Configure DHCP OPTION 43 for Lightweight Access Points
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to use DHCP Option 43 for lightweight access points.
Prerequisites
The document provides sample configurations for DHCP Option 43 for lightweight Cisco Aironet access points (LAPs) for these DHCP servers:
-
Microsoft Windows 2008 Enterprise DHCP Server
-
Cisco IOS® DHCP Server
-
Linux Internet Systems Consortium (ISC) DHCP Server
-
Cisco Network Registrar DHCP Server
-
Lucent QIP DHCP Server
When a Cisco Wireless Unified architecture is deployed, the LAPs can use a vendor-specific DHCP Option 43 to join specific Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs) when the WLC is in a different subnet than the LAP. Refer to Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Point Basic Configuration Example and Lightweight AP (LAP) Registration to a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) for information on how to configure an access point (AP) to join a WLC.
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
Basic knowledge on Cisco Unified Wireles Network (CUWN)
-
Basic knowledge of DHCP
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Vendor Specific DHCP Options
RFC 2132 defines two DHCP Options that are relevant to vendor specific options. They are Option 60 and Option 43. DHCP Option 60 is the Vendor Class Identifier (VCI). The VCI is a text string that uniquely identifies a type of vendor device. This table lists the VCIs used by Cisco APs:
| Access Point | Vendor Class Identifier (VCI) |
| Cisco Aironet 1530 Series | Cisco AP c1530 |
| Cisco 3201 Lightweight Access Point | Cisco Bridge/AP/WGB c3201 |
| Cisco 521 Wireless Express Access Point | Cisco AP c520 |
| AP801 (embedded in 86x/88x Series ISRs) | Cisco AP801 |
| Cisco Aironet 3600 Series | Cisco AP c3600 |
| AP802 (embedded in 88x Series ISRs) | Cisco AP802 |
| Cisco Aironet 2700 Series | Cisco AP c27006 |
| Cisco Aironet 3700 Series | Cisco AP c37007 |
| Cisco Aironet 700 Series | Cisco AP c7006 |
| Cisco Aironet 1600 Series | Cisco AP c1600 |
| Cisco Aironet 1700 Series |
Cisco AP c1700 |
| Cisco Aironet 1800s Series |
Cisco AP c1800 |
| Cisco Aironet 1810 Series (incl OEAP) |
Cisco AP c1810 |
| Cisco Aironet 1815 Series (I,W,T) |
Cisco AP c18159 |
| ISR-AP1100AC (embedded in C1100 series ISR) |
Cisco AP c1815 |
| Cisco Aironet 1830 Series |
Cisco AP c1830 |
| Cisco Aironet 1840 Series |
Cisco AP c1840 |
| Cisco Aironet 1850 Series | Cisco AP c1850 |
|
Cisco Industrial Wireless 3700 Series |
Cisco AP iw3702 |
|
Cisco Aironet 1570 series |
Cisco AP c1570 |
| Cisco Aironet 3800 series | Cisco AP c3800 |
| Cisco Aironet 2800 series | Cisco AP c2800 |
| Cisco Aironet 4800 series | Cisco AP c4800 |
| Cisco Aironet 1560 Series | Cisco AP c1560 |
| Cisco Aironet 1540 Series8 | Cisco AP c1540 |
| 6300 Series Embedded Services Access Points | Cisco AP ESW6300 |
| Catalyst IW6300 Heavy Duty Series Access Points | Cisco AP IW6300 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9105AX Series | Cisco AP C9105AX |
| Cisco Catalyst 9115AX Series | Cisco AP C9115AX |
| Cisco Catalyst 9117AX Series | Cisco AP C9117AX |
| Cisco Catalyst 9120AX Series | Cisco AP C9120AX |
| Cisco Catalyst 9124AX Series | Cisco AP C9124AX |
| Cisco Catalyst 9130AX Series | Cisco AP C9130AX |
| Cisco Catalyst 9136 Series | Cisco AP C9136¹ |
| Cisco 9162 Series | Cisco AP CW9162 |
| Cisco 9164 Series | Cisco AP CW9164 |
| Cisco 9166 Series | Cisco AP CW9166 |
| Cisco 9176I | Cisco Wireless AP CW9176I |
| Cisco 9178I | Cisco Wireless AP CW9178I |
¹ Early manufactured 9136 can ship with a software that send "Cisco AP" in the option 60. This was fixed in 17.8 and later software versions.
6Any 2700/700/1530 Series AP that runs 7.6 or later
7Any 3700 Series AP that runs 7.6 or later software
81540s that run pre-FCS manufacturing code can use "Cisco AP c1560"
91815s that run pre-FCS manufacturing code can use "Cisco AP c1810"
Also, see the the Cisco Wireless Solutions Software Compatibility Matrix.
Option 60 is included in the initial DHCP discover message that a DHCP client broadcasts in search of an IP address. Option 60 is used by DHCP clients (LAPs in this case) in order to identify itself to the DHCP server.
Leveraging option 60 is not a required and your DHCP pools can return option 43 for any type of clients. However, the DHCP server can be programmed in order to return one or more WLAN controller management interface IP addresses based on the VCI of the AP. In order to do this, program the DHCP server to recognize the VCI for each access point type, and then define the vendor specific information.
On the DHCP server, the vendor specific information is mapped to VCI text strings. When the DHCP server sees a recognizable VCI in a DHCP discover from a DHCP client, it returns the mapped vendor specific information in its DHCP offer to the client as DHCP Option 43. On the DHCP server , option 43 is defined in each DHCP pool (Scope) that offers IP address to the LAPs.
RFC 2132 defines that DHCP servers must return vendor specific information as DHCP Option 43. The RFC allows vendors to define encapsulated vendor-specific sub-option codes between 0 and 255. The sub-options are all included in the DHCP offer as type-length-value (TLV) blocks embedded within Option 43. The definition of the sub-option codes and their related message format is left to the vendors.
Option 43 Format explained
The classic WLC provision method (f1xxx)
When DHCP servers are programmed to offer WLAN Controller IP addresses as Option 43 for Cisco Aironet LAPs, the sub-option TLV block is defined in this way:
-
Type - 0xf1 (decimal 241).
-
Length - Number of controller IP addresses * 4.
-
Value - List of the WLC management interfaces, typically translated to hexadecimal values.
Examples :
- If you want to provision WLC IP address 192.168.1.10 for your APs, use option 43 0xf104.c0a8.010a
f1 for the option type. 04 because you only provide one WLC IP address (so the length is 4). c0 is 192 in hex. a8 is 168 in hex. 01 is 01 in hex and 01 is 10 in hex.
- If you want to provision WLC IP addresses 192.168.1.10 and 192.168.1.11 for your APs, use option 43 0xf108.c0a8.010a.c0a8.010b
-
f1 for the option type. 08 because you provide two WLC IP addresses (so the length is 2*4). c0 is 192 in hex. a8 is 168 in hex. 01 is 01 in hex and 01 is 10 in hex. and we repeat the second address with 0b at the end for "11".
The EWC conversion method(f2xxx)
It is possible to convert a group of APs from EWC to CAPWAP mode via option 43 by using the F2 start.
- F2<size><WLC-IP(s)>
- F2 is the type
- Size is the number of WLC IP adresses provided multiplied by 4 + 1
- Example : f205c0a88202 gives the WLC IP address 192.168.130.2 and convertrs the AP to CAPWAP mode
The fast offline migration(f3xxx)
The option 43 string for DHCPv4 Fast offline migration allows to auto-convert a Wi-Fi7 AP between Catalyst and Meraki mode and is as follows:
- F3 <size> <IP array> Mode=<1|2>, where Mode = 1 -> Meraki and 2 -> Catalyst
- Example String:
o f305ac10011802 (“normal” option 43 “f104ac100118” becomes “f305ac10011802”)
- Change type from f1 to f3
- Change length from 04 to 05 (because we are adding "01" or "02" at the end of the WLC IPs to precise which mode is desired), or 09 in case of 2 WLC IPs (so basically <amount of WLC IPs provided> * 4 + 1)
- Add the suboption at the end; 01 for Meraki, 02 for Catalyst
- IOS/IOS-XE configuration example for WLC discovery using DHCPv4:
ip dhcp pool vlan192
network 192.168.200.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 192.168.200.1
option 43 hex f305.ac10.0118.02
Refer to the Global Use AP deployment guide for more details on this mode.
The semantics of DHCP server configuration vary based on the DHCP server vendor. This document contains specific instructions on the Microsoft DHCP server, Cisco IOS DHCP server, Linux ISC DHCP Server, Cisco Network Registrar DHCP server, and Lucent QIP DHCP Server. For other DHCP server products, consult the vendor documentation for instructions on vendor specific options.
Configure
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Microsoft DHCP Server
This section describes the configurations necessary on the Microsoft DHCP server in order to use DHCP Option 43 for WLAN Controller discovery.
Cisco Lightweight Access Points
The method described in the previous section can be used if you have multiple device types on the same scope and you want them to receive different WLC IP addresses via Option 43. But, if all of the DHCP clients in the scope are Cisco IOS APs, you can use this procedure to define DHCP Option 43.
Before you begin, you must know this information:
-
Option 43 sub-option code
-
Management IP address(es) of WLAN controller(s)
Complete these steps in order to define DHCP Option 43 on the Windows DHCP server:
-
In the DHCP Server scope, right-click Server Options and choose Configure Options.
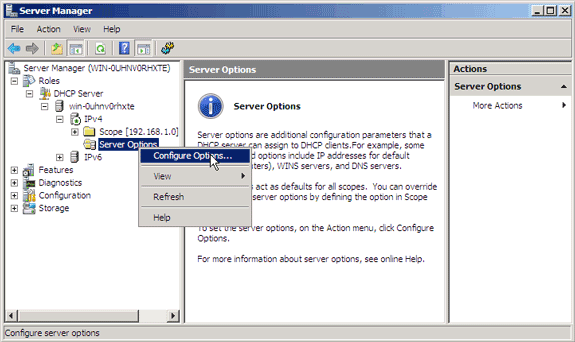
-
On the General tab, scroll to Option 43 and check the 043 Vendor Specific Info check bo
-
Enter the Option 43 sub-option in hex.
Note: TLV values for the Option 43 suboption: Type + Length + Value. Type is always the suboption code 0xf1. Length is the number of controller management IP addresses times 4 in hex. Value is the IP address of the controller listed sequentially in hex. For example, suppose there are two controllers with management interface IP addresses, 192.168.10.5 and 192.168.10.20. The type is 0xf1. The length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 0x08. The IP addresses translates to c0a80a05 (192.168.10.5) and c0a80a14 (192.168.10.20). When the string is assembled, it yields f108c0a80a05c0a80a14. The Cisco IOS command that is added to the DHCP scope is option 43 hex f108c0a80a05c0a80a14.
-
Click Apply and then click OK.
Once you complete this step, the DHCP Option 43 is configured and the DHCP server sends the option 43 to the LAPs.

Cisco IOS® DHCP Server
Cisco Aironet APs (Cisco IOS)
Complete these steps in order to configure DHCP Option 43, in the embedded Cisco IOS DHCP server, for all Cisco Aironet APs that run Cisco IOS. This includes all APs except for the VxWorks 1000 Series (see the next section) and the 600 Series OEAP which does not use Option 43.
-
Enter configuration mode at the Cisco IOS CLI.
-
Create the DHCP pool, which includes the necessary parameters such as the default router and server name. This is an example DHCP scope:
ip dhcp pool <pool name>
network <ip network> <netmask>
default-router <default-router IP address>
dns-server <dns server IP address> -
Add the Option 43 line with this syntax:
option 43 hex <hexadecimal string>
The hexadecimal string in step 3 is assembled as a sequence of the TLV values for the Option 43 suboption: Type + Length + Value. Type is always the suboption code 0xf1. Length is the number of controller management IP addresses times 4 in hex. Value is the IP address of the controller listed sequentially in hex.
For example, suppose there are two controllers with management interface IP addresses, 192.168.10.5 and 192.168.10.20. The type is 0xf1. The length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 0x08. The IP addresses translate to c0a80a05 (192.168.10.5) and c0a80a14 (192.168.10.20). When the string is assembled, it yields f108c0a80a05c0a80a14. The Cisco IOS command that is added to the DHCP scope is:
option 43 hex f108c0a80a05c0a80a14
Linux ISC DHCP Server
The information in this section describes how the Linux ISC server is configured in order to return vendor specific information to lightweight Cisco Aironet Series APs. This example configures the Linux ISC server to return vendor specific information to the 1140, 1200, 1130 and 1240 Series Lightweight APs. This configuration can be modified and applied to other series of LAPs.
ddns-update-style interim;
allow bootp;
option space Cisco_LWAPP_AP;
option Cisco_LWAPP_AP.server-address code 241 = array of ip-address;
subnet 192.168.247.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
authoritative;
option routers 192.168.247.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option domain-name "cisco.com";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.247.2, 192.168.247.3;
range dynamic-bootp 192.168.247.11 192.168.247.254;
default-lease-time 300;
class "Cisco-AP-c1140" {
match if option vendor-class-identifier = "Cisco AP c1140";
option vendor-class-identifier "Cisco AP c1140";
vendor-option-space Cisco_LWAPP_AP;
option Cisco_LWAPP_AP.server-address 192.168.247.5; }
class "Cisco AP c1200" {
match if option vendor-class-identifier = "Cisco AP c1200";
option vendor-class-identifier "Cisco AP c1200";
vendor-option-space Cisco_LWAPP_AP;
option Cisco_LWAPP_AP.server-address 192.168.247.55; }
class "Cisco AP c1130" {
match if option vendor-class-identifier = "Cisco AP c1130";
option vendor-class-identifier "Cisco AP c1130";
vendor-option-space Cisco_LWAPP_AP;
option Cisco_LWAPP_AP.server-address 192.168.247.5; }
class "Cisco AP c1240" {
match if option vendor-class-identifier = "Cisco AP c1240";
option vendor-class-identifier "Cisco AP c1240";
vendor-option-space Cisco_LWAPP_AP;
option Cisco_LWAPP_AP.server-address 192.168.247.5; }
}
Cisco Network Registrar DHCP Server
The Cisco Network Registrar DHCP server supports Vendor Specific attributes. Refer to the product documentation : https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/prime/network_registrar/11-2/dhcp/guide/DHCP_Guide/DHCP_Guide_chapter_0110.html?bookSearch=true#task_jsq_sdr_1nb
Lucent QIP DHCP Server
This section provides a few tips for how to configure the Lucent QIP DHCP server in order to return vendor specific information to lightweight Cisco Aironet Series APs.
Note:For complete information and the steps involved, refer to the documentation provided by the vendor.
The DHCP Option 43 can contain any vendor specific information. The DHCP server passes this information in the form of a hex string to the clients that receive the DHCP offer.
On the Lucent QIP DHCP server, the vendor-specific information can be provided on the DHCP Option Template- Modify page. In the Active Options area, choose Vendor Specific Information, and enter the information in the Value field.
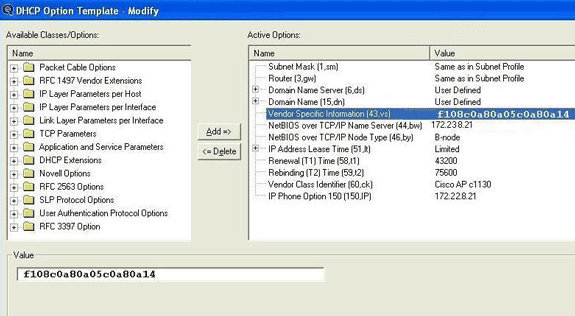
In order to include the controller IP addresses in the DHCP option 43 message, enter the information to the DHCP Option template in QIP as a single hex value: [ip hex].
In order to send more than one IP address with DHCP Option 43, enter the information to the DHCP Option template in QIP as a single hex value:[ip hex ip hex] and not [ip hex],[ip hex]. In this case, the comma in the middle causes problems for DHCP to parse the string passed from QIP.
For example, suppose there are two controllers with management interface IP addresses, 192.168.10.5 and 192.168.10.20. The type is 0xf1. The length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 0x08. The IP addresses translate to c0a80a05 (192.168.10.5) and c0a80a14 (192.168.10.20). When the string is assembled, it yields f108c0a80a05c0a80a14. On the Lucent QIP DHCP server, the hex string that needs to be added to the DHCP scope is:
[f108c0a80a05c0a80a14]
The hex string must be given within square brackets. The square brackets are mandatory. Once the DHCP option 43 is modified to reflect this value, the LAPs are able to find and register with the controller.
Verify
Use this section in order to verify your configuration.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) supports certain show commands. Use the Output Interpreter Tool in order to view an analysis of show command output.
If you use 1130 /1200/1230/1240 Series LAPs, which have a console port, you can check that the WLC IP addresses are provided to the LAPs during DHCP IP address assignment. This is a sample output from a Cisco 1230 Series LAP:
*Mar 1 00:00:17.497: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Dot11Radio1, changed state to down
*Mar 1 00:00:17.898: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Dot11Radio0, changed state to down
*Mar 1 00:00:25.352: %DOT11-6-FREQ_USED: Interface Dot11Radio0, frequency
2447 selected
*Mar 1 00:00:25.353: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state
to up
*Mar 1 00:00:26.352: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
*Mar 1 00:00:29.440: %LWAPP-5-CHANGED: LWAPP changed state to DISCOVERY
*Mar 1 00:00:29.475: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state
to reset
*Mar 1 00:00:29.704: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio1, changed state
to up
*Mar 1 00:00:30.121: Logging LWAPP message to 255.255.255.255.
%SYS-6-LOGGINGHOST_STARTSTOP: Logging to host 255.255.255.255 started - CLI
initiated
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Dot11Radio1, changed state to reset
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio1, changed state to up
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to reset
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio1, changed state
to up
Translating "CISCO-LWAPP-CONTROLLER"...domain server (255.255.255.255)
%DHCP-6-ADDRESS_ASSIGN: Interface FastEthernet0 assigned DHCP address
A.B.C.D, mask 255.0.0.0, hostname AP001b.d4e3.a81b
%LWAPP-3-CLIENTEVENTLOG: Controller address 192.168.10.5 obtained through DHCP
%LWAPP-3-CLIENTEVENTLOG: Controller address 192.168.10.5 obtained through DHCP
If you use a Cisco IOS DHCP server, enter the show ip dhcp binding command in order to view the list of the DHCP addresses assigned to DHCP clients. Here is an example:
2800-ISR-TSWEB#show ip dhcp binding
Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF:
IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type
Hardware address/
User name
192.168.25.1 000b.855b.fbd0 Jun 29 2007 11:49 AM Automatic
On the WLC CLI, you can enter the show ap summary command in order to verify that the APs registered with the WLC. Here is an example:
((Cisco Controller) >show ap summary
AP Name Slots AP Model Ethernet MAC Location Port
------------- ----- --------- ----------------- ---------------- ----
ap:5b:fb:d0 2 AP1010 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 default_location 1
If you have Wireless LANs configured, you can enter the show client summary command in order to see the clients that are registered with the WLC:
(Cisco Controller) >show client summary
Number of Clients................................ 1
MAC Address AP Name Status WLAN Auth Protocol Port
----------------- ------------- ------------- ---- ---- -------- ----
00:40:96:a1:45:42 ap:64:a3:a0 Associated 4 Yes 802.11a 1
Troubleshoot
Use this section in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) supports certain show commands. Use the Output Interpreter Tool in order to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
Enter the debug dhcp message enable command on the WLC in order to view the sequence of events that occur between the DHCP server and client. Here is an example:
(Cisco Controller) >Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0
dhcp option len,
including the magic cookie = 38
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option:
received DHCP DISCOVER msg
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option:
skipping option 57, len 2
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option:
skipping option 55, len 6
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option:
vendor class id = Airespace.AP1200 (len 16)
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcpParseOptions: options end,
len 38, actual 64
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: dhcpd: sending 300 bytes raw
0.0.0.0:68 -> 10.77.244.212:1067
Thu Jun 28 17:07:53 2007: dhcpd: Received 300 byte dhcp packet
from 0xd4f44d0a 10.77.244.212:68
Thu Jun 28 17:07:58 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option len, including
the magic cookie = 50
Thu Jun 28 17:07:58 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option: received DHCP
REQUEST msg
Thu Jun 28 17:07:58 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option: requested ip =
192.168.25.1
Thu Jun 28 17:07:58 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option: server id =
192.168.25.10
Thu Jun 28 17:07:58 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option: skipping option 57,
len 2
Thu Jun 28 17:07:58 2007: 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 dhcp option: skipping option 55,
len 6
This is the debug lwapp packet enable command output from the WLC that indicates that DHCP option 43 is used as the discovery method in order to discover WLC IP addresses:
Thu Jun 28 17:51:47 2007: Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0
to 00:0b:85:33:84:a0 on port '1'
Thu Jun 28 17:51:47 2007: Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response
to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 1
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: Start of Packet
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: Ethernet Source MAC (LRAD): 00:D0:58:AD:AE:CB
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: Msg Type :
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: DISCOVERY_REQUEST
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: Msg Length : 31
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: Msg SeqNum : 0
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007:
IE : UNKNOWN IE 58
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: IE Length : 1
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: Decode routine not available, Printing Hex Dump
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007: 00000000: 03 .
Thu Jun 28 19:22:39 2007:
The value of the IE 58 parameter indicates the discovery type. For DCHP Option 43 it is 3.
If you use the Cisco IOS DHCP server on the router, you can enter the debug dhcp detail command and the debug ip dhcp server events command in order to view the DHCP client and server activity. Here is an example from the debug ip dhcp server events command:
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: Sending notification of DISCOVER:
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 000b.855b.fbd0
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: remote id 020a0000c0a8190a01000000
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: circuit id 00000000
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: Seeing if there is an internally specified
pool class:
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 000b.855b.fbd0
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: remote id 020a0000c0a8190a01000000
*Jun 28 11:49:33.107: DHCPD: circuit id 00000000
*Jun 28 11:49:38.603: DHCPD: Sending notification of ASSIGNMENT:
*Jun 28 11:49:38.603: DHCPD: address 192.168.25.1 mask 255.255.255.0
*Jun 28 11:49:38.603: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 000b.855b.fbd0
*Jun 28 11:49:38.603: DHCPD: lease time remaining (secs) = 86400
*Jun 28 11:49:38.607: DHCPD: Sending notification of ASSIGNMENT:
*Jun 28 11:49:38.607: DHCPD: address 192.168.25.1 mask 255.255.255.0
*Jun 28 11:49:38.607: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 000b.855b.fbd0
*Jun 28 11:49:38.607: DHCPD: lease time remaining (secs) = 86400
Enter the show ip dhcp binding command in order to view the list of the DHCP addresses assigned to DHCP clients.
2800-ISR-TSWEB#show ip dhcp binding
Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF:
IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type
Hardware address/
User name
192.168.25.1 000b.855b.fbd0 Jun 29 2007 11:49 AM Automatic
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
5.0 |
21-Dec-2024 |
Updated with Wi-Fi7 APs |
4.0 |
17-Sep-2024 |
Updated the Network Registrar section |
3.0 |
03-Nov-2022 |
Added recent AP models |
2.0 |
05-Apr-2022 |
Add multiple new AP VCI values |
1.0 |
28-Jul-2014 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Surendra BGCisco Engineering
- Shankar RamanathanCisco TAC
- Nicolas DarchisCisco TAC
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback