Catalyst Express 500 Series Switches Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the procedure you use to configure Cisco Catalyst Express 500 series switches for Smartport roles, VLANs, EtherChannels, Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN) and to perform interVLAN routing with the Cisco Catalyst Express 500 series switch.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
EtherChannels
-
InterVLAN routing
-
SPAN
Configure the Cisco Catalyst 500 series switch with initial network settings as mentioned in the Initial Swicth Configuration section of this document.
You can see the data sheet for the Cisco Catalyst 500 series switches to learn about the different models and the supported features in Cisco Catalyst Express 500 Series Switches.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco Catalyst Express 500G-12TC that runs Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2(25)FY
-
Cisco 2800 Router that supports IEEE 802.1Q Trunk Encapsulation.
-
Cisco Catalyst 3750 switches that support 802.1Q Trunk Encapsulation.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Initial Switch Configuration
Complete these steps in order to perform initial setup of the switch. Refer to the Getting Started Guide for the Catalyst Express 500 Switches for more information on the configuration procedure.
-
Make sure that nothing is connected to the switch.
-
Power the switch.
-
Wait for the SETUP LED to blink green.
-
Click Setup. A switch port LED begins to blink green.
-
When a switch port LED blinks green, connect your PC to that port.
The LAN adapter of this PC must be configured to get the IP address via DHCP. The LEDs on the PC and the switchport blink green while the switch configures the connection (this takes around one minute).
-
Open a web browser. Complete these steps if the browser does not pull up the GUI automatically:
-
Issue the ipconfig command in order to view the dynamic address allocation.
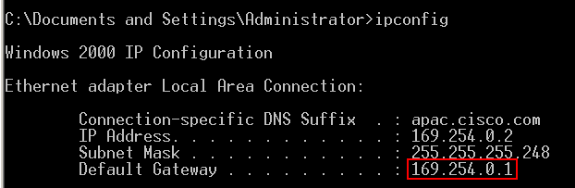
The switch configures its management address as the Default Gateway for the LAN adapter card of the PC.
Note: For Cisco IOS Software FY series releases, the management IP address is 10.0.0.1. For Cisco IOS Software SEG series releases, the IP address is 169.254.0.1.
-
From the browser, go to the mentioned IP address. For example, http://169.254.0.1.
-
-
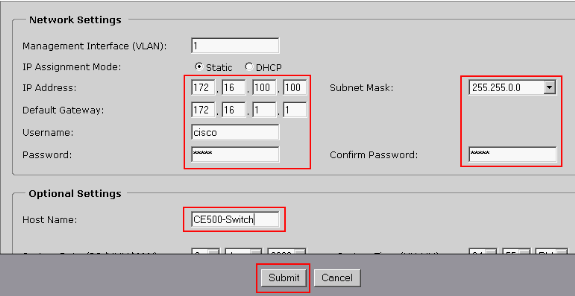
Enter the Network Settings and Optional Settings (if required). Click Submit in order to save changes and finish the basic configuration.
-
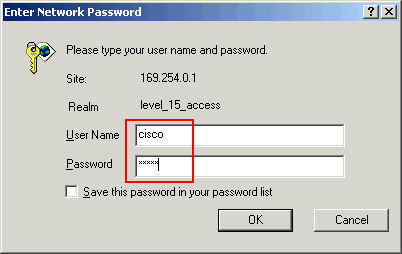
Enter the configured User Name and Password in order to continue the configuration of the switch.
-
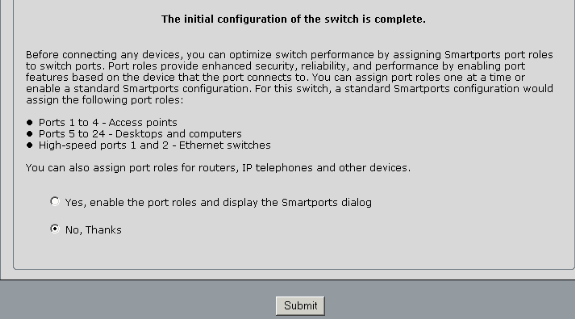
For the Smartports dialog window:
-
Click Yes and Submit in order to accept the predefined port roles. The Smartports window appears. Here you can change the predefined roles or apply new port roles.
-
Click No and Submit in order to apply the Smartports roles yourself.
-
-
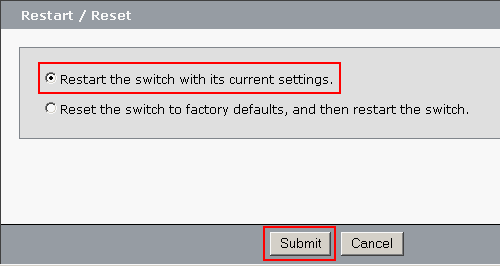
Restart the switch without turning off the power.
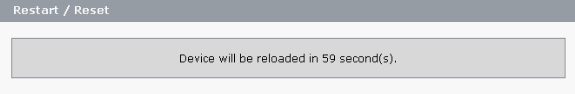
The switch automatically reloads in 60 seconds. A counter displays the time that remains for the reload.
-
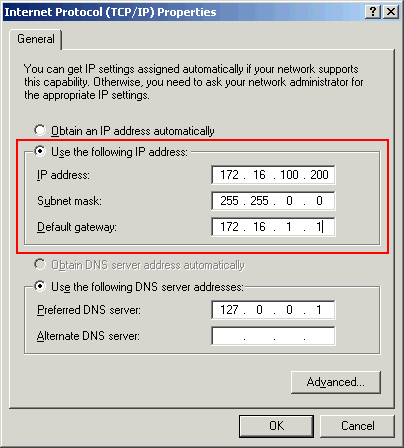
Close the web browser and reconfigure the LAN adapter with an IP address within the same subnet of the new management address of the switch.
-
When the switch comes up, open a web browser and go to http://<CE500_Management_IP_Address> . For example, http://172.16.100.100.
Note: Once the initial configuration is complete, the switch can be managed through any switchport that is configured for the same VLAN as that of the management IP address.
Smartports
Smartport Roles
The Smartports are preconfigured switch ports that provide preset Cisco recommended network enhancements, Quality of Service (QoS) and security. Catalyst Express 500 series switches have a number of Smartport roles. Each port role is just a configuration template. With these templates, users can consistently and reliably configure essential security, availably, and QoS features with minimal effort and expertise. Smartport roles simplify the configuration of critical features.
The port roles are based on the type of devices to be connected to the switch ports. For example, the Desktop port role is specifically for the switch ports that are connected to desktop or laptop PCs.
| Smartport Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Desktop | Apply this role to ports that are connected to desktop devices, such as desktop PCs, workstations, notebook PCs, and other client-based hosts.
|
| Switch | Apply this role to ports that are connected to other switches.
|
| Router | Apply this role to ports that are connected to WAN devices that connect to the Internet, such as routers and Layer 3 switches with routing service capabilities, firewalls, or VPN Concentrators.
|
| IP Phone+Desktop | Apply this role to ports that are connected to IP phones. A desktop device, such as a PC, can be connected to the IP phone. Both the IP phone and connected PC have access to the network and the Internet through the switch port. This role prioritizes voice traffic over data traffic to ensure clear voice reception on the IP phones.
|
| Access Point | Apply this role on switch ports that connect to non-Power over Ethernet (PoE) and PoE-capable wireless access points (APs). Connected to the AP are mobile devices, such as wireless laptop PCs.
Note: Functionality of Cisco Wireless Bridges are more similar to that of a switch. So, Cisco recommends the Switch smartport role for Wireless Bridges. |
| Server | Apply this role to ports that are connected to servers that provide network services, such as Exchange servers, collaborative servers, terminal servers, file servers, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers, IP private branch exchange (PBX) servers, and so on. This role is for Gigabit or non-Gigabit ports, based on the server type to be connected.
|
| Printer | Apply this role on switch ports that connect to a printer, such as a network printer or an external print server. This role prevents printer traffic from affecting voice and critical data traffic.
|
| Guest | Apply this role to ports that are connected to desktop devices and to APs to provide guest wireless access.
|
| Other | Apply this role on switch ports if you do not want to assign a specialized role on the port. This role can be used on connections to guest or visitor devices, printers, desktops, servers, and IP phones. It allows for flexible connectivity of non-specified devices.
|
| Diagnostic | Customers can connect diagnostics devices to monitor traffic on other switches (can be configured using Cisco Network Assistant only). |
Apply Smartport Roles to Ports
Use the Smartports window to apply port roles to the switch ports. Select Configure > Smartports from the device manager menu to display this window. You can also click Smartports  from the device manager tool bar.
from the device manager tool bar.
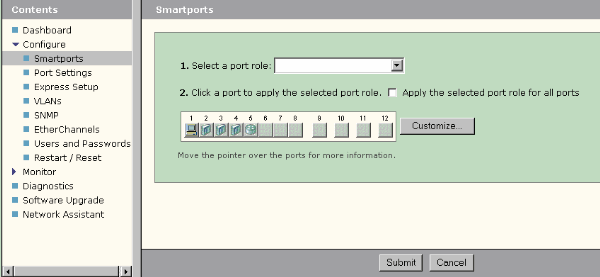
From the Smartports window, you can see which Smartports role is applied to each port. Move the pointer over a port to display its port number, Smartports role, and VLAN ID (VLAN membership).
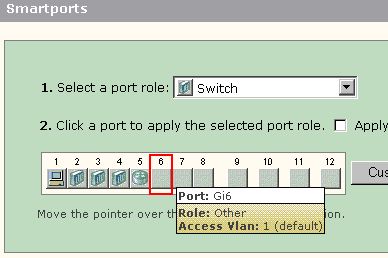
Before you use Smartports, decide which switch port you intent to connect to which device type. You can apply a Smartports role to a specific port or to all ports on the switch.
Restrictions
-
We recommend that you do not change specific port settings after you enable a Smartports role on a port. Any port setting changes can alter the effectiveness of the Smartports role.
-
Do not apply the Desktop role to ports that are connected to switches, routers, or APs.
-
The Smartport role Switch automatically enables 802.1Q trunking on the port. If a remote switch does not support 802.1Q trunking or the trunking is manually turned off, the spanning tree state of the port on the remote switch goes to blocking for type inconsistency. If the remote switch is the root bridge, the switch port does not go to blocking mode. In this case, the switch port trunk status is ON at both ends of the switches, but there is not any communication between the switches through these ports. There are no diagnostic messages displayed on the Catalyst Express 500 device.
Output from Remote Switch
%SPANTREE-7-RECV_1Q_NON_TRUNK: Received 802.1Q BPDU on non trunk GigabitEthernet2/0/1 VLAN2. %SPANTREE-7-BLOCK_PORT_TYPE: Blocking GigabitEthernet2/0/1 on VLAN0002. Inconsistent port type. %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan2, changed state to down Switch2#show spanning-tree vlan 2 VLAN0002 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 32770 Address 0012.01c7.7c80 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32770 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 2) Address 0012.01c7.7c80 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type ---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- -------------------------------- Gi2/0/1 Desg BKN*4 128.53 P2p *TYPE_Inc -
The Smartport role Router automatically enables 802.1Q trunking on the port. If the main interface of the remote router is used, make sure the interface of the router is part of the native VLAN of the switch port. The interface of the router can be sub-interfaced to provide interVLAN routing for the Cisco Catalyst Express 500 switch. See the Configure InterVLAN Routing with a Cisco Router section of this document for configuration details.
-
You should have an additional VLAN named Cisco-Voice (case sensitive) to apply the IP Phone+Desktop Smartport role to the ports.
-
You should have an additional VLAN named Cisco-Guest (case sensitive) to apply the Guest Smartport role to the ports.
-
Do not apply the Other role to the ports that are connected to a sniffer or intrusion detection system devices.
Apply a Smartports Role to a Single Port
Complete these steps to apply a Smartports role to a specific port:
-
Choose a Smartports role from the Select a port role list.
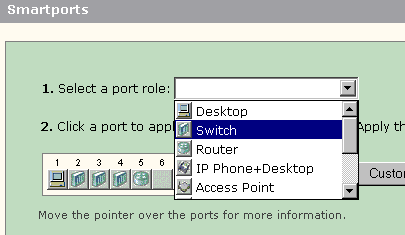
-
Click on the port. The icon for the selected Smartports role appears on the port.
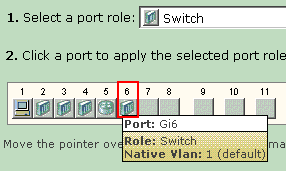
-
Click Submit to save your changes.
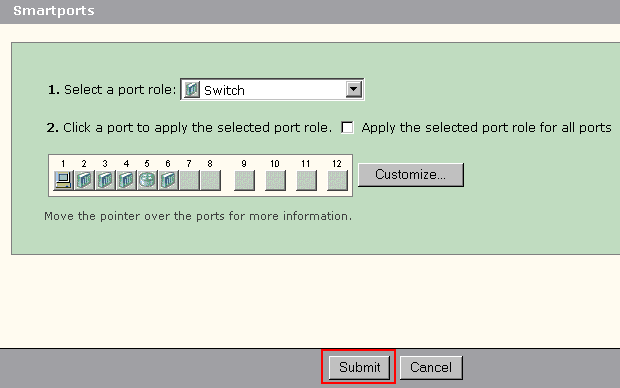
Complete these steps to remove the Smartports role applied to a port:
-
Choose Other from the Select a port role list.
-
Click on the port. The Other icon appears on the port.
-
Click Submit to save your changes.
Apply a Smartports Role to All Ports
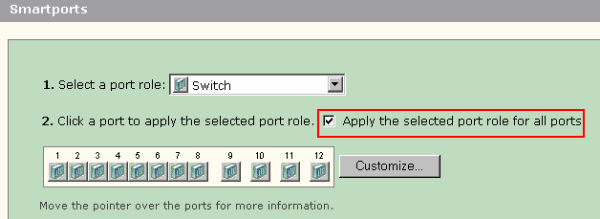
Complete these steps to apply the selected Smartports role to all ports:
-
Choose a Smartports role from the Select a port role list.
-
Check Apply the selected port role to all ports. The icon for the selected Smartports role appears on the ports.
-
Complete these steps for any port(s) that should not be applied with the selected port role:
-
Choose another Smartports role from the Select a port role list.
-
Click on the port. The icon for the selected Smartports role appears on the port.
-
-
Click Submit to save your changes.
Complete these steps to remove the Smartports role applied to all ports:
-
Choose Other from the Select a port role list.
-
Check Apply the selected port role for all ports. The Other icon appears on the ports.
-
Click Submit to save your changes.
Create / Delete VLANs
VLAN Types
The switch ships with a default VLAN to which all the switch ports initially belong. The switch supports a maximum of 32 VLANs, including the default VLAN. Using only the default VLAN might be sufficient based on the size and requirements of your network. We recommend that you first determine your VLAN needs before you create VLANs.
Note: Cisco Catalyst 500 series switches work in VTP Transparent mode. VLAN creation, modification, or deletion done on this switch does not affect the other switches in the domain.
This depends on the type of device that is connected to the switch port:
-
A switch port applied with one of these port roles can belong only to an access VLAN:
-
Desktop
-
IP Phone+Desktop
-
Printer
-
Server
-
Guest
-
Other
The access VLAN provides the attached device with the specific access designed for that VLAN.
-
-
A switch port applied with one of these port roles can send and receive traffic for all VLANs configured on the switch, one of which can be identified as a native VLAN:
-
Switch
-
Router
-
Access Point
On this port, any traffic that is received or sent without the VLAN explicitly identified is assumed to belong to the native VLAN. Both the switch port and the attached device port must be in the same native VLAN.
-
Note: Select Configure > Smartports > Customize on the Device Manager to see the Port roles and associated VLANs.
If your network requires that you segregate either or both voice and guest traffic, you need to create additional VLANs. If you create additional VLANs on the switch where you have IP Phone+Desktop and Voice Smartports, you must also create these VLANs:
-
Cisco-Guest—The VLAN to which all ports that are applied with the Guest port role must be assigned. This VLAN ensures that all guest and visitor traffic is segregated from the rest of your network traffic and resources. Ports with Guest Smartport roles should be assigned to this VLAN.
-
Cisco-Voice—The VLAN to which all ports that are applied with the IP Phone+Desktop port role must be assigned. This VLAN ensures that all voice traffic has better QoS and is not mixed with data traffic. The voice VLAN of ports with IP Phone+Desktop Smartport roles should be assigned to this VLAN.
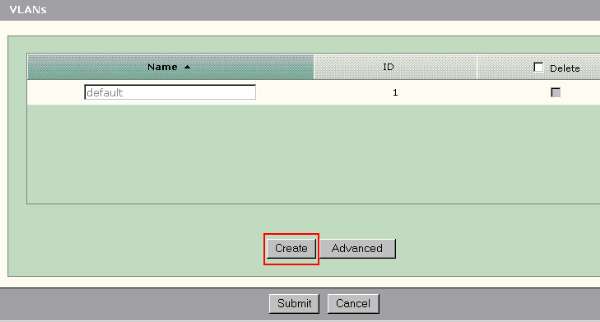
Use the VLANs window to create and delete VLANs. Select Configure > VLANs from the Device Manager menu to display this window.
-
Click Create on the VLANs window.
-
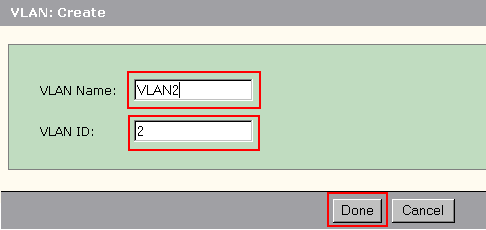
Enter the name and ID for the VLAN.
-
Click Done.
-
Repeat steps 1 through 3 until you create the necessary VLANs.
-
Click Submit to save the changes.
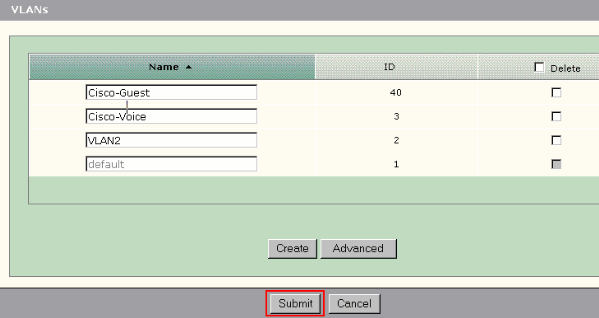
Note: If you have any ports with the IP Phone+Desktop role, you must create the Cisco-Voice VLAN. If you have any ports with the Guest port role, you must create the Cisco-Guest VLAN. If you create VLANs without Cisco-Voice and Cisco-Guest VLANs and you click Submit, this error message appears.
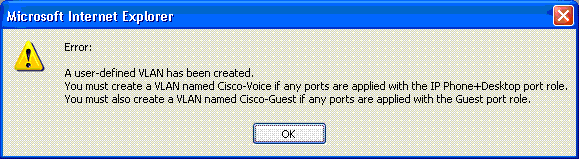
Complete these steps to create a VLAN:
Complete these steps to delete VLAN(s):
-
Check the check box at the top of the Delete column to select all VLANs or check the check box for one or more specific VLANs.
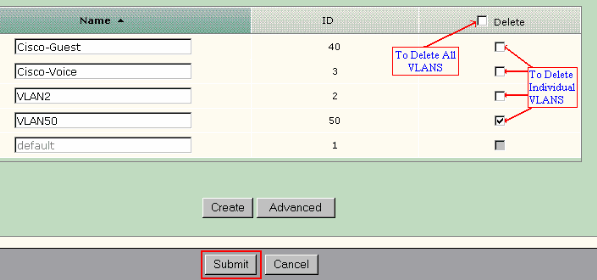
-
Click Submit to save your changes. Click OK in the Delete VLAN confirmation pop-up window.
Change VLAN Memberships
Specific VLAN memberships can be changed for the ports part of these Smartport roles:
-
Native VLAN—Switch, Router, and Access Point
-
Access VLAN—Desktop, IP Phone+Desktop, Server, Printer, Guest, and Other
Note: Access VLAN for the Guest role should be Cisco-Guest VLAN.
-
Voice VLAN—IP Phone+Desktop. Voice VLAN should be only the Cisco-Voice VLAN.
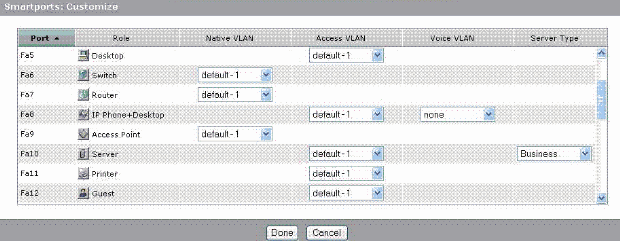
Use the Smartports Customize window to assign ports to VLANs. Select Configure > Smartports from the Device Manager menu to display this window.
-
Click Customize on the Smartports window.
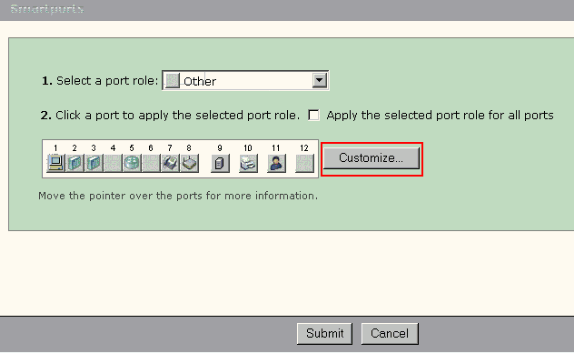
-
Choose appropriate VLAN(s) for each port.
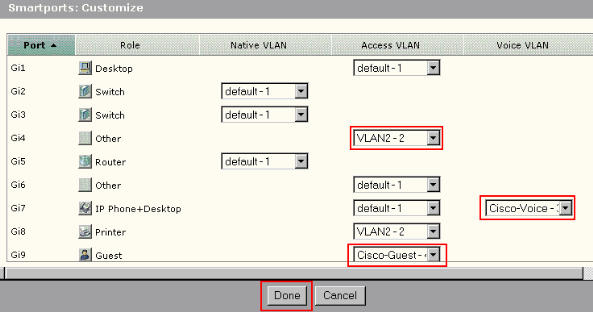
-
Click Done.
-
Click Submit to save your changes.
Configure EtherChannels
An EtherChannel is a group of two or more Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet switch ports bundled into a single logical link that create a higher bandwidth link between two switches. The switch supports up to six EtherChannels.
All ports in an EtherChannel must have the same characteristics:
-
All ports are either 10/100 ports or all 10/100/1000 ports. You cannot group a mix of 10/100 and 10/100/1000 ports in an EtherChannel.
-
All ports have the same speed and duplex mode settings.
-
All ports are applied with the Smartports Switch port role and belong to the same VLAN.
Complete these steps to create EtherChannels between a Cisco Catalyst Express 500 and another switch:
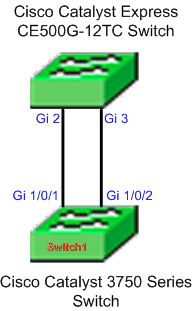
-
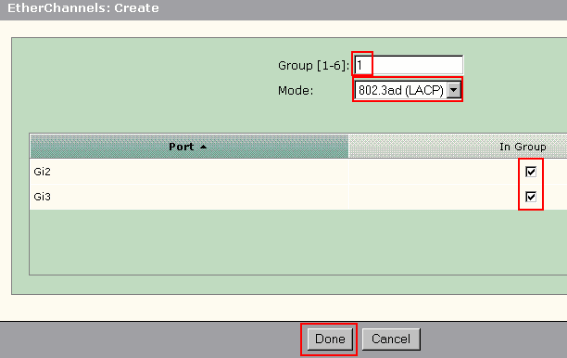
From the Device Manager of the Cisco Catalyst Express 500 switch, select Configure > EtherChannels to display the EtherChannels window.
-
Click Create.
-
Enter the Channel Group ID.
-
Choose the Channel Protocol (mode) for the Mode list.
Note: The Catalyst Express 500 switch supports two modes called LACP and Static. Configure the remote switch according to the mode you have chosen.
-
Click on the checkboxes against the ports which should be part of the channel.
-
Click Done and click Submit to save your changes.
-
If you have chosen LACP protocol to negotiate the channel, then configure the remote switch as this output shows:
Switch1(config)#interface gi1/0/1 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode active Switch1(config-if)#interface gi1/0/2 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode activeIf you choose to configure the channel statically, then configure the remote switch as this output shows:
Switch1(config)#interface gi1/0/1 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode on Switch1(config-if)#interface gi1/0/2 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode on
Verify
Open the Configure > EtherChannels window to verify the status of the EtherChannel created. The status should be displayed as 'In Use'. Otherwise, you can run diagnostics on the ports to determine the problem.
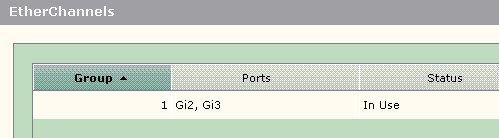
Issue the show etherchannel summary command in the Cisco 3750 switch to verify the status of the EtherChannel configuration. The Protocol field in the output displays LACP if it is used to negotiate the channel, blank or otherwise.
Switch#show etherchannel summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
u - unsuitable for bundling
w - waiting to be aggregated
d - default port
Number of channel-groups in use: 1
Number of aggregators: 1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+---------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) LACP Gi1/0/1(P) Gi1/0/2(P)
You can also see the Catalyst 500 switch log from Monitor > Alert Log on the Device Manager. This example shows the EtherChannel error message due to the EtherChannel misconfiguration on the remote switch.
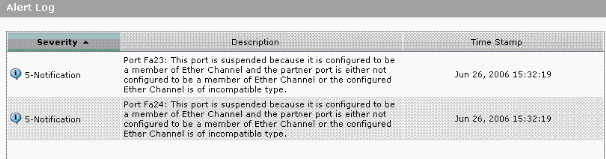
Configure InterVLAN Routing with a Cisco Router
Network Diagram
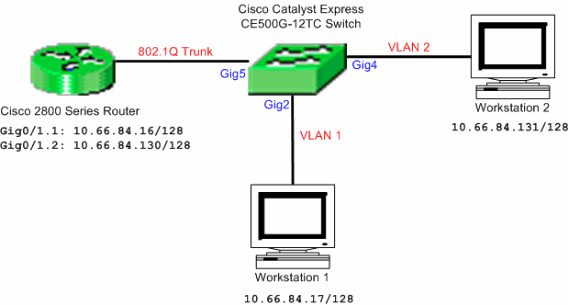
Note: The sample configuration makes use of the Cisco 2800 series router. This can be replaced with any Cisco router that supports IEEE 802.1Q trunking.
Complete these steps to configure interVLAN routing with a Cisco router:
-
Complete these steps to configure the Cisco Catalyst Express 500 switch:
-
Apply the Desktop Smartport role to ports Gig2 and Gig4. See the Apply Smartport Roles to Ports section of this document for the configuration procedure.
-
Apply the Router Smartport role to port Gig5.
-
Apply the appropriate VLAN IDs to the ports.
-
Assign VLAN 1 as the access VLAN for the port Gig2.
-
Assign VLAN 2 as the access VLAN for the port Gig4.
-
Assign VLAN 1 as the native VLAN for port Gig5.
See the Change VLAN Memberships section of this document for the configuration procedure.
-
-
-
Configure the Cisco 2800 series router:
Router(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/1.1 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q 1 native Router(config-subif)#ip address 10.66.84.16 255.255.255.128 Router(config-subif)#interface GigabitEthernet0/1.2 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q 2 Router(config-subif)#ip address 10.66.84.130 255.255.255.128
Verify
Select Monitor > Port Status on the Device Manager to see the switch port trunk status on the Catalyst Express 500 switch.
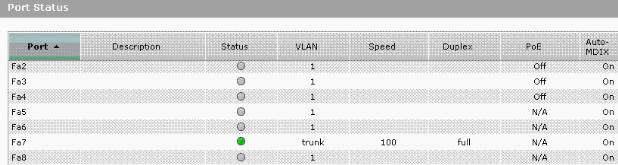
Verify if the ping from Workstation 1 to Workstation 2 passes.
C:\>ping 10.66.84.131
Pinging 10.66.84.131 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.66.84.131: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 10.66.84.131: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 10.66.84.131: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 10.66.84.131: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 10.66.84.131:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Run a trace to verify the path taken to communicate between Workstation 1 and Workstation 2.
C:\>tracert 10.66.84.131 Tracing route to 10.66.84.131 over a maximum of 30 hops 1 <10 ms <10 ms <10 ms 10.66.84.16 2 <10 ms <10 ms <10 ms 10.66.84.131 Trace complete.
Configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN)
The Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) feature, which is sometimes called port mirroring or port monitoring, selects network traffic for analysis by a network analyzer. The network analyzer can be a Cisco SwitchProbe device or other Remote Monitoring (RMON) probe. The switch supports only the Local SPAN and does not support Remote SPAN.
The destination port should be configured with the Diagnostics Smartport role. This can only be done using the Cisco Network Assistant software. Refer to SPAN on Catalyst Express 500 for configuring the Catalyst Express 500 switch to monitor traffic.
Reset the Catalyst Express 500 Switch to Factory Default Settings
If you have connectivity to the Device Manager of the switch and you want to reset the switch to factory default settings and retain the current Cisco IOS system software, refer to the Reset the Switch Using the Device Manager section of Reset the Catalyst Express 500 Series Switches to Default Factory Settings.
If you do not have connectivity to the Device Manager of the switch and you want to reset the switch to the factory default, refer to the Reset the Switch When the Device Manager Is Not Available section of Reset the Catalyst Express 500 Series Switches to Default Factory Settings.
Refer to the Recover the Switch Software section of User Guide for the Catalyst Express 500 Switches - Troubleshooting for more information on the recovery procedure.
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information
- Getting Started Guide for the Catalyst Express 500 Switches
- User Guide for the Catalyst Express 500 Switches
- Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches
- Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using an External Router
- Switches Product Support
- LAN Switching Technology Support
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-Jun-2008 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)



















 Feedback
Feedback