Q.A for CUCM PHONE CERTIFICATES (LSC/MIC)
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document covers some of the questions and answers for Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) Phone Certificates. Here is a quick view of the Phone Certificates.
Manufacturer Installed Certificate (MIC):
As the name indicates, phones are pre-installed with the MIC and this cannot be deleted / modified by the administrators. The Certificate Authority (CA) certificates CAP-RTP-001, CAP-RTP-002, Cisco_Manufacturing_CA and Cisco Manufacturing CA SHA2 are pre-installed in the CUCM to trust the MIC. MIC can’t be used once the validity is expired as the MIC CA cant be re generated,
Locally Significant Certificate (LSC):
The LSC possesses the public key for the Cisco IP phone, which is signed by the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) private key. It is not installed on the phone by default. Administrator have full control over LSC. CAPF CA Certificate can be regenerated in turn can issue new LSC to the phones whenever required.
What are the common uses for Phone Certificates?
Here are some common uses for the Phone Certificates
Between CAPF and Phone for Installing/upgrading, deleting, or troubleshooting
Phone establishes the connection with CAPF to Install/upgrade,delete, or troubleshoot certificate on the Phone. Phone Certficate is used to establish the connection with CAPF when Authentication Mode under Certification Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) Information set to By Existing Certificate (Precedence to LSC) or By Existing Certificate (Precedence to MIC).
By Existing Certificate (Precedence to LSC): Phone uses LSC to authenticate with CAPF. It will use MIC if LSC is not installed. Installation fails with reason "invalid LSC" if there are issues with the used certificate. Example, the signed CA for the LSC is not available in the CAPF Trust. Update the authentication mode using other certificate method or by null string for such failure cases.
By Existing Certificate (Precedence to MIC): Phone uses MIC to authenticate with CAPF.
Between CallManager and Phone for Trasnsport Layer Security (TLS) Connection
Phone uses LSC or MIC to establish TLS connection with CallManager. CallManager will Validate the Certficate presented by the Phone by checking CallManager-trust. Respective CAPF Certificate has to be available in CallManager-trust for LSC and Cisco Manufacture CA’s for MIC.
Between Phone and Authentication server for 802.1x Authentication
CAPF/Manufacturing CA certs are uploaded to Authentication servers like Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) or Identity Services Engine (ISE). Authentication server uses the uploaded certificates to authenticate the Phone when it present its certificate (LSC or MIC).
For Certificate based authentication between Phone and Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) for VPN
CAPF/Manufacture CA certs are uploaded in ASA, when phone present LIC/MIC, ASA validates it by checking it trust.
When LSC and MIC are present, is there any way to select LSC or MIC explicitly for connections?
No option to select whether LSC or MIC for the connections. If LSC is installed, Phone uses LSC. Phone uses the MIC if LSC is not installed .
Console entry when LSC is not present:
SECD: -PXY_NO_LSC: No LSC for [SCCP], will try MIC
Console entry when LSC is present:
SECD: -PXY_CERT_CIPHER: [SCCP], [TLSv1], cert [LSC]
Selection of LSC or MIC is possible only between CAPF and Phone installing/upgrading, deleting, or troubleshooting.
What is the reason the LSC installed phones with secured profile are not getting registered when moving to new cluster?
This can happen for the phones those already having an LSC from OLD Cluster. When both MIC and LSC are present, LSC is used to establish the TLS connection. TLS cannot be established since the new CUCM doesn’t have the CA for this LSC in its CallManager- trust.
Console logs shows which certificate is used to establish the TLS. Below entry shows LSC is used.
3469 NOT 00:01:31.935298 SECD: -PXY_CERT_CIPHER: [SCCP], [TLSv1], cert [LSC], cipher [AES256-SHA:AES128-SHA]
SSL3_Alert with “unknown CA” for such failed cases in console logs :-
3486 ERR 00:01:31.938954 SECD: -STATE_SSL3_ALERT: SSL3 alert [read]:[fatal]:[unknown CA
One of the ways to resolve this issue is, get the phone registered using non –secure profile then delete the existing LSC. Install the LSC from new cluster then register the phone using secured profile. It is also possible to have the phone with secured profile registered using MIC without installing the LSC.
Is it required to have the LSC installed for the Phones to get it registered using Authenticated or Encrypted secured profile?
No. If LSC is not installed, Phone uses MIC to establish the TLS connection to the CUCM.
4878 WRN 15:47:34.756063 SECD: -PXY_NO_LSC: No LSC for [SCCP], tries MIC.
Is it mandatory that device Security Mode in the respective device Security Profile to be Authenticated or Encrypted to install/Upgrade/Delete an LSC?
It is not mandatory, it can be done using default standard Non-Secure Profile too where in Device Security Mode is non secure.
Is it mandatory the Cluster to be in Mixed Mode to install the LSC in the Phone?
It is not mandatory. LSC install/Delete can be done even when cluster security mode in non-secure.
How to test quickly if there is an issue with the LSC used by the Phone?
Delete the LSC in one of the phone by going to the Phone Admin Page. This forces the Phone to use MIC. If all fine with MIC then proceed the troubleshooting with LSC.
How to get the Phone Certificates for Troubleshooting?
Set the Certificate Operation to Troubleshoot under the Device/Phone. Hit Save then Apply Config. Wait to see Certificate Operation Status to Troubleshoot Success. Collect Cisco Certificate Authority Proxy Function Logs from Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT). It contains the certificates from the Phone.
How to verify from packet captures, if LSC or MIC of the Phone is used to establish the TLS connection with CallManager?
Collect the Packet Captures covering the Phone restart.
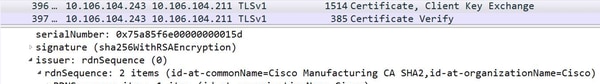
Check the Certificate, Client key Exchange Message. Verify the Certificate sent from IP Phone.
Example LSC:
For the LSC, CAPF CN is seen in the issuer field. Respective CAPF root has to be present in CallManager-trust.

Example MIC:
For the MIC, Cisco Manufacturing CA in the issuer field. Respective Root CA has to be present in CallManager-trust.
What is the significance of Authentication Mode under Certification Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) Information? Any significance for the TLS connection between CUCM and Phone?
It is nothing but an authentication method between Phone and CAPF for installing/upgrading/deleting and troubleshooting operations. It doesn’t have any significance for TLS connection between CUCM and Phone.
What are the basic LSC operations for the phones to consider after the CAPF Certificate regenerated?
This section covers the idle scenario where no offline CA is used to issue the LSC.
TLS Connection with CallManager
Ensure to install the new LSC on phone before deleting the previous CAPF Certificate from CallManager-trust. Deleting the previous CAPF Certificate followed by a restart of CallManager service cause the registration issues to the Phones those have the LSC issued by this CAPF Certificate.
LSC Operations with CAPF-Trust
Ensure to install the new LSC on phone before deleting the previous CAPF Certificate from CAPF-trust. LSC Operations like install/delete using authentication mode by Existing Certificate (Precedence to LSC) fails with error Invalid LSC for the Phones those have the LSC issued by this CAPF Certificate.
Between Phone and Authentication server for 802.1x Authentication
Ensure not to delete the previous CAPF certificate from Authentication server until the new CAPF certificate uploaded and Phone gets the LSC issued by new CAPF.
Between ASA and Phone
Ensure not to delete the previous CAPF certificate from ASA until the phone gets the new LSC and uploaded new CAPF CA certificate to ASA.
Refer to Certificate Regeneration for the steps to be followed to regenerate the CAPF Certificate.
Related information
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Jebin Joseph KalaritharaCisco TAC Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback