NAT Support Parameters Configuration on SPA8000 Phone Adapter
Available Languages
Objective
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a process that modifies IP addresses while in transit across a traffic routing device for the purpose of remapping one IP address in an IP packet header. NAT is used for security purposes to keep the internal IP address hidden to avoid conflict of IP addresses. The objective of this document is to configure NAT Support Parameters on a SPA8000 Analog Telephone Adapter. NAT Support Parameters play an important function in the configuration of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) which assists the NAT topology.
Applicable Device
- SPA8000
Software Version
- 6.1.12
NAT Support Parameters Configuration
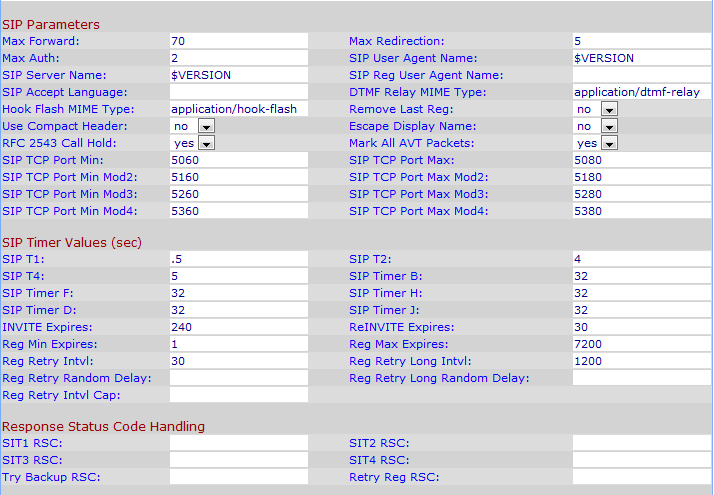
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility as an administrator and choose Admin Login > Advanced > Voice > SIP. The SIP page opens:
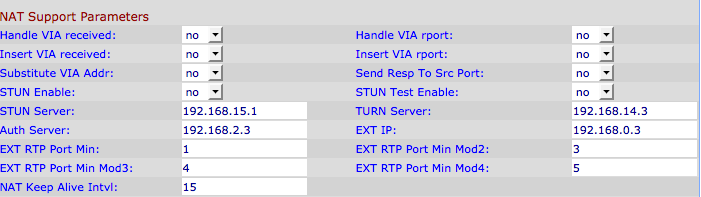
Step 2. Choose yes from the Handle VIA received drop-down list to enable the adapter to process the received parameter in the VIA header. If set to no then the parameter would be ignored. The default value is no.
Step 3. Choose yes from the Handle VIA rport drop-down list to enable the adapter to process the received rport parameter in the VIA header. If set to no then the parameter would be ignored. The default value is no.
Step 4. Choose yes from the Insert VIA received drop-down list to enable the adapter to insert the received insert parameter into the VIA header of SIP responses, if the received-from IP and VIA sent-by IP values differ. The default is no.
Step 5. Choose yes from the Insert VIA rport drop-down list to enable the adapter to insert the received rport parameter into the VIA header of SIP responses if the received-from IP and VIA sent-by IP values differ. The default is no.
Step 6. Choose yes from the Substitute VIA Addr to make use of NAT-mapped IP port values in the VIA header. The default value is no.
Step 7. Choose yes from Send Resp To Src Port drop-down list. This option allows responses to be sent to the request source port instead of the VIA sent-by port. The default value is no.
Step 8. Choose yes from the STUN Enable drop-down list to discover NAT mappings. The default is no.
Step 9. If the STUN Enable feature is enabled in Step 9 and a valid STUN server is available, the adapter can perform a NAT-type discovery operation when it would power on. It contacts the configured stun server and the result of the discovery would be reported in a warning header in all subsequent REGISTER requests. If the adapter would detect a symmetric NAT or a symmetric firewall, NAT mapping would be disabled. The default value of this field is no. To set the value to yes, choose yes from the STUN Test Enable drop-down list.
Step 10. In the STUN Server field, enter the IP Address or the Fully Qualified Domain Name of the STUN server to contact for NAT mapping discovery.
Step 11. Enter the TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) Server in the TURN Server field. TURN server allows applications behind the NAT to receive data.
Step 12. Enter the Auth Server in the Auth Server field. Auth server is an authentication server used to authenticate the username and password of a device.
Step 13. In the EXT IP field, enter the External IP Address that would substitute the actual IP address of the adapter in all outgoing SIP messages. The default value is 0.0.0.0. If 0.0.0.0 is entered, then no substitution is performed.
Step 14. In EXT RTP Port Min enter the external port mapping number of the RTP Port Min. The default value for this field is zero. If it is not zero, then the RTP port number in all outgoing SIP messages would be substituted for the corresponding port value in the external RTP port range.
Step 15. Enter a value in the NAT Keep Alive Intvl field that provides the interval between NAT-mapping keep alive messages. NAT keep alive messages prevent the expiration of NAT mappings on NAT device. The default value is 15 seconds.
Step 16. Click Submit All Changes to save the settings.
 Feedback
Feedback