Configure Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Parameters on SPA300/SPA500 Series IP Phones
Available Languages
Objective
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used to create, manage and terminate sessions in an IP based network. SIP is a mechanism for call management. It also allows for the establishment of user location, provides for feature negotiation so that all of the participants in a session can agree on the features to be supported among them, and allows for changes to be made to features of a session while it is in progress.
The objective of this document is to show you the configuration of SIP Parameter on SPA300 and SPA500 Series IP Phone.
Applicable Devices
• SPA300 Series IP Phone
• SPA500 Series IP Phone
Linksys Key Configuration
Note: On the actual SPA300 or SPA500 Series IP Phone set signaling protocol as SIP, use navigation keys to go to Device Administration > Call Control Settings > Signaling Protocol SIP.
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose Admin Login > Advanced > Voice > SIP. The SIP page opens:
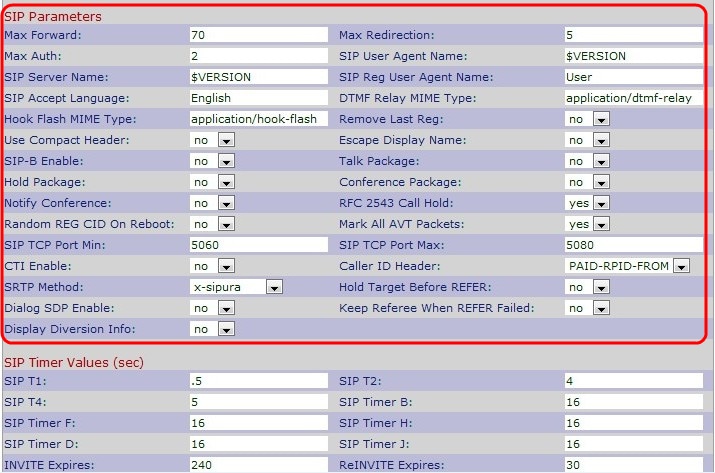
Step 2. Enter the number of proxies or gateways that can forward the request to the next downstream server in the Max Forward field. This is the value which indicates the remaining number of times the request message is allowed to be forwarded. The range is from 0 to 255. The initial value is 70.
Step 3. Enter the number of times an invite can be redirected to avoid an infinite loop in the Max Redirection field. The default is 5.
Step 4. Enter the maximum number of times a request might be challenged in the Max Auth field. The range is from 0 to 255. The default is 2.
Step 5. Enter the User-Agent header used in outbound requests in the SIP User Agent Name field. The default is $VERSION. If empty, the header is not included.
Step 6. Enter the server header used in responses to inbound responses in the SIP Server Name field. The default is $VERSION.
Step 7. Enter the User-Agent name used in a register request in the SIP Reg User Agent Name field. If not specified, the SIP User Agent Name is used for the register request.
Step 8. Enter the name of the preferred language in the SIP Accept Language field for reason phrases, session descriptions, or status responses which are carried as message bodies in the response. If blank, the header is not included and the server assumes that all languages are acceptable to the client. The default is blank.
Step 9. Enter the DTMF relay MIME in the DTMF Relay MIME Type field. MIME Type is used in a SIP INFO message to signal a DTMF event. This parameter must match with the service provider. The default is application/dtmf-relay.
Step 10. Enter the Hook Flash MIME in the Hook Flash MIME Type field. MIME Type used in a SIPINFO message to signal a hook flash event.
Step 11. Choose Yes or No from the Remove Last Reg drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will remove the last registration used before registering a new one if the value is different. The default is No.
Step 12. Choose Yes or No from the Use Compact Header drop-down list. If you choose Yes, the Cisco IP phone uses compact SIP headers in outbound SIP messages. If you choose no, the Cisco SPA IP phones use normal SIP headers. The default is No.
Step 13. Choose Yes or No from the Escape Display Name drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will enclose the configured Display Name string in a pair of double quotes for outbound SIP messages.
Step 14. Choose Yes or No from the SIP-B Enable drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will enable SIP for Business (supports Sylantro call flows) call features.
Step 15. Choose Yes or No from the Talk Package drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will enable support for the BroadSoft Talk Package that lets users answer or resume a call by clicking a button in an external application. The default is No.
Step 16. Choose Yes or No from the Hold Package drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will enable support for the BroadSoft Hold Package, which lets users place a call on hold by clicking a button in an external application. The default is No.
Step 17. Choose Yes or No from the Conference Package drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will enable support for the BroadSoft Conference Package that enables users to start a conference call by clicking a button in an external application. The default is No.
Step 18. Choose Yes or No from the Notify Conference drop-down list. If you choose Yes, Cisco SPA IP phones send out a NOTIFY with event conference when starting a conference call (with the BroadSoft Conference Package). The default is No.
Step 19. Choose Yes or No from the RFC 2543 Call Hold drop-down list. If you choose Yes, Cisco SPA IP phones include Session Description Protocol (SDP) syntax c=0.0.0.0 when sending a SIP re-INVITE to a peer to hold the call. The default is Yes.
Step 20. Choose Yes or No from the Random REG CID On Reboot drop-down list. If you choose Yes, Cisco SPA IP phones use a different random call-ID for registration after the next software reboot. The default is No.
Step 21. Choose Yes or No from the Mark ALL AVT Packets drop-down list. If you choose Yes, all audio video transport (AVT) tone packets (encoded for redundancy) have the marker bit set. The default is Yes.
Step 22. Enter the lowest TCP port number that can be used for SIP sessions in the SIP TCP Port Min field. The default is 5060.
Step 23. Enter the highest TCP port number that can be used for SIP sessions in the SIP TCP Port Max field. The default is 5080.
Step 24. Choose Yes or No from the Keep Referee When REFER Failed drop-down list. If you choose Yes, the phone immediately handles NOTIFY sipfrag messages.
Step 25. Choose Yes or No from the CTI Enable drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will enable the computer telephony integration (CTI), where a computer can act as a call center handling all sorts of incoming and outgoing communications, including phone calls, faxes, and text messages. The CTI interface allows a third-party application to control and monitor the state of a Cisco IP phone and, for example, initiate or answer a call by clicking a mouse on a PC. The default is no.
Note: CTI must be enabled on the Cisco SPA300 Series or Cisco SPA500 Series IP phones for an attached Cisco Attendant Console to properly monitor the IP phone line status.
Step 26. Choose the specific caller ID header from the Caller ID Header drop-down list. The default is PAID-RPID-FROM.
Step 27. Choose the specific SRTP method from the SRTP Method drop-down list. SRTP is the method to use for secure real time transport protocol. The default is x-sipura.
Step 28. Choose Yes or No from the Hold Target Before REFER drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it will control whether to hold the call leg with the transfer target before sending REFER to the transferee when initiating a fully attended call transfer (where the transfer target has answered). The default is No.
Step 29. Choose Yes or No from the Dialog SDP Enable drop-down list. If you choose Yes, you will get simplified Notify message xml.
Step 30. Choose Yes or No from the Display Diversion Info drop-down list. If you choose Yes, it displays the Diversion Header information, if it exists, in the INVITE message.
Step 31. Click Submit All Changes to save the settings.
 Feedback
Feedback