Supported Platforms for Unique MAC Address Configuration on VLAN or L3 Interfaces for Catalyst Switches
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes support for the configuration of a unique MAC address on VLAN (switched virtual interface [SVI]) or Layer 3 (L3) interfaces on Cisco Catalyst switches.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Difference Between CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
Catalyst OS (CatOS) on the Supervisor Engine and Cisco IOS® Software on the Multilayer Switch Feature Card (MSFC) (Hybrid): a CatOS image can be used as the system software to run the Supervisor Engine on Catalyst 6500/6000 switches. If the optional MSFC is installed, a separate Cisco IOS Software image is used to run the MSFC.
Cisco IOS Software on both the Supervisor Engine and MSFC (Native): a single Cisco IOS Software image can be used as the system software to run both the Supervisor Engine and MSFC on Catalyst 6500/6000 switches.
Note: For more information, refer to Comparison of the Cisco Catalyst and Cisco IOS Operating Systems for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch.
MAC Address on a VLAN (SVI) or L3 Interface on Catalyst Switches
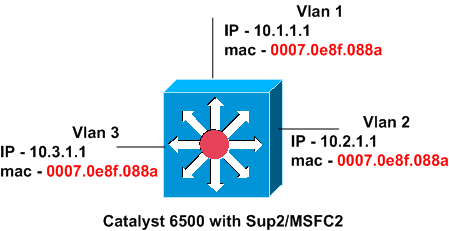
By default, Catalyst switches come with the same MAC address configured on all interfaces. The diagram in this section shows a Catalyst 6500 with Supervisor Engine 2 and MSFC2. However, the MAC address on all three VLAN interfaces is the same, even though the IP addresses are different.
Catalyst switches have varied support for the ability to change the MAC address for a VLAN (SVI) or L3 interface. You do not need to change the burned-in MAC address if the network devices support multiple IPs to a single MAC Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table, which is common. Also, you do not need to change the MAC address if the switches support a per-VLAN MAC address table. Cisco switches support a per-VLAN MAC address table or content-addressable memory (CAM) table. This support allows the switches to maintain a MAC address table per VLAN. Therefore, the switches can have the same MAC address on multiple VLAN interfaces without issue.
Note: A Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) group uses the same virtual MAC address if the HSRP group ID is reused on multiple interfaces. So you must understand and use different HSRP groups when possible. In order to understand the HSRP group limitation on the Catalyst 6500/6000, refer to this document:
The Catalyst 3550 switches, Catalyst 4500/4000 switches with Supervisor Engine III/IV, and Catalyst 6500 switches with Supervisor Engine 720 support up to 256 unique HSRP group IDs in the 0 to 255 range.
MAC Addresses on Layer 2 Interfaces
MAC addresses of Layer 2 Interfaces (Switchports) are unique and are assigned to that particular line module. In Cisco 6500/6000, 4500/4000, 3750, 3560, 3550, and 2970 series switches, you are not able to change the MAC address on a switchport. In Cisco 2940, and 2950/2955 series switches you can change the MAC address of switch ports using the command mac-address, under the interface configuration mode.
MAC Addresses for Spanning Tree Computation
MAC addresses used for Spanning Tree calculations are stored in an EEPROM present in the Supervisor module. Regardless of the types of line modules installed, the Layer 2 MAC addresses for VLANs do not change unless you replace the Supervisor module. If you do replace the Supervisor module, the Layer 2 MAC addresses of all VLANs change to those specified in the address allocator on the new Supervisor module. In the fixed configuration Catalyst switches, MAC addresses for VLANs cannot be changed.
Catalyst Switch with Support for CLI Configuration of a Unique MAC Address per Interface
This section discusses switches that support a change in MAC addresses per interface.
Catalyst 6500/6000 Supervisor Engine 720 and Supervisor Engine I with MSFC1, MSFC2, or MSFC3 That Runs CatOS System Software
This output is from the MSFC1 in which the default MAC address is the same for all interfaces:
cs-6506-24a#show interfaces | include line | address Vlan1 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat6k RP Virtual Ethernet, address is 00d0.bcf1.ee5c (bia 00d0.bcf1.ee5c) Internet address is 14.18.2.182/16 Vlan2 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat6k RP Virtual Ethernet, address is 00d0.bcf1.ee5c (bia 00d0.bcf1.ee5c) cs-6506-24a#
Use the mac-address mac_address interface configuration command in order to change the MAC address. Here is an example:
cs-6506-24a#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. cs-6506-24a(config)#interface vlan 1 cs-6506-24a(config-if)#mac-address 0007.0001.0001 cs-6506-24a(config-if)#exit cs-6506-24a(config)#interface vlan 2 cs-6506-24a(config-if)#mac-address 0007.0001.0002 cs-6506-24a(config-if)#end cs-6506-24a#
Verify the change in the MAC address in this way:
cs-6506-24a#show interfaces | include line | address Vlan1 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat6k RP Virtual Ethernet, address is 0007.0001.0001 (bia 00d0.bcf1.ee5c) Internet address is 14.18.2.182/16 Vlan2 is down, line protocol is down Hardware is Cat6k RP Virtual Ethernet, address is 0007.0001.0002 (bia 00d0.bcf1.ee5c) cs-6506-24a#
When you run Cisco IOS system software, the same commands apply for the VLAN (SVI) and L3 interfaces. The Layer 2 (L2) interfaces, however, have MAC addresses assigned from the range of MAC addresses in each module. Issue the show module command in order to see this range:
cat6kIOS#show module 3 Mod Ports Card Type Model Serial No. --- ----- -------------------------------------- ------------------ ----------- 3 16 SFM-capable 16 port 1000mb GBIC WS-X6516-GBIC SAD0438056W Mod MAC addresses Hw Fw Sw Status --- ---------------------------------- ------ ------------ ------------ ------- 3 0030.f270.ce3b to 0030.f270.ce4a 1.0 6.1(3) 7.5(0.6)HUB1 Ok
This MAC address is used when the particular L2 interface sends out control traffic, such as bridge protocol data units (BPDUs). But if you use the no switchport command in order to configure the same L2 port as an L3 interface, the MAC address reverts to the global default MAC address for the SVI and L3 interface. You can change this on a Catalyst 6500 with Supervisor Engine I that runs Cisco IOS system software, as this example shows:
cat6kIOS#show interfaces | include line | address Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 00d0.003f.880a (bia 00d0.003f.880a) Internet address is 10.48.72.111/23 Vlan3 is administratively down, line protocol is down Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 00d0.003f.880a (bia 00d0.003f.880a) !--- Output suppressed. GigabitEthernet3/1 is up, line protocol is down (notconnect) Hardware is C6k 1000Mb 802.3, address is 0030.f270.ce3f (bia 0030.f270.ce3f) !--- Gigabit Ethernet 3/5 is an L2 interface. The MAC address !--- is from the module MAC address pool. !--- Output suppressed. GigabitEthernet3/10 is up, line protocol is down (notconnect) Hardware is C6k 1000Mb 802.3, address is 00d0.003f.880a (bia 00d0.003f.880a) !--- Gigabit Ethernet 3/10 is an L3 interface. The MAC address !--- is the default for SVI and L3 interface.
Now, configure the interface 3/10 as an L2 port and verify the change in the MAC address:
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. cat6kIOS(config)#interface gigabitethernet cat6kIOS(config)#interface gigabitethernet 3/10 cat6kIOS(config-if)#switchport cat6kIOS(config-if)#
As this example shows, the Gigabit Ethernet 3/10 interface now uses the MAC address from the module MAC address pool:
cat6kIOS#show interface gigabitethernet 3/10
GigabitEthernet3/10 is up, line protocol is down (notconnect)
Hardware is C6k 1000Mb 802.3, address is 0030.f270.ce44 (bia 0030.f270.ce44)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Full-duplex mode, link type is autonegotiation, GBIC not connected
output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported, 1000Mb/s
If you change the Gigabit Ethernet 3/10 back so that it is an L3 interface, the default MAC address is assigned:
cat6kIOS(config)#interface gigabitethernet 3/10
cat6kIOS(config-if)#no switchport
cat6kIOS(config-if)#end
cat6kIOS#show interface gigabitethernet 3/10
GigabitEthernet3/10 is up, line protocol is down (notconnect)
Hardware is C6k 1000Mb 802.3, address is 00d0.003f.880a (bia 00d0.003f.880a)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Catalyst 4000 L3 Module
The Catalyst 4000 L3 module supports a change in the MAC address. Use the mac-address mac_address command on the physical interfaces and port channel interfaces in order to make the change.
Catalyst Switch That Does Not Support CLI Configuration of a Unique MAC Address per Interface
Catalyst 6500/6000 Supervisor Engine II
The Catalyst 6500/6000 Supervisor Engine II supports a change of MAC address from the default burned-in-address (BIA). However, if you change the MAC address for one interface, the MAC addresses for all the configured SVIs change to the newly configured MAC address. As a result, you cannot have a unique MAC address per interface. This is a hardware limitation of the Supervisor Engine II and will not be fixed in a future software release.
This example changes the MAC address from the BIA of 0007.0e8f.088a to 0007.0001.0001:
Router#show interfaces | include line | address Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 0007.0e8f.088a (bia 0007.0e8f.088a) Vlan2 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 0007.0e8f.088a (bia 0007.0e8f.088a) !--- Output suppressed.
Use the mac-address mac_address command in order to change the MAC address under the interface configuration:
Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#interface vlan 1 Router(config-if)#mac-address 0007.0001.0001 Router(config-if)#end Router#
The MAC address change in the VLAN 1 interface modifies the MAC address on all interfaces, as this example shows:
Router#show interfaces | include line | address Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 0007.0001.0001 (bia 0007.0e8f.088a) Vlan2 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 0007.0001.0001 (bia 0007.0e8f.088a)
Catalyst 4500/4000 Supervisor Engine III/IV
The Catalyst 4500/4000 Supervisor Engine III/IV does not currently support a change of MAC address. The MAC address on the interface is the default BIA, which is the same for all interfaces.
The mac-address command is unrecognized for the Catalyst 4500/4000 with Supervisor Engine III/IV.
cat4kIOS(config)#interface vlan 110 cat4kIOS(config-if)#mac-address ? % Unrecognized command cat4kIOS(config-if)#mac-address
Catalyst L2 and L3 Fixed Configuration Switches
This section pertains to the Catalyst L2 fixed configuration switches 2940, 2950/2955 and 2970 (VLAN interface) as well as the Catalyst L3 fixed configuration switches 3550, 3560 and 3750 (VLAN and L3 interface).
| Switch Series | Support for Changing MAC Address of a L2 Switchport | Support for Changing MAC Address of a L3 Interface | Support for Changing the MAC Address of a VLAN Interface | Same or Unique MAC Addresses to the VLAN Interfaces |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2940, 2950, 2955 | Yes | Not Applicable | Yes | Same MAC Address |
| 2970 | No | No | No | Unique MAC Address |
| 3550 | No | No | No | Same MAC Address |
| 3560, 3750 | No | No | No | Unique MAC Address |
This sample configuration shows the steps you use to change MAC addresses in a Cisco Catalyst 2950 series switch that runs Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(22)EA9.
2950(config)#interface fa0/2 2950(config-if)#mac-address 0007.0007.0002 2950(config-if)#interface vlan 2 2950(config-if)#mac-address 0007.0007.0022 2950#show interfaces | include line | address Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is CPU Interface, address is 0009.b740.8900 (bia 0009.b740.8900) Internet address is 172.16.200.1/16 Vlan2 is administratively down, line protocol is down Hardware is CPU Interface, address is 0007.0007.0022 (bia 0009.b740.8900) FastEthernet0/1 is down, line protocol is down (notconnect) Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0009.b740.8901 (bia 0009.b740.8901) FastEthernet0/2 is down, line protocol is down (notconnect) Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0007.0007.0002 (bia 0009.b740.8902) FastEthernet0/3 is down, line protocol is down (notconnect) Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0009.b740.8903 (bia 0009.b740.8903)
In this example, the 3550 with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(14)EA1 does not recognize the mac-address command:
3550(config)#interface vlan 2 3550(config-if)#mac-address 0007.0001.0001 ^ % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. 3550(config-if)#
Note: In Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(13)EA1 and earlier, the switch allows configuration of the mac-address command in the interface. But this command causes connectivity issues. This command-line interface (CLI) configuration issue has been fixed in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(14)EA and later.
Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL
The Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL switches recognize the mac-address command but do not accept or support the command. This output is from a Catalyst 3500XL with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(5)WC3b:
Cat3512XL(config)#interface vlan 1 Cat3512XL(config-if)#mac-address Cat3512XL(config-if)#mac-address 005.0005.0005 "mac-address" override is not allowed in this system Cat3512XL(config-if)#
 Feedback
Feedback