Regenerate Certificates In Unified Communications Manager
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the procedure to regenerate certificates in Unified Communications Manager.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT)
- Security Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- CUCM Certificates
- Certificate Authority Proxy Function
Components Used
Cisco Recommends that you have these tools installed:
- Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT)
- Information based on Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) releases 10.5, 12.0, 14.0, 15.0.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
This document describes the step-by-step procedure on how to regenerate certificates in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) release 8.X and newer. Reference the Security Guide for your specific release.
Communications Manager (CUCM) release 8.X – 11.5.X the ITL is signed by the Call Manager Certificate.
Communications Manager (CUCM) release 12.0+ the ITL is signed by the ITLRecovery Certificate.
ITL and CTL File Interaction
The Cisco IP Phone relies on the CTL file to know about the cluster security mode (non-secure or mixed mode). The CTL File tracks the cluster security mode by including the Unified Communications Manager certificate in the Unified Communications Manager record. The ITL File also contains the cluster security mode indication.
 ITL Signer Comparison
ITL Signer Comparison
Install Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT)
- Download and install RTMT Tool from Call Manager.
- Navigate to Call Manager (CM) Administration: Application > Plugins > Find > Cisco Unified Real-Time Monitoring Tool - Windows > Download. Install and launch.
Monitor Endpoints with RTMT
- Launch RTMT and enter the IP address or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), then username and password to access the tool:
- Select the Voice/Video Tab.
- Select Device Summary.
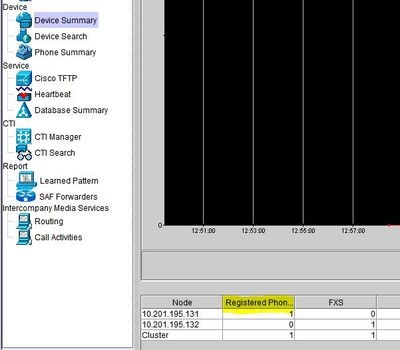
- This section identifies the total number of registered end-points and how many to each node.
- Monitor during endpoint reset to ensure registration prior to the regeneration of the next certificate.
Tip: The regeneration process of some certificates can impact endpoints. Consider an action plan after regular business hours due to the requirement to restart services and reboot phones. Verify phone registration via RTMT before, during, and after the process is highly recommended. You are only required to restart services if the services are running on the server.
Warning: Endpoints that currently have an ITL mismatch (Bad ITL) can have registration issues after this process. For devices with a bad ITL, the deletion of the ITL on the endpoint is a typical best practice solution after the regeneration process is completed, and all other phones have registered. Please review specific phone models on how to delete ITL/CTL (Security) certificates.
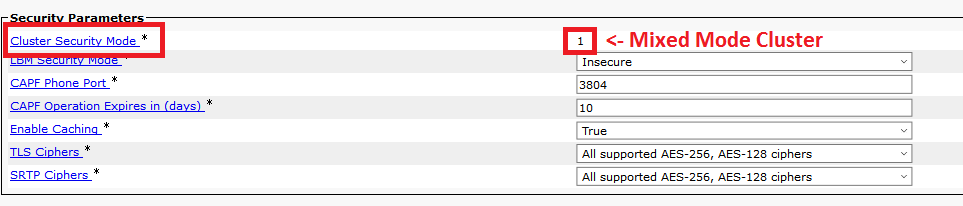
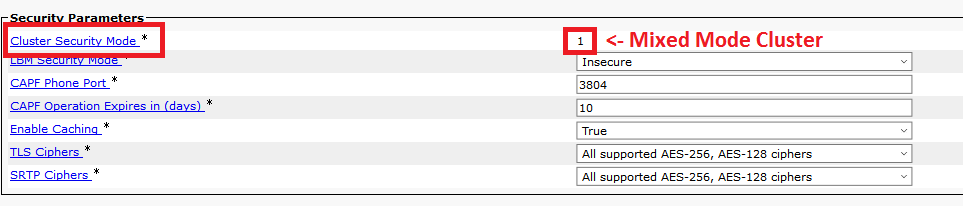
Identify Cluster Security Mode
- Navigate to CM Administration: System > Enterprise Parameters > Security Parameters > Cluster Security Mode.
ITL and CTL
- Initial Trust List (ITL) contains the certificate role for Call Manager TFTP, ITLRecovery, and all TVS certificates in the cluster. It also contains the Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) if the service is running. Beginning in version 12.0, the ITL is signed by the ITLRecovery certificate. You can see this by logging into CLI and entering the command show itl. Prior to version 12.0, the ITL was signed by the Call Manager certificate.
- CTL contains entries for System Administrator Security Token (SAST), Cisco CallManager and Cisco TFTP services that are run on the same server, CAPF, ITLRecovery, TFTP server(s), and Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) firewall. TVS is not referenced in CTL. The CTL is provided to endpoints if the service, Cisco CTL Provider, is running.
- As of CUCM 14SU(3), Cisco CTL Provider service no longer supports CTL Tokens, and Tokenless is the default supported method.
Impact by the Certificate Store
It is critical for successful system functionality to have all certificates updated across the CUCM cluster. If certificates are expired or invalid, they can significantly affect normal functionality of the system. The impact can differ dependent upon your system setup. A list of services for the specific certificates that are invalid or expired is shown here:
CallManager.pem
- Encrypted/authenticated phones do not register.
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is not trusted (phones do not accept signed configuration files and/or ITL files).
- Phone services can be affected.
- Secure Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunks or media resources (Conference bridges, Media Termination Point (MTP), Xcoders, and so on) do not register or work.
- The AXL request fails.
Tomcat.pem
- Phones are not able to access HTTPs services hosted on the CUCM node, such as Corporate Directory.
- CUCM can have various web issues, such as unable to access service pages from other nodes in the cluster.
- Extension Mobility (EM) or Extension Mobility Cross Cluster issues.
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Expressway Traversal Zone down (TLS Verify is enabled).
- If Unified Contact Center Express (UCCX) is integrated, due to security change from CCX 12.5, it is required to have uploaded CUCM Tomcat certificate (self-signed) or the Tomcat root and intermediate certificate (for CA signed) in UCCX tomcat-trust store since it effects Finesse desktop logins.
CAPF.pem
- This certificate is used to issue LSC to the endpoints (except online and offline CAPF mode), Phone VPN, 802.1x, and Phone Proxy.
- Beginning from Unified Communications Manager Release 11.5(1) SU1, all the LSC certificates issued by CAPF service are signed with SHA-256 algorithm.
- Authentication and Encryption setup for CTI, JTAPI, and TAPI.
IPSec.pem
- Disaster Recovery System (DRS)/Disaster Recovery Framework (DRF) is unable to function properly.
- IPsec tunnels to Gateway (GW) or to other CUCM clusters do not work.
Trust Verification Service (TVS)
Trust Verification Service (TVS) is the main component of Security by Default. TVS enables Cisco Unified IP Phones to authenticate application servers, such as EM services, directory, and MIDlet, when HTTPS is established.
TVS provides these features:
- Scalability - Cisco Unified IP Phone resources are not impacted by the number of certificates to trust.
- Flexibility - Addition or removal of trust certificates are automatically reflected in the system.
- Security by Default - Non-media and signal security features are part of the default installation and do not require user intervention.
ITLRecovery (Trust Verification Service)
- 8.X – 11.5 Recovery of phones with mismatched ITL, Phone migration and EMCC to CUCM 12.0+.
- 12.0+ Used in SSO, EMCC and primary signer of ITL/CTL.
- 12.5+ ITL Recovery is only generated by the Publisher.
Certificate Manager ECDSA Support
In Unified Communications Manager Release 11.0, the certificate manager supports both generation of self-signed ECDSA certificates and the ECDSA certificate signing request (CSR). Earlier releases of Unified Communications Manager supported RSA certificate only. However, Unified Communications Manager Release 11.0 onwards, CallManager-ECDSA certificate has been added along with the existing RSA certificate.
Both the CallManager and CallManager-ECDSA certificates share the common certificate trust store—CallManager-Trust. Unified Communications Manager uploads these certificates to this trust store.
Third-Party CA Signed Identity Certificate
Note: Third-party can mean internal Certificate Authority (CA) or external sources like Go-Daddy, Verisign, and others. Identity certificate is the server certificate for the specific roll (Tomcat, Call Manager, and so on).
- Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser unless you are creating Multi-SAN CSR) begin with the publisher, succeeded by each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management.
- Select Generate CSR.
- Select Certificate Purpose drop-down and select the certificate.
- Select Distribution type. Single Server or Multi-sever (SAN).
- Multi-server (SAN) includes all CUCM and CUPs nodes in the SANs section.
- Select Generate.
- Download the CSR and provide to your Certificate Authority.
- After receiving the signed certificate, upload the certificates by chain order.
- Upload the ROOT as a trust certificate.
- Upload the Intermediate as a trust certificate.
- Upload the Signed Certificate as the certificate type.
- Restart the appropriate services identified in the pop-up.
Certificate Regeneration Process
Note: All the endpoints need to be powered on and registered before the certificates regeneration. Otherwise, the not connected phones require the removal of the ITL.
Tomcat Certificate
The process of regenerating Tomcat and Tomcat-ECDSA are identical, including service restarts.
Identify if third party certificates are in use:
- Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser) begin with the publisher, proceeded by each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Observe from the Description column if Tomcat states Self-signed certificate generated by system. If Tomcat is third party signed, use the link provided and perform those steps after the Tomcat regeneration.
- Third-Party Signed certificates, refer to CUCM Uploading CCMAdmin Web GUI Certificates.
- Select Find to show all the certificates:
- Select the Find Tomcat Pem.
- Once open, select Regenerate and wait until you see the Success pop-up, then close pop-up or go back and select Find/List.
- Continue with each subsequent Subscriber, perform the same procedure in step 2 and complete on all Subscribers in your cluster.
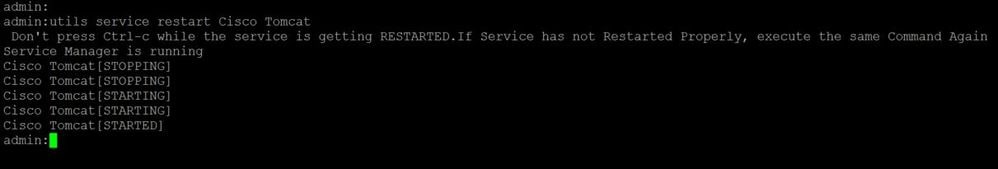
- After all Nodes have regenerated the Tomcat certificate, restart the tomcat service on all the nodes. Begin with the publisher, continue with the subscribers.
- In order to restart Tomcat, you need to open a CLI session for each node and execute the command utils service restart Cisco Tomcat.
5. These steps are used from the CCX environment, if applicable:
- If self-signed certificate is used, upload the Tomcat certificates from all nodes of the CUCM cluster to Unified CCX Tomcat trust store.
- If CA signed or private CA signed certificate is used, upload root CA certificate of CUCM to Unified CCX Tomcat trust store.
- Restart the servers as mentioned in the certificate regeneration document for CCX.
Additional References:
IPSEC Certificate
Note: CUCM/Instant Messaging and Presence (IM&P) before version10.X, the DRF Master Agent runs on both CUCM Publisher and IM&P Publisher. DRF Local service runs on the subscribers respectively. Versions 10.X and higher, DRF Master Agent runs on the CUCM Publisher only and DRF Local service on CUCM Subscribers and IM&P Publisher and Subscribers.
Note: The Disaster Recovery System uses an Secure Socket Layer (SSL) based communication between the Master Agent and the Local Agent for authentication and encryption of data between the CUCM cluster nodes. DRS makes use of the IPSec certificates for its Public/Private Key encryption. Be aware that if you delete the IPSEC truststore (hostname.pem) file from the Certificate Management page, then DRS does not work as expected. If you delete the IPSEC-trust file manually, then you must ensure that you upload the IPSEC certificate to the IPSEC trust-store. For more details, refer to the certificate management help page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Security Guides.
- Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser) and begin with the publisher, succeeded by each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Select the
IPSEC PEMCertificate. - Once open, select Regenerate and wait until you see the Success pop-up, then close pop-up or go back and select Find/List.
- Select the
- Continue with subsequent Subscribers; perform the same procedure in step 1 and complete on all subscribers in your cluster.
- After all Nodes have regenerated the IPSEC certificate then restart services.
- Navigate to the Publisher Cisco Unified Serviceability.
- Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Network Services
- Select Restart on Cisco DRF Master Service.
- Once the service restart completes, select Restart on the Cisco DRF Local Service on the publisher, then continue with the subscribers and select Restart on the Cisco DRF Local.
- Navigate to the Publisher Cisco Unified Serviceability.
The IPSEC.pem certificate in the publisher must be valid and must be present in all subscribers as IPSEC truststores. The subscriber's IPSEC.pem certificate is not present in the publisher as IPSEC-trust in a standard deployment. In order to verify the validity compare the serial numbers in the IPSEC.pem certificate from the PUB with the IPSEC-trust in the SUBs. They must match.
CAPF Certificate
Note: Beginning in CUCM 14, the CAPF certificate can only be found on the Publisher.
Warning: Ensure you have identified if your Cluster is in Mixed-Mode before you proceed. Refer to section Identify Cluster Security Mode.
- Navigate to the Cisco Unified CM Administration > System > Enterprise Parameters.
- Check the section Security Parameters and verify if the Cluster Security Mode is set to 0 or 1. If the value if 0, then the cluster is in Non-Secure Mode. If it is 1, then the cluster is in mixed-mode and you need to update the CTL file prior to the restart of services. See Token and Tokenless links.
- Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser) begin with the publisher, then each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Select the
CAPF PEMCertificate. - Once open, select Regenerate and wait until you see the Success pop-up then close pop-up or go back and select Find/List.
- Select the
- Continue with subsequent subscribers; perform the same procedure in step 2, and complete on all subscribers in your cluster.
- If cluster is in Mixed-Mode or the CTL is being used for 802.1X, you must update the CTL before you proceed further.
- Log into the CLI of the Publisher and enter the command utils ctl update CTLFile.
- Reset all encrypted and authenticated phones for the CTL file update to take affect.
- If cluster is in Mixed-Mode or the CTL is being used for 802.1X, you must update the CTL before you proceed further.
- After all Nodes have regenerated the CAPF certificate, restart services.
- Navigate to publisher Cisco Unified Serviceabillity.
- Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
- Select the publisher and select Restart on the Cisco Certificate Authority Proxy Function Service, only if active.
- Navigate to publisher Cisco Unified Serviceabillity.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Centr - Network Services.
- Begin with the publisher, then continue with the subscribers, select Restart on Cisco Trust Verification Service.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
- Begin with the publisher then continue with the subscribers, restart Cisco TFTP Service where status shows Started.
- Reboot all Phones:
- Option 1
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > System > Enterprise Parameters
- Select Reset, then you see a pop-up with the statement "You are about to reset all devices in the system. This action cannot be undone. Continue?",select OK, and then select Reset.
- This method resets ALL components in Call Manager.
- Option 2
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > Bulk Administration > Phones > Update Phones > Query
- Search for Device Name begins with SEP > Next > Reset Phones > Run Immediately.
The phones now reset. Monitor their actions via RTMT tool to ensure the reset was successful and that devices register back to CUCM. Wait for the phone registration to complete before you proceed to next certificate. This process of phones registration can take some time. Be advised, devices that had bad ITLs prior to regeneration process do not register back to the cluster until it is remove.
CallManager Certificate
The process of regenerating CallManager and CallManager-ECDSA are identical including service restarts.
Warning: Ensure you have identified if your Cluster is in Mixed-Mode before you proceed. Refer to section Identify Cluster Security Mode.
Warning: Do not regenerate CallManager.PEM and TVS.PEM certificates at the same time in versions 8.x-11.5, or if the ITL is signed by the Call Manager Certificate. This causes an unrecoverable mismatch to the installed ITL on endpoints which require the removal the ITL from ALL endpoints in the cluster, or restore from DRS to begin the certificate updates again.
- Navigate to the Cisco Unified CM Administration > System > Enterprise Parameters:
- Check the section Security Parameters and verify if the Cluster Security Mode is set to 0 or 1. If the value if 0, then the cluster is in Non-Secure Mode. If it is 1, then the cluster is in mixed-mode and you need to update the CTL file prior to the restart of services. See Token and Tokenless links.
- Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser) begin with the publisher, then each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Select the CallManager pem Certificate.
- Once open, select Regenerate and wait until you see the Success pop-up, then close pop-up or go back and select Find/List.
- Continue with subsequent subscribers; perform the same procedure in step 2, and complete on all subscribers in your cluster.
- If cluster is in Mixed-Mode, or the CTL is being used for 802.1X, you must update the CTL before you proceed further.
- Log into the CLI of the Publisher and enter the command utils ctl update CTLFile.
- Reset all encrypted and authenticated phones for the CTL file update to take affect.
- If cluster is in Mixed-Mode, or the CTL is being used for 802.1X, you must update the CTL before you proceed further.
- Log into Publisher Cisco Unified Serviceability:
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
- Begin with the publisher, then continue with the subscribers, only restart Cisco CallManager Service where status shows Started.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
- Begin with the Publisher, then continue with the subscribers, restart Cisco CTIManager Service where status shows Started.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Network Service.
- Begin with the Publisher, then continue with the subscribers, restart Cisco Trust Verification Service.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
- Begin with the Publisher, then continue with the subscribers, restart Cisco TFTP Service where status shows Started.
- Reboot all Phones:
- Option 1
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > System > Enterprise Parameters
- Select Reset, then you see a pop-up with the statement "You are about to reset all devices in the system. This action cannot be undone. Continue?",select OK, and then select Reset.
- This method resets ALL components in Call Manager.
- Option 2
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > Bulk Administration > Phones > Update Phones > Query
- Search for Device Name begins with SEP > Next > Reset Phones > Run Immediately
The phones now reset. Monitor their actions via RTMT tool to ensure the reset was successful and that devices register back to CUCM. Wait for the phone registration to complete before you proceed to next certificate. This process of phones registration can take some time. Be advised, devices that had bad ITLs prior to regeneration process do not register back to the cluster until ITL is remove.
TVS Certificate
Warning: Do not regenerate CallManager.PEM and TVS.PEM certificates at the same time in versions 8.x-11.5, or if the ITL is signed by the Call Manager Certificate. This causes an unrecoverable mismatch to the installed ITL on endpoints which require the removal the ITL from ALL endpoints in the cluster, or restore from DRS to begin the certificate updates again.
Note: TVS authenticates certificates on behalf of Call Manager. Regenerate this certificate last.
Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser) begin with the publisher, then each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Select the TVS pem Certificate.
- Once open, select Regenerate and wait until you see the Success pop-up then close pop-up or go back and select Find/List.
- Continue with subsequent subscribers; perform the same procedure in step 1 and complete on all subscribers in your cluster.
- After all Nodes have regenerated the TVS certificate, restart the services:
- Log into Publisher Cisco Unified Serviceabililty.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Network Services
- On the publisher select Restart on Cisco Trust Verification Service.
- Once the service restart completes, continue with the subscribers and restart the Cisco Trust Verification Service.
- Log into Publisher Cisco Unified Serviceabililty.
- After all Nodes have regenerated the TVS certificate, restart the services:
- Begin with the Publishe,r then continue with the subscribers, restart Cisco TFTP Service where status shows Started.
- Reboot all Phones:
- Option 1
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > System > Enterprise Parameters
- Select Reset, then you see a pop-up with the statement "You are about to reset all devices in the system. This action cannot be undone. Continue?",select OK, and then select Reset.
- This method resets ALL components in Call Manager.
- Option 2
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > Bulk Administration > Phones > Update Phones > Query
- Search for Device Name begins with SEP > Next > Reset Phones > Run Immediately.
The phones now reset. Monitor their actions via RTMT tool to ensure the reset was successful and that devices register back to CUCM. Wait for the phone registration to complete before you proceed to next certificate. This process of phones registration can take some time. Be advised, devices that had bad ITLs prior to regeneration process do not register back to the cluster until ITL is remove.
ITLRecovery Certificate
Note: The ITLRecovery Certificate is used when devices lose their trusted status. The certificate appears in both the ITL and CTL (when CTL provider is active, Cisco bug IDCSCwf85275).
Beginning in 12.5+, the ITLRecovery is a single certificate generated by the publisher and distributed to the subscribers.
If devices lose their trust status, you can use the command utils itl reset localkey for non-secure clusters and the command utils ctl reset localkey for mix-mode clusters. Read the security guide for your Call Manager version to become familiar with how the ITLRecovery certificate is used and the process required to recover trusted status.
If the cluster has been upgraded to a version that supports a key length of 2048, and the clusters server certificates have been regenerated to 2048, and the ITLRecovery has not been regenerated and is currently 1024 key length, the ITL recovery command fails and the ITLRecovery method is not used.
- Navigate to each server in your cluster (in separate tabs of your web browser) begin with the publisher, then each subscriber. Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Select the ITLRecovery pem Certificate.
- Once open, select Regenerate and wait until you see the Success pop-up then close pop-up or go back and select Find/List.
- After ITLRecovery has been regenerated the ITLRecovery certificate, services need to be restarted.
- If cluster is in Mixed-Mode or the CTL is being used for 802.1X, you must update the CTL before you proceed further.
- Log into the CLI of the Publisher and enter the command utils ctl update CTLFile.
- Reset all encrypted and authenticated phones for the CTL file update to take affect.
- Log into Publisher
Cisco Unified Serviceability.- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Network Services.
- On the publisher, select Restart on Cisco Trust Verification Service.
- Once the service restart completes, continue with the subscribers and restart the Cisco Trust Verification Service.
- If cluster is in Mixed-Mode or the CTL is being used for 802.1X, you must update the CTL before you proceed further.
- Begin with the Publisher, then continue with the subscribers, restart Cisco TFTP Service where status shows Started.
- Reboot all Phones:
- Option 1
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > System > Enterprise Parameters
- Select Reset, then you see a pop-up with the statement "You are about to reset all devices in the system. This action cannot be undone. Continue?",select OK, and then select Reset.
- This method resets ALL components in Call Manager.
- Option 2
- Cisco Unified CM Administration > Bulk Administration > Phones > Update Phones > Query
- Search for Device Name begins with SEP > Next > Reset Phones > Run Immediately.
Delete Expired Trust Certificates
Warning: Deleting a certificate can affect your system operations. It can also break a certificate chain if the certificate is part of an existing chain. Verify this relationship from the username and subject name of the relevant certificates in the Certificate List window.
Note: A trusted certificate is the only type of certificate that you can delete. You cannot delete a self-signed certificate that is generated by your system. Identify the trust certificates that need to be deleted, no longer required, or have expired. Do not delete the five base certificates which include the CallManager.pem, tomcat.pem, ipsec.pem, CAPF.pem and TVS.pem. Trust certificates can be deleted when appropriate. The next service that restarts is designed to clear information of legacy certificates within those services.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Control Center - Network Services.
- From the drop-down select the CUCM Publisher.
- For CUCM 11.5 and lower,
- Select Stop Certificate Change Notification. This requirement is not needed for CUCM version 12.0 and higher.
- Repeat for every Call Manager node in your cluster.
- If you have an IMP Server:
- From the drop-down menu select your IMP servers one at a time and Select Stop Platform Administration Web Services and Cisco Intercluster Sync Agent. This requirement is not needed for IMP version 12.0 and higher.
- From the drop-down select the CUCM Publisher.
- Navigate to Cisco Unified OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Find.
- Find the expired trust certificates. (For versions 10.X and higher you can filter by Expiration. For versions lower than 10.0, manually identify the certificates or use the RTMT alerts if received.)
- The same trust certificate can appear in multiple nodes. It must be deleted individually from each node.
- Select the trust certificate to be deleted (dependent on your version, you either get a pop-up or you navigated to the certificate on same page)
- Select Delete. (You get a pop-up that begins with "you are about to permanently delete this certificate".)
- Select OK.
- Repeat the process for every trust certificate to be deleted.
- Upon Completion, services need to be restarted that are directly related to the certificates deleted. You do not need to reboot phones in this section. Call Manager and CAPF be endpoint impacting.
- Tomcat-trust: restart Tomcat Service via command line (See Tomcat Section).
- CAPF-trust: restart Cisco Certificate Authority Proxy Function (see CAPF Section). Do not reboot endpoints.
- CallManager-trust: CallManager Service/CTIManager (See CallManager Section). Do not reboot endpoints.
- Impacts endpoints and causes restarts.
- IPSEC-trust: DRF
Master/DRF Local (See IPSEC Section). - TVS (Self-Signed) does not have trust certificates.
- Restart Services Previously Stopped in Step 1.
Verification
Verification procedure are not available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
Troubleshoot procedures are not available for this configuration.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
4.0 |
30-Oct-2024 |
Updated Machine Translation, Style Requirements, and Formatting. |
3.0 |
28-Sep-2022 |
Updated |
2.0 |
16-Sep-2022 |
Republished. |
1.0 |
03-Apr-2019 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Ken RyderTechnical Consulting Engineer
- Danny DuranProject Manager
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback