Configure Global Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Settings on a Switch through the Command Line Interface (CLI)
Available Languages
Objective
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Media Endpoint Discovery (MED) provides additional capabilities to support media endpoint devices such as to enable the advertisement of network policies for applications like voice or video, device location discovery, and troubleshooting information. LLDP and Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) are both similar protocols, and the difference is that LLDP facilitates vendor interoperability and CDP is Cisco proprietary.
LLDP can be used in scenarios where you need to work between devices which are not Cisco proprietary and devices which are Cisco proprietary. You can use the LLDP protocol for troubleshooting purposes. The switch gives all the information about the current LLDP status of ports and you can use this information to fix connectivity problems within the network.
This article provides instructions on how to configure the LLDP properties on the switch.
Note: To learn how to configure the LLDP properties of your switch through the web-based utility, click here.
Applicable Devices
- Sx300 Series
- Sx350 Series
- SG350X Series
- Sx500 Series
- Sx550X Series
Software Version
- 1.4.7.05 — Sx300, Sx500
- 2.2.8.4 — Sx350, SG350X, Sx550X
Configure Global LLDP Properties on the Switch through the CLI
Configure Global LLDP Properties
Step 1. Log in to the switch console. The default username and password is cisco. If you have configured a new username or password, enter the credentials instead.

Note: In this example, the SG350X switch is accessed through Telnet.
Step 2. In the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, enter the Global Configuration context by entering the following:
Step 3. To globally enable the LLDP feature on the switch, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp runNote: LLDP is globally enabled by default.

Step 4. (Optional) To globally disable the LLDP feature, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp runStep 5. (Optional) To define the LLDP packet handling when LLDP is globally disabled, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp lldpdu [filtering | flooding]The options are:
- filtering — Specifies that when LLDP is globally disabled, LLDP packets are filtered or deleted.
- flooding — Specifies that when LLDP is globally disabled, LLDP packets are flooded or forwarded to all interfaces in the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN).
Note: In this example, flooding is entered.

Note: LLDP packets are filtered when LLDP is globally disabled.
If LLDP is globally disabled, and the LLDP packet handling mode is flooding, LLDP packets are treated as data packets with the following exceptions:
- VLAN ingress rules are not applied to LLDP packets. The LLDP packets are trapped on all ports for which the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) state is Forwarding.
- Default deny-all rules are not applied to LLDP packets.
- VLAN egress rules are not applied to LLDP packets. The LLDP packets are flooded to all ports for which the STP state is Forwarding.
- LLDP packets are sent as untagged.
Step 6. To configure the maximum transmission rate of LLDP notifications, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp notifications interval [seconds]- interval seconds — The device does not send more than a single notification in the indicated period. The range is from 5 up to 3600 seconds. The default interval is every 5 seconds.
Note: In this example, the interval used is 360 seconds.

Step 7. (Optional) To return the maximum transmission rate of LLDP notifications to the default setting, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp notifications intervalStep 8. To specify how often the software sends LLDP updates, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp timer [seconds]- timer seconds — Specifies how often the software sends LLDP updates in seconds. The range is 5 to 32768 seconds. The default value is 30 seconds.
Note: In this example, the timer used is 60 seconds.

Step 9. (Optional) To restore the default LLDP timer configuration, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp timerStep 10. To specify how long the receiving device holds an LLDP packet before discarding it, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp hold-multiplier [number]- hold-multiplier number — Specifies the LLDP packet hold time interval as a multiple of the LLDP timer value. The range is 2 to 10, and the default value is 4.
Note: In this example, the hold multiplier value is set to 5.

Step 11. (Optional) To return the maximum transmission rate of LLDP notifications to the default setting, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp hold-multiplierStep 12. To specify the minimum time an LLDP port waits before reinitializing LLDP transmission, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp reinit [seconds]- reinit seconds — Specifies the minimum time in seconds an LLDP port waits before reinitializing LLDP transmission. The range is from 1 to 10 and the default value is 2 seconds.
Note: In this example, the reinitializing LLDP transmission time is set to 3 seconds.

Step 13. (Optional) To revert the reinitializing LLDP transmission configuration setting on your switch, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp reinitStep 14. To configure the amount of time that passes between successive LLDP frame transmissions due to changes in the LLDP local systems MIB, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp tx-delay [seconds]- tx-delay seconds — Specifies the delay in seconds between successive LLDP frame transmissions initiated by value or status changes in the LLDP local systems MIB. The range is from 1 up to 8192 seconds and the default transmission delay is 2 seconds.
Note: In this example, the transmission delay is set to 15 seconds.
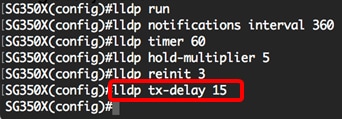
Step 15. (Optional) To return the transmit delay values to the default configuration, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp tx-delayStep 16. (Optional) To configure the source of the chassis ID advertisement in the LLDP messages, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp chassis-id [mac-address | host-name]The options are:
- mac-address — Specifies the chassis ID to use the device Media Access Control (MAC) address. This is the default setting.
- host-name — Specifies the chassis ID to use the device configured host name.
Note: In this example, host-name is used.

Step 17. (Optional) To restore the chassis ID source to the default configuration, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp chassis-idStep 18. When a port comes up, LLDP can send packets more quickly than usual using its fast start mechanism. To configure the number of packets that is sent during the activation of the fast start mechanism, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#lldp med fast-start repeat-count [number]- repeat-count number — Specifies the number of times the fast start LLDP Data Unit (LLDPDU) is being sent during the activation of the fast start mechanism. The range is 1 to 10 and the default value is 3.
Note: In this example, the repeat count number is set to 5.

Step 19. (Optional) To return the repeat counter to the default setting, enter the following:
SG350X(config)#no lldp med fast-start repeat-countStep 20. Enter the exit command to go back to the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch.
SG350X#exit
Step 21. (Optional) In the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, save the configured settings to the startup configuration file, by entering the following:
SG350X#copy running-config startup-config
Step 22. (Optional) Press Y for Yes or N for No on your keyboard once the Overwrite file [startup-config]… prompt appears.
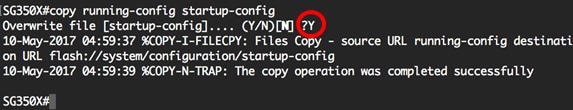
Note: In this example, Y is pressed.
You should now have successfully configured the global LLDP properties on your switch through the CLI.
To learn how to configure the LLDP settings on specific ports on your switch through the web-based utility, click here for instructions. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
Show LLDP Configuration Settings
Step 1. In the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, enter the following to display the global LLDP configuration settings:
SG350X#show lldp configuration [interface-id | detailed]The options are:
- interface-id — (Optional) Specifies the port ID.
- Detailed — (Optional) Displays information for non-present ports in addition to present ports.
Note: In this example, detailed LLDP configuration is displayed.

The LLDP configuration displays the following information:
- LLDP state — The state of LLDP in the switch.
- Timer — The time interval between LLDP updates.
- Hold multiplier — The amount of time (as a multiple of the timer interval) that the receiving device holds an LLDP packet before discarding it.
- Reinit delay — The minimum time interval an LLDP port waits before re-initializing an LLDP transmission.
- Tx delay — The delay between successive LLDP frame transmissions initiated by value/status changes in the LLDP local systems MIB.
- Notifications Interval — The maximum transmission rate of LLDP notifications.
- LLDP packets handling — The LLDP packet handling when LLDP is globally disabled.
- Chassis ID — Identifier of chassis.
- Port — The port number.
- State — The LLDP state of the port.
- Optional TLVs — Optional TLVs that are advertised. Possible values are:
- PD — Port description
- SN — System name
- SD — System description
- SC — System capabilities
- Address — The management address that is advertised.
- Notifications — Indicates whether LLDP notifications are enabled or disabled.
- PVID — (Interface) Port VLAN ID advertised.
- PPVID — (Interface) Protocol Port VLAN ID advertised.
- Protocols — (Interface) The selected protocols.
You should now have displayed the configured LLDP settings on your switch through the CLI.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback