Configure WorkGroup Bridge Settings on WAP125 or WAP581 Access Points
Available Languages
Objective
The WorkGroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless Local Area Network (LAN) that is connected with the WorkGroup Bridge Mode. The WAP device associated with the remote interface is known as an access point interface, while the WAP device associated with the wireless LAN is known as an infrastructure interface. The WorkGroup Bridge lets devices that only have wired connections connect to a wireless network. WorkGroup Bridge Mode is recommended as an alternative when the Wireless Distribution System (WDS) feature is unavailable.
The topology below illustrates a sample WorkGroup Bridge model. Wired devices are tethered to a switch, which connects to the LAN interface of the WAP. In the example below, the WAP125 acts as an access point interface which connects to the infrastructure client interface.

This article provides instructions on how to configure WorkGroup Bridge settings between two wireless access points.
Applicable Devices
- WAP125
- WAP581
Software Version
- 1.0.0.4 — WAP581
- 1.0.0.5 — WAP125
Configure WorkGroup Bridge Settings
Before you configure Work Group Bridge on the WAP device, note these guidelines:
- All WAP devices participating in WorkGroup Bridge must have the following identical settings:
- Radio
- IEEE 802.11 Mode
- Channel Bandwidth
- Channel (Auto is not recommended)
Note: To learn how to configure these settings on WAP125, click here for instructions. For WAP581, click here.
- WorkGroup Bridge mode currently supports only IPv4 traffic.
- WorkGroup Bridge mode is not supported across a Single Point Setup. If you have WAP581 access points, disable SPS or clustering first before configuring the WorkGroup Bridge settings. For instructions on how to configure the SPS settings on your WAP, click here.
Configure Infrastructure Client Interface
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility of the WAP then choose Wireless Bridge.
Note: The available options may vary depending on the exact model of your device. In this example, WAP125 is used.

Step 2. Click the WorkGroup radio button.

Step 3. Check the Uplink check box.

Step 4. Click the Edit icon.

Step 5. Check the Enabled check box to enable Infrastructure Client Interface.

Step 6. Choose the radio interface for the WorkGroup Bridge. When you configure one radio as a WorkGroup Bridge, the other radio remains operational. The radio interfaces correspond to the radio frequency bands of the WAP. The WAP is equipped to broadcast on two different radio interfaces. Configuring settings for one radio interface will not affect the other.

Note: In this example, Radio 2 (5 GHz) is chosen.
Step 7. Enter the Service Set Identifier (SSID) name in the SSID field. This serves as the connection between the device and the remote client. You may enter 2 to 32 characters for the Infrastructure Client SSID.
Note: In this example, WAP125 Upstream is used.

Note: The arrow next to SSID is available for SSID Scanning. This feature is disabled by default, and is enabled only if AP Detection is enabled in Rogue AP Detection, which is also disabled by default.
Step 8. Choose the type of security to authenticate as a client station on the upstream WAP device from the Encryption drop-down list. The options are:
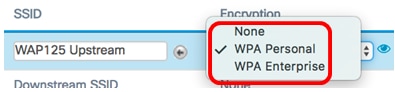
- None — Open or no Security. This is the default. If this is chosen, skip to Step 22.
- WPA Personal — WPA Personal can support keys of length 8-63 characters. WPA2 is recommended as it has a more powerful encryption standard.
- WPA Enterprise — WPA Enterprise is more advanced than WPA Personal and is the recommended security for authentication. It uses Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). Skip to Step 12 to configure. This type of security is often used in an office environment and needs a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server configured. Click here to know more about RADIUS servers.
Note: In this example, WPA Personal is chosen.
Step 9. Click the  icon and check the WPA-TKIP or WPA2-AES check box to determine which kind of WPA encryption the infrastructure client interface will use.
icon and check the WPA-TKIP or WPA2-AES check box to determine which kind of WPA encryption the infrastructure client interface will use.

Note: If all of your wireless equipment support WPA2, set the infrastructure client security to WPA2-AES. The encryption method is RC4 for WPA and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for WPA2. WPA2 is recommended as it has a more powerful encryption standard. In this example, WPA2-AES is used.
Step 10. (Optional) If you checked WPA2-AES in Step 9, choose an option from the Management Frame Protection (MFP) drop-down list whether you want the WAP to require to have protected frames or not. To learn more about MFP, click here. The options are:
- Not Required — Disables the client support for MFP.
- Capable — Allows both MFP-capable and clients that do not support MFP to join the network. This is the default MFP setting on the WAP.
- Required — Clients are allowed to associate only if MFP is negotiated. If the devices do not support MFP, they are not allowed to join the network.

Note: In this example, Capable is chosen.
Step 11. Enter the WPA encryption key in the Key field. The key must be 8-63 characters long. This is a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. It is the password that is used when connecting to the wireless network for the first time. Then, skip to Step 21.

Step 12. If you chose WPA Enterprise in Step 8, click a radio button for the EAP Method.
The available options are defined as follows:
- PEAP —This protocol gives each wireless user under the WAP individual usernames and passwords that support AES encryption standards. Since PEAP is a password based security method, your Wi-Fi security is based on the device credentials of the client. PEAP can pose a potentially serious security risk if you have weak passwords or unsecured clients. It relies on TLS but avoids the installation of digital certificates on every client. Instead, it provides authentication through a username and password.
- TLS — TLS requires each user to have an additional certificate to be granted access. TLS is more secure if you have the additional servers and necessary infrastructure to authenticate users into your network. If you choose this option, skip to Step 14.

Note: For this example, PEAP is chosen.
Step 13. Enter the username and password for the infrastructure client in the Username and Password fields. This is the login information that is used to connect to the infrastructure client interface; refer to your infrastructure client interface to find this information. Then, skip to Step 21.

Step 14. If you clicked TLS in Step 12, enter the identity and private key of the infrastructure client in the Identity and Private Key fields.

Step 15. In the transfer method area, click a radio button of the following options:
- TFTP — Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simplified unsecured version of File Transfer Protocol (FTP). It is mainly used to distribute software or authenticate devices among corporate networks. If you clicked TFTP, skip to Step 18.
- HTTP — Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) provides a simple challenge-response authentication framework that can be used by a client to provide authentication framework.

Note: If a certificate file is already present on the WAP, the Certificate File Present and Certificate Expiration Date fields will already be filled in with the relevant information. Otherwise, they will be blank.
HTTP
Step 16. Click the Browse button to find and select a certificate file. The file must have the proper certificate file extension (such as .pem or .pfx) otherwise, the file will not be accepted.

Note: In this example, Certificate.pfx is chosen.
Step 17. Click Upload to upload the selected certificate file. Skip to Step 21.

The Certificate File Present and Certificate Expiration Date fields will be updated automatically.
TFTP
Step 18. (Optional) If you clicked TFTP in Step 15, enter the filename of the certificate file in the Filename field.

Note: In this example, Certificate.pfx is used.
Step 19. Enter the TFTP Server address in the TFTP Server IPv4 Address field.

Note: In this example. 192.168.100.108 is used as the TFTP Server address.
Step 20. Click the Upload button to upload the specified certificate file.

The Certificate File Present and Certificate Expiration Date fields will be updated automatically.
Step 21. Click OK to close the Security Setting window.

The Connection Status area indicates whether the WAP is connected to the upstream WAP device.

Step 22. Enter the VLAN ID for the infrastructure client interface. The default is 1.

Note: For this example, the default VLAN ID is used.
Step 23. Click Save to save the configured settings.

You should now have successfully configured the Infrastructure Client Interface settings on your WAP.
Configure Access Point Client Interface
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility of the WAP then choose Wireless Bridge.
Note: The available options may vary depending on the exact model of your device. In this example, WAP125 is used.

Step 2. Click the WorkGroup radio button.

Step 3. Check the Downlink check box.

Step 4. Click the Edit button.

Step 5. Check the Enabled check box to enable bridging on the access point interface.

Step 6. Enter the SSID for the access point in the SSID field. The SSID length must be between 2 to 32 characters. The default is Downstream SSID.

Note: For this example, the SSID used is WAP125 Downstream.
Step 7. Choose the type of security to authenticate downstream client stations to the WAP from the Security drop-down list.
The available options are defined as follows:
- None — Open or no security. This is the default value. Skip to Step 13 if you choose this option.
- WPA Personal — Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Personal can support keys of 8 to 63 characters long. The encryption method is either TKIP or Counter Cipher Mode with Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP). WPA2 with CCMP is recommended as it has a more powerful encryption standard, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), compared to the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) that uses only a 64-bit RC4 standard.

Step 8. (Optional) Check the WPA-TKIP check box to determine WPA-TKIP encryption the access point interface will use. This is enabled by default.
Note: WPA-AES is grayed-out and cannot be disabled. In this example, WPA-TKIP is unchecked.

Step 9. Enter the shared WPA key in the Key field. The key must be 8-63 characters long and can include alphanumeric characters, upper and lower case characters, and special characters.

Step 10. Enter the rate in the Broadcast Key Refresh Rate field. The broadcast key refresh rate specifies the interval at which the security key is refreshed for clients associated to this access point. The rate must be between 0-86400, with a value of 0 disabling the feature.

Note: In this example, 86400 is used.
Step 11. Choose an option from the MFP drop-down list whether you want the WAP to require to have protected frames or not. To learn more about MFP, click here. The options are:
- Not Required — Disables the client support for MFP.
- Capable — Allows both MFP-capable and clients that do not support MFP to join the network. This is the default MFP setting on the WAP.
- Required — Clients are allowed to associate only if MFP is negotiated. If the devices do not support MFP, they are not allowed to join the network.

Note: For this example, Capable is chosen.
Step 12. Click OK to save the security settings.

The Connection Status area indicates Not Applicable or N/A.

Step 13. Enter the VLAN ID in the VLAN ID field for the access point interface.
Note: To allow the bridging of packets, the VLAN configuration for the access point interface and wired interface should match that of the infrastructure client interface.

Step 14. Check the SSID Broadcast check box if you want the downstream SSID to be broadcast. SSID Broadcast is enabled by default.

Step 15. Choose the type of MAC filtering you wish to configure for the access point interface from the MAC Filtering drop-down list. When enabled, users are granted or denied access to the WAP based on the MAC address of the client they use.
The available options are defined as follows:
- Disabled — All clients can access the upstream network. This is the default value.
- Local — The set of clients that can access the upstream network is restricted to the clients specified in a locally defined MAC address list.
- RADIUS — The set of clients that can access the upstream network is restricted to the clients specified in a MAC address list on a RADIUS server.
Note: In this example, Disabled is chosen.
Step 16. Click Save to save your changes.

You should now have successfully configured the WorkGroup Bridge settings on your wireless access points.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
12-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback