Wireless LAN Controller and Light Weight Access Points Failover Outside the Mobility Group Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document explains how to configure the failover feature on Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs). This feature allows the Lightweight Access Points (LAPs) to failover to WLCs outside their mobility groups.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Basic knowledge of the configuration of Lightweight Access Points (APs) and Cisco WLCs
-
Basic knowledge of Lightweight AP Protocol (LWAPP)
-
Basic understanding of WLC failover and mobility groups.
Refer to WLAN Controller Failover for Lightweight Access Points Configuration Example for more information about the WLC failover feature.
Refer to Configuring Mobility Groups for more information on Mobility Groups for more information.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco Aironet 1000 Series Lightweight AP
-
A Cisco 2100 Series WLC that runs firmware version 4.2.61.0
-
A Cisco 4400 Series WLC that runs firmware version 4.2.61.0
The feature explained in this document is introduced in WLC version 4.2.61.0. This configuration works only with Cisco WLCs that run version 4.2.61.0 or later.
Note: If you run the latest WLC release, 5.0.148.0, make sure that you are aware of these limitations:
-
The 2000 series controllers are not supported for use with controller software release 5.0.148.0.
-
The 1000 series access points are not supported for use with controller software release 5.0.148.0.
Note: Refer to Release Notes for Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Lightweight Access Points for Release 5.0.148.0 for more information.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
In all WLC versions earlier than 4.2.61.0, when a WLC goes "down," the LAP registered to this WLC can failover only to another WLC of the same mobility group, in the event that the LAP is configured for failover. Refer to WLAN Controller Failover for Lightweight Access Points Configuration Example for more information.
From the Cisco WLC version 4.2.61.0, a new feature called Backup Controller Support is introduced for access points to failover to controllers even outside the mobility group.
A single controller at a centralized location can act as a backup for access points when they lose the primary controller in the local region. Centralized and regional controllers need not be in the same mobility group. Through the use of the controller CLI, you can specify a primary, secondary, and tertiary controller for the access points of your network. In controller software release 4.2.61.0, you can specify the IP address of the backup controller, which allows the access points to failover to controllers outside of the mobility group. This feature is currently supported only through the controller CLI.
This document uses this initial configuration setup to explain this feature:
-
Two Cisco WLCs that run firmware version 4.2.61.0.
For the sake of clarity, this document uses the names WLC1 and WLC2 in order to refer to the WLCs throughout the configuration.
-
The management interface IP address of WLC1 is 10.77.244.210/27.
-
The management interface IP address of WLC2 is 10.77.244.204/27.
-
A Cisco 1000 series LAP that is currently registered to WLC1. In our configuration, the name of this LAP is AP1.
Refer to Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Point Basic Configuration Example for more information about how to configure the basic parameters on a WLC.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Complete these steps in order to configure this feature:
Configure Mobility Groups for the WLCs
The first step is to configure WLC1 and WLC2 in two different mobility groups.
In this example, WLC1 is configured in the TSWEB mobility group and WLC2 is configured in the backupwlc mobility group. This section shows how to configure mobility groups for the WLCs through the CLI of the controller.
Enter these commands in the CLI mode of the WLC in order to configure mobility groups:
-
WLC1>config mobility group domain TSWEB
-
WLC2>config mobility group domain backupwlc
Hence, WLC1 and WLC2 are configured to be in two different mobility groups.
You can also configure this with the WLC GUI. Refer to Configure Mobility Groups for the WLCs for more information.
Configure the WLC and LAP for Failover Outside the Mobility Group
The next step is to configure the WLC and LAP for failover outside the mobility group.
As mentioned earlier in this document, the LAP is currently registered to WLC1. You can verify this on WLC1, which in our example is 10.77.244.210. In order to do this, click Wireless from the controller GUI. In this example, the LAP name is AP1.
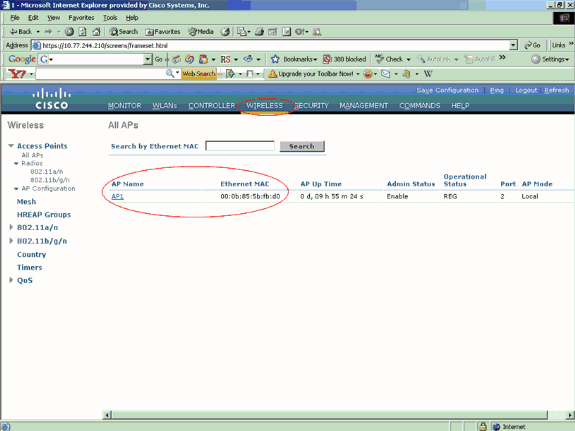
The objective is to configure this LAP in such a way that it can failover to WLC2 (10.77.244.204) which is in a different mobility group. In order to achieve this, login to the CLI mode of the WLC to which the LAP is currently registered (WLC1) through the Telnet application or through a direct console connection and configure the primary and secondary WLCs of this LAP.
-
In the CLI mode of WLC1, issue this command:
WLC1>config ap primary-base controller_name Cisco_AP [controller_ip_address]-
The controller_name field represents the system name of the primary WLC. In our example, WLC1 itself is the primary WLC of the AP1 LAP. Here, WLC1 is the System Name of WLC1.. You can see the controller name in GUI mode on the Monitor screen of the WLC.
-
The Cisco_AP field represents the name of the Cisco AP. In our example, it is AP1.
-
The [controller_ip_address] field represents the management interface IP address of the primary WLC. In this example, 10.77.244.210 is the management interface IP address of WLC1.
Note: If the backup controller is outside the mobility group to which the access point is connected (the primary controller), then you always need to provide the IP address of the primary, secondary, or tertiary controller, respectively. Otherwise, the access point cannot join the backup controller.
Hence, the command used to configure in this example is WLC1 >config ap primary-base WLC1 AP1 10.77.244.210
-
-
Now, configure WLC2 as the secondary WLC for the LAP to failover in case the primary WLC, WLC1, goes down. In order to configure WLC2, which is from a different mobility group, issue this command from the CLI mode of WLC1:
WLC1>config ap secondary-base controller_name Cisco_AP [controller_ip_address]-
The controller_name field represents the system name of the backup or secondary WLC. In our example, WLC2 is the secondary WLC of the AP1 LAP. Here, WLC2 is the system name of WLC2.
-
The Cisco_AP field represents the name of the Cisco AP. In our example, it is AP1.
-
The [controller_ip_address] field represents the management interface IP address of the secondary WLC, WLC2. In this example, 10.77.244.204 is the management interface IP address of WLC2.
Note: If the backup controller is always outside the mobility group to which the access point is connected (the primary controller), then you need to provide the IP address of the primary, secondary, or tertiary controller, respectively. Otherwise, the access point cannot join the backup controller.
Hence, the command used to configure in our example is WLC1 >config ap secondary-base WLC2 AP1 10.77.244.204.
-
This is the CLI screen that demonstrates the configuration from WLC1.
WLC1 >config ap primary-base WLC1 AP1 10.77.244.210
WLC1 >config ap secondary-base WLC2 AP1 10.77.244.204
WLC1 >save config
Are you sure you want to save? (y/n) y
Configuration Saved!
Verify
You need to verify whether your configuration works properly. In the example, when WLC1 goes down, AP1 must failover and register to WLC2, which is in a different mobility group.
In order to verify this, complete these steps:
-
Disconnect the power supply or the ethernet cable that connects the WLC1 and AP1. Once disconnected, the LAP de-registers itself from the WLC and searches for a different WLC.
-
According to the normal registration process of the LAP with a WLC, AP1 must be able to register successfully with WLC2. Verify this from the GUI mode of WLC2 (10.77.244.204).
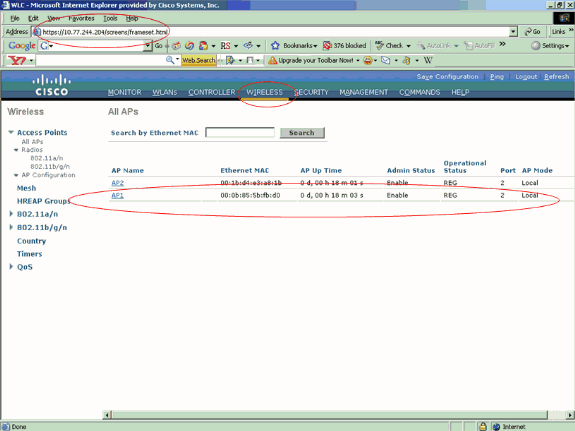
Notice the encircled parameters in this screen shot. Here, you see that AP1 is registered to WLC2 (10.77.244.204).
You can also verify the registration process from the CLI mode of WLC2 with the debug lwapp events enable command. Here is an example:
(Cisco Controller) >Fri Apr 4 04:31:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP ECHO_REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Ech o-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP PRIMARY_DISCOVERY_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Pri mary Discovery Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP ECHO_REQUEST from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Ech o-Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP PRIMARY_DISCOVERY_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:37 2008: 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b Successful transmission of LWAPP Pri mary Discovery Response to AP 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b Fri Apr 4 04:31:38 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:38 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:56 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:31:56 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:06 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP ECHO_REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:06 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Ech o-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:06 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP PRIMARY_DISCOVERY_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:06 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Pri mary Discovery Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:07 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP ECHO_REQUEST from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:07 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Ech o-Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:07 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP PRIMARY_DISCOVERY_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:07 2008: 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b Successful transmission of LWAPP Pri mary Discovery Response to AP 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b Fri Apr 4 04:32:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP ECHO_REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Ech o-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP PRIMARY_DISCOVERY_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Pri mary Discovery Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP STATISTICS_INFO from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:36 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Sta tistics Info Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP STATISTICS_INFO from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Sta tistics Info Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP STATISTICS_INFO from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Sta tistics Info Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP ECHO_REQUEST from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Ech o-Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP PRIMARY_DISCOVERY_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:37 2008: 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b Successful transmission of LWAPP Pri mary Discovery Response to AP 00:1b:d4:e3:a8:1b Fri Apr 4 04:32:38 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:38 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:56 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Received LWAPP RRM_DATA_REQ from AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Fri Apr 4 04:32:56 2008: 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Air ewave-Director-Data Response to AP 00:1c:58:05:e9:c0
In this output, you can see that all configuration parameters are successfully downloaded from WLC2 to AP1. This download process happens only when the LAP is registered to that WLC.
The show ap config general Cisco_AP command is used in order to view the configuration explained in this document. Here is an example:
WLC2 >show ap config general AP1 Cisco AP Identifier.............................. 5 Cisco AP Name.................................... AP1 ..................................................... ..................................................... ..................................................... ..................................................... Name Server...................................... Cisco AP Location................................ default_location Cisco AP Group Name.............................. default-group Primary Cisco Switch Name........................ WLC1 Primary Cisco Switch IP Address.................. 10.77.244.210 Secondary Cisco Switch Name...................... WLC2 Secondary Cisco Switch IP Address................ 10.77.244.204 Tertiary Cisco Switch Name.......................
Troubleshoot
You can use these debug commands in order to troubleshoot your configuration:
-
debug lwapp errors enable—Configures the debug of LWAPP errors.
-
debug dhcp message enable—Configures the debug of DHCP messages that are exchanged to and from the DHCP server.
-
debug dhcp packet enable—Configures the debug of DHCP packet details that are sent to and from the DHCP server.
Related Information
- Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release 4.2 - Controlling Lightweight Access Points
- Lightweight AP (LAP) Registration to a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC)
- WLAN Controller Failover for Lightweight Access Points Configuration Example
- Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Point Basic Configuration Example
- Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Configuration Best Practices
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)

 Feedback
Feedback