Cisco Unity Express Installation and Upgrade Guide
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document explains the procedures to install or upgrade Cisco Unity Express (CUE) system software and the process for how to choose the most appropriate method in order to accomplish this result. The goal of this document is to explain the methods you use to load software on the Cisco Unity Express module—the boot helper installation method, the clean installation method, and the upgrade installation method.
A special section is also included to answer some frequently asked questions, such as license upgrades and integration types.
Prerequisites
Requirements
This document requires knowledge of Cisco Unity Express. In particular, knowledge on how to access the system via the command line interface (CLI) and a web page (GUI).
Components Used
The information in this document is based on Cisco Unity Express.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Software Installation and Upgrade Preparation
These preparation steps are required for when you prepare for a Cisco Unity Express upgrade or software installation:
-
Note the current Cisco Unity Express version and license.
Take note of the number of personal and group mailboxes as well as the integration type (CallManager Express or CallManager) and language.
-
Review the Cisco Unity Express software Release Notes for the release that you plan to install or upgrade to.
-
If you plan to restore an existing configuration, be sure to understand these backup/restore caveats:
-
The backup information you want to restore must be from a Cisco Unity Express system whose version is less than or equal to the version of the system you want to restore. For instance, do not attempt to restore a backup for a 2.1.3 system to a 2.0.1 system.
-
The backed-up system needs to have a license that is the same type (CallManager or CallManager Express) as the one you plan to restored.
-
The backed-up system needs to have a license with the same or less capacity as the system you plan to restore. Technically, there is no problem restoring to a system with a smaller license. However, the restore fails if the backup has more mailboxes or consumes more voicemail storage than the new system can support.
-
The backed-up system needs to have the same language as the system you plan to restore (see the Frequently Asked Questions section).
-
-
If you plan a new installation, always load the new license after you install the software.
-
Choose the appropriate software installation method (upgrade, clean, or boot helper methods).
-
Make sure that you have the required servers (FTP and possibly TFTP) available.
Based on the upgrade method (see Choose a Software Installation Method), a TFTP server might be required. The TFTP server must support file sizes greater than 16 MB (some older TFTP servers only support file sizes up to 16 MB).
The FTP server must support Passive FTP (PASV). Although any FTP server that meets these requirements is expected to operate correctly, there are a few specific products that Cisco has successfully used:
-
For the Microsoft Windows Operating system:
-
FileZilla FTP Server
-
GuildFTPd
-
Serv-U FTP server
-
Microsoft IIS FTP server
-
-
For the Linux Operating System:
-
ProFTPD Server
-
PureFTPd
-
WU-FTPD
-
Note: Cisco does not endorse or support any of these FTP server products. This is only a list of some of the software Cisco has used in the past that has proven successful. If the backup/restore or software load fails due to FTP errors and the account/password/access level privileges have been verified, try one of these servers to eliminate any possible incompatibility.
Ensure the FTP server (and possibly the TFTP server) is up and running. In the case of a PC, ensure the TFTP and FTP programs on the PC are activated. Use the Microsoft Windows TFTP client command-line tool to test the TFTP server. For example:
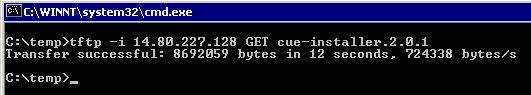
The FTP server can be tested similarly. In a browser that supports FTP (Internet Explorer, Firefox, and so forth), enter the URL that you plan to use along with the username and password. For example, ftp://user:password@14.80.227.128/2.2.1/. This means that you are attempting to access host 14.80.227.128 in the 2.2.1 directory using the username "user" with password "password". All the files necessary in the directory listing can be viewed and you can download each one. This does not test all aspects of the FTP process, but it tests for the most common problems.
Note: Although there might be more recent releases available, Cisco Unity Express 2.2.2 is the recommended release for installations at the time of publication. In particular, do not use 2.0.1, 2.1.1, 2.1.2, and earlier 1.x releases, especially for AIM-Cisco Unity Express deployments. Refer to the Cisco Unity Express Release Notes for the latest release documentation and caveats.
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is optional for initialization. If DNS is desired, install and activate a DNS server on the PC or server before you proceed.
Choose a Software Installation Method
Note: For all upgrade and installation methods for Cisco Unity Express software, a backup of the system is either recommended and in most cases required in order to preserve all the data and configuration information.
Based on a number of factors, there are three possible methods to upgrade or (re-)install Cisco Unity Express software:
-
Use the online installer with the "upgrade" option. In this document, this software installation method is referred to as the upgrade method.
-
Use the online installer with the "clean" option. In this document, this software installation method is referred to as the clean method.
-
Use the boot helper (installer) image from a TFTP server. In this document, this software installation method is referred to as the boot helper method.
Note: All installation methods require an FTP server for backup and software installation. The boot helper method additionally requires a TFTP server.
Each of these methods installs new software on the Cisco Unity Express module. The boot helper and clean methods both wipe the module out completely and then install the software fresh. The upgrade method applies the changes from one release to another without reinstalling everything. This is the reason why the software images required for the upgrade method are typically much smaller than a full install using the boot helper or clean methods. The upgrade method does not require that you restore the data and configuration after an upgrade.
Always note the existing Cisco Unity Express software version. In order to do this, issue the show software version command from the CLI. Then refer to the Cisco Unity Express Release Notes for the software version you plan to upgrade to, since any information contained in this documentation might have other caveats documented.
Several factors affect your choice of the correct method for the installation of Cisco Unity Express:
-
If the system is currently not able to boot for some reason (for example, the Cisco Unity Express command-line prompt is never presented) or the system currently runs a release prior to Cisco Unity Express 2.0.1, then the only option is to use the boot helper method. This option can be considered the last resort option since it is the only method that requires a TFTP server and the system is unavailable to callers during the entire upgrade process.
-
If the system runs Cisco Unity Express version 2.0.1 or later and you are able to access the Cisco Unity Express CLI, then the online installer methods are a better choice. The upgrade method is only available under specific circumstances. You can only use the upgrade method when you go from one specific release to another specific release, such as from 2.1.1 to 2.1.2 or from 2.1.2 to 2.1.3. Typically, it is not possible to use this method to go from one major release to another (such as from 2.1.3 to 2.2.1). Refer to the Cisco Unity Express Release Notes for specific release requirements. It does not support changing the language or integration method at the time of the upgrade. The benefit of the upgrade method is that it is the fastest method and does not require a restore at the end in order to reload all the configurations and data.
-
For any system that currently runs 2.0.1 or later and the upgrade method is not possible, then the online installer using the clean method is the next best choice. It can be used in situations where the language must be changed (for example, current system runs US English and the desired language is UK English), or between major releases. This method requires that you backup the system first and then restore after the installation.
Note: The boot helper method and the clean method can both be used to downgrade a Cisco Unity Express system. After the downgrade, you cannot restore the information backed-up in a later Cisco Unity Express release. If you downgrade the system to a release earlier than 2.0, the boot helper method is required.
Installation Procedures
Required Installation Files
Based on which method you choose to install your software, different files are required on the FTP (and TFTP server). This is a list of files for Cisco Unity Express 2.1.3. Other versions typically have the same naming convention but a different version number. The files must be placed on the FTP server, unless specified.
Table 1
| File Name | Description | Required for Installation Method (Clean, Upgrade, or Boot Helper) |
|---|---|---|
| cue-installer.2.1.3 | The installer for the boot helper method. | boot helper (on TFTP server) |
| cue-vm-installer.2.1.3.prt1 | The installer for online installer methods. | clean and upgrade methods |
| cue-vm.2.1.3.pkg | The main voicemail package file. | clean, upgrade, and boot helper methods |
| cue-vm-lang-pack.2.1.3.pkg | The language package file. | clean, upgrade, and boot helper methods |
| cue-vm-full.2.1.3.prt1 | The full payload of the voicemail package file. | clean and boot helper methods |
| cue-vm-en_US-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | The language prompt payload files. Only one of these is required. | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with US English language) |
| cue-vm-da_DK-lang-pack.21.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with Danish language) | |
| cue-vm-en_GB-lang-pack.21.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with British (UK) language) | |
| cue-vm-fr_FR-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with French language) | |
| cue-vm-de_DE-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with German language) | |
| cue-vm-pt_BR-lang-pack.21.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper (if you install with Portuguese [Brasilian] language) | |
| cue-vm-it_IT-lang-pack.21.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with Italian language) | |
| cue-vm-es_ES-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with Spanish [European] language) | |
| cue-vm-es_CO-lang-pack.21.3.prt1 | clean and boot helper methods (if you install with Spanish [Colombian] language) | |
| cue-vm-upgrade.2.1.2_2.1.3.prt1 | The main voicemail payload for the upgrade. | upgrade method |
| cue-vm-en_US-upg-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | The individual language prompt upgrade payload files. Only one of these is required. | upgrade method (if currently use US English) |
| cue-vm-fr_FR-upg-lang-pack.2.1.3 | upgrade method (if currently use French) | |
| cue-vm-de_DE-upg-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | upgrade method (if currently use German) | |
| cue-vm-es_ES-upg-lang-pack.2.1.3.prt1 | upgrade method (if currently use Spanish [European]) | |
| cue-vm-license_XXmbx_ccm_2.1.3.pkg | The XX Mailbox License for Cisco CallManager. | Only required for capacity increases or if the integration type is to change. |
| cue-vm-license_XXmbx_cme_2.1.3.pkg | XX Mailbox License for Cisco CallManager Express | Only required for capacity increases or if the integration type is to change. |
Note: The files required for the upgrade method might be different. If the language files between releases has not changed, for example (when you go from 2.1.3 to 2.2.2), then there is no language upgrade files (for example, there is no cue-vm-en_US-upg-lang-pack.2.2.2.prt1).
Perform a System Backup
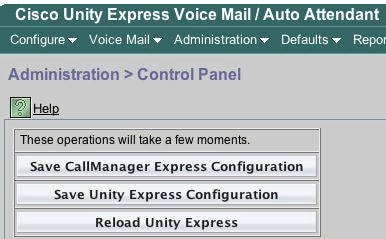
Regardless of the installation method, the first step is to always save the active configuration.
This can be done with the write memory CLI command or in the GUI when you select Administration > Control Panel and choose Save Unity Express Configuration. This graphic provides an example:
Back up the data.
For this, Cisco Unity Express must be offline. Therefore, if it is possible to route inbound calls to an operator or other user for the time being, this is a good idea since The Cisco Unity Express voicemail and auto attendant are not operational during the duration of the backup (or the software installation). No restore of any information is required for the upgrade method.
If you use the online installer (clean or upgrade methods) you can download the software to the card first, perform the backup, and then the installation. This reduces the amount of time the system is unavailable, especially when you must download the software across a slow wide area network (WAN).
Refer to the Cisco Unity Express documentation for proper backup instructions. It is possible to perform the backup via the GUI or the CLI. If not already configured, enter the backup server in advance and then save that as part of the configuration. For example:
cue-3745-44a>configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- This command is wrapped to a second line due to spatial reasons: cue-3745-44a(config)>backup server url ftp://172.18.106.11/back/ username user password mypass cue-3745-44a(config)>end cue-3745-44a> cue-3745-44a>write memory
Place the system offline and issue the backup category all command in order to perform the backup:
cue-3745-44a>offline !!!WARNING!!!: If you are going offline to do a backup, it is recommended that you save the current running configuration using the 'write' command, prior to going to the offline state. Are you sure you want to go offline[n]? : y cue-3745-44a(offline)>backup category all Backup progress: 2253549 bytes Backup Complete. Check Backup history for detailed in INFO: Backup Successful! cue-3745-44a(offline)>continue
The continue command brings the system online again. Between this point and the time at which the clean or boot helper install are done, no changes (new voicemails, and so forth) are saved. Therefore, keep this time to a minimum.
For GUI users, you can do the backup configuration when you select Administration > Backup/Restore > Configuration and then select Administration > Backup/Restore > Start Backup to start the backup. Make sure that Configuration and Data are both checked.
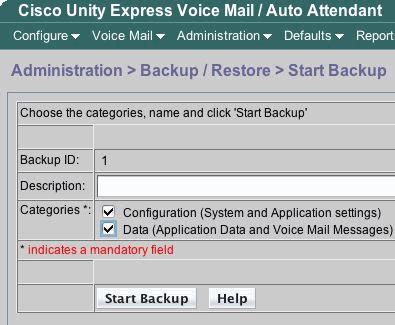
If the boot helper method is required, you can skip to the Boot Helper Installation Method section. Otherwise, continue with the Use the Online Installer section.
Use the Online Installer
The online installer is used for both the upgrade and clean installation methods. It allows you to download the software in the background before you install it. This means that for the entire time the image is downloaded, the Cisco Unity Express module still functions normally. Therefore, download the software, perform the system backup, and then begin the install using the files already downloaded in order to minimize downtime.
The online installer consists of a few commands which are useful to understand its operation.
In configuration mode, it is necessary to configure the download server and path (the place where the files are downloaded from). For example:
!--- This command is wrapped to a second line due to spatial reasons: cue-3745-44a(config)>software download server url ftp://10.1.1.4/2.2.1/ username user password mypass
All other commands are not in configuration mode, they are in command mode.
-
software download abort—Aborts the current file download.
-
software download clean <package name> —Downloads all the installation files for the clean method using the URL specified in the configuration.
-
software download clean url <url with package name> username <user> password <passwd> —Downloads all the installation files for the clean method using the URL specified on the command line.
-
software download status—Displays the status of the file download after you issue a software download clean or software download upgrade command.
-
software download upgrade <package name> —Downloads all the upgrade files for the upgrade method using the URL specified in the configuration.
-
software download upgrade url <url with package name> username <user> password <passwd> —Downloads all of the upgrade files for the upgrade method using the URL specified on the command line.
-
software install clean <package name> —Downloads and installs all files for the clean method using locally downloaded files.
-
software install clean url <url> username <user> password <passwd>—Downloads and installs all files for the clean method using the URL specified on the command line.
-
software install upgrade <package name> —Downloads and installs all files for the upgrade method using locally downloaded files.
-
software install upgrade url <url> username <user> password <passwd> —Downloads and installs all files for the upgrade method using the URL specified on the command line.
-
software install downgrade—Currently not supported for any release. Downgrades the system to the previous release. This is usable after a software install upgrade. Check Cisco Unity Express Release Notes for support information.
-
software remove all—Removes all downloaded files.
-
software remove downgradefiles—Removes all files that would be used for the downgrade process.
-
software remove downloadfiles—Removes all downloaded files previously downloaded using the software download command.
-
show software directory download—Displays the contents of the download directory.
-
show software directory downgrade—Displays the contents of the downgrade directory.
-
show software download server—Displays the download server as configured via the software download server command in configuration mode.
Clean Installation Method
Use the clean installation method any time a functioning Cisco Unity Express system of version 2.0 or later (show software version from the CLI) is upgraded to a release that does not support the upgrade method.
A typical installation consists of a sequence of these tasks:
-
Configure the FTP server and path of the software in the Cisco Unity Express configuration mode. For example:
cue-3745-44a>configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- This command is wrapped to a second line due to spatial reasons: cue-3745-44a(config)>software download server url ftp://10.1.1.4/2.2.1/ username george password mypass cue-3745-44a(config)>end
-
Initiate the software download. For example:
!--- This command is wrapped to a second line due to spatial reasons: cue-3745-44a>software download clean cue-vm.2.2.1.pkg username george password mypass
Note: For 512 MB AIM-Cisco Unity Express cards, the background download feature is not supported.
-
Confirm that you want to continue.
The main package, installer, and language pack (cue-vm.2.2.1.pkg, cue-vm-installer.2.2.1.prt1, and cue-vm-lang-pack.2.2.1.pkg in this case) are downloaded. The language menu is presented.
-
Pick the correct number in order to select the desired language.
The menu choice for a given language can vary from release to release. At the publication time of this document, only a single language is supported on the system at a time.
-
The language menu is presented again. Press x to finish language selection.
The payload files are now downloaded in the background.
-
Check the status of the software download (often done repeatedly until finished). Issue the software download status command. For example:
cue-3745-44a>software download status Download request in progress. downloading file : cue-vm-de_DE-lang-pack.2.2.1.prt1 bytes downloaded : 26424744When completed, the message Download request completed successfully displays. If there is a problem (FTP server becomes unreachable, and so forth), issue the software remove all command to remove all of the downloaded files before you restart the download.
-
Save the configuration (issue the write memory command), if desired.
-
Perform the Cisco Unity Express backup. See Perform a System Backup.
-
Start the install.
cue-3745-44a>software install clean cue-vm.2.2.1.pkg
-
Confirm that you want to continue.
Note: At this point the URL is checked again (as set in the software download server command). If for some reason a file that the installer requires is not found locally, the file is downloaded again from the FTP server. If the URL is not entered using the software download server command, then an error appears.
-
Select the language again from the language menu.
-
Press x to finish the language selection.
-
The system installs the files and reboots.
-
After the system startup, a message is presented which begins the post-installation steps. You always want to begin the installation and confirm it.
IMPORTANT:: Welcome to Cisco Systems Service Engine IMPORTANT:: post installation configuration tool. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: This is a one time process which will guide IMPORTANT:: you through initial setup of your Service Engine. IMPORTANT:: Once run, this process will have configured IMPORTANT:: the system for your location. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you do not wish to continue, the system will be halted IMPORTANT:: so it can be safely removed from the router. IMPORTANT:: Do you wish to start configuration now (y,n)? y Are you sure (y,n)? y -
The system detects the previous configuration.
This runs the configuration (show running-config) of the previously installed system. It does not include any voicemail greetings, messages, scripts, prompts, and so forth. If this is an upgrade, then restore the information. If it is meant to be a clean installation, then you usually do not restore the configuration.
IMPORTANT:: A Cisco Unity Express configuration has been found in flash. IMPORTANT:: You can choose to restore this configuration into the IMPORTANT:: current image. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: A stored configuration contains some of the data from a IMPORTANT:: previous installation, but not as much as a backup. For IMPORTANT:: example: voice messages, user passwords, user PINs, and IMPORTANT:: auto attendant scripts are included in a backup, but are IMPORTANT:: not saved with the configuration. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you are recovering from a disaster and do not have a IMPORTANT:: backup, you can restore the saved configuration. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you are going to restore a backup from a previous IMPORTANT:: installation, you should not restore the saved configuration. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you choose not to restore the saved configuration, it IMPORTANT:: will be erased from flash. IMPORTANT:: Would you like to restore the saved configuration? (y,n) y Are you sure (y,n)? y -
If the system is not restored in the previous step, then the system is at the point where you can follow the normal installation steps. The NTP server(s), DNS server(s) and time zone must be entered along with an administrator account for GUI access. If the saved configuration is restored, then all the settings are retrieved from the previous configuration.
-
The system now initializes all components completely. The system starts a count which can vary widely. On AIM-Cisco Unity Express cards this can be 15 minutes or longer. You are then prompted for the administrator account.
waiting 562 ... IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: Administrator Account Creation IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: Create an administrator account. With this account, IMPORTANT:: you can log in to the Cisco Unity Express GUI and IMPORTANT:: run the initialization wizard. IMPORTANT:: Enter administrator user ID: (user ID): administrator Enter password for administrator: (password): Confirm password for administrator by reentering it: (password):
-
The system is now upgraded. Follow the restore instructions within this document.
Upgrade Installation Method
The upgrade installation method is the best choice when you upgrade from one release to another, where supported. Always check the Cisco Unity Express Release Notes of the release that you plan to upgrade to and know the version that you plan to upgrade from. If it is not supported, then the clean installation method is the next best option.
A typical upgrade method consists of a sequence of these tasks:
-
Configure the FTP server and path of the software in Cisco Unity Express configuration mode.
cue-3745-44a>configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- This command is wrapped to a second line due to spatial reasons: cue-3745-44a(config)>software backup server url ftp://1.1.1.40/2.2.2/ user jdoe password mypass cue-3745-44a(config)>end
-
Initiate the software download.
cue-3745-44a>software download upgrade cue-vm.2.2.1.pkg WARNING:: This command will download the necessary software to WARNING:: complete an upgrade. It is recommended that a backup be done WARNING:: before installing software.
-
Confirm that you want to continue.
Would you like to continue? [n] y Validating package signature ... done Validating installed manifests ..........complete. Validating package signature ... done[17797 refs]
The main package, upgrade, and installer files (for example, cue-vm.2.2.1.pkg, cue-vm-upgrade.2.1.3_2.2.2.prt1, and cue-vm-installer.2.2.1.prt1) are downloaded.
-
Check the status of the software download (often done repeatedly until finished). Issue the software download status command.
cue-3745-44a>software download status Download request in progress. downloading file : cue-vm-upgrade.2.1.3_2.2.2.prt1 bytes downloaded : 21327592 cue-3745-44a>software download status Download request completed successfully.
When complete, the output of the software download status displays the Download request completed successfully message.
-
Issue the write memory command to save the configuration, if desired.
-
Perform the Cisco Unity Express backup. See Perform a System Backup.
-
Start the installation and confirm in order to begin the installation.
cue-3745-44a>software install upgrade cue-vm.2.2.2.pkg WARNING:: This command will install the necessary software to WARNING:: complete an upgrade. It is recommended that a backup be done WARNING:: before installing software. Would you like to continue? [n] y Validating package signature ... done Validating installed manifests ..........complete. Validating package signature ... done Validating payloads match registered checksums... - cue-vm-upgrade.2.1.3_2.2.2.prt1 ......................verified Calculating delta.... complete. Retrieving calculated file change sets: - Installed file sets...complete. - Target file change sets...complete. Comparing changed source and target files...complete. Calculating upgrade work order ... complete. Creating uninstall change sets: - backing up removed components ... complete. No added files found. - logging added components ... complete. No removed files found. Clearing previous downgrade files ... complete. Uninstall change set processing complete. Writing upgrade work order to disk ... complete. [20104 refs]
Note: If a file is not available locally then the system automatically attempts to download the missing file(s) from the FTP server, if configured. If the FTP server is unconfigured, then an error message displays.
The system shuts down, applies the upgrade, and then reboots again. When it finally comes back up, the upgrade is complete and the system functions again.
Boot Helper Installation Method
The boot helper method is a last resort installation method. It must be used when the system is corrupt and no longer boots successfully, or the software runs any version earlier than 2.0.
This method is described in detail in Unity Express Upgrade from 1.1 to 2.0 or 2.1 Releases.
Upgrade Procedures
The software upgrade of Cisco Unity Express Release 1.x involves three software loading activities:
-
Load and configure the boot loader.
-
Load the appropriate new license.
-
Load the Cisco Unity Express software.
Load and Configure the Boot Loader
Complete these steps
-
Place the cue-installer.2.0.1 (or the installer file for whichever Cisco Unity Express software release you plan to load) installation file in the TFTP server and the other files on the FTP server (see Table 1).
-
Establish a connection (via Telnet or directly via the console) to the Cisco IOS router that contains the Cisco Unity Express module. From there, issue the service-module service-engine <slot/0> session command to connect to the Cisco Unity Express module. For the Cisco Unity Express AIM, the slot number is 0. For example:
[user1-mac:~] root%telnet 14.80.227.140 Trying 14.80.227.140... Connected to 14.80.227.140. Escape character is '^]'. vnt-3660-41c>enable Password: vnt-3660-41c#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 14.80.227.140 YES NVRAM up up Service-Engine5/0 14.80.227.140 YES TFTP up up vnt-3660-41c#service-module service-Engine 5/0 session Trying 14.80.227.140, 2161 ... % Connection refused by remote host vnt-3660-41c#clear line 161 [confirm] [OK] vnt-3660-41c#service-module service-Engine 5/0 session Trying 14.80.227.140, 2161 ... cue-3660-41c>
-
Make sure you note the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway of the Cisco Unity Express. Obtain this from the CLI with the show interfaces and show ip route commands.
cue-3660-41c>show interfaces FastEthernet 1 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 14.80.227.141 mask 255.255.255.0 !--- Configured on the router. Broadcast address is 14.255.255.255 176 input, 18507 bytes 0 input errors 172 output, 16756 bytes 0 output errors IDE hd0 is up, line protocol is up 3385 reads, 39324672 bytes 0 read errors 2393 write, 23195648 bytes 0 write errors cue-3660-41c>show ip route DEST GATE MASK IFACE 14.80.227.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 eth1 127.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 lo 0.0.0.0 14.80.227.140 0.0.0.0 eth1
-
After the backup successfully completes, issue the reload command to reload the Cisco Unity Express NM.
-
When you are prompted to Please enter '***' to change boot configuration, enter ***.
This allows Cisco Unity Express to go into boot loader mode.
-
Enter config at the ServicesEngine boot loader> prompt.
-
Enter these details for the various prompts shown in the config output:
-
The Cisco Unity Express IP address
-
The Cisco Unity Express subnet mask
-
The TFTP server address
-
The Cisco Unity Express default gateway
The Ethernet interface is internal. Enter cue-installer.2.0.1 for the default helper image. Ensure that the default boot is always disk, the default boot loader is always primary, and the Ethernet interface is always set to internal.
ServicesEngine boot-loader>config IP Address [14.80.227.141] >14.80.227.141 Subnet mask [255.255.255.0] >255.255.255.0 TFTP server [14.80.227.128] >14.80.227.128 Gateway [14.80.227.140] >14.80.227.140 Default Helper-file [cue-installer.2.0.1] >cue-installer.2.0.1 Ethernet interface [internal] >internal Default Boot [disk] >disk Default bootloader [primary|secondary] [primary] >primary Updating flash with bootloader configuration
-
-
The system writes the information onto the Flash, and the ServicesEngine boot loader> prompt appears again.
Load New Cisco Unity Express Software from the Installer
Complete these steps:
-
Enter boot helper from the ServicesEngine boot loader> prompt.
Cisco Unity Express boots the helper image from the TFTP server.
The system now loads the installer package from the TFTP server and boots from it.
At the end of the boot process, this menu is presented:
Welcome to Cisco Systems Service Engine Helper Software Please select from the following 1 Install software 2 Reload module (Type '?' at any time for help)
-
Enter 1 to install the new software.
-
The package name, server URL, and FTP username/password are required followed by a confirmation:
Package name: cue-vm.2.0.1.pkg Server url: ftp://14.80.227.128/2.0.1 Username: jdoe Password: WARNING:: Software installation will clear disk contents Continue [n]? y Downloading cue-vm.2.0.1.pkg Bytes downloaded : 1448 Validating package signature ... done Downloading cue-vm-lang-pack.2.0.1.pkg Bytes downloaded : 147456 Validating package signature ... done
Note: In this example output, the system FTPs to 14.80.227.128, logs in as the user "jdoe" with the password specified, maneuvers to the 2.0.1 directory, and retrieves the file cue-vm.2.0.1.pkg. From this same directory, the file cue-vm-lang-pack.2.0.1.pkg is also retrieved. If this step fails for any reason, make sure that these files both exist in the path specified and that the specified FTP user has the correct permissions to download those files.
-
A language menu is presented. In this example, 4 (US English) is selected. Only one language is possible. After the language is selected (noted by the * next to it), press x to finish.
Language Selection Menu: # Selected SKU Language Name ----------------------------------------------------------------- 1 FRA CUE Voicemail European French (2.0.1) 2 ESP CUE Voicemail European Spanish (2.0.1) 3 DEU CUE Voicemail German (2.0.1) 4 ENG CUE Voicemail US English (2.0.1) Available commands are: # - enter the number for the language to select one r # - remove the language for given # i # - more information about the language for given # x - Done with language selection > 4 Language Selection Menu: # Selected SKU Language Name ----------------------------------------------------------------- 1 FRA CUE Voicemail European French (2.0.1) 2 ESP CUE Voicemail European Spanish (2.0.1) 3 DEU CUE Voicemail German (2.0.1) 4 * ENG CUE Voicemail US English (2.0.1) Available commands are: # - enter the number for the language to select one r # - remove the language for given # i # - more information about the language for given # x - Done with language selection > x
Note: From the same FTP directory and path, the files cue-vm-full.2.0.1.prt1 and cue-vm-en_US-lang-pack.2.0.1.prt1 are now downloaded. The cue-vm-en_US-lang-pack.2.0.1.prt1 file is only downloaded if US English is selected in this step. Other languages have different language packs.
-
The system finishes the installation, reboots (do not press the *** combination at this time), and the post installation script runs.
IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: Welcome to Cisco Systems Service Engine IMPORTANT:: post installation configuration tool. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: This is a one time process which will guide IMPORTANT:: you through initial setup of your Service Engine. IMPORTANT:: Once run, this process will have configured IMPORTANT:: the system for your location. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you do not wish to continue, the system will be halted IMPORTANT:: so it can be safely removed from the router. IMPORTANT:: Do you wish to start configuration now (y,n)? y Are you sure (y,n)? y
-
Choose whether or not to restore the existing configuration.
This is not an option if a configuration was never saved on the system. In most cases, when an upgrade is done, the goal is to have the configuration and data the same as it was before the upgrade. In this case, it is slightly faster to restore the saved configuration. This saved configuration is only the running configuration (visible from the show run command) on a system. It does not include any greetings, spoken names, messages, and so forth. Those still have to be restored. However, it does contain the DNS server, NTP server, and time zone information which otherwise needs to be entered manually.
IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: A Cisco Unity Express configuration has been found in flash. IMPORTANT:: You can choose to restore this configuration into the IMPORTANT:: current image. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: A stored configuration contains some of the data from a IMPORTANT:: previous installation, but not as much as a backup. For IMPORTANT:: example: voice messages, user passwords, user PINs, and IMPORTANT:: auto attendant scripts are included in a backup, but are IMPORTANT:: not saved with the configuration. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you are recovering from a disaster and do not have a IMPORTANT:: backup, you can restore the saved configuration. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you are going to restore a backup from a previous IMPORTANT:: installation, you should not restore the saved configuration. IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: If you choose not to restore the saved configuration, it IMPORTANT:: will be erased from flash. IMPORTANT:: Would you like to restore the saved configuration? (y,n) y Are you sure (y,n)? y
-
If "n" is selected in step 6, you are prompted for the DNS server, NTP server, and time zone. Once completed, the system finishes the post install by starting up all of its applications. This can take several minutes. At the end, the user is prompted to create an administrator user ID and password.
Configuring the system. Please wait... Changing owners and file permissions. Change owners and permissions complete. INIT: Switching to runlevel: 4 INIT: Sending processes the TERM signal STARTED: cli_server.sh STARTED: ntp_startup.sh STARTED: LDAP_startup.sh STARTED: superthread_startup.sh STARTED: SQL_startup.sh STARTED: HTTP_startup.sh STARTED: ${ROOT}/usr/wfavvid/run STARTED: probe STARTED: dwnldr_startup.sh waiting 160 ... IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: Administrator Account Creation IMPORTANT:: IMPORTANT:: Create an administrator account. With this account, IMPORTANT:: you can log in to the Cisco Unity Express GUI and IMPORTANT:: run the initialization wizard. IMPORTANT:: Enter administrator user ID: (user ID): administrator Enter password for administrator: (password): Confirm password for administrator by reentering it: (password): cue-3660-41c> -
Important: For systems that are integrated with Cisco CallManager, the system now attempts to register with the Cisco CallManager.
With Cisco Unity Express 2.0 and later, if during the registration process Cisco Unity Express detects a JTAPI version other than what it is currently running, it installs compatible JTAPI libraries and reboots. For example, Cisco Unity Express Release 2.1 ships with JTAPI libraries compatible with Cisco CallManager 4.1. The first time a Cisco Unity Express 2.1 system registers with a Cisco CallManager other than the 4.1 that it supports (such as 4.0 or 3.3), it loads the new libraries and reboots automatically. If the Cisco CallManager is upgraded from one version to the other, the same thing happens. This is normal. Review the release notes to ensure proper Cisco Unity Express and Cisco CallManager compatibility. Cisco Unity Express 2.0 (for example) does not support Cisco CallManager 4.1. Therefore, it does not work.
-
Enter the show software versions command to verify the system software.
cue-3660-41c>show software versions Installed Packages: - Bootloader (Primary) 1.0.17 - Global 2.0.1 - Voice Mail 2.0.1 - Bootloader (Secondary) 2.0.1 - Core 2.0.1 - Installer 2.0.1 - Auto Attendant 2.0.1 Installed Languages: - US English 2.0.1
Note: You do not have to be concerned about the difference in the primary and secondary boot loader versions. This is normal.
-
Verify the software license applied. Specifically, the integration type (Cisco CallManager Express or Cisco CallManager) and the number of ports and mailboxes.
cue-3660-41c>show software licenses Core: - application mode: CCME - total usable system ports: 4 Voicemail/Auto Attendant: - max system mailbox capacity time: 6000 - max general delivery mailboxes: 5 - max personal mailboxes: 12 Languages: - max installed languages: 1 - max enabled languages: 1 cue-3660-41c>
-
If desired, perform a system restoration.
Restore the System
You can use either the GUI or CLI to restore the system. The Cisco Unity Express documentation discusses this topic in further detail. This particular section illustrates an example for using the CLI. There are a few considerations in preparing for a restore:
-
The backup information you want to restore must be from a Cisco Unity Express system whose version is less than or equal to the version of the system you want to restore. For example, do not attempt to restore a backup for a 2.1.3 system to a 2.0.1 system.
-
The backed up system should have a license that is the same type (CallManager or CallManager Express) as the one you plan to restore.
-
The backed up system should have a license with the same or less capacity as the system you plan to restore. Technically, there is no problem restoring to a system with a smaller license. However, the restore fails if the backup has more mailboxes or consumes more voicemail storage than the new system can support.
-
The backed up system should have the same language as the system you plan to restore. See the Frequently Asked Questions section for more information.
Complete these steps to restore the system:
-
Take the system offline.
If you did not restore the previous configuration (or something changed) then you possibly need to change the backup server information. After the restore, the Cisco Unity Express must be rebooted to load the restored configuration. For example:
cue-3660-41c>offline !!!WARNING!!!: Putting the system offline will terminate all active calls. Do you wish to continue[n]? : y cue-3660-41c(offline)> restore id 1 category all Restore progress: 417227 bytes Restore Complete. Check Restore history for detailed information. cue-3660-41c(offline)>show backup history #Start Operation Category: Configuration Backup Server: ftp://172.18.106.10/cue/41c Operation: Restore Backupid: 1 Restoreid: 1 Date: Mon Jan 10 15:01:02 EST 2005 Result: Success Reason: #End Operation #Start Operation Category: Data Backup Server: ftp://172.18.106.10/cue/41c Operation: Restore Backupid: 1 Restoreid: 1 Date: Mon Jan 10 15:01:04 EST 2005 Result: Success Reason: #End Operation
-
Reboot Cisco Unity Express after the restore in order to load the restored configuration.
cue-3660-41c(offline)>reload cue-3660-41c(offline)> MONITOR SHUTDOWN...
Note: The actual restore ID (1 in this example) is specific to your backup set. Examine the history.log file to get the most recent ID.
Refer to Perform Backup and Restore of Cisco Unity Express with Microsoft FTP Server for more information about backup and restore. You can also refer to the backup and restore guides in the regular documentation, such as Backing Up and Restoring Data.
-
Point your web browser to http://<ip address of the CUE>/ in order to log into the Cisco Unity Express web page. Log in with the administrator account.
If a restore was previously done, you do not need to change any information. However, it asks you to re-run the Initialization Wizard. At the end of the wizard, you are logged out.
Frequently Asked Questions
I have a working system and I want to change the language (while saving all the data on the system). Which procedure do I need to follow?
Officially, this process was not considered. However it can be done with a certain amount of planning in advance. The problem is that all users, audio prompts, triggers, as well as some custom script steps might have a language defined other than the system default (the one that is loaded). If those items are not handled properly, there is no audio after you log into voicemail and other issues can result.
First, from the CLI, issue the show users command to get a list of users. Then issue the show user detail username userid command in order to go through each one. For the language, make sure systemDefault is specified. In most versions, you can also issue the command show sysdb /sw/local/users | inc preferredLanguage. This outputs a list of all users with their language. If the field is blank, then it uses the systemDefault language. For example:
cue-3745-44a>show sysdb /sw/local/users | include preferredLanguage Administrator/Language/preferredLanguage ckent/Language/preferredLanguage gpburdell/Language/preferredLanguage en_US
In this example output, userid gpburdell has the en_US language configured (ckent and Administrator do not have a language specified and therefore use the systemDefault language). This means that if the system is changed to anything other than US English (en_US), then this user does not work properly. For example, when this user logs into voicemail, after they authenticate, there is no more audio. In order to correct this, each user who has a set language should have it removed. For this example output you configure no user gpburdell language en_US.
Note: This is done from the command mode, not configuration mode of the CLI.
Next, issue the show ccn prompts command to get a list of all audio prompts. Each of those must be backed up manually. You can either log in via the GUI and download each one individually, or use the ccn copy prompt myprompt.wav url ftp://1.2.3.4/myprompt.wav username userid password mypass command to copy each file to an FTP server. If this step is not done, the prompts disappear and cannot be restored via the regular restore procedure. When the system is re-initialized with the new language, the prompts can be uploaded via the GUI or via the CLI again.
Make sure all triggers have the systemDefault locale. Issue the show ccn trigger command from the CLI. If one is set for anything other than systemDefault, enter configuration mode and remove that locale from the trigger.
Finally, if there is a custom auto attendant in use, each step should be examined for any possible language dependencies. Most steps do not have this. However, some steps such as those that generate prompts, allow the language to be specified. This is not very common. But since Cisco Unity Express currently does not support more than one language on the system, any custom scripts should be backed up separately. Similar to how the prompts were downloaded via the GUI, the scripts can be downloaded from the Voicemail > Scripts menu in the GUI. These need to be uploaded from this same place after you change the language.
Once these steps have been completed, you can perform a regular installation using the clean method or the boot helper method. Then proceed with the restore and re-upload all prompt and script files.
If you have already performed a backup, loaded new software (with a different language), and have restored the old configuration and data, then check to see if any users have a language configured other than the systemDefault. Issue either the show users detail command or the show sysdb /sw/local/users | inc preferredLanguage command in order to accomplish this. Any users that have a language configured that does not match the installed language must be changed. All custom scripts and prompts have been removed. Those all have to be manually uploaded to the system and configured.
Next, test the auto attendants and a few voicemail boxes. Make sure that you can hear the system greeting ("you have no new messages", and so forth) when you log into a voicemail mailbox. The auto attendants should also be checked to make sure all prompts have been uploaded properly.
I need to install a new license file for upgraded capacity. Which procedure should I use?
With the assumption that you run Cisco Unity Express version 2.0 or later, you need to use the clean install method. Remember to get a backup before you make this change. Follow the clean installation instructions with the exception that you will issue the software install clean <licensefilename> command (not the Cisco Unity Express voicemail package name). The license file needs to be of the same type (CallManager or CallManager Express) and must be from the same Cisco Unity Express version which currently runs. The show software version command verifies this. It also needs to be no smaller than the one currently installed. The show software license command verifies this. You are asked to confirm what you are about to do, then install the file. When completed, issue the reload command so the system can boot with the new license. When finished, issue a show software license command to verify the change. You might also need to reconfigure the mailbox defaults to account for the additional number of mailbox support. For example, if you initially installed the system with a 12-user license, then the default voicemail mailbox size becomes very large. (The system takes the amount of voicemail storage and divides by the maximum number of group and personal mailboxes to calculate the default mailbox size). If the system is upgraded to support additional mailboxes but the amount of voicemail storage remains the same, then the system does not allow you add anymore mailboxes once the total voicemail limit is reached. (When a new mailbox is created, the default storage amount is carved out from this maximum mailbox storage space at the time of creation). Therefore, typically existing mailboxes might need to be reduced and/or the default mailbox size (used for new mailboxes) changed. The show voicemail limits, show voicemail usage, and show voicemail mailboxes commands are useful for making these decisions.
I need to change the license type from a CallManager/CallManager Express to a CallManager Express/CallManager license and save all the data. How can I do this?
Officially, this is currently not supported.
When trying to upgrade CUE, this error message is received: "ERROR: Upgrade of subsystem [Global manifest] from [2.3.3] to [2.3.4] not allowed." How do I troubleshoot this issue?
If you receive this error when using the UPGRADE method, it is recommended to use the Clean Installation Method method to avoid this error.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback