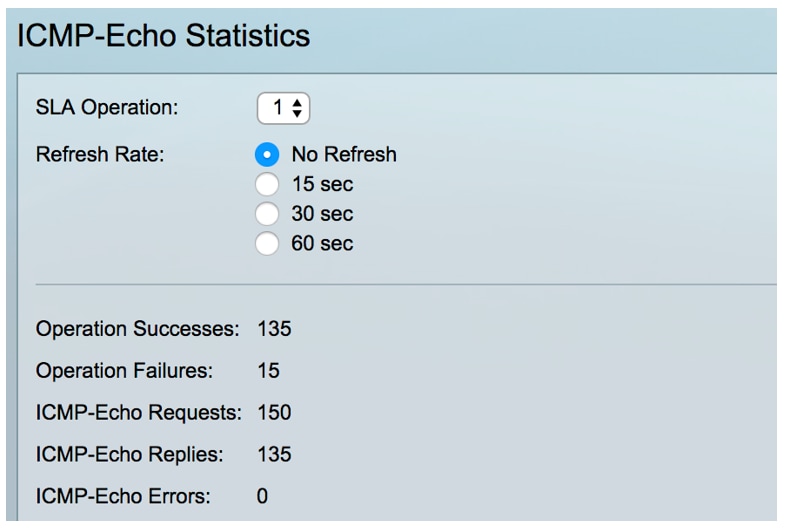
Step 1. Choose IP Configuration >SLA > ICMP-Echo Statistics.

Step 2. Choose the SLA Operation that you want to view from the SLA Operation drop-down list.

Note: In this example, operation 1 is chosen.
Step 3. (Optional) Choose a refresh rate from Refresh Rate drop-down list. This is the time period that passes before the statistics are refreshed. The options are:
- No Refresh - Statistics are not refreshed. In this example, this option is chosen.
- 15 sec - Statistics are refreshed every 15 seconds.
- 30 sec - Statistics are refreshed every 30 seconds.
- 60 sec - Statistics are refreshed every 60 seconds.

The ICMP-Echo Statistics page displays the following:
- Operation Successes - Number of times the SLA track echo was successful.
- Operation Failures - Number of times the SLA track echo was successful.
- ICMP-Echo Requests - Number of request packets that were sent.
- ICMP-Echo Replies - Number of reply packets that were received.
- ICMP-Echo Errors - Number of error packets that were received.
Step 4. (Optional) To clear the counters of the chosen SLA Operation, click the Clear Counters button.
Step 5. (Optional) To clear all statistics of all SLA operations, click the Clear All Operations Counters button.
Step 6. (Optional) Click Refresh to refresh the statistics page.
You should now have successfully displayed the ICMP Echo statistics of a specific SLA operation on your switch.
© 2017 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback