Local to Remote Network Using the Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway Feature
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for a local to remote network using the Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway (IPIPGW) feature. The IPIPGW feature provides a mechanism to enable H.323 Voice over IP (VoIP) calls from one IP network to another.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Perform a basic H.323 gateway configuration. For detailed instructions, refer to the Cisco IOS H.323 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library, Release 12.3.
-
Perform a basic H.323 gatekeeper configuration. For detailed instructions, refer to the Cisco IOS H.323 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library, Release 12.3.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Three Cisco H.323 Gatekeeper Routers (Cisco 2610, Cisco 2611, Cisco 2612, Cisco 2613, Cisco 2620, Cisco 2621, Cisco 2650, Cisco 2651, Cisco 2691, Cisco 2610XM, Cisco 2611XM, Cisco 2620XM, Cisco 2621XM, Cisco 2650XM, Cisco 2651XM, Cisco 3620, Cisco 3640, Cisco 3660, Cisco 3725, Cisco 3745, Cisco 7200 Series, or Cisco 7400 Series) with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(13)T or later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
The Cisco Multiservice IPIPGW feature introduces gatekeeper via-zones. Via-zone is a Cisco term for a zone that contains IP-to-IP gateways and via-zone-enabled gatekeepers. A via-zone-enabled gatekeeper can recognize via-zones and send traffic to via-zone gateways. Cisco via-zone enabled gatekeepers include a via-zone command-line interface (CLI) command.
Via-zones are usually located on the edge of an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP) network, and are like a VoIP transfer point, or tandem zone, where traffic passes through on the way to the remote zone destination. Gateways in this zone terminate requested calls and re-originate traffic to its final destination. Via-zone gatekeepers operate as usual for non-IP-to-IP applications. Gatekeepers in via-zones support resource management (for example, gateway selection and load balancing) using the capacities field in the H.323 Version 4 RAS messages.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to find more information on the commands used in this document.
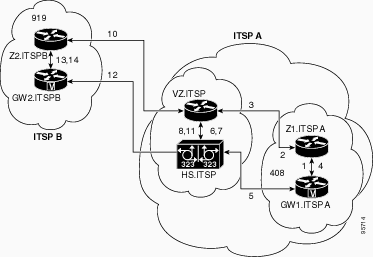
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
In this example, a caller from area code 408 calls a party in area code 919, and these actions occur:
-
GW1.ITSPA sends an Admission Request (ARQ) message with the 919-based number to Z1.ITSPA.
-
Z1.ITSPA resolves 919 to VZ.ITSP and sends a Location Request (LRQ) message to VZ.ITSP.
-
The LRQ for the 919 number from Z1ITSPA zone is received by VZ.ITSP. VZ.ITSP checks the zone remote configuration for Z1ITSPA and finds that its zone VZITSP is configured as "invia" zone. It then sends a Location Confirm (LCF) message to Z1.ITSPA and specifies HS.ITSP as the destination gateway for the 919 call.
-
Z1.ITSPA sends an Admission Confirm (ACF) message to GW1.ITSPA and specifies HS.ITSP as the destination gateway.
-
GW1.ITSPA sends a SETUP message to HS.ITSP for the 919 call.
-
HS.ITSP consults VZ.ITSP with an ARQ (containing answerCall=true) to admit the incoming call.
-
VZ.ITSP responds with an ACF to admit the call.
-
HS.ITSP has a dial peer specifying RAS VZ.ITSP for the 919 prefix (or for all prefixes), so it sends an ARQ (with answerCall set to FALSE) to VZ.ITSP for prefix 919.
-
VZ.ITSP gatekeeper identifies that Z2ITSPB zone handles the prefix "919" by looking up the zone prefix table. It then uses the zone remote configuration and knows that its own local zone VZITSP is configured as "outvia" zone. It then sends the LRQ to Z2.ITSPB gatekeeper instead of sending an LRQ to another IP-to-IP gatekeeper.
-
Z2.ITSPB sees prefix 919 as in its own zone and returns an LCF that points to GW2.ITSPB.
-
VZ.ITSP returns an ACF that specifies GW2.ITSPB as the destination gateway to HS.ITSP.
-
HS.ITSP sends a SETUP message to GW2.ITSPB for the 919 call.
-
GW2.ITSPB sends an ARQ (containing answerCall=true) to Z2.ITSPB.
-
Z2.ITSPB sends an ACF for answerCall.
-
The H.323 call between HS.ITSP and GW2.ITSPB gets connected. The H.323 call between GW1.ITSPA and HS.ITSP gets connected.
| Originating Gatekeeper (Z1.ITSPA) |
|---|
origgatekeeper#show running-config Building configuration... . . . gatekeeper zone local Z1ITSPA cisco 10.16.8.158 zone remote VZITSP cisco 10.16.10.139 zone remote Z2ITSPB china 10.16.8.139 1719 zone prefix VZITSP 919* . . . ! end |
| Via-zone Gatekeeper (VZ.ITSP) |
|---|
vzgatekeeper#show running-config Building configuration... . . . gatekeeper zone local VZITSP cisco 10.16.10.139 zone remote Z1ITSPA cisco 10.16.8.158 invia VZITSP zone remote Z2ITSPB china 10.16.8.144 1719 outvia VZITSP zone prefix Z2ITSPB 919* . . . ! end |
| Terminating Gatekeeper (Z2.ITSPB) |
|---|
termgatekeeper#show running-config Building configuration... . . . gatekeeper zone local Z2ITSPB china 10.16.8.144 . . . ! end |
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: These show command outputs were obtained from VZ.ITSP gatekeeper.
Issue the show running config | begin gatekeeper command to verify the gatekeeper configuration:
gatekeeper
zone local VZITSP cisco 10.16.10.139
zone remote Z1ITSPA cisco 10.16.8.158 invia VZITSP
zone remote Z2ITSPB china 10.16.8.144 1719 outvia VZITSP
zone prefix Z2ITSPB 919*
no shutdown
You can also use the show gatekeeper zone status command to verify the gatekeeper configuration:
GATEKEEPER ZONES
================
GK name Domain Name RAS Address PORT FLAGS
------- ----------- ----------- ----- -----
VZITSP cisco 10.16.128.40 1719 LSV
BANDWIDTH INFORMATION (kbps) :
Maximum total bandwidth :unlimited
Current total bandwidth :0
Maximum interzone bandwidth :unlimited
Current interzone bandwidth :0
Maximum session bandwidth :unlimited
Total number of concurrent calls :3
SUBNET ATTRIBUTES :
All Other Subnets :(Enabled)
PROXY USAGE CONFIGURATION :
Inbound Calls from all other zones :
to terminals in local zone hurricane :use proxy
to gateways in local zone hurricane :do not use proxy
to MCUs in local zone hurricane :do not use proxy
Outbound Calls to all other zones :
from terminals in local zone hurricane :use proxy
from gateways in local zone hurricane :do not use proxy
from MCUs in local zone hurricane :do not use proxy
Z1.ITSPA cisco 10.16.10.139 1719 RS
VIAZONE INFORMATION :
invia:VZ.ITSP, outvia:VZ.ITSP
Z2.ITSPB cisco 10.16.8.144 1719 RS
VIAZONE INFORMATION :
invia:VZ.ITSP, outvia:VZ.ITSP
Issue the show gatekeeper status command to view call capacity thresholds:
Gatekeeper State: UP
Load Balancing: DISABLED
Flow Control: DISABLED
Zone Name: hurricane
Accounting: DISABLED
Endpoint Throttling: DISABLED
Security: DISABLED
Maximum Remote Bandwidth: unlimited
Current Remote Bandwidth: 0 kbps
Current Remote Bandwidth (w/ Alt GKs): 0 kbps
Issue the show gatekeeper performance stats command to view RAS information, including via-zone statistics:
Performance statistics captured since: 08:16:51 GMT Tue Jun 11 2002
RAS inbound message counters:
Originating ARQ: 462262 Terminating ARQ: 462273 LRQ: 462273
RAS outbound message counters:
ACF: 924535 ARJ: 0 LCF: 462273 LRJ: 0
ARJ due to overload: 0
LRJ due to overload: 0
RAS viazone message counters:
inLRQ: 462273 infwdLRQ 0 inerrLRQ 0
outLRQ: 0 outfwdLRQ 0 outerrLRQ 0
outARQ: 462262 outfwdARQ 0 outerrARQ 0
Load balancing events: 0
Real endpoints: 3
The following significant RAS via-zone fields are shown in the display:
-
inLRQ: —Associated with the invia keyword. If the invia is a local zone, this counter identifies the number of LRQs terminated by the local invia gatekeeper.
-
infwdLRQ—Associated with the invia keyword. If the invia is a remote zone this counter identifies the number of LRQs that were forwarded to the remote invia gatekeeper.
-
inerrLRQ—Associated with the invia keyword. Number of times the LRQ could not be processed because the invia gatekeeper ID could not be found. Usually caused by a misspelled gatekeeper name.
-
outLRQ—Associated with the outvia keyword. If the outvia is a local zone, this counter identifies the number of LRQs terminated by the local outvia gatekeeper. This counter applies only in configurations where no invia gatekeeper is specified.
-
outfwdLRQ—Associated with the outvia keyword. If the outvia is a remote zone, this counter identifies the number of LRQs that were forwarded to the remote outvia gatekeeper. This counter applies only in configurations where no invia gatekeeper is specified.
-
outerrLRQ—Associated with the outvia keyword. Number of times the LRQ could not be processed because the outvia gatekeeper ID could not be found. Usually caused by a misspelled gatekeeper name. This counter applies only in configurations where no invia gatekeeper is specified.
-
outARQ—Associated with the outvia keyword. Identifies the number of originating ARQs handled by the local gatekeeper if the outvia is that local zone.
-
outfwdARQ—Associated with the outvia keyword. If the outvia gatekeeper is a remote zone, this number identifies the number of originating ARQs received by this gatekeeper that resulted in LRQs being sent to the outvia gatekeeper.
-
outerrARQ—Associated with the outvia keyword. Number of times the originating ARQ could not be processed because the outvia gatekeeper ID could not be found. This is usually caused by a misspelled gatekeeper name.
Enter the show gatekeeper circuit command to view information on calls in progress:
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
===================
Circuit Endpoint Max Calls Avail Calls Resources Zone
------- -------- --------- ----------- --------- ----
ITSP B Total Endpoints: 1
hs.itsp 200 198 Available
Note: The word “calls” refers to call legs in some commands and output.
Enter the show gatekeeper endpoint command to view information on endpoint registrations:
GATEKEEPER ENDPOINT REGISTRATION
================================
CallSignalAddr Port RASSignalAddr Port Zone Name Type Flags
--------------- ----- --------------- ----- --------- ---- -----
10.16.10.140 1720 10.16.10.140 50594 vz.itsp H323-GW
H323-ID: hs.itsp
H323 Capacity Max.= 200 Avail.= 198
Total number of active registrations = 1
Troubleshoot
Use this section to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Procedure
This is troubleshooting information relevant to this configuration. Complete these steps to troubleshoot your configuration.
The procedures for troubleshooting an IPIPGW are similar to troubleshooting a TDM-to-IP H.323 gateway. Generally, your troubleshooting efforts should proceed as seen here:
-
Isolate and reproduce the failing scenario.
-
Collect relevant information from debug and show commands, configuration files, and protocol analyzers.
-
Identify the first indication of failure in protocol traces or internal debug output.
-
Look for the cause in configuration files.
If the via-zone is suspected as the source of a call failure, isolate the problem to an IPIPGW or gatekeeper by identifying the affected sub-function and focus on show and debug commands related to that sub-function.
Before you can begin troubleshooting, you first must isolate the problem to either a gateway or gatekeeper. Gateways and gatekeepers are responsible for these tasks:
Gateway Tasks:
-
Media stream handling and speech path integrity
-
DTMF relay
-
Fax relay and passthrough
-
Digit translation and call processing
-
Dial-peers and codec filtering
-
Carrier ID handling
-
Gateway-based billing
Gatekeeper Tasks:
-
Gateway selection and load balancing
-
Call routing (zone selection)
-
Gatekeeper-based billing
-
Control of call admission, security, and bandwidth
-
Enforcement of call capacities
Troubleshooting Commands
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
Gateway debug Commands:
-
debug voip ipipgw —This command displays information related to the handling of IP-to-IP calls.
-
debug h225 asnl—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 part of H.225 messages and associated events.
-
debug h225 events—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 part of H.225 messages and associated events.
-
debug h245 asn1—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 part of H.245 messages and associated events.
Gatekeeper debug Commands:
-
debug h225 asn1—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 portion of H.225 RAS messages and associated events.
-
debug h225 events—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 portion of H.225 RAS messages and associated events.
-
debug gatekeeper main 10—This command traces major gatekeeper functions, such as LRQ processing, gateway selection, admission request processing, prefix matching, and call capacities.
-
debug gatekeeper zone 10—This command traces gatekeeper zone-oriented functions.
-
debug gatekeeper call 10—This command traces gatekeeper call-oriented functions, such as tracking call references.
-
debug gatekeeper gup asn1—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 portion of gatekeeper update protocol messages and associated events for communication between gatekeepers in a cluster.
-
debug gatekeeper gup events—This command displays the actual contents of the asn1 portion of gatekeeper update protocol messages and associated events for communication between gatekeepers in a cluster.
-
debug ras—This command displays the types and addressing of RAS messages sent and received.
Gateway show Commands:
-
show h323 gateway h225—This command maintains counts of H.225 messages and events.
-
show h323 gateway ras—This command maintains counts of RAS messages sent and received.
-
show h323 gateway cause—This command shows counts of cause codes received from connected gateways.
-
show call active voice [brief]—These commands aggregate information about active and cleared calls.
-
show crm—This command shows the call capacity counts associated with IP circuits on the IPIPGW.
-
show processes cpu—This command shows detailed CPU utilization statistics (CPU use per process).
-
show gateway—This command shows the current status of the gateway.
Gatekeeper show Commands:
-
show/clear gatekeeper performance stats—This command shows the gatekeeper statistics associated with processing calls.
-
show gatekeeper zone status—This command lists information about the local and remote zones known to the gatekeeper.
-
show gatekeeper endpoint—This command lists key information about the endpoints registered to the gatekeeper, including IPIPGWs.
-
show gatekeeper circuit—This command combines information about circuit utilization across multiple gateways.
-
show gatekeeper calls—This command lists key information about calls being handled in the local zone.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Feb-2006 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback