How to Change the IP Address of One or More Cisco ICM NT Servers
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document details the steps needed to change the IP addresses of one or more of these Cisco Intelligent Contact Management (ICM) Microsoft Windows NT servers:
-
Call Router
-
Logger
-
Peripheral Gateway (PG)
-
Administrative Workstation (AW)
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
On a server with more than one Ethernet card, you can see more than one adapter in the Adapter scroll bar under the IP Address tab as Figure 1 shows. On a Call Router, Logger, and duplexed PG server, the Adapter scroll bar contains multiple adapters.
These types of ICM servers are also known as redundant servers or duplexed servers because they provide redundancy. If one server goes offline, the redundant server activates. One adapter is the public adapter, and the other adapter is the private adapter.
All servers always have a public network adapter, and redundant ICM servers also contain a private network adapter.
The public adapter connects the server to the public network and supports communication with other ICM servers. Figure 1 shows the configuration items you need to consider for the public adapter. This adapter should be the top (first) item in the Adapter scroll bar. Change the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway fields on the public adapter as required.
Figure 1 – Microsoft TCP/IP Properties 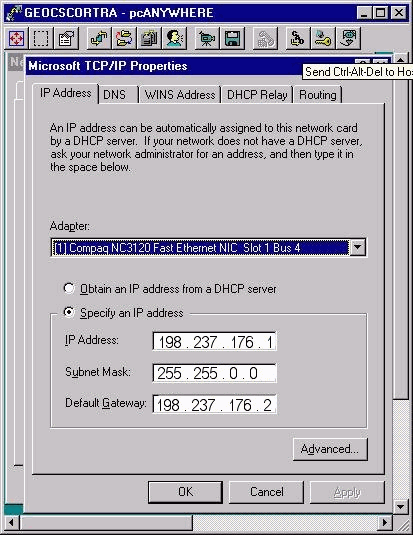
The second adapter, which is the private adapter, connects to the private network between the two redundant servers. It is used only by the redundant pair of servers for communication between them.
The private network does not have a default gateway address and should be the bottom (second) item in the Adapter scroll bar.
Figure 2 – Microsoft TCP/IP Properties: IP Address 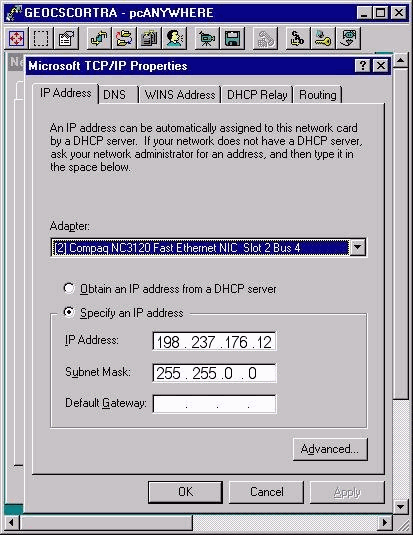
Private high IP addresses are on all duplexed ICM Routers and PGs. Click Advanced when a private high IP address is needed. The Advanced IP Addressing window opens as Figure 3 shows. You can add, edit, or remove as necessary.
A private high IP address may or may not be configured on all or some ICM servers. This depends on the ICM installation. Ninety-nine percent of the time, you do not ever need to change the private and private high IP addresses.
Figure 3 – Advanced IP Addressing 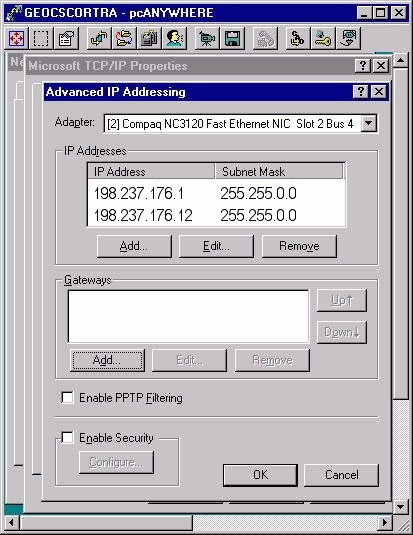
How Do I Change the IP Addresses on Cisco ICM Servers?
The changes required for the IP addresses on ICM Microsoft Windows NT server(s) are completed through the Microsoft Windows NT Network window, as Figure 4 shows.
Figure 4 – Network: Protocols 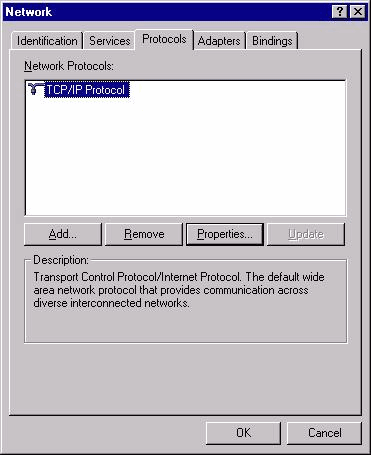
-
Select Start > Settings > Control Panel > Network from the Desktop.
-
Click Protocols.
-
Click TCP/IP Protocol.
-
Click Properties.
See Figure 4.
Modify Network Interface Card(s)
Complete these steps:
-
Refer to the previous steps to make the required IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway changes to the public network adapter.
-
Change the IP address and subnet mask on the private network adapter if required.
Modify Host Files
It is best to modify these files with the Microsoft Notepad text editor available on all Microsoft Windows NT servers. There might be shortcuts on the Desktop to the host and LMHost files. If not, you can open and edit the files with Notepad.
Complete these steps:
-
Use one of these methods to launch Notepad:
-
Open a command prompt and enter Notepad. Press Enter.
-
Select Start > Programs > Accessories > Notepad from the taskbar.
-
-
Select File > Open in Notepad.
-
Select All Files.
-
Locate c:\Winnt\System32\Drivers\Etc\hosts and click the file to Open.
-
Make the necessary modifications to all affected system IP addresses.
Note: You can see duplicate entries for the server name in the host file in servers with more than one network adapter. This is because of a bug in Microsoft Windows NT. One entry is the normal machine name and the other entry has the letter "v" at the end. You must change the IP addresses of both entries to the new value.
-
Select File > Save to save the file.
Note: Make sure that a .txt extension is not added to the file. The file name must remain as "hosts" with no extension.
Modify IMHost Files
Complete these steps to modify the LMHost files:
-
Select File > Open from Notepad.
-
Select All Files.
-
Locate c:\Winnt\System32\Drivers\Etc\lmhosts.
Click to highlight and then click Open.
-
Make the necessary modifications to all affected system IP addresses.
Note: In servers with more than one network adapter, you can see duplicate entries for the server name in the host file. This is because of a bug in Microsoft Windows NT. One entry is the normal machine name and the other entry has the letter "v" at the end. You must change the IP addresses of both entries to the new value.
-
Select File > Save to save the file.
Note: Make sure that a .txt extension is not added to the file. The file name must remain as "hosts" with no extension.
Verify Accuracy of sendall.bat on LoggerA
The batch file sendall.bat copies the host and IMHost files from Logger A to all servers on the ICM domain. There are two entries for each server on the ICM domain: one for the host file and one for the IMHost file. For example:
copy hosts \\geocscortra\c$\winnt\system32\drivers\etc copy lmhosts \\geocscortra\c$\winnt\system32\drivers\etc
-
Open sendall.bat in Notepad.
-
Complete these steps to verify that all required servers are listed:
-
Launch Notepad.
-
Select File > Open.
-
Select All Files.
-
Locate c:\Winnt\System32\Drivers\Etc\sendall. Click to highlight and then click Open.
-
Verify all servers are listed. Add or delete server entries as required.
-
Select File > Save to save the file.
Note: Make sure that a .txt extension is not added to the file. The file must retain a .bat extension.
-
Propagate New Host and LMHost Files to all ICM Servers from Logger A
Go to the c:\winnt\system32\drivers\etc directory from a command prompt on Logger A and enter sendall.bat. This action copies the new host and LMHost files to all servers on the ICM network.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2005 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback