Determine how VM traffic is getting pinned
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides information and examples about Virtual Machine (VM) pinning both on the VMWare vSwitch/Distributed Switch and on the Cisco Nexus 1000v. It is important to understand which uplink a VM is using for communication, both for troubleshooting and design aspects.
Both the VMWare vSwitch/Distributed Switch and the Nexus 1000v support link aggregation with hashing as well as pinning to a particular port. Starting with vSphere 5.1, the vDS supports LACP as well as other methods, such as "Route Based IP Hash". The Cisco Nexus 1000v supports LACP and "Mode On" port-channels.
Hard VM pinning to an uplink is known as "Route Based on Virtual Port ID" on the vSwitch and "mac-pinning" on the Cisco Nexus 1000v. This document guides you through determining which uplink the VM is using for communication.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
VMWare ESX(i)
-
Cisco Nexus 1000v
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Commands
Use the vSwitch or vDS and run the esxtop command from the CLI of the VMWare ESX(i) host. Then, press n to get to the networking section:
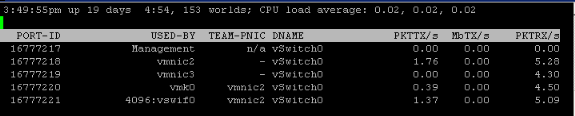
Based on this output you can see the Virtual Machine in the USED-BY column and the vmnic it is using in the TEAM-PNIC column. If a hashing algorithm was used you will see "All" in the TEAM-PNIC column.
If the Cisco Nexus 1000v is being used, the command is different. From the CLI of the ESX(i) host, run the vemcmd show port command. In a mac-pinning configuration, each vmnic is assigned a unique Sub-Group ID (SGID).
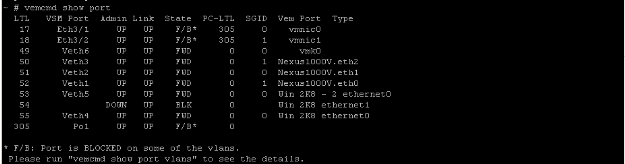
This output shows the SGID mapping for VM's to vmnic's. Matching up the SGID of the VM to the SGID of the vmnic will show you the vmnic the Virtual Machine is using for communication. If LACP or Manual Port channels are used, the SGIDs for everything will be unique.
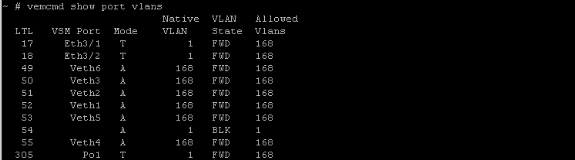
By running the vemcmd show port vlans command, vmnics and VMs will display the VLANs they are forwarding on. This is also useful when troubleshooting. The Allowed VLANs list displays the VLAN that is forwarding for that specific Local Target Logic (LTL). In order to figure out which LTL maps to which VM name, see the above output of the vemcmd show port command.
The following can be run from the VSM as well if the host CLI access is unavailable:
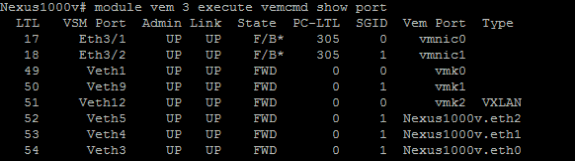
Alternatively, check the MAC address tables on the upstream switches for the VM's MAC address. This can also inform you of the port the switch is learning the MAC address on.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
15-Jan-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback