VLAN Configuration on the WAP351 Access Point
Available Languages
Objective
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a switched network that is logically segmented by function, area, or application, without regard to the physical locations of the users. VLANs have the same attributes as physical LANs, but you can group end stations even if they are not physically located on the same LAN segment.
A tagged VLAN between a trunk port and a switch port contains the VLAN information in the Ethernet frame. An untagged VLAN sends traffic without the VLAN tag. A VLAN tag inserts information into Ethernet frames identifying which frame belongs to which VLAN. A trunk port is a port that handles multiple VLANs.
To add more security to the network, your network configuration must include a secured management VLAN. The management VLAN is the VLAN used to access the WAP with the web configuration utility. An attack on the management VLAN can compromise network security, so changing the management and untagged VLANs to something other than the default is recommended. The management VLAN ID on the WAP351 access point is configured to VLAN 1 by default.
The objective of this document is to show you how to configure VLANs on the WAP351 Access Point.
Applicable Devices
• WAP351
Software Version
• 1.0.0.39
Global Settings
Step 1. Log in to the Access Point Configuration Utility and choose LAN > VLAN Configuration. The VLAN Configuration page opens:
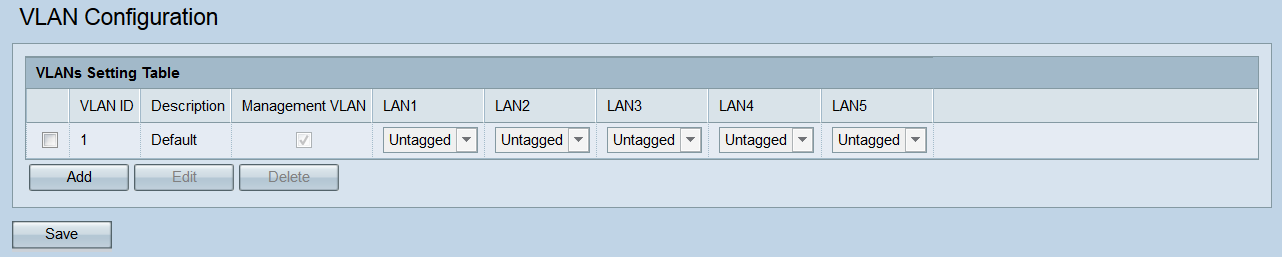
Step 2. To add a new VLAN, click the Add button. If you want to edit or delete an existing VLAN, skip to the next step.

An empty VLAN will be added to the table.
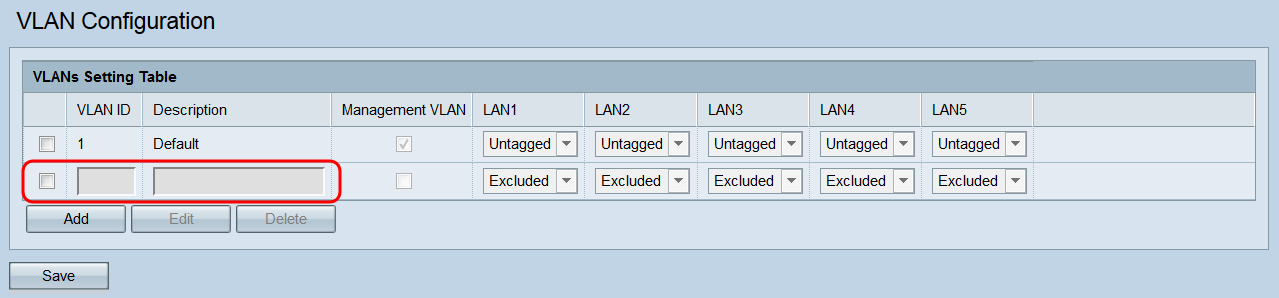
Step 3. To edit or delete an existing or newly added VLAN, click the checkbox next to the VLAN(s) you want to edit/delete.

Step 4. Click Edit or Delete. If you clicked Delete, skip to Step 10. If you want to edit an existing (not empty) VLAN, skip to Step 7.
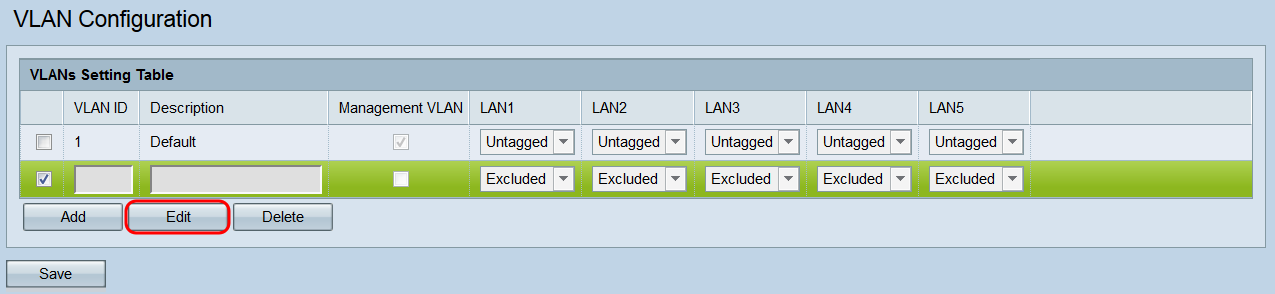
Note: VLAN ID 1 cannot be deleted.
Step 5. Enter a VLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The valid range is 1 – 4094, and each VLAN must have a different ID.

Step 6. Enter a description of the VLAN in the Description field. This field can only consist of alphanumeric characters and underscores, and must be only 64 or less characters long. The description does not have any effect on the functionality of the VLAN. Each VLAN must have a different description.

Step 7. If you want a VLAN to be a management VLAN, click its corresponding checkbox in the Management VLAN field. The management VLAN is the VLAN used to access the web configuration utility.
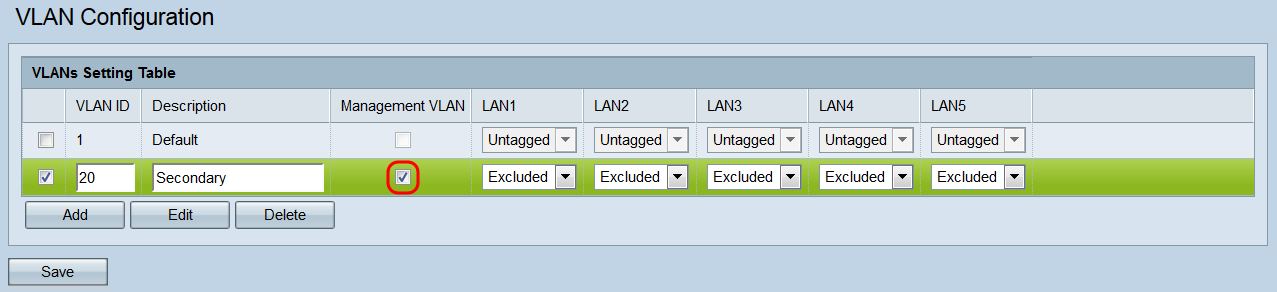
Note: By default, VLAN 1 is the management VLAN. If you do not want VLAN 1 to be the management VLAN, uncheck its checkbox. There can only be one management VLAN at a time. If there is no management VLAN, users will be unable to access the web configuration utility.
Step 8. If you are setting a VLAN to be a management VLAN, a notice will appear saying that the previous management VLAN will be set to unmanaged. Click OK to continue.

Step 9. Each port on the WAP351 corresponds to a LAN field (LAN1, LAN2, etc.). For each port, choose an option from the drop-down menu.

The options are:
• Untagged — Sets the port as a member of the VLAN. A packet of the VLAN sent out from the port will not be tagged with the VLAN header. However, an untagged packet received by the port will be tagged.
• Tagged — Sets the port as a member of the VLAN. A packet of the VLAN sent out from the port will be tagged with the VLAN header.
• Excluded — This port is not a member of the VLAN.
Step 10. Click Save. Your changes will be applied, and the WAP may lose connectivity depending on the settings applied.

 Feedback
Feedback