Set up a Wireless Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
Available Languages
Objective
A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to a wired network. Instead of using wires and cables to connect every computer or device in the network, installing WAPs is a more convenient, more secure, and cost-efficient alternative.
Setting up a wireless network provides a lot of advantages and benefits for you and your small business.
- It is easier to set up compared to setting up a wired network.
- It is more convenient to access.
- It is less complicated to add new users in the network.
- It gives users more flexibility to stay online even when moving from one area in the office to another.
- Guest users can have Internet access by just using a password.
- Wireless network protection can be set up even if the network is visible to the public by configuring maximum wireless security.
- Segmentation of users, such as guests and employees, is possible by creating Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) to protect your network resources and assets.
There are different purposes of setting up a wireless network using a WAP. With a WAP, you can do the following:
- Create a wireless network within your existing wired network.
- Extend the signal range and strength of your wireless network to provide complete wireless coverage and get rid of dead spots especially in larger office spaces or buildings.
- Accommodate wireless devices within a wired network.
- Configure the settings of your wireless access points in one device.
This article aims to show you the different types of wireless network setups and their uses.
Applicable Devices | Firmware Version
- WAP121 | 1.0.6.5 (Download latest)
- WAP131 | 1.0.2.8 (Download latest)
- WAP150 | 1.0.1.7 (Download latest)
- WAP321 | 1.0.6.5 (Download latest)
- WAP351 | 1.0.2.8 (Download latest)
- WAP361 | 1.0.1.7 (Download latest)
- WAP371 | 1.3.0.3 (Download latest)
- WAP551 | 1.2.1.3 (Download latest)
- WAP561 | 1.2.1.3 (Download latest)
- WAP571 | 1.0.0.17 (Download latest)
- WAP571E | 1.0.0.17 (Download latest)
Set up a Wireless Network using a WAP
Listed below are different types of wireless network setup. Click on any one of the links depending on your network preference:
- Adding a wireless network to an existing wired network
- Connecting multiple access points together through Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
- Configuring clustering of Wireless Access Points
- Configuring Workgroup Bridge
1. Adding a wireless network to an existing wired network
Adding a WAP to your existing wired network is useful to accommodate those devices that are only capable of wireless connection. It is like creating another network only for wireless devices but still be a part of your existing wired network.
Adding a WAP in the existing network is like joining two networks together to form a single network for both wired and wireless devices such as shown in the diagram below.
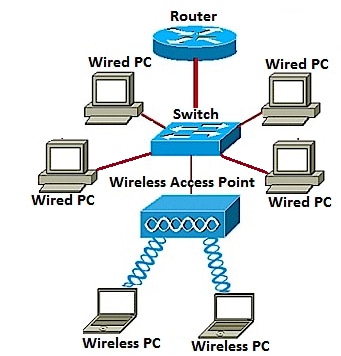
To learn how to add a wireless network to an existing wired network, click here.
2. Connecting multiple access points together through Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
WDS lets you connect multiple access points together. WDS allows the connected access points to communicate with each other via wireless connection. This feature enables clients who roam to have a seamless experience. This makes it easier to manage multiple wireless networks as well as reduces the amount of cables required to connect the networks.
The WAP can act as a single point-to-point mode access point, point-to-multipoint bridge, or as a repeater. On a repeater mode, a WAP can establish a connection between other access points that are far apart. It will simply act as a wireless extender. Wireless clients can connect to this repeater. A WDS role system can be compared similar to the role of the repeater.

In the example diagram above, a WDS connection is configured between the WAP121 and the WAP321 Access Points.
Guidelines in configuring WDS:
1. WDS works only with specific pairs of Cisco WAP devices. The pairs are as listed below.
- WAP121 with WAP321
- WAP131 with WAP351
- WAP150 with WAP361
- WAP551 with WAP561
- Multiple WAP371
- Multiple WAP571
- Multiple WAP571E
2. You can have only one WDS link between any pair of these devices. That is, a remote Media Access Control (MAC) address may appear only once on the WDS page for a particular WAP.
3. The devices should have the same settings for radio, IEEE 802.11 mode, Channel Bandwidth, and Channel.
4. Channel selection should be specified and not set to Auto.
To learn how to configure WDS on your WAP, click any of the links below depending on the device you are using:
3. Configuring clustering of Wireless Access Points
Clustering is when multiple WAPs are joined together in the same network. This technology is advanced intelligence that allows them to work together dynamically and simplifies wireless networking. You will be able to configure and manage a clustered wireless network as a single entity, and without having to configure and reconfigure the settings in each access point separately. Up to ten WAPs can be clustered in a wireless network.
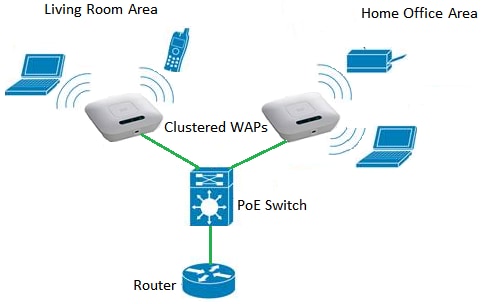
The WAP acts as a transmitter and receiver of Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) radio signals, providing a larger wireless range as well as the ability to support more clients on a network.
Benefits of clustering Wireless Access Points:
- Saves the cost of a wireless controller.
- Reduces operations costs by saving hours of (internal or outsourced) technical staff time.
- Increases security.
- Increases productivity by improving roaming.
- Increases productivity by improving application performance.
Guidelines in configuring a cluster through Single Point Setup:
- A cluster can be created only among the same model of two or more WAPs, each of which has Single Point Setup enabled and reference the same Single Point Setup name.
- You can edit the Single Point Setup settings only when Single Point Setup is disabled.
- The cluster name is not sent to other WAPs that belong to a cluster. You must configure the same name on each device that is a member of the cluster.
- The cluster name must be unique for each Single Point Setup that you configure on the network.
- Single Point Setup works only with WAPs that are using the same type of IP addressing. Devices will not cluster if IP versions are not similar.
- You cannot enable Single Point Setup if Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is enabled.
To learn how to configure clustering of WAPs, click here.
4. Configuring Workgroup Bridge
The WorkGroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless Local Area Network (LAN) that is connected with the WorkGroup Bridge Mode. The WAP device associated with the remote interface is known as an access point interface, while the WAP device associated with the wireless LAN is known as an infrastructure interface. The WorkGroup Bridge lets devices that only have wired connections connect to a wireless network. WorkGroup Bridge Mode is recommended as an alternative when the Wireless Distribution System (WDS) feature is unavailable.

The topology above illustrates a sample WorkGroup Bridge model. Wired devices are tethered to a switch, which connects to the LAN interface of the WAP. The WAP acts as an access point interface, connects to the infrastructure interface.
To learn how to configure Workgroup Bridge mode, click here.