Configure Log Module on SPA100 Series
Available Languages
Objective
Logging is the process which records traffic lists for various events that can occur on the network. Logging is useful if an administrator wants to monitor activities or troubleshoot issues on the network. Incoming and outgoing traffic can be saved locally, sent as an e-mail, or sent as a Syslog to the administrator.
The objective of this document is to show you how to enable logging and configure methods to save the logging on the SPA100 Series.
Note: Logging consumes resources and affects system performance. Cisco recommends to enable logging only when it is required, and to disable logging when the investigation is finished.
Applicable Devices
• SPA100 Series
Software Version
• v1.1.0
Log Module
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose Administration > Log > Log Module. The Log Module page opens:
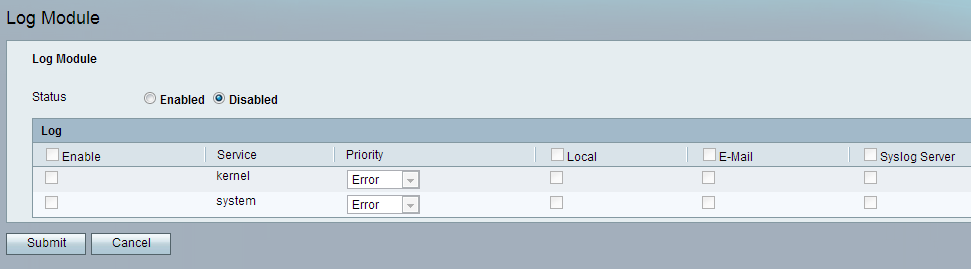
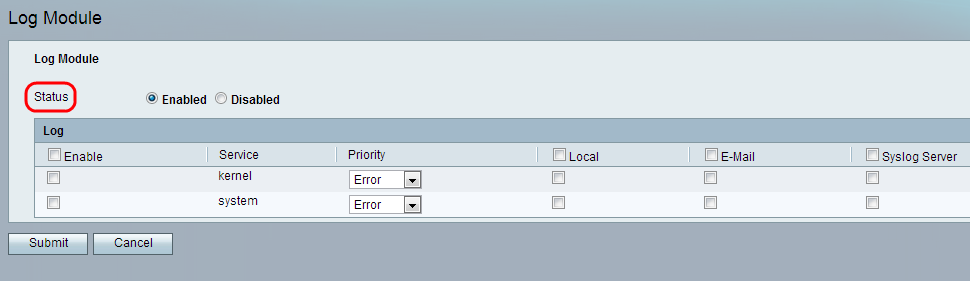
Step 2. In the Status field, click the Enabled radio button to enable logging on the device. The default status of the log module is set as Disabled.
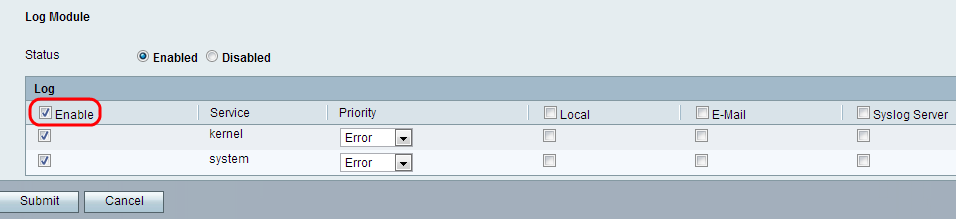
Step 3. Under Log, check the Enable check box to enable logging for all services. Alternatively, the administrator can individually check the desired check boxes in the left column to only include particular services.
The available options are defined as follows:
• Kernel — Kernel is the initial part of the operating system that is loaded into the memory and remains in that location throughout the entire session. This field displays logs that are a part of the kernel code.
• System — This displays user-space applications logs such as Network Time Protocol (NTP), Session and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
Step 4. Choose a value for the priority of each service from the Priority drop-down list. The priority determines the types of events that will be included in the log.
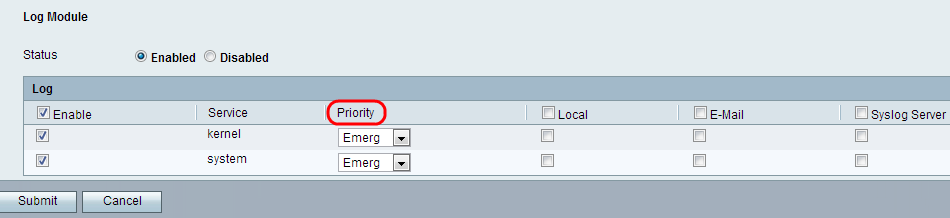
The available options are defined as follows by order of highest to lowest priority:
• Emergency — An emergency log message is logged if a device is down or unusable.
• Alert — An alert log message is logged if there is a serious device malfunction, such as a case in which all device features stop working.
• Critical — A critical log message is logged if there is a critical device malfunction, such as two ports not functioning properly while the remaining ports work fine.
• Error — A device error log message is logged if there is an error within a device, such as a single port being offline.
• Warning — A warning log message is logged if a device is functioning properly, but an operational problem occurs.
• Notification — A notification log message is logged if a device is functioning properly, but a system notice occurs.
• Information — An informational message on a device is logged if a condition that is not an error condition exists, but may require attention or special handling.
• Debug — Provides all detailed debugging messages.
Step 5. Check the Local check box in the heading row to include all services in the local logs that can be viewed by the Log Viewer page. Alternatively the administrator can check the desired check box for either kernel or system service to be saved in the local logs.
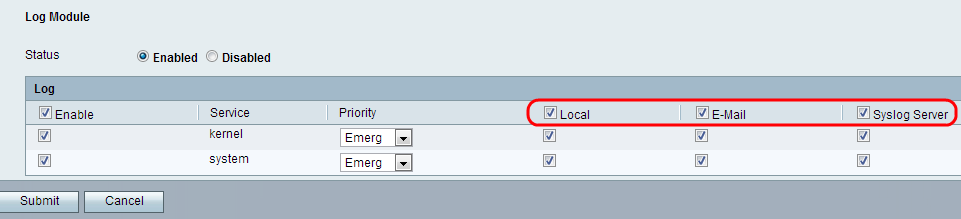
Step 6. Check the E-Mail check box in the heading row to include all services in the emailed logs, if configured on the Log Setting page. Alternatively the administrator can check the desired check box for either kernel or system service to be in the emailed logs.
Step 7. Check the Syslog Server check box in the heading row to include all services in the log file that are transmitted to the Syslog server. Alternatively the administrator can check the desired check box for either kernel or system service to be transmitted to the Syslog server.
Note: If you want to configure the Syslog server, refer to the document Configuration of Voice System Settings on the SPA100 Series for further information.
Step 8. Click Submit. The changes are configured and the device is updated.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback