SIP Settings on the SPA100 Series
Available Languages
Objective
In order to start communication between two or more end points, a session must be established. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is in charge of creating a session, and terminating it. Configuration of SIP timers enables users to improve the interoperability and performance of their devices and network environment. This article explains the different SIP parameters on the SPA100 Series, and how to configure them.
Applicable Devices
• SPA100 Series
Software Version
• v1.1.0
SIP Settings
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose Voice > SIP. The SIP page opens:
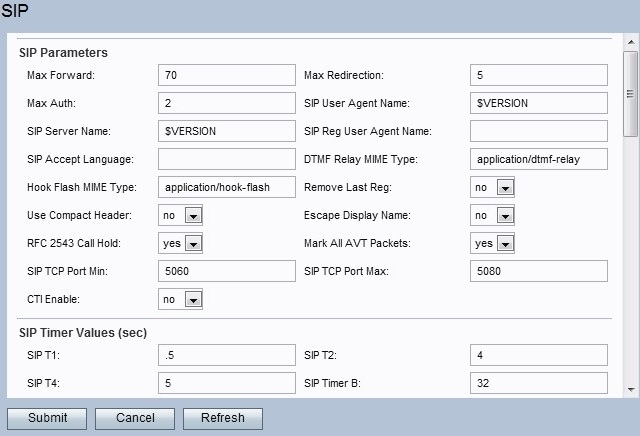
Step 2. The SIP main page offers a set of parameters. Configure each of these parameters accordingly.

• Max Forward — The maximum value for forwarding. The range is from 1 to 255. The default is set to 70.
• Max Redirection — The number of times the SPA will redirect an invite to avoid an infinite loop. The default is set to 5.
• Max Auth — The maximum number of times a request may be challenged. The range is from 0 to 255. The default is set to 2.
• SIP User Agent Name — The user agent name used in outbound requests. The range used is the macro EXPANSION FROM $A to $D, GPP_A to GPP_D respectively. The default is set to $VERSION.
• SIP Server Name — The name used for inbound responses.The default is set to $VERSION.
• SIP Reg User Agent Name — The name used in a REGISTER request. If the value is not specified, then it will use the name set for the user agent name. The default value is set to blank.
• SIP Accept Language — The accept language name. If the value is not specified, then this field is not included.
• DTMF Relay MIME Type — The MIME type used for a SIP INFO message to signal a DTMF event. The default is set to application/dtmf-relay.
• Hook Flash MIME Type — The MIME type used for a SIP INFO message to signal a hook flash event. The default is set to application/hook-flash.
• Remove last Reg — This option lets you remove the last registration before registering a new one if the value is different. Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. The default is set to No.
• Use Compact Header — This option lets you use compact SIP headers in outbound SIP messages. If you choose Yes, it will use SIP compact headers in outbound messages. Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose No, it will use normal headers. If an inbound SIP request contains SIP compact headers, then the SPA reuses this headers regardless of the settings. If you choose Yes, then If an inbound SIP request contains normal headers, the SPA substitutes this header with compact headers. The default is set to No.
• Escape display name — This option lets you keep the display name private. From the drop-down menu, choose Yes if you want the name to be enclosed in a pair of quotes, otherwise choose No. The default value is set to No.
• RFC 2543 Call Hold — This option is set to configure the type of call hold (a:sendonly or 0.0.0.0). Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If choose to Yes, all AVT tone packets have the marker bit set. If you choose No, then only the first packet has the marker bit set for each DTMF event. The default is set to Yes.
• Mark All AVT packets — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, all AVT tone packets have the marker bit set. If choose No, then only the first packet has the marker bit set for each DTMF event. The default is set to Yes.
• SIP TCP Port Min — The lowest TCP port number that can be used for SIP sessions. The default value is set to 5060.
• SIP TCP Port Max — The highest TCP port number that can be used for SIP Sessions. The default value is set to 5080.
Step 3. Configure the SIP Timer Values.

• SIP T1 — The RTT estimate value, which range from 0 to 64 seconds. The default is set to 0.5.
• SIP T2 — The maximum retransmit interval for non-INVITE requests and INVITE responses. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. the default is set to 4.
• SIP T4 — The maximum duration a message remains in the network. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. The default is set to 5.
• SIP Timer B — The INVITE time-out value. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. The default is set to 32.
• SIP Timer F — The NON-INVITE time-out value. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. The default is set to 16.
• SIP Timer H — The H INVITE final response. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. The default is set to 32.
• SIP Timer D — The ACK hang-around time. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. The default setting is 32.
• SIP Timer J — The NON-INVITE response hang-around time. The range is from 0 to 64 seconds. The default is 32.
• INVITE Expires — The value for the expiration of the invite. If set to 0, then this header is not included. The default setting is 240.
• ReINVITE Expires — The value for the expiration of the re-invite. If set to 0, then this header is not included. The default is set to 30.
• Reg Min Expires — The minimum registration expiration time allowed from the proxy in the Expires header or as a Contact Header Parameter. If the proxy returns a value that is less than this setting, then the minimum value is used. The default value is set to 1.
• Reg Max Expires — The maximum registration expiration time allowed from the proxy in the Min-Expires header. If the value is larger than this setting, then the maximum value is used. The default value is set to 7200.
• Reg Retry Intvl — The interval to wait before the SPA retries registration after failing in the last registration. The default value is set to 30.
• Reg Retry Long Intvl —The interval used in the case when registration fails with a SIP response code that do not match the Retry Reg RSC. This value should be greater than the Reg Retry Intvl. The default is set to 1200.
• Reg Retry Random Delay — The random delay range (in seconds) to add a Register Retry Intvl. The default value is set to 0 (disabled).
• Reg Retry Long Random Delay — The random delay range (in seconds) to add a Register Retry Long Intvl. The default is set to 0 (disabled).
• Reg Retry Intvl Cap — The maximum value to cap the exponential back-off retry delay. If enabled, Reg Retry Random Delay is added on top of the exponential back-off adjusted delay value. The default value is set to 0(disabled).
Step 4. Configure the Response Status Code Handling.
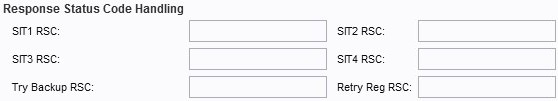
• SIT1 RSC — SIP response status code for the appropriate Special Information Tone (SIT).
• SIT2 RSC — SIP response status code to INVITE. The SIT2 tone is played.
• SIT3 RSC — SIP response status code to INVITE. The SIT3 tone is played.
• SIT4 RSC — SIP response status code to INVITE. The SIT4 tone is played.
• Try Backup RSC — SIP response status code that retries a backup server for the current request.
• Retry Reg RSC — Interval to wait before the SPA retries registration after failing during the last registration attempt.
Step 5. Configure the RTP Parameters.
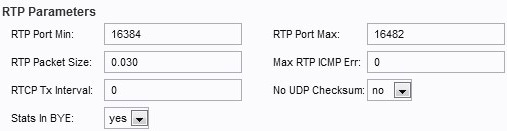
• RTP Port Min — The minimum port number you can use for RTP transmission and reception. The default value is set to is 16384.
• RTP Port Max — The maximum port number you can use for transmission and reception. The default value is set to 16482.
• RTP Packet Size — The packet size in a transmission per second. The default value is set to 0.030.
• Max RTP ICMP Err — The number of successive ICMP errors allowed when transmitting RTP packets before the call is terminated. The default value is set to 0.
• RTCP Tx Interval — The interval in seconds (range from 0 to 255) for sending out RTCP sender reports on an active connection. The default value is set to 0.
• No UDP Checksum — From the drop-down menu choose Yes or No to calculate the UDP checksum. Choose Yes if you want the SPA to do this calculation. The default value is set to No.
• Stats in Bye — From the drop-down menu, choose Yes or No. This field determines whether the SPA includes in its header the P-RTP stat in a BYE message.
Step 6. Configure the SDP Payload types.
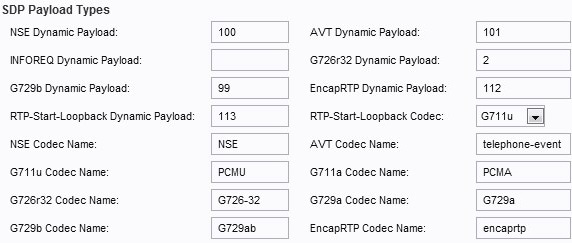
• NSE Dynamic Payload — The NSE dynamic payload. The range is from 97 to 127. The default value is set to 100.
• AVT Dynamic Payload — The AVT dynamic payload. The range is from 96 to 127. The default value is set to 101.
• INFOREQ Dynamic Payload — The type of the INFOREQ payload. There is no default value set for this field.
• G726r32 Dynamic Payload — The G726r32 payload. The default value is set to 2.
• G729b Dynamic Payload — The G729b payload. The range is from 96 to 127. The default is set to 99.
• EncapRTP Dynamic Payload — The EncapRTP payload. The default value is set to 112.
• RTP-start-Loopback Dynamic Payload — The RTP-Start-Loopback payload. The default value is set to 113.
• RTP Start-Loopback Codec — From the drop-down menu, choose one of the following codecs:
- G711u — Provides the best voice quality. G711u is the version used in the USA, Canada, and Japan.
- G711a — Provides the best voice quality. G711a is the version used in the rest of the world.
- G726-32 — Covers the transmission of voice at a rate of 32 Kbit/s.
- G729a — Compress digital voice in packets of 10 milliseconds of duration with lower computational power.
Note: The default is set to G711u.
• NSE Codec Name — The name of the NSE codec. The default name is set to NSE.
• AVT Codec Name — The AVT codec name. The default name is set to telephone-event.
• G711u Codec Name — The G711u codec name. The default name is set to PCMU.
• G711a Codec Name — The G711a codec name. The default name is set to PCMA.
• G726r32 Codec Name — The G726r32 codec name. The default name is set to G726-32.
• G729a Codec Name — The G729a codec name. The default name is set to G729a.
• G729b Codec Name — The G729b codec name. The default name is set to G729ab.
• EncapRTP Codec Name — The EncapRTP codec name. The default name is set to encaprtp.
Step 7. Configure the NAT Support Parameters.
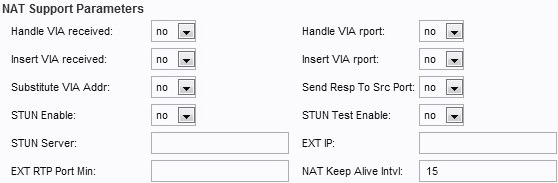
• Handle VIA received — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, then the SPA process the received parameter in the VIA header. If you choose No, the parameter is ignored. The default value is set to No.
• Handle VIA rport — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, the ATA handles the rport parameter in the VIA header. If you select No, the parameter is ignored. The default value is set to No.
• Insert VIA received — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, the received parameter will be inserted in the VIA header of the SIP response. The default value is set to No.
• Insert VIA rport — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, the rport parameter will be inserted in the VIA header. The default value is set to No.
• Substitute VIA Addr — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, it will use NAT-mapped IP:port values in the VIA header. The default value is set to No.
• Send Resp to Src Port — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, it will send responses to the request source port instead of using the VIA sent-by-port. The default value is set to No.
• STUN Enable — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, it enables the use of STUN to discover NAT mapping. The default value is set to No.
• STUN Test Enable — Choose Yes or No from the drop-down menu. If you choose Yes, the SPA performs a NAT-type discovery operation when it powers on, then proceeds to contact the STUNT server, and the result of the discovery is reported in a Warning header to the following REGISTER requests. The default value is set to No.
• STUN Server — The IP address or the domain name of the STUNT server.
• EXT IP — The external IP address that substitutes the actual IP address of the SPA for all outgoing SIP messages. The default value is set to blank.
• EXT RTP Port Min — The external port mapping number of the RTP Port Min. There is no default value.
• NAT Keep Alive Intvl — The interval between NAT-mapping keep alive messages. The default is set to 15.
Step 8. Click Submit to save your changes.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback