Fix EVPN RMAC ExtCommunity Transmission Issues to ACI Fabric
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Introduction
This document describes the impact of misconfigured Router MAC extended community attribute on an ACI fabric when received from an external Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) peer.
Background Information
With BGP, there is an option to send community and extended community attributes with the prefixes that are advertised to BGP peers. These community attributes allow us to modify routing policies and dynamically alter the way routed traffic is handled.
Problem
When the Router MAC extended community attribute is sent with an IPv4 AFI prefix from an external BGP peer to an ACI fabric, FIB and HAL misprogramming occurs on any leaf in the fabric that receives the route from the border leaf(s) via the internal MP-BGP process. This is because the RMAC extcommunity attribute belongs to the BGP L2VPN EVPN address family, and when it is injected into the BGP IPv4 address family, it gets rejected. This is due to a violation of rule 5.2 (Uniform-Propagation-Mode), which is described in the IETF document entitled, "EVPN Interworking with IPVPN". On page 15, item 4c, the specific issue is called out:
4. As discussed, Communities, Extended Communities and Large
Communities SHOULD be kept by the gateway PE from the originating
SAFI route. Exceptions of Extended Communities that SHOULD NOT
be kept are:
C. All the extended communities of type EVPN.
The gateway PE SHOULD NOT copy the above extended communities
from the originating ISF route to the re-advertised ISF route.Link to document: EVPN Interworking with IPVPN
Here is an example of the problem with iBGP, however, the problem is also seen with eBGP.
Topology Diagram:
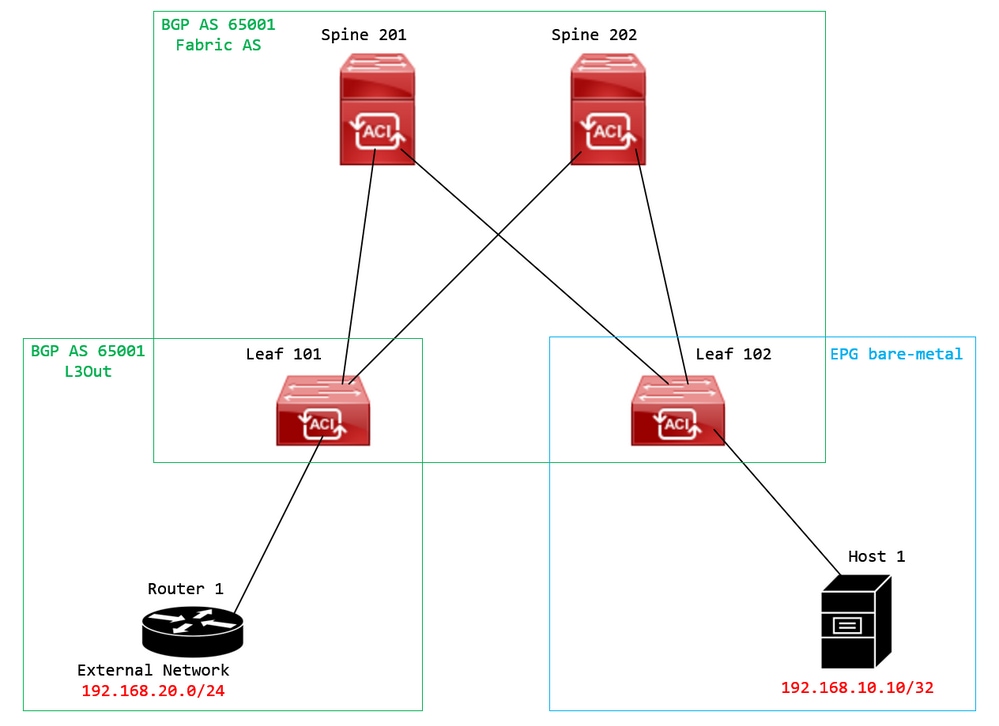 Topology diagram
Topology diagram
Configure route map on external BGP peer device (Router 1) and set the EVPN RMAC extcommunity attribute:
Router-1# show run | sec route-map
route-map RMAC permit 10
set extcommunity evpn rmac aaaa.bbbb.cccc
Under the BGP neighbor IPv4 address family configuration, configure BGP extended communities, and configure the route map in the outbound direction:
Router-1# show run bgp
<output omitted>
feature bgp
router bgp 65001
vrf example
router-id 192.168.20.20
address-family ipv4 unicast
network 192.168.20.0/24
neighbor 192.168.30.30
remote-as 65001
update-source loopback1
address-family ipv4 unicast
send-community extended
route-map RMAC out
Check the BGP status on BL 101:
leaf-101# show ip bgp 192.168.20.0 vrf example:example
BGP routing table information for VRF example:example, address family IPv4 Unicast
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.20.0/24, version 40 dest ptr 0xa0fec840
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x80c001a 00000000) on xmit-list, is in urib, is best urib route, is in HW, exported
vpn: version 2725, (0x100002) on xmit-list
Multipath: eBGP iBGP
Advertised path-id 1, VPN AF advertised path-id 1
Path type (0xa96485b8): internal 0x18 0x0 ref 0 adv path ref 2, path is valid, is best path
AS-Path: NONE, path sourced internal to AS
192.168.20.20 (metric 5) from 192.168.20.20 (192.168.20.20)
Origin IGP, MED not set, localpref 100, weight 0 tag 0, propagate 0
Extcommunity:
RT:65001:2162688
COST:pre-bestpath:163:1879048192
Router MAC:aaaa.bbbb.cccc
***Notice that the router mac is present here.***
VNID:2162688
VRF advertise information:
Path-id 1 not advertised to any peer
VPN AF advertise information:
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
10.0.216.65 10.0.216.66
Check RIB on CL 102:
leaf-102# show ip route 192.168.20.0 vrf example:example
IP Route Table for VRF "example:example"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
192.168.20.0/24, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via 10.0.210.70%overlay-1, [200/0], 00:00:43, bgp-65001, internal, tag 65001, rwVnid: vxlan-2162688
recursive next hop: 10.0.210.70/32%overlay-1
***Notice that we have the route here and our next-hop address is correct (showing the TEP IP of BL 101). Also, notice that there is an rwVnid entry here.***
leaf-102# acidiag fnvread | grep 101
101 1 leaf-101 <output omitted> 10.0.210.70/32 leaf active 0
Check FIB on CL 102:
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# show forwarding route 192.168.20.0 vrf example:example
ERROR: no longest match in IPv4 table 0xf5df36b0
***No entry is present.***
Check the HAL table on CL 102:
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# show platform internal hal l3 routes | grep 192.168.20.0
***No entry is present.***
Pings from EP (Host 1) to host in external network that comes from external BGP peer (192.168.20.20):
Host-1# ping 192.168.20.20 vrf example
PING 192.168.20.20 (192.168.20.20): 56 data bytes
Request 0 timed out
Request 1 timed out
Request 2 timed out
Request 3 timed out
Request 4 timed out
--- 192.168.20.20 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100.00% packet loss
***No connectivity.***
Check ELAM on CL 102:
leaf-102# vsh_lc
module-1# debug platform internal roc elam asic 0
module-1(DBG-elam)# trigger reset
module-1(DBG-elam)# trigger init in-select 6 out-select 0
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# set outer ipv4 src_ip 192.168.10.10 dst_ip 192.168.20.20
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# start
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# stat
ELAM STATUS
===========
Asic 0 Slice 0 Status Armed
Asic 0 Slice 1 Status Triggered
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# ereport
Python available. Continue ELAM decode with LC Pkg
ELAM REPORT
<output omitted>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lookup Drop
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LU drop reason : UC_PC_CFG_TABLE_DROP
***Notice the drop vector here.***
Solution
The solution is to stop sending the Router MAC extended community attribute with an IPv4 address family prefix from an external BGP peer to an ACI fabric.
Remove the previously configured route map and stop sending extended communities from the external BGP peer device (Router 1). Removing either one of these configs, or both, will work:
Router-1# show run bgp
<output omitted>
feature bgp
router bgp 65001
vrf example
router-id 192.168.20.20
address-family ipv4 unicast
network 192.168.20.0/24
neighbor 192.168.30.30
remote-as 65001
update-source loopback1
address-family ipv4 unicast
Another (less preferred) solution is to simply filter out all communities received from the external BGP peer device by creating a route map in the configured L3Out in ACI.
Navigate to your Tenant > Policies > Protocol > Route Maps for Route Control > Create Route Maps for Route Control:
 Select the option to Create Route Maps for Route Control
Select the option to Create Route Maps for Route Control
Name your route map, enable the Route-Map Continue option, and then add a context. Select the + icon in the Contexts table:
 Create Route Map and create Context
Create Route Map and create Context
Name your context, and leave the default action of Permit selected, then create a match rule by selecting the + icon in the Associated Matched Rules table, and select Create Match Rule for a Route Map:
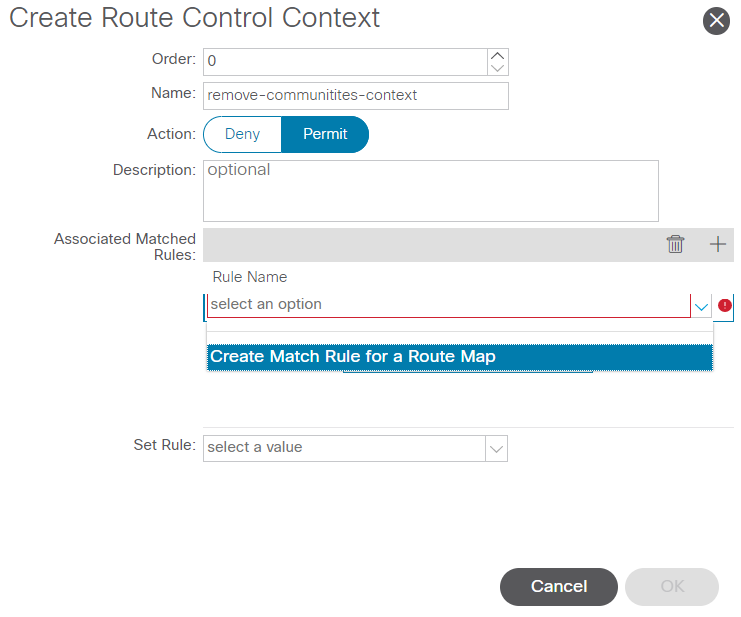 Create Route Control Context and select option for Create Match Rule for a Route Map
Create Route Control Context and select option for Create Match Rule for a Route Map
Name your match rule then add a new prefix by selecting the + icon in the Match Prefix table:
 Create Match Rule and create Match Prefix
Create Match Rule and create Match Prefix
Add your desired prefix. This example shows how to add an aggregate of all prefixes:
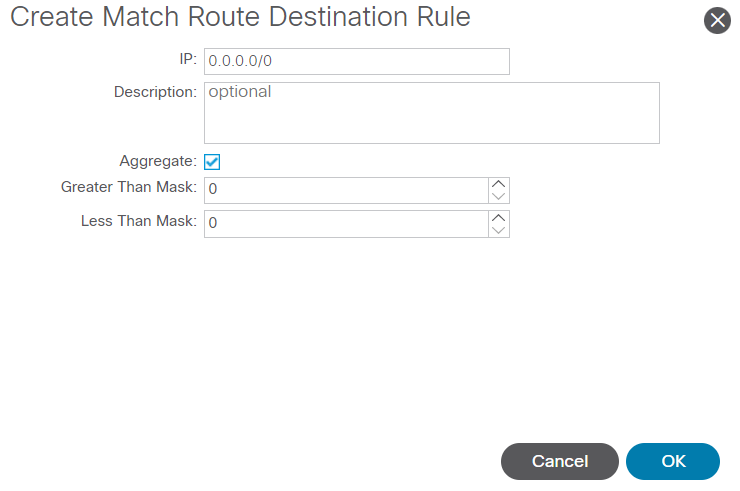 Create Match Route Destination Rule
Create Match Route Destination Rule
After you select OK in the Create Match Route Destination Rule window, you see that your prefix has been added to the Match Prefix table in the Create Match Rule window:
 Match Prefix is now added to Match Rule
Match Prefix is now added to Match Rule
After you select Submit in the Create Match Rule window, select Update in the Associated Matched Rules table in the Create Route Control Context window:
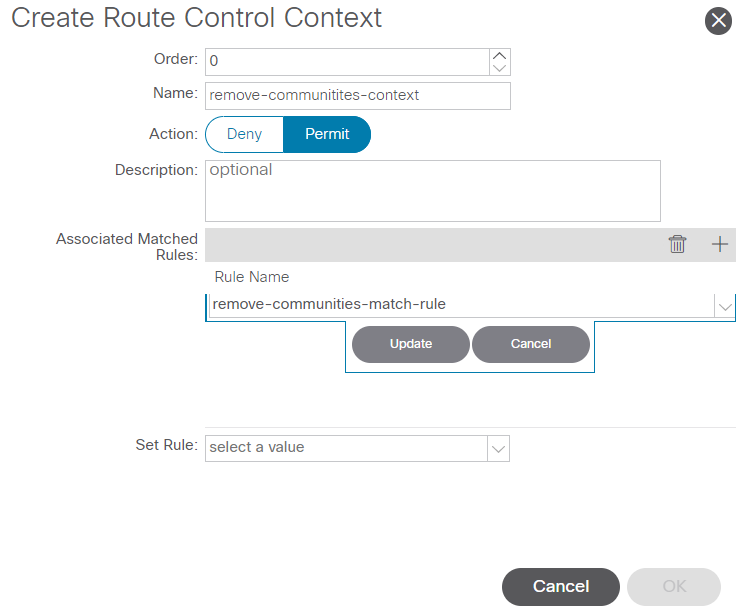 Add Associated Match Rule to Route Control Context
Add Associated Match Rule to Route Control Context
Your associated match rule is now added to your context:
 Associated Match Rule is now added to Route Control Context
Associated Match Rule is now added to Route Control Context
Next, select the dropdown menu next to Set Rule and select Create Set Rules for a Route Map:
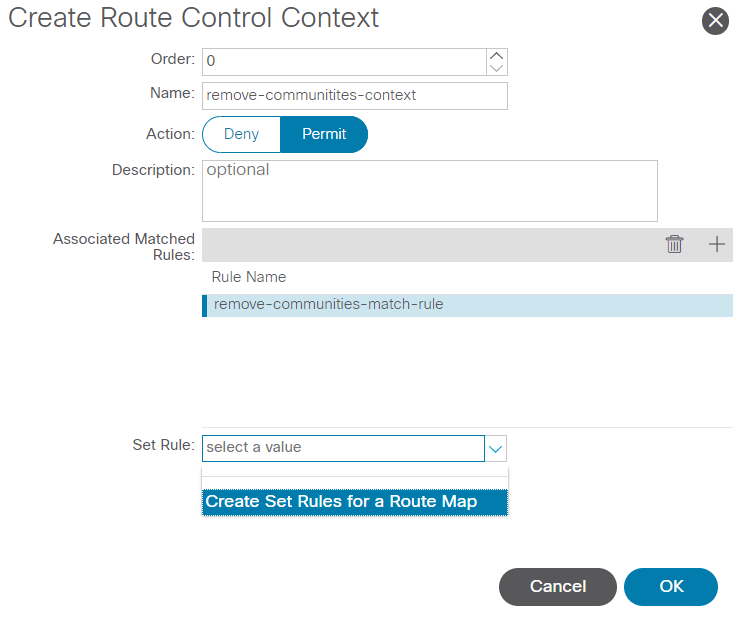 Select option to Create Set Rules for a Route Map
Select option to Create Set Rules for a Route Map
Name your set rule, then select the Set Community option and leave the default criteria of No community selected:
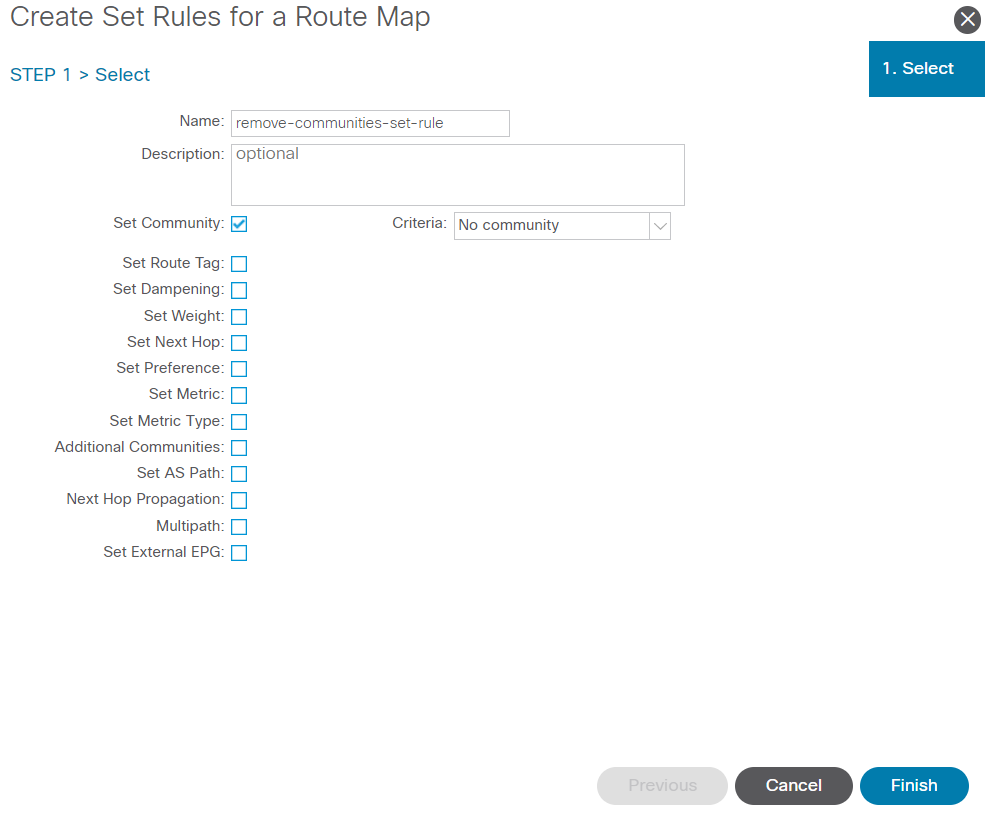 Create Set Rule for Route Map
Create Set Rule for Route Map
After you select Finish in the Create Set Rules for a Route Map window, you see your set rule selected in the Create Route Control Context window:
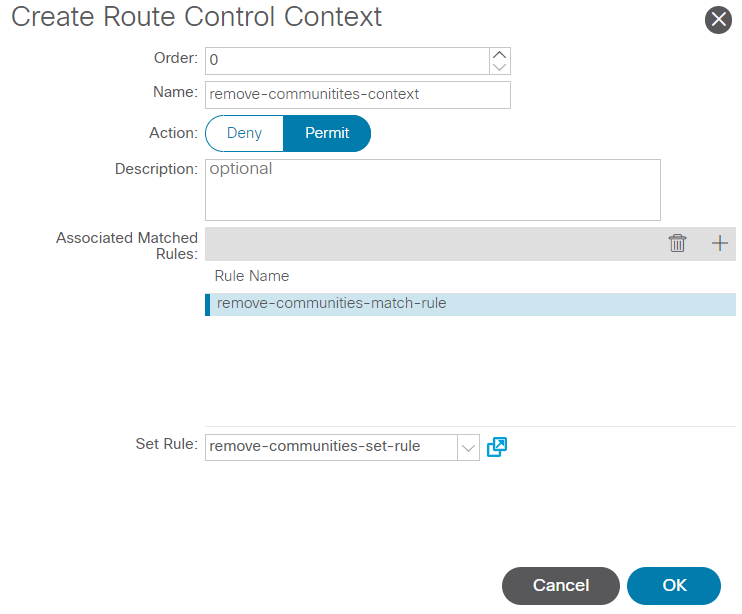 Set Rule is now added to Route Control Context
Set Rule is now added to Route Control Context
After you select OK in the Create Route Control Context window, you see your context added to the Contexts table in the Create Route Maps for Route Control window. Finally, select Submit to complete the configuration:
 Context is now added to Route Map
Context is now added to Route Map
Navigate to the BGP Peer Connectivity Profile in the L3Out and select the + icon in the Route Control Profile table, then add your route map with the default direction of Route Import Policy selected:
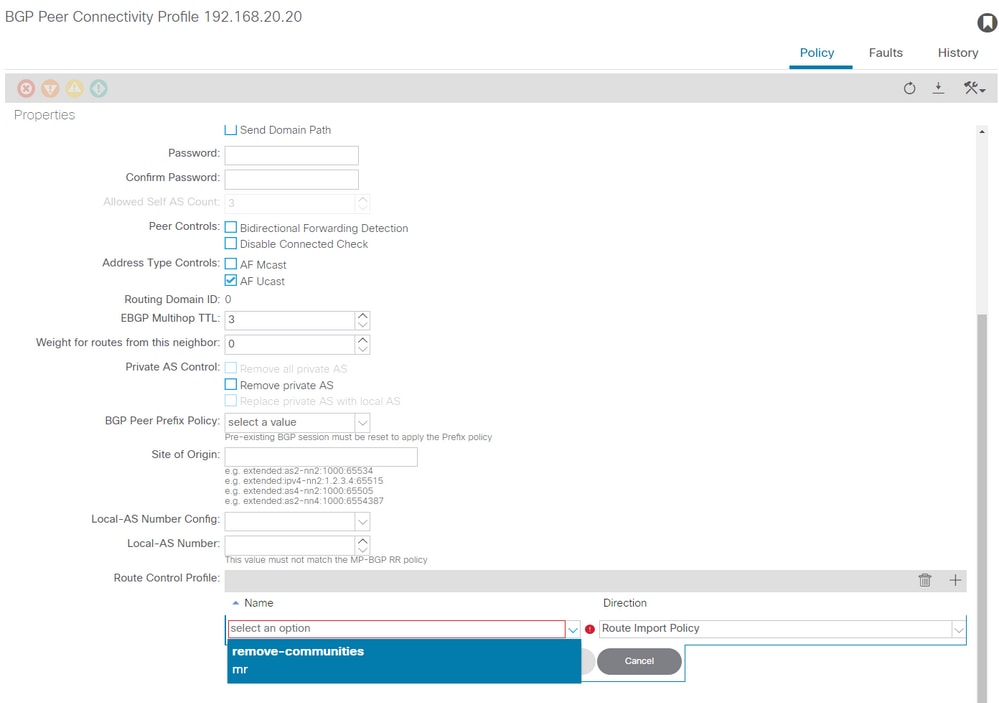 Add Route Map to BGP Peer Connectivity Profile
Add Route Map to BGP Peer Connectivity Profile
After you select Update for the route map, you see your route map added to the Route Control Profile table:
 Route Map is now added to BGP Peer Connectivity Profile
Route Map is now added to BGP Peer Connectivity Profile
*For more information on route map configuration options in ACI, refer to the ACI Fabric L3Out White Paper
After implementing one of the above solutions, verify if the problem is solved.
Check the BGP status on BL 101:
leaf-101# show ip bgp 192.168.20.0 vrf example:example
BGP routing table information for VRF example:example, address family IPv4 Unicast
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.20.0/24, version 46 dest ptr 0xa0fec840
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Flags: (0x80c001a 00000000) on xmit-list, is in urib, is best urib route, is in HW, exported
vpn: version 2731, (0x100002) on xmit-list
Multipath: eBGP iBGP
Advertised path-id 1, VPN AF advertised path-id 1
Path type (0xa96485b8): internal 0x18 0x0 ref 0 adv path ref 2, path is valid, is best path
AS-Path: NONE, path sourced internal to AS
192.168.20.20 (metric 5) from 192.168.20.20 (192.168.20.20)
Origin IGP, MED not set, localpref 100, weight 0 tag 0, propagate 0
Extcommunity:
RT:65001:2162688
COST:pre-bestpath:163:1879048192
***Notice that no router mac is present here.***
VNID:2162688
VRF advertise information:
Path-id 1 not advertised to any peer
VPN AF advertise information:
Path-id 1 advertised to peers:
10.0.216.65 10.0.216.66
Check RIB on CL 102:
leaf-102# show ip route 192.168.20.0 vrf example:example
IP Route Table for VRF "example:example"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
192.168.20.0/24, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via 10.0.210.70%overlay-1, [200/0], 00:00:06, bgp-65001, internal, tag 65001
recursive next hop: 10.0.210.70/32%overlay-1
***Notice that no rwVnid entry is present here.***
Note: The absence or presence of the rwVnid entry alone does not determine whether the issue is occuring or not. In many cases, the rwVnid entry gets removed from the route in question once the issue is resolved. However, this is not always the case. Always check FIB and HAL tables in order to verify if the issue is resolved or not.
Check FIB on CL 102:
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# show forwarding route 192.168.20.0 vrf example:example
IPv4 routes for table example:example/base
------------------+------------------+----------------------+------------------------
Prefix | Next-hop | Interface/VRF | Additional Info
------------------+------------------+----------------------+------------------------
*192.168.20.0/24 10.0.210.70 overlay-1
***Notice that we have the route here and our next-hop address is correct (showing the TEP IP of BL 101).***
Route Class-id:0x0
Policy Prefix 0.0.0.0/0
leaf-102# acidiag fnvread | grep 101
101 1 leaf-101 <output omitted> 10.0.210.70/32 leaf active 0
HAL table on CL 102:
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# show platform internal hal l3 routes | grep 192.168.20.0
| 4662| 192.168.20.0/ 24| UC| 686| 20601| TRIE| a5| 5/ 0| 60a5|A| 8443| 86b6| ef5| 1/ 2| a5| 0| 0| f| 3| 0| 0| 1| sc,spi,dpi
***Notice that we have an entry here and it's in the correct VRF.***
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# hex 4662
0x1236
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# show platform internal hal l3 vrf pi
============================================================================================================
| -- TOR -- | - Spine - | ACL | |
Vrf Hw I I Vrf | SB NB | Proxy ACI | Ing Egr | vpn |
VrfId Name VrfId I S Vnid | BDId BDId | Ou Bd Enc | Lbl Msk Lbl Msk | lbl |
============================================================================================================
26 example:example 1236 0 0 210000 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
Pings from EP (Host 1) to host in external network that comes from external BGP peer (192.168.20.20):
Host-1# ping 192.168.20.20 vrf example
PING 192.168.20.20 (192.168.20.20): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 192.168.20.20: icmp_seq=0 ttl=252 time=1.043 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.20.20: icmp_seq=1 ttl=252 time=1.292 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.20.20: icmp_seq=2 ttl=252 time=1.004 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.20.20: icmp_seq=3 ttl=252 time=0.769 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.20.20: icmp_seq=4 ttl=252 time=1.265 ms
--- 192.168.20.20 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 0.769/1.074/1.292 ms
***Connectivity is there.***
ELAM on CL 102:
leaf-102# vsh_lc
module-1# debug platform internal roc elam asic 0
module-1(DBG-elam)# trigger reset
module-1(DBG-elam)# trigger init in-select 6 out-select 0
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# set outer ipv4 src_ip 192.168.10.10 dst_ip 192.168.20.20
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# start
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# stat
ELAM STATUS
===========
Asic 0 Slice 0 Status Armed
Asic 0 Slice 1 Status Triggered
module-1(DBG-elam-insel6)# ereport
Python available. Continue ELAM decode with LC Pkg
ELAM REPORT
<output omitted>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lookup Drop
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LU drop reason : no drop
***Traffic forwards correctly.***
Related Information
- This behavior is also documented in this defect: Cisco bug ID CSCvx28929
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
12-Jun-2023
|
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Matthew RichCisco TAC Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback