Cisco Airespace VSAs on Microsoft IAS Radius Server Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document shows you how to configure a Microsoft Internet Authentication Service (IAS) server to support Cisco Airespace Vendor Specific Attributes (VSAs). The Vendor Code for Cisco Airespace VSAs is 14179.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Knowledge of how to configure an IAS server
-
Knowledge of the configuration of Lightweight Access Points (LAPs) and Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs)
-
Knowledge of Cisco Unified Wireless Security Solutions
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Microsoft Windows 2000 server with IAS
-
Cisco 4400 WLC that runs software version 4.0.206.0
-
Cisco 1000 Series LAPs
-
802.11 a/b/g wireless client adapter with firmware 2.5
-
Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) version 2.5
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Note: This document is intended to give the reader an example on the configuration required on the IAS server to support Cisco Airespace VSAs. The IAS server configuration presented in this document has been tested in the lab and works as expected. If you have trouble configuring the IAS server, contact Microsoft for help. Cisco TAC does not support Microsoft Windows server configuration.
This document assumes that the WLC is configured for basic operation and that the LAPs are registered to the WLC. If you are a new user trying to setup the WLC for basic operation with LAPs, refer to Lightweight AP (LAP) Registration to a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC).
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
In most wireless LAN (WLAN) systems, each WLAN has a static policy that applies to all clients associated with a service set identifier (SSID). Although powerful, this method has limitations because it requires clients to associate with different SSIDs in order to inherit different QoS and security policies.
However, the Cisco Wireless LAN Solution supports identity networking, which allows the network to advertise a single SSID and specific users to inherit different QoS or security policies based on their user profiles. The specific policies that you can control using identity networking include:
-
Quality of Service—When present in a RADIUS Access Accept, the QoS-Level value overrides the QoS value specified in the WLAN profile.
-
ACL—When the Access Control List (ACL) attribute is present in the RADIUS Access Accept, the system applies the ACL-Name to the client station after it authenticates. This overrides any ACLs that are assigned to the interface.
-
VLAN—When a VLAN Interface-Name or VLAN-Tag is present in a RADIUS Access Accept, the system places the client on a specific interface.
-
WLAN ID—When the WLAN-ID attribute is present in the RADIUS Access Accept, the system applies the WLAN-ID (SSID) to the client station after it authenticates. The WLAN ID is sent by the WLC in all instances of authentication except IPSec. In case of web authentication, if the WLC receives a WLAN-ID attribute in the authentication response from the AAA server, and it does not match the ID of the WLAN, authentication is rejected. Other types of security methods do not do this.
-
DSCP Value—When present in a RADIUS Access Accept, the DSCP value overrides the DSCP value specified in the WLAN profile.
-
802.1p-Tag—When present in a RADIUS Access Accept, the 802.1p value overrides the default specified in the WLAN profile.
Note: The VLAN feature only supports MAC filtering, 802.1X, and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). The VLAN feature does not support web authentication or IPSec. The operating system's local MAC Filter database has been extended to include the interface name. This allows local MAC filters to specify which interface the client should be assigned. A separate RADIUS server can also be used, but the RADIUS server must be defined using the Security menus.
Refer to Configuring Identity Networking for more information on identity networking.
Configure the IAS for Airespace VSAs
In order to configure the IAS for Airespace VSAs, you need to complete these steps:
Note: The VSAs are configured under the Remote Access Policy.
Configure the WLC as an AAA Client on the IAS
Complete these steps in order to configure the WLC as an AAA client on the IAS:
-
Click Programs > Administrative Tools > Internet Authentication Service in order to launch IAS on the Microsoft 2000 server.
-
Right-click the Clients folder and choose New Client in order to add a new RADIUS client.
-
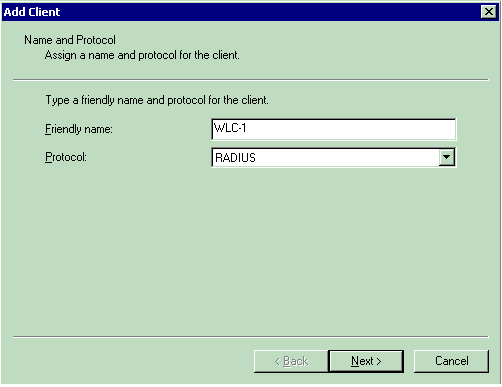
In the Add Client window, enter the name of the client and choose RADIUS as the Protocol. Then, click Next.
In this example, the client name is WLC-1.
Note: By default, the protocol is set to RADIUS.
-
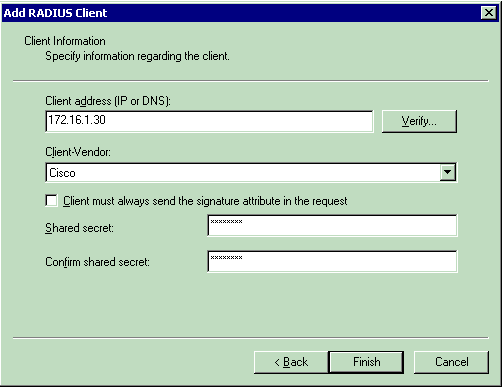
In the Add RADIUS Client window, enter the Client IP address, Client-Vendor, and Shared secret. After you enter the client information, click Finish.
This example shows a client named WLC-1 with an IP address of 172.16.1.30, the Client-Vendor is set to Cisco, and the Shared secret is cisco123:
With this information, the WLC named WLC-1 is added as AAA client of the IAS server.
The next step is to create a Remote Access Policy and configure the VSAs.
Configure the Remote Access Policy on the IAS
Complete these steps in order to configure a new Remote Access Policy on the IAS:
-
Right-click Remote Access Policies and choose New Remote AcceMSss Policy.
The Policy Name window appears.
-
Enter the name of the policy and click Next.
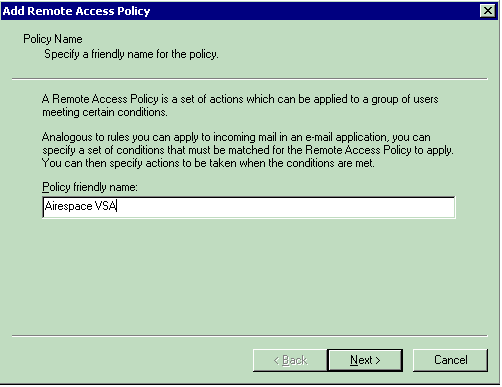
-
In the next window, select the conditions for which the Remote Access Policy will apply. Click Add in order to select the conditions.
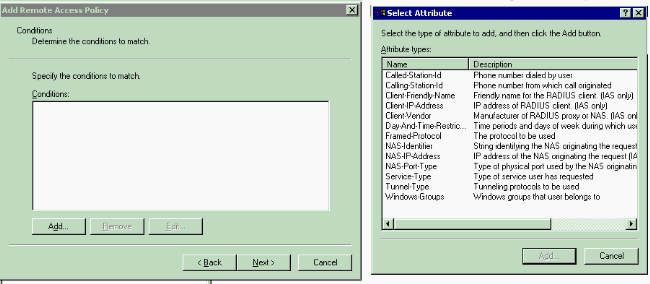
-
From the Attribute types menu, select these attributes:
-
Client-IP-Address—Enter the IP address of the AAA client. In this example, the WLCs IP address is entered so that the policy applies to packets from the WLC.
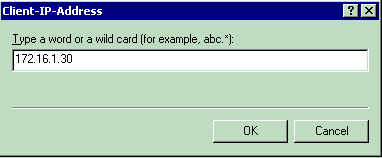
-
Windows Groups—Select the Windows group (the user group) for which the policy will apply. Here is an example:
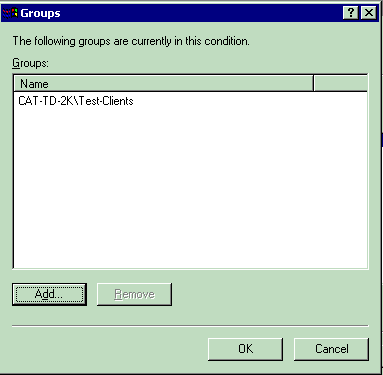
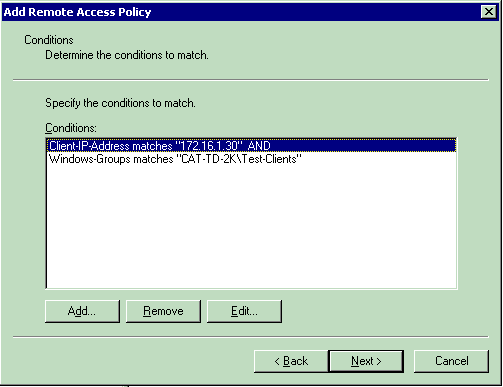
This example shows only two conditions. If there are more conditions, add those conditions as well and click Next.
The Permissions window appears.
-
-
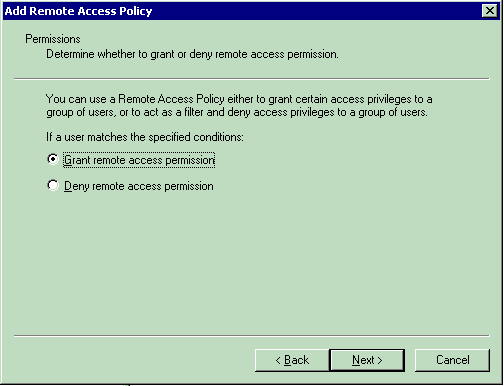
In the Permissions window, choose Grant remote access permission.
After you choose this option, the user is given access, provided the user matches the specified conditions (from step 2).
-
Click Next.
-
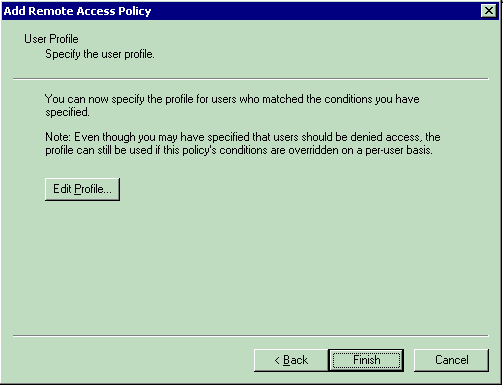
The next step is to set up the user profile.
Even though you might have specified that users should be denied or granted access based on the conditions, the profile can still be used if this policy's conditions are overridden on a per-user basis.
-
In order to configure the user profile, click Edit Profile on the User Profile window.
The Edit Dial-in Profile window appears.
-
Click the Authentication tab, then choose the authentication method that is used in the WLAN.
This example uses Unencrypted Authentication (PAP,SPAP).
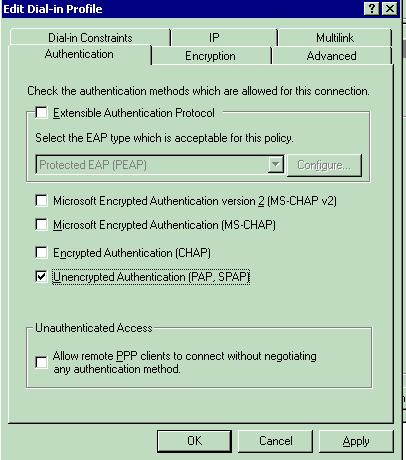
-
Click the Advanced tab. Remove all the default parameters and click Add.
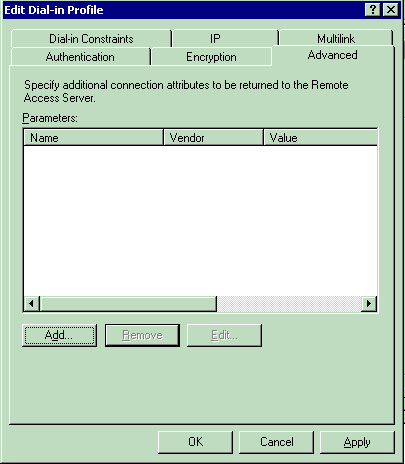
-
From the Add Attributes window, select Service-Type, then choose the Login value from the next window.
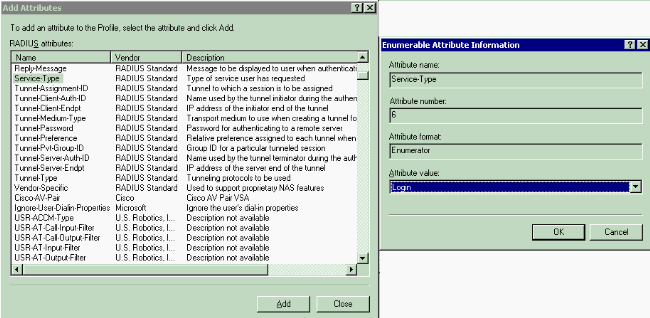
-
Next, you need to select the Vendor-Specific attribute from the RADIUS attributes list.
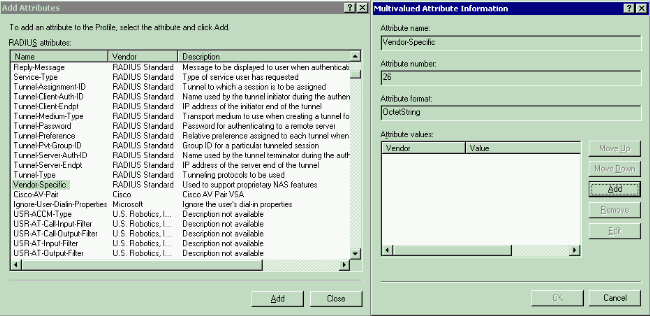
-
In the next window, click Add in order to select a new VSA.
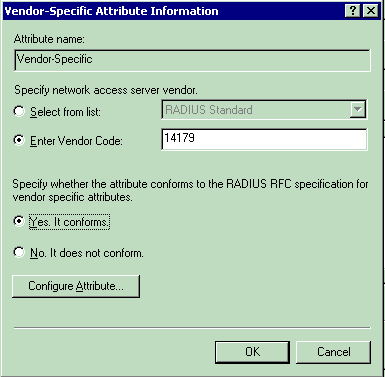
The Vendor-Specific Attribute Information window appears.
-
Under Specify network access server vendor, choose Enter Vendor Code.
-
Enter the Vendor Code for Airespace VSAs. The Vendor Code for Cisco Airespace VSAs is 14179.
-
Because this attribute conforms with the RADIUS RFC specification for VSAs, choose Yes. It conforms..
-
Click Configure Attribute.
-
In the Configure VSA (RFC compliant) window, enter the Vendor-assigned attribute number, the Attribute format and the Attribute value, which depend on the VSA that you want to use.
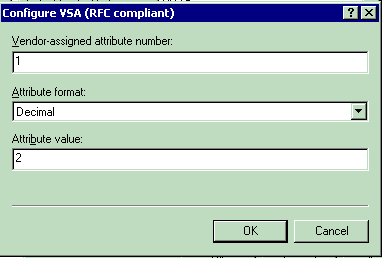
For setting the WLAN-ID on a per-user basis:
-
Attribute Name—Airespace-WLAN-Id
-
Vendor-assigned attribute number—1
-
Attribute Format—Integer/Decimal
-
Value—WLAN-ID
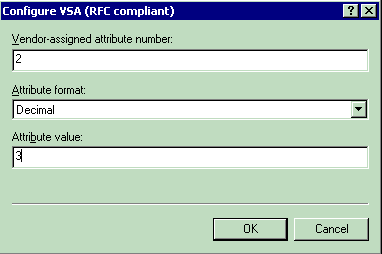
For setting the QoS profile on a per-user basis:
-
Attribute Name—Airespace-QoS-Level
-
Vendor-assigned attribute number—2
-
Attribute Format—Integer/Decimal
-
Value—0 - Silver; 1 - Gold; 2 - Platinum; 3 - Bronze
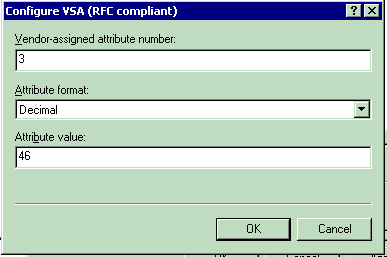
For setting the DSCP Value on a per-user basis:
-
Attribute Name—Airespace-DSCP
-
Vendor-assigned attribute aumber—3
-
Attribute Format—Integer/Decimal
-
Value—DSCP Value
For setting the 802.1p-Tag on a per-user basis:
-
Attribute Name—Airespace-802.1p-Tag
-
Vendor-assigned attribute number—4
-
Attribute Format—Integer/Decimal
-
Value—802.1p-Tag
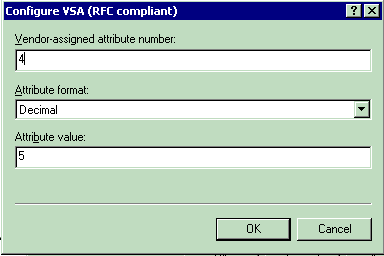
For setting the Interface (VLAN) on a per-user basis:
-
Attribute Name—Airespace-Interface-Name
-
Vendor-assigned attribute number—5
-
Attribute Format—String
-
Value—Interface-Name
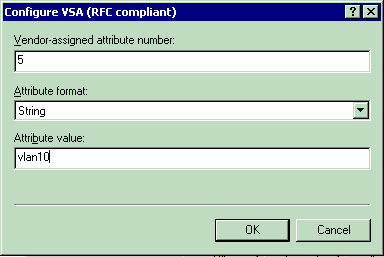
For setting the ACL on a per-user basis:
-
Attribute Name—Airespace-ACL-Name
-
Vendor-assigned attribute number—6
-
Attribute Format—String
-
Value—ACL-Name
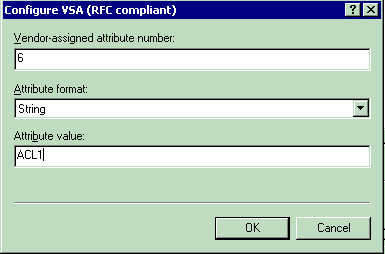
-
-
-
Once you have configured the VSAs, click OK until you see the User profile window.
-
Then, click Finish in order to complete the configuration.
You can see the new policy under Remote Access Policies.
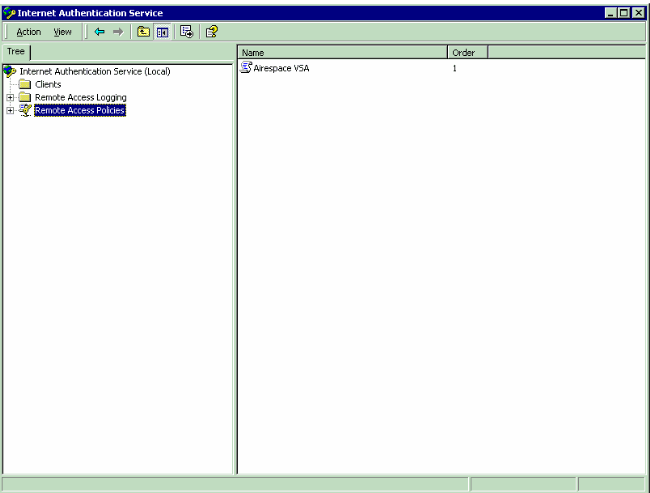
Example Configuration
In this example, a WLAN is configured for web authentication. Users are authenticated by the IAS RADIUS server, and the RADIUS server is configured to allot QoS policies on a per-user basis.
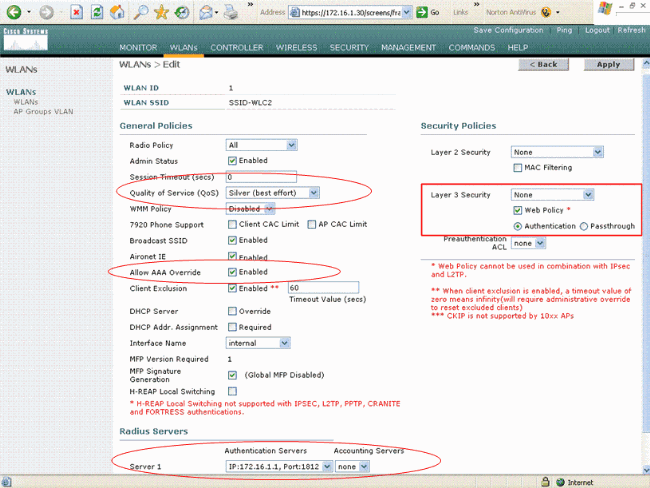
As you can see from this window, web authentication is enabled, the authentication server is 172.16.1.1, and AAA override is also enabled on the WLAN. The default QoS setting for this WLAN is set to Silver.
On the IAS RADIUS server, a Remote Access Policy is configured which returns the QoS attribute Bronze in the RADIUS accept request. This is done when you configure the VSA specific to the QoS attribute.

See the Configure the Remote Access Policy on the IAS section of this document for detailed information on how to configure a Remote Access Policy on the IAS server.
Once the IAS server, the WLC, and the LAP are configured for this setup, the wireless clients can use web authentication in order to connect.
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
When the user connects to the WLAN with a user ID and password, the WLC passes the credentials to the IAS RADIUS server which authenticates the user against the conditions and the user profile configured in the Remote Access Policy. If the user authentication is successful, the RADIUS server returns a RADIUS accept request which also contains the AAA override values. In this case, the QoS policy of the user is returned.
You can issue the debug aaa all enable command in order to see the sequence of events that occurs during authentication. Here is a sample output:
(Cisco Controller) > debug aaa all enable
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: User admin authenticated
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: 28:1f:00:00:00:00 Returning AAA Error 'Success' (0) for
mobile 28:1f:00:00:00:00
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: AuthorizationResponse: 0xbadff97c
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: structureSize................................70
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: resultCode...................................0
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: protocolUsed.................................0x00000008
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: proxyState...................................
28:1F:00:00:00:00-00:00
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: Packet contains 2 AVPs:
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: AVP[01] Service-Type.............................
0x00000006 (6) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: AVP[02] Airespace / WLAN-Identifier..............
0x00000000 (0) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: User admin authenticated
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: 29:1f:00:00:00:00 Returning AAA Error 'Success' (0) for
mobile 29:1f:00:00:00:00
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: AuthorizationResponse: 0xbadff97c
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: structureSize................................70
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: resultCode...................................0
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: protocolUsed.................................0x00000008
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: proxyState...................................
29:1F:00:00:00:00-00:00
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: Packet contains 2 AVPs:
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: AVP[01] Service-Type.............................
0x00000006 (6) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:14:24 2007: AVP[02] Airespace / WLAN-Identifier..............
0x00000000 (0) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: Unable to find requested user entry for User-VLAN10
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: AuthenticationRequest: 0xa64c8bc
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: Callback.....................................0x8250c40
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: protocolType.................................0x00000001
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: proxyState...................................
00:40:96:AC:E6:57-00:00
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: Packet contains 8 AVPs (not shown)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00:40:96:ac:e6:57 Successful transmission of Authentication Packet
(id 26) to 172.16.1.1:1812, proxy state 00:40:96:ac:e6:57-96:ac
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000000: 01 1a 00 68 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
...h............
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000010: 00 00 00 00 01 0d 55 73 65 72 2d 56 4c 41 4e 31
......User-VLAN1
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000020: 30 02 12 fa 32 57 ba 2a ba 57 38 11 bc 9a 5d 59
0...2W.*.W8...]Y
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000030: ed ca 23 06 06 00 00 00 01 04 06 ac 10 01 1e 20
..#.............
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000040: 06 57 4c 43 32 1a 0c 00 00 37 63 01 06 00 00 00
.WLC2....7c.....
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000050: 01 1f 0a 32 30 2e 30 2e 30 2e 31 1e 0d 31 37 32
...20.0.0.1..172
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000060: 2e 31 36 2e 31 2e 33 30 .16.1.30
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000000: 02 1a 00 46 3f cf 1b cc e4 ea 41 3e 28 7e cc bc
...F?.....A>(~..
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000010: 00 e1 61 ae 1a 0c 00 00 37 63 02 06 00 00 00 03
..a.....7c......
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000020: 06 06 00 00 00 01 19 20 37 d0 03 e6 00 00 01 37
........7......7
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000030: 00 01 ac 10 01 01 01 c7 7a 8b 35 20 31 80 00 00
........z.5.1...
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00000040: 00 00 00 00 00 1b ......
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: ****Enter processIncomingMessages: response code=2
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: ****Enter processRadiusResponse: response code=2
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00:40:96:ac:e6:57 Access-Accept received from RADIUS server
172.16.1.1 for mobile 00:40:96:ac:e6:57 receiveId = 0
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: AuthorizationResponse: 0x9802520
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: structureSize................................114
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: resultCode...................................0
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: protocolUsed.................................0x00000001
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: proxyState...................................
00:40:96:AC:E6:57-00:00
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: Packet contains 3 AVPs:
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: AVP[01] Airespace / QOS-Level....................
0x00000003 (3) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: AVP[02] Service-Type.............................
0x00000001 (1) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: AVP[03] Class....................................
DATA (30 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00:40:96:ac:e6:57 Applying new AAA override for station
00:40:96:ac:e6:57
Wed Apr 18 18:15:08 2007: 00:40:96:ac:e6:57 Override values for station 00:40:96:ac:e6:57
source: 48, valid bits: 0x3
qosLevel: 3, dscp: 0xffffffff, dot1pTag: 0xffffffff, sessionTimeout: -1
dataAvgC: -1, rTAvgC: -1, dataBurstC: -1, rTimeBurstC: -1
vlanIfName: '', aclName: '
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AccountingMessage Accounting Start: 0xa64c8bc
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: Packet contains 13 AVPs:
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[01] User-Name................................
User-VLAN10 (11 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[02] Nas-Port.................................
0x00000001 (1) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[03] Nas-Ip-Address...........................
0xac10011e (-1408237282) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[04] NAS-Identifier...........................
0x574c4332 (1464615730) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[05] Airespace / WLAN-Identifier..............
0x00000001 (1) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[06] Acct-Session-Id..........................
4626602c/00:40:96:ac:e6:57/16 (29 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[07] Acct-Authentic...........................
0x00000001 (1) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[08] Tunnel-Type..............................
0x0000000d (13) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[09] Tunnel-Medium-Type.......................
0x00000006 (6) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[10] Tunnel-Group-Id..........................
0x3230 (12848) (2 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[11] Acct-Status-Type.........................
0x00000001 (1) (4 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[12] Calling-Station-Id.......................
20.0.0.1 (8 bytes)
Wed Apr 18 18:15:12 2007: AVP[13] Called-Station-Id........................
172.16.1.30 (11 bytes)
As you can see from the output, the user is authenticated. Then, AAA override values are returned with the RADIUS accept message. In this case, the user is given the QoS policy of Bronze.
You can verify this on the WLC GUI as well. Here is an example:
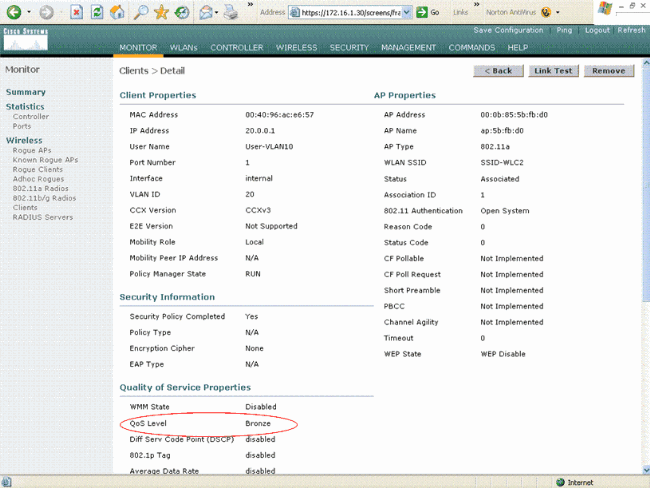
Note: The default QoS profile for this SSID is Silver. However, because AAA override is selected and the user is configured with a QoS profile of Bronze on the IAS server, the default QoS profile is overridden.
Troubleshoot
You can use the debug aaa all enable command on the WLC to troubleshoot the configuration. An example of the output of this debug in a working network is shown in the Verify section of this document.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)























 Feedback
Feedback