Configuring Class of Restrictions (COR)
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
This document was migrated to the Self-Publishing Workflow. It was originally published to https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/voice/call-routing-dial-plans/42720-configuring-cor.html.
This document should be updated to meet current guidelines and this note should be removed before publishing. When you publish this document to preview, ensure that the Document ID is 42720 and the URL matches the original URL located in this paragraph. If the Document ID or URL doesn't match, contact tz-writers@cisco.com.
Introduction
This document describes how to configure Classes of Restriction (CORs).
A COR is a Cisco voice gateway feature that enables Class of Service (COS) or calling privileges to be assigned. It is most commonly used with Cisco Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) and Cisco CallManager Express but can be applied to any dial peer.
The COR feature provides the ability to deny certain call attempts based on the incoming and outgoing CORs provisioned on the dial-peers. COR is required only when you want to restrict the ability of some phones to make certain types of calls but allow other phones to place those calls.
COR is used to specify which incoming dial-peer can use which outgoing dial-peer to make a call. Each dial-peer can be provisioned with an incoming and an outgoing COR list. The corlist command sets the dial-peer COR parameter for dial-peers and the directory numbers that are created for Cisco IP phones associated with the Cisco CallManager Express router. COR functionality provides the ability to deny certain call attempts on the basis of the incoming and outgoing CORs that are provisioned on the dial-peers. This functionality provides flexibility in network design, allows users to block calls (for example, calls to 900 numbers), and applies different restrictions to call attempts from different originators.
If the COR applied on an incoming dial-peer (for incoming calls) is a super set or equal to the COR applied to the outgoing dial-peer (for outgoing calls), the call goes through. Incoming and outgoing are terms used with respect to the "voice ports". COR is often described as a lock and key mechanism. Locks are assigned to dial peers with an outgoing COR list. Keys are assigned to dial peers with an incoming COR list.
For example, if you hook up a phone to one of the Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports of the router and try to make a call from that phone, it is an incoming call for the router/voice-port. Similarly, if you make a call to that FXS phone, then it is an outgoing call.
By default, an incoming call leg has the highest COR priority and the outgoing COR list has the lowest COR priority. This means that if there is no COR configuration for incoming calls on a dial-peer, then you can make a call from this dial-peer (a phone attached to this dial-peer) going out of any other dial-peer, irrespective of the COR configuration on that dial-peer.
This document provides examples of how to configure COR.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Before you attempt this configuration, ensure that you are familiar with how to configure a Cisco IOS® Telephony Service on a router. Cisco IOS Telephony Service version 3.0 is referred to as CallManager Express 3.0.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(8)T or later with a minimum of IP Plus (IP/VOX Plus on the Cisco 1700 series) feature set. This document assumes Cisco IOS Telephone Services (ITS) 2.0 support in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(8)T or later. Refer to Cisco IOS Telephony Services Version 2.1 for more information on ITS and Cisco IOS Software releases.
-
Cisco 3725 Gateway with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(4)T with the IP Plus feature set is used in the configuration example, although most IAD 2400s, 1700, 2600, 2800, 3600, 3700, 3800 series routers are currently applicable. Cisco CallManager Express 3.0 is supported in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.4(10). Check the Cisco IOS release notes for current version and software support information.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure COR Example
Figure 1 illustrates the concept of COR lists.
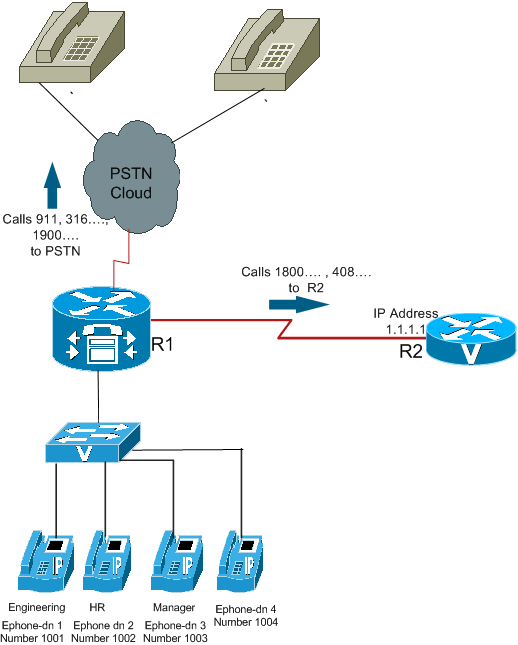
Use this procedure as an example for how to configure COR:
| ephone-dn | COR list incoming | Calling Patterns |
| 1001 | Engineering | 911, 408.... (local_call) and 316….numbers |
| 1002 | HR | 911, 1800.... , 408.... (local_call) and 316…. numbers |
| 1003 | Manager | 911, 1800.... , 1900...., 408....(local_call) and 316…. numbers |
| 1004 | none | can call all the numbers possible from the router R1. |
-
Configure dial-peer cor custom and assign a meaningful name that specifies the way CORs apply to dial-peers. For example:
Dial-peer cor custom name 911 name 1800 name 1900 name local_call
-
Create the actual lists of the restrictions that apply to the dial-peer.
Dial-peer cor list call911 Member 911 Dial-peer cor list call1800 Member 1800 Dial-peer cor list call1900 Member 1900 Dial-peer cor list calllocal Member local_call Dial-peer cor list Engineering Member 911 Member local_call Dial-peer cor list Manager Member 911 Member 1800 Member 1900 Member local_call Dial-peer cor list HR Member 911 Member 1800 Member local_call
-
Create dial-peers and specify the COR list to be used.
In this example, five dial-peers are created for the destination numbers 408…., 1800…, 1900…, 911, and 316…. The appropriate corlist is applied to each of the dial-peers.
Dial-peer voice 1 voip Destination-pattern 408…. Session target ipv4:1.1.1.1 Corlist outgoing calllocal Dial-peer voice 2 voip Destination-pattern 1800… Session target ipv4:1.1.1.1 Corlist outgoing call1800 Dial-peer voice 3 pots Destination-pattern 1900… Port 1/0/0 Corlist outgoing call1900 Dial-peer voice 4 pots Destination-pattern 911 Port 1/0/1 Corlist outgoing call911 Dial-peer voice 5 pots Destination-pattern 316…. Port 1/1/0
Note: There is no COR applied on the dial-peer 5 POTS.
Note: If either the incoming dial peer or the outgoing dial peer does not have a COR list applied, the call succeeds.
Use the telephony-service command in global configuration mode to enter telephony-service configuration mode to configure a Cisco CallManager Express system. By default, no Cisco CallManager Express or ITS configuration is present.
-
Apply the COR list to the individual phones/Ephone-dns.
Ephone-dn 1 Number 1001 Cor incoming Engineering Ephone-dn 2 Number 1002 Cor incoming HR Ephone-dn 3 Number 1003 Cor incoming Manager Ephone-dn 4 Number 1004
Note: On the Ephone-dn 4 there is no COR applied.
With this configuration:
-
Ephone-dn 1 (1001) can call 408…., 911, and 316….numbers.
-
Ephone-dn 2 (1002) can call 408…., 1800... , 911, and 316…. numbers.
-
Ephone-dn 3 (1003) can call all the numbers possible from that router.
-
Ephone-dn 4 (1004) can call all the numbers possible from that router.
Note: All Ephone-dns can call 316…. numbers.
Various combinations of COR lists and the results are shown in this table:
| COR List on Incoming dial-peer | COR List on Outgoing dial-peer | Result | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| No COR. | No COR. | Call succeeds. | COR is not in the picture. |
| No COR. | COR list applied for outgoing calls. | Call succeeds. | The incoming dial-peer, by default, has the highest COR priority when no COR is applied. Therefore, if you apply no COR for an incoming call leg to a dial-peer, then this dial-peer can make calls out of any other dial-peer, irrespective of the COR configuration on the outgoing dial-peer. |
| The COR list applied for incoming calls. | No COR. | Call succeeds. | The outgoing dial-peer, by default, has the lowest priority. Since there are some COR configurations for incoming calls on the incoming/originating dial-peer, it is a super set of the outgoing call COR configurations on the outgoing/terminating dial-peer. |
| The COR list applied for incoming calls (super set of COR lists applied for outgoing calls on the outgoing dial-peer). | The COR list applied for outgoing calls (subset of COR lists applied for incoming calls on the incoming dial-peer.) | Call succeeds. | The COR list for incoming calls on the incoming dial-peer is a super set of COR lists for outgoing calls on the outgoing dial-peer |
| The COR list applied for incoming calls (subset of COR lists applied for outgoing calls on the outgoing dial-peer). | The COR list applied for outgoing calls (super set of COR lists applied for incoming calls on the incoming dial-peer). | Call cannot be completed using this outgoing dial-peer. | COR lists for incoming calls on the incoming dial-peer are not a super set of COR lists for outgoing calls on the outgoing dial-peer. |
COR vs Cisco CallManager
-
The COR feature in the Cisco IOS Software feature is like a Cisco CallManager calling search space and partitions.
-
Cisco IOS Software bases its restriction via dial-peer matching. The Cisco CallManager does it based on digit analysis.
-
The dial-peer cor custom command is equivalent to creating Cisco CallManager partitions.
-
The dial-peer cor list command is equivalent to creating a Cisco CallManager calling search space with partitions in it.
Partitions and calling search spaces provide the capability for implementing calling restrictions and creating closed dial groups on the same Cisco CallManager. There are resemblances between the COR operation and the Cisco CallManager calling search spaces and partitions feature. The one thing that COR cannot do is separate line and device calling search spaces and partitions like Cisco CallManager can.
Verify
After you enter the configurations shown in this document into your router, it is important that you verify the network is operating correctly. These commands and respective output show you a successful implementation of the configurations in this document.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show ephone-dn summary —Displays brief information about Cisco IP phone extensions (Ephone-dns),
-
show telephony-service ephone-dn —Displays information about extensions (Ephone-dns) in a Cisco CallManager Express system.
-
show telephony-service dial-peer —Displays dial-peer information for extensions in a Cisco CallManager Express system
-
show telephony-service all —Displays detailed configuration for phones, voice ports, and dial-peers in a Cisco CallManager Express system.
-
show dial-peer cor—Displays the list of corlist and the members in each list.
This is sample output of some of the commands with respect to the configuration in this document:
Router3725#show ephone-dn summary PORT DN STATE MWI_STATE CODEC VAD VTSP STATE VPM STATE ======== ========== ============ ======== === ===================== ========= 50/0/1 CH1 IDLE NONE - - - EFXS_ONHOOK 50/0/2 CH1 IDLE NONE - - - EFXS_ONHOOK 50/0/3 CH1 IDLE NONE - - - EFXS_ONHOOK 50/0/4 CH1 IDLE NONE - - - EFXS_ONHOOK Router3725#show telephony-service dial-peer dial-peer voice 20001 pots destination-pattern 1001 calling-number local huntstop corlist incoming Engineering progress_ind setup enable 3 port 50/0/1 dial-peer voice 20002 pots destination-pattern 1002 calling-number local huntstop corlist incoming HR progress_ind setup enable 3 port 50/0/2 dial-peer voice 20003 pots destination-pattern 1003 calling-number local huntstop corlist incoming Manager progress_ind setup enable 3 port 50/0/3 dial-peer voice 20004 pots destination-pattern 1004 calling-number local huntstop progress_ind setup enable 3 port 50/0/4 Router3725#show dial-peer cor Class of Restriction name: 911 name: 1800 name: 1900 name: local_call COR list <call911> member: 911 COR list <call1800> member: 1800 COR list <call1900> member: 1900 COR list <calllocal> member: local_call COR list <Engineering> member: 911 member: local_call COR list <Manager> member: 911 member: 1800 member: 1900 member: local_call COR list <HR> member: 911 member: 1800 member: local_call
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
Place a few test calls over the gateways through the IP WAN or the PSTN to verify that your configuration is correct. You can see if the call that comes into the gaetway is ringing when you run a debug on the target gateway.
Refer to the instructions in Cisco IOS Telephony Service (ITS) Configuration and Troubleshooting for additional information on troubleshooting.
-
debug voip ccapi inout —Used to debug end-to-end VoIP calls.
-
debug ephone detail —Used to set detail debugging for the Cisco IP phone.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you issue debug commands.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-May-2003 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- delynch
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback