Unified Wireless Network Local EAP Server Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the configuration of a local Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) server in a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) for the authentication of wireless users.
Local EAP is an authentication method that allows users and wireless clients to be authenticated locally. It is designed for use in remote offices that want to maintain connectivity to wireless clients when the back-end system becomes disrupted or the external authentication server goes down. When you enable local EAP, the controller serves as the authentication server and the local user database, thereby removing dependence on an external authentication server. Local EAP retrieves user credentials from the local user database or the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) back-end database to authenticate users. Local EAP supports Lightweight EAP (LEAP), EAP-Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST), and EAP-Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) authentication between the controller and wireless clients.
Note that the local EAP server is not available if there is a global external RADIUS server configuration in the WLC. All authentication requests are forwarded to the global external RADIUS until the Local EAP Server is available. If the WLC looses connectivity to the external RADIUS server, then the local EAP server becomes active. If there is no global RADIUS server configuration, the local EAP server becomes immediately active. The local EAP server cannot be used to authenticate clients, which are connected to other WLCs. In other words, one WLC cannot forward its EAP request to another WLC for authentication. Every WLC should have its own local EAP server and individual database.
Note: Use these commands in order to stop WLC from sending requests to an external radius server .
config wlan disable
config wlan radius_server auth disable
config wlan enable
The local EAP server supports these protocols in 4.1.171.0 software release and later:
-
LEAP
-
EAP-FAST (both username/password, and certificates)
-
EAP-TLS
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
Knowledge of how to configure WLCs and lightweight access points (LAPs) for basic operation
-
Knowledge of Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) and wireless security methods
-
Basic knowledge of local EAP authentication.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Windows XP with CB21AG Adapter Card and Cisco Secure Services Client Version 4.05
-
Cisco 4400 Wireless LAN Controller 4.1.171.0
-
Microsoft Certification Authority on Windows 2000 server
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure Local EAP on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
This document assumes that the basic configuration of the WLC is already completed.
Local EAP Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure Local EAP:
-
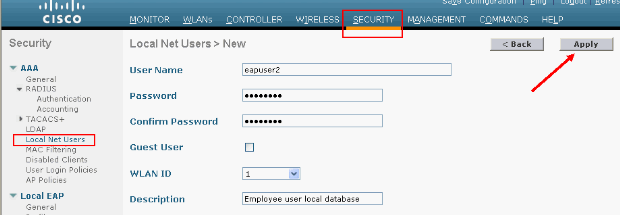
Add a local net user:
From the GUI. choose Security > Local Net Users > New, enter the User Name, Password, Guest User, WLAN ID, and Description and click Apply.
From the CLI you can use the config netuser add <username> <password> <WLAN id> <description> command:
Note: This command has been brought down to a second line due to spatial reasons.
(Cisco Controller) >config netuser add eapuser2 cisco123 1 Employee user local database -
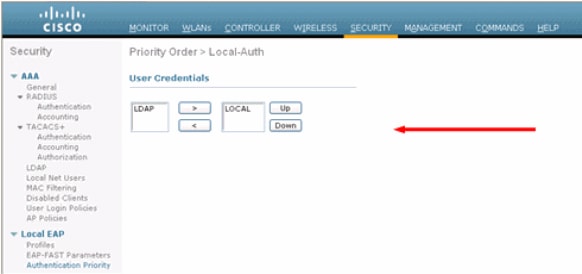
Specify the user credential retrieval order.
From the GUI, choose Security > Local EAP > Authentication Priority. Then select LDAP, click the "<" button and click Apply. This puts the user credentials in the local database first.
From the CLI:
(Cisco Controller) >config local-auth user-credentials local
-
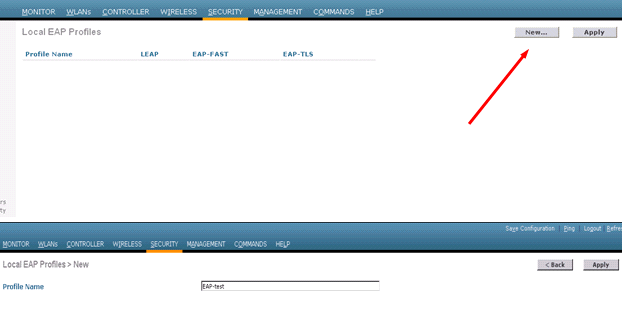
Add an EAP profile:
In order to do this from the GUI, choose Security > Local EAP > Profiles and click New. When the new window appears, type the Profile Name and click Apply.
You can also do this using the CLI command config local-auth eap-profile add <profile-name>. In our example, the profile name is EAP-test.
(Cisco Controller) >config local-auth eap-profile add EAP-test -
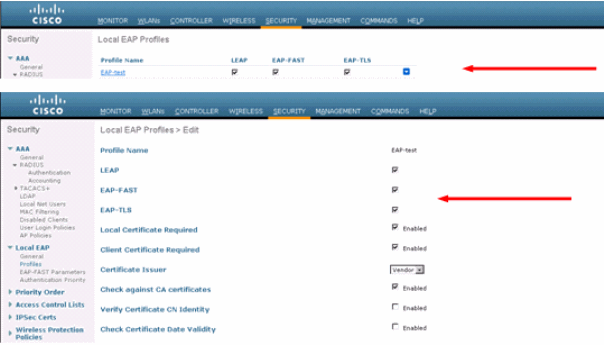
Add a method to the EAP profile.
From the GUI choose Security > Local EAP > Profiles and click on the profile name for which you want to add the authentication methods. This example uses LEAP, EAP-FAST, and EAP-TLS. Click Apply in order to set the methods.
You can also use the CLI command config local-auth eap-profile method add <method-name> <profile-name> . In our example configuration we add three methods to the profile EAP-test. The methods are LEAP, EAP-FAST, and EAP-TLS whose method names are leap, fast, and tls respectively. This output shows the CLI configuration commands:
(Cisco Controller) >config local-auth eap-profile method add leap EAP-test (Cisco Controller) >config local-auth eap-profile method add fast EAP-test (Cisco Controller) >config local-auth eap-profile method add tls EAP-test
-
Configure the parameters of the EAP method. This is only used for EAP-FAST. The parameters to be configured are:
-
Server Key (server-key)—Server key to encrypt/decrypt Protected Access Credentials (PACs) (in hexadecimal).
-
Time to Live for PAC (pac-ttl)—Sets the Time to Live for the PAC.
-
Authority ID (authority-id) —Sets the authority identifier.
-
Annonymous Provision (anon-provn)—Configures whether anonymous provision is allowed. This is enabled by default.
For configuration through the GUI, choose Security > Local EAP > EAP-FAST Parameters and enter the Server key, Time to live for the PAC, authority ID (in hex), and Authority ID Information values.
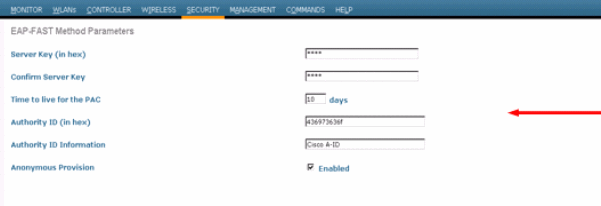
These are the CLI configuration commands to use in order to set these parameters for EAP-FAST:
(Cisco Controller) >config local-auth method fast server-key 12345678 (Cisco Controller) >config local-auth method fast authority-id 43697369f1 CiscoA-ID (Cisco Controller) >config local-auth method fast pac-ttl 10
-
-
Enable local authentication per WLAN:
From the GUI choose WLANs on the top menu and select the WLAN for which you want to configure local authentication. A new window appears. Click the Security > AAA tabs. Check Local EAP authentication and select the right EAP Profile Name from the pull-down menu as this example shows:
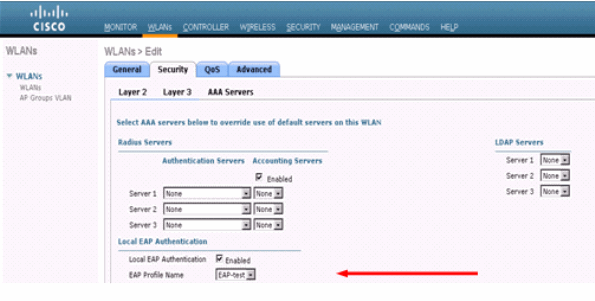
You can also issue the CLI config wlan local-auth enable <profile-name> <wlan-id> configuration command as shown here:
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan local-auth enable EAP-test 1
-
Set the Layer 2 Security parameters.
From the GUI interface, in the WLAN Edit window go to the Security > Layer 2 tabs and chose WPA+WPA2 from the Layer 2 Security pull-down menu. Under the WPA+WPA2 Parameters section, set the WPA Encryption to TKIP and WPA2 Encryption AES. Then click Apply.
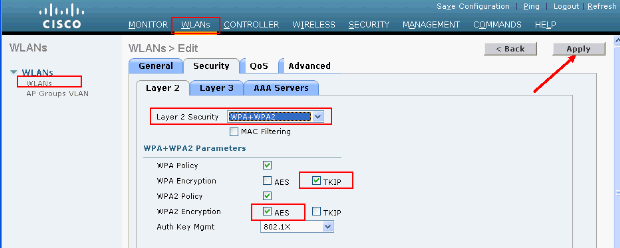
From the CLI, use these commands:
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa enable 1 (Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa wpa1 ciphers tkip enable 1 (Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa wpa2 ciphers aes enable 1
-
Verify the configuration:
(Cisco Controller) >show local-auth config User credentials database search order: Primary ..................................... Local DB Timer: Active timeout .............................. Undefined Configured EAP profiles: Name ........................................ EAP-test Certificate issuer ........................ cisco Peer verification options: Check against CA certificates ........... Enabled Verify certificate CN identity .......... Disabled Check certificate date validity ......... Enabled EAP-FAST configuration: Local certificate required .............. No Client certificate required ............. No Enabled methods ........................... leap fast tls Configured on WLANs ....................... 1 EAP Method configuration: EAP-FAST: --More-- or (q)uit Server key ................................ <hidden> TTL for the PAC ........................... 10 Anonymous provision allowed ............... Yes Authority ID .............................. 43697369f10000000000000000000 Authority Information ..................... CiscoA-IDYou can see specific parameters of wlan 1 with the show wlan <wlan id> command:
(Cisco Controller) >show wlan 1 WLAN Identifier.................................. 1 Profile Name..................................... austinlab Network Name (SSID).............................. austinlab Status........................................... Disabled MAC Filtering.................................... Disabled Broadcast SSID................................... Enabled AAA Policy Override.............................. Disabled Number of Active Clients......................... 0 Exclusionlist Timeout............................ 60 seconds Session Timeout.................................. 1800 seconds Interface........................................ management WLAN ACL......................................... unconfigured DHCP Server...................................... Default DHCP Address Assignment Required................. Disabled Quality of Service............................... Silver (best effort) WMM.............................................. Disabled CCX - AironetIe Support.......................... Enabled CCX - Gratuitous ProbeResponse (GPR)............. Disabled Dot11-Phone Mode (7920).......................... Disabled Wired Protocol................................... None --More-- or (q)uit IPv6 Support..................................... Disabled Radio Policy..................................... All Local EAP Authentication......................... Enabled (Profile 'EAP-test') Security 802.11 Authentication:........................ Open System Static WEP Keys............................... Disabled 802.1X........................................ Disabled Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2)............. Enabled WPA (SSN IE)............................... Enabled TKIP Cipher............................. Enabled AES Cipher.............................. Disabled WPA2 (RSN IE).............................. Enabled TKIP Cipher............................. Disabled AES Cipher.............................. Enabled Auth Key Management 802.1x.................................. Enabled PSK..................................... Disabled CCKM.................................... Disabled CKIP ......................................... Disabled IP Security................................... Disabled IP Security Passthru.......................... Disabled Web Based Authentication...................... Disabled --More-- or (q)uit Web-Passthrough............................... Disabled Conditional Web Redirect...................... Disabled Auto Anchor................................... Disabled Cranite Passthru.............................. Disabled Fortress Passthru............................. Disabled H-REAP Local Switching........................ Disabled Infrastructure MFP protection................. Enabled (Global Infrastructure MFP Disabled) Client MFP.................................... Optional Tkip MIC Countermeasure Hold-down Timer....... 60 Mobility Anchor List WLAN ID IP Address StatusThere are other local authentication parameters that can be configured, in particular the active timeout timer. This timer configures the period during which local EAP is used after all RADIUS servers have failed.
From the GUI, choose Security > Local EAP > General and set the time value. Then click Apply.
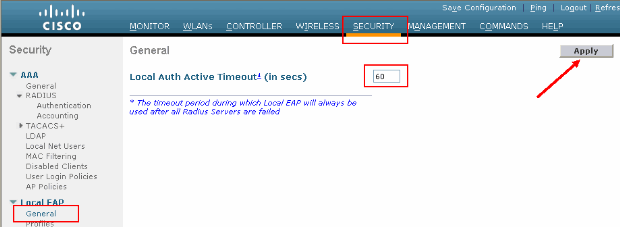
From the CLI, issue these commands:
(Cisco Controller) >config local-auth active-timeout ? <1 to 3600> Enter the timeout period for the Local EAP to remain active, in seconds. (Cisco Controller) >config local-auth active-timeout 60
You can verify the value to which this timer is set up when you issue the show local-auth config command.
(Cisco Controller) >show local-auth config User credentials database search order: Primary ..................................... Local DB Timer: Active timeout .............................. 60 Configured EAP profiles: Name ........................................ EAP-test ... Skip -
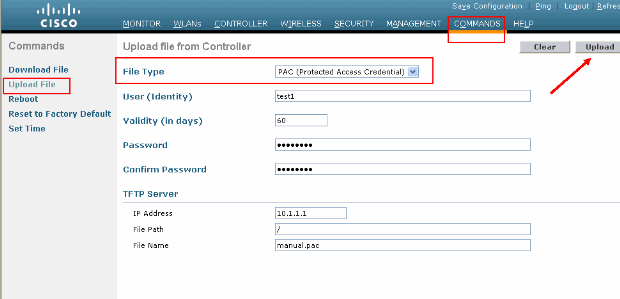
If you need to generate and load the manual PAC, you can use either the GUI or the CLI.
From the GUI, select COMMANDS from the top menu and chose Upload File from the list in the right-hand side. Select PAC (Protected Access Credential) from the File Type pull-down menu. Enter all the parameters and click on Upload.
From the CLI, enter these commands:
(Cisco Controller) >transfer upload datatype pac (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload pac ? username Enter the user (identity) of the PAC (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload pac test1 ? <validity> Enter the PAC validity period (days) (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload pac test1 60 ? <password> Enter a password to protect the PAC (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload pac test1 60 cisco123 (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload serverip 10.1.1.1 (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload filename manual.pac (Cisco Controller) >transfer upload start Mode............................................. TFTP TFTP Server IP................................... 10.1.1.1 TFTP Path........................................ / TFTP Filename.................................... manual.pac Data Type........................................ PAC PAC User......................................... test1 PAC Validity..................................... 60 days PAC Password..................................... cisco123 Are you sure you want to start? (y/N) y PAC transfer starting. File transfer operation completed successfully.
Microsoft Certification Authority
In order to use EAP-FAST version 2 and EAP-TLS authentication, the WLC and all the client devices must have a valid certificate and must also know the public certificate of the Certification Authority.
Installation
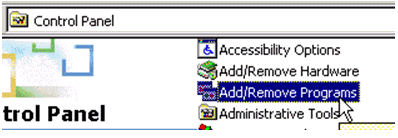
If the Windows 2000 Server does not already have Certification Authority services installed, you need to install it.
Complete these steps in order to activate the Microsoft Certification Authority on a Windows 2000 Server:
-
From the Control Panel, choose Add/Remove Programs. :
-
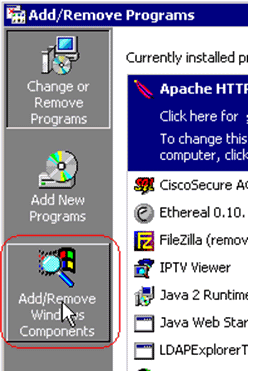
Select Add/Remove Windows Components on the left side.
-
Check Certificate Services.
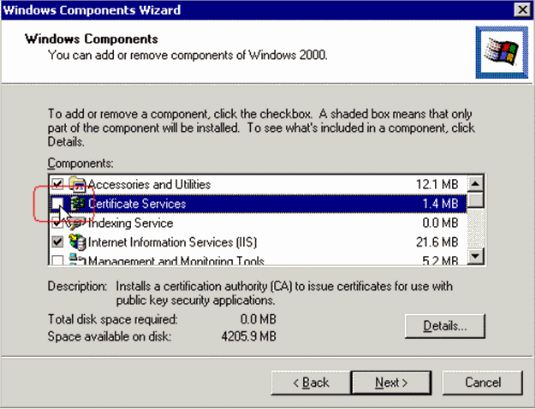
Review this warning before you proceed:
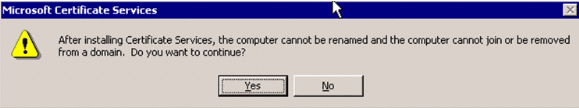
-
Select which type of Certification Authority you want to install. In order to create a simple stand-alone authority, select Stand-alone root CA.
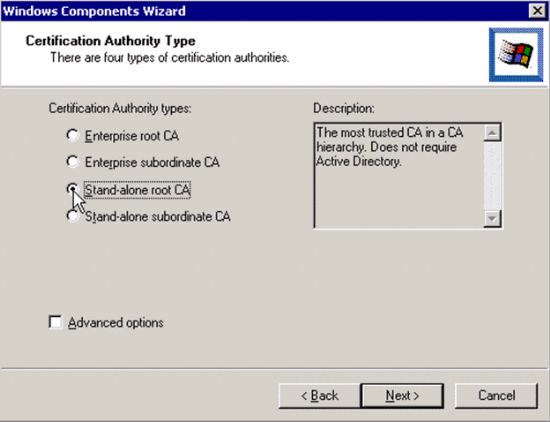
-
Enter the necessary information about the Certification Authority. This information creates a self-signed certificate for your Certification Authority. Remember the CA name that you use.
The Certification Authority stores the certificates in a database. This example uses the default setup proposed by Microsoft:
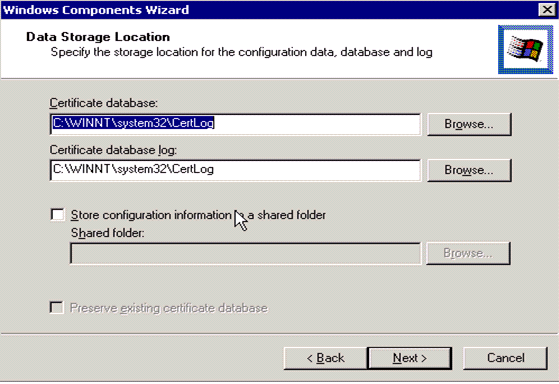
-
Microsoft Certification Authority services use the IIS Microsoft Web Server in order to create and manage client and server certificates. It needs to restart the IIS service for this:
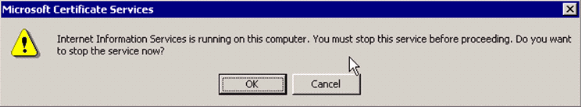
The Microsoft Windows 2000 Server now installs the new service. You need to have your Windows 2000 Server installation CD in order to install new Windows Components.
The Certification Authority is now installed.
Install the Certificate in the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
In order to use EAP-FAST version 2 and EAP-TLS on the local EAP server of a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, follow these three steps:
-
Install the device certificate on the Wireless LAN Controller.
-
Download a Vendor CA Certificate to the Wireless LAN Controller.
Note that in the example shown in this document, the Access Control Server (ACS) is installed on the same host as the Microsoft Active Directory and Microsoft Certification Authority, but the configuration should be the same if the ACS server is on a different server.
Install the Device Certificate on the Wireless LAN Controller
Complete these steps:
-
. Complete these steps in order to generate the certificate to import to the WLC:
-
Go to http://<serverIpAddr>/certsrv.
-
Choose Request a Certificate and click Next.
-
Choose Advanced Request and click Next.
-
Choose Submit a certificate request to this CA using a form and click Next.
-
Choose Web server for Certificate Template and enter the relevant information. Then mark the keys as exportable.
-
You now receive a certificate that you need to install in your machine.
-
-
Complete these steps in order to retrieve the certificate from the PC:
-
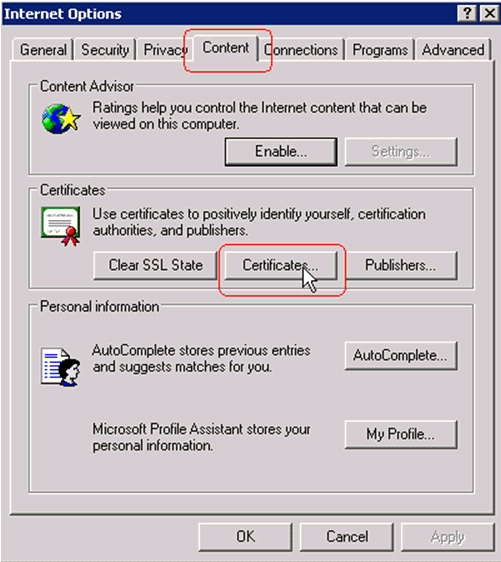
Open an Internet Explorer browser and choose Tools > Internet Options > Content.
-
Click Certificates.
-
Select the newly installed certificate from the pull-down menu.
-
Click Export.
-
Click Next twice and choose Yes export the private key. This format is the PKCS#12 (.PFX format).
-
Choose Enable strong protection.
-
Type a password.
-
Save it in a file <tme2.pfx>.
-
-
Copy the certificate in the PKCS#12 format to any computer where you have Openssl installed in order to convert it to PEM format.
openssl pkcs12 -in tme2.pfx -out tme2.pem !--- The command to be given, -in <inputfilename>. Enter Import Password: !--- Enter the password given previously, from step 2g. MAC verified OK Enter PEM pass phrase: !--- Enter a phrase. Verifying - Enter PEM pass phrase:
-
Download the converted PEM format device certificate onto the WLC.
(Cisco Controller) >transfer download datatype eapdevcert (Cisco Controller) >transfer download certpassword password !--- From step 3. Setting password to <cisco123> (Cisco Controller) >transfer download filename tme2.pem (Cisco Controller) >transfer download start Mode............................................. TFTP Data Type........................................ Vendor Dev Cert TFTP Server IP................................... 10.1.1.12 TFTP Packet Timeout.............................. 6 TFTP Max Retries................................. 10 TFTP Path........................................ / TFTP Filename.................................... tme2.pem This may take some time. Are you sure you want to start? (y/N) y TFTP EAP Dev cert transfer starting. Certificate installed. Reboot the switch to use new certificate.
-
Once rebooted, check the certificate.
(Cisco Controller) >show local-auth certificates Certificates available for Local EAP authentication: Certificate issuer .............................. vendor CA certificate: Subject: C=US, ST=ca, L=san jose, O=cisco, OU=wnbu, CN=tme Issuer: C=US, ST=ca, L=san jose, O=cisco, OU=wnbu, CN=tme Valid: 2007 Feb 28th, 19:35:21 GMT to 2012 Feb 28th, 19:44:44 GMT Device certificate: Subject: C=US, ST=ca, L=san jose, O=cisco, OU=wnbu, CN=tme2 Issuer: C=US, ST=ca, L=san jose, O=cisco, OU=wnbu, CN=tme Valid: 2007 Mar 28th, 23:08:39 GMT to 2009 Mar 27th, 23:08:39 GMT
Download a Vendor CA Certificate to the Wireless LAN Controller
Complete these steps:
-
Complete these steps in order to retrieve the Vendor CA Certificate:
-
Go to http://<serverIpAddr>/certsrv.
-
Choose Retrieve the CA Certificate and click Next.
-
Choose the CA Certificate.
-
Click DER encoded.
-
Click on Download CA certificate and save the certificate as rootca.cer.
-
-
Convert the Vendor CA from DER format into PEM format with the openssl x509 -in rootca.cer -inform DER -out rootca.pem -outform PEM command.
The output file is rootca.pem in the PEM format.
-
Download the Vendor CA Certificate:
(Cisco Controller) >transfer download datatype eapcacert (Cisco Controller) >transfer download filename ? <filename> Enter filename up to 16 alphanumeric characters. (Cisco Controller) >transfer download filename rootca.pem (Cisco Controller) >transfer download start ? (Cisco Controller) >transfer download start Mode............................................. TFTP Data Type........................................ Vendor CA Cert TFTP Server IP................................... 10.1.1.12 TFTP Packet Timeout.............................. 6 TFTP Max Retries................................. 10 TFTP Path........................................ / TFTP Filename.................................... rootca.pem This may take some time. Are you sure you want to start? (y/N) y TFTP EAP CA cert transfer starting. Certificate installed. Reboot the switch to use new certificate.
Configure the Wireless LAN Controller to use EAP-TLS
Complete these steps:
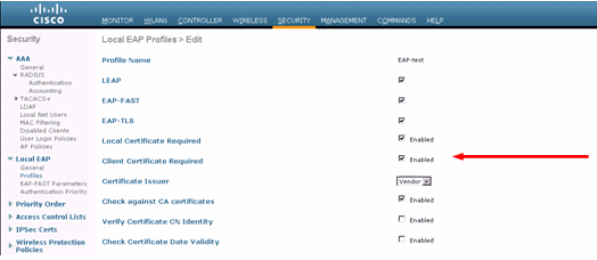
From the GUI, choose Security > Local EAP > Profiles, choose the profile and check for these settings:
-
Local Certificate Required is enabled.
-
Client Certificate Required is enabled.
-
Certificate Issuer is Vendor.
-
Check against CA certificates is enabled.
Install the Certificate Authority Certificate on the Client Device
Download and Install a Root CA Certificate for the Client
The client must obtain a root CA Certificate from a Certification Authority server. There are several methods you can use to obtain a client certificate and install it on the Windows XP machine. In order to acquire a valid certificate, the Windows XP user has to be logged in using their user ID and must have a network connection.
A web browser on the Windows XP client and a wired connection to the network were used to obtain a client certificate from the private root Certification Authority server. This procedure is used to obtain the client certificate from a Microsoft Certification Authority server:
-
Use a web browser on the client and point the browser to the Certification Authority server. In order to do this, enter http://IP-address-of-Root-CA/certsrv.
-
Log in using Domain_Name\user_name. You must log in using the username of the individual who is to use the XP client.
-
On the Welcome window, choose Retrieve a CA certificate and click Next.
-
Select Base64 Encoding and Download CA certificate.
-
On the Certificate Issued window, click Install this certificate and click Next.
-
Choose Automatically select the certificate store and click Next, for successful Import message.
-
Connect to the Certification Authority for retrieving the Certificate Authority certificate:
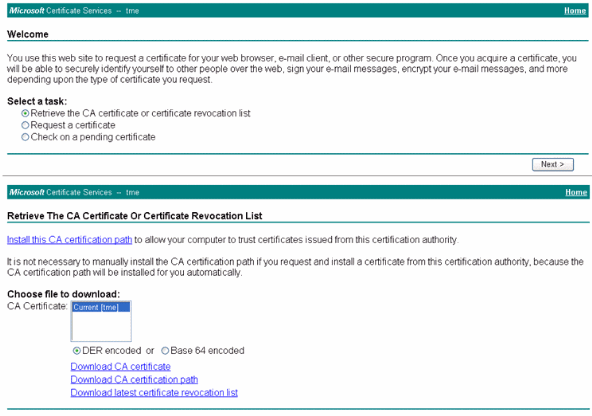
-
Click Download CA certificate.
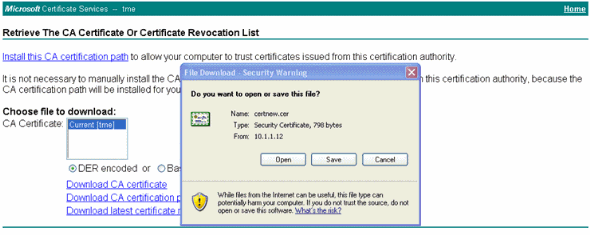
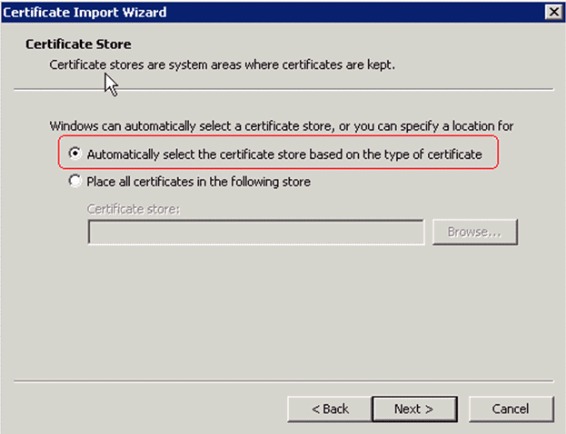

-
In order to check that the Certification Authority certificate is correctly installed, open Internet Explorer and choose Tools > Internet Options > Content > Certificates.

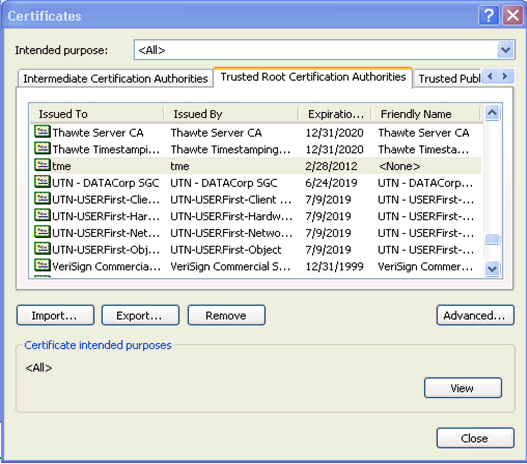
In Trusted Root Certification Authority, you should see your newly installed Certification Authority:
Generate a Client Certificate for a Client Device
The client must obtain a certificate from a Certification Authority server for the WLC to authenticate a WLAN EAP-TLS client. There are several methods that you can use in order to obtain a client certificate and install it on the Windows XP machine. In order to acquire a valid certificate, the Windows XP user has to be logged in using their user ID and must have a network connection (either a wired connection or a WLAN connection with 802.1x security disabled).
A web browser on the Windows XP client and a wired connection to the network are used to obtain a client certificate from the private root Certification Authority server. This procedure is used to obtain the client certificate from a Microsoft Certification Authority server:
-
Use a web browser on the client and point the browser to the Certification Authority server. In order to do this, enter http://IP-address-of-Root-CA/certsrv.
-
Log in using Domain_Name\user_name. You must log in using the username of the individual who uses the XP client. (The username gets embedded into the client certificate.)
-
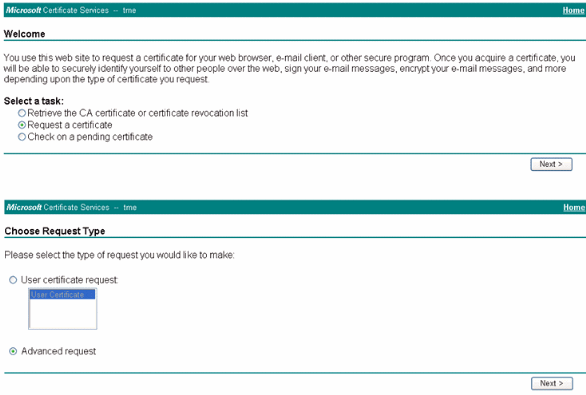
On the Welcome window, choose Request a certificate and click Next.
-
Choose Advanced request and click Next.
-
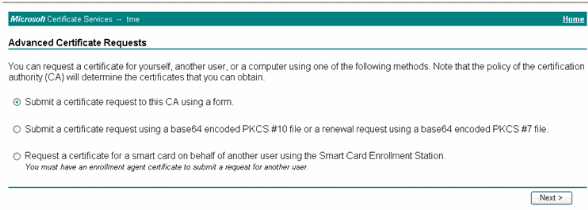
Choose Submit a certificate request to this CA using a form and click Next.
-
On the Advanced Certificate Request form, choose the Certificate Template as User, specify the Key Size as 1024 and click Submit.
-
On the Certificate Issued window, click Install this certificate. This results in the successful installation of a client certificate on the Windows XP client.
-
Select Client Authentication Certificate.
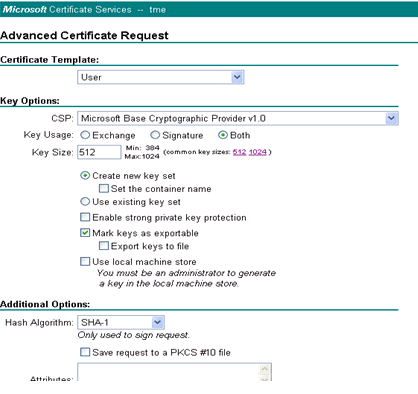
The client certificate is now created.
-
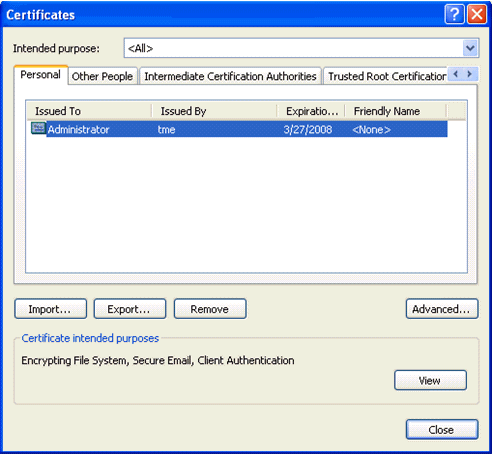
In order to check that the certificate is installed, go to Internet Explorer and choose Tools > Internet Options > Content > Certificates. In the Personal tab, you should see the certificate.
EAP-TLS with Cisco Secure Services Client on the Client Device
Complete these steps:
-
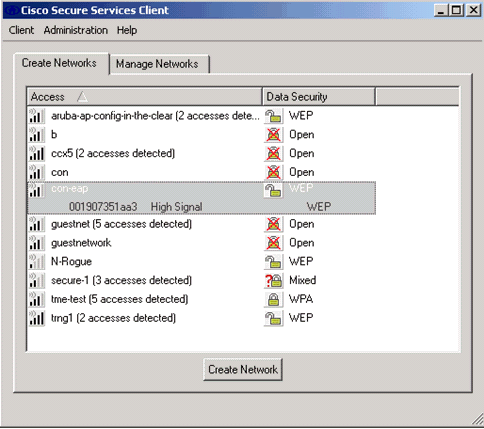
The WLC, by default, broadcasts the SSID, so it is shown in the Create Networks list of scanned SSIDs. In order to create a Network Profile, you can click the SSID in the list (Enterprise) and click Create Network.
If the WLAN infrastructure is configured with broadcast SSID disabled, you must manually add the SSID. In order to do this, click Add under Access Devices and manually enter the appropriate SSID (for example, Enterprise). Configure active probe behavior for the client. That is, where the client actively probes for its configured SSID. Specify Actively search for this access device after you enter the SSID on the Add Access Device window.
Note: The port settings do not permit enterprise modes (802.1X) if the EAP authentication settings are not first configured for the profile.
-
Click Create Network in order to launch the Network Profile window, which permits you to associate the chosen (or configured) SSID with an authentication mechanism. Assign a descriptive name for the profile.
Note: Multiple WLAN security types and/or SSIDs can be associated under this authentication profile.
-
Turn on authentication and check the EAP-TLS method. Then click Configure in order to configure EAP-TLS properties.
-
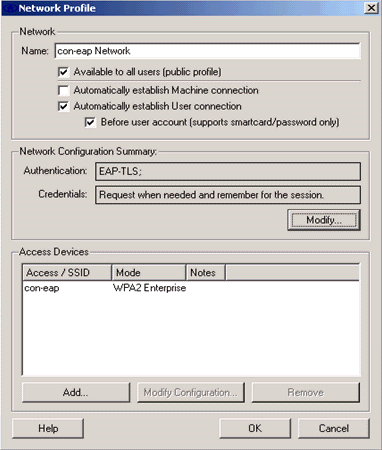
Under Network Configuration Summary, click Modify in order to configure the EAP / credentials settings.
-
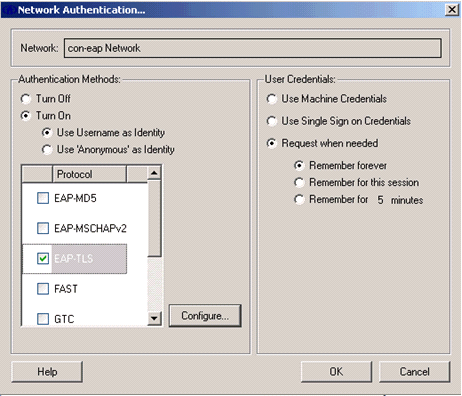
Specify Turn On Authentication, choose EAP-TLS under Protocol, and choose Username as the Identity.
-
Specify Use Single Sign on Credentials to use log on credentials for network authentication. Click Configure to set up EAP-TLS parameters.
-
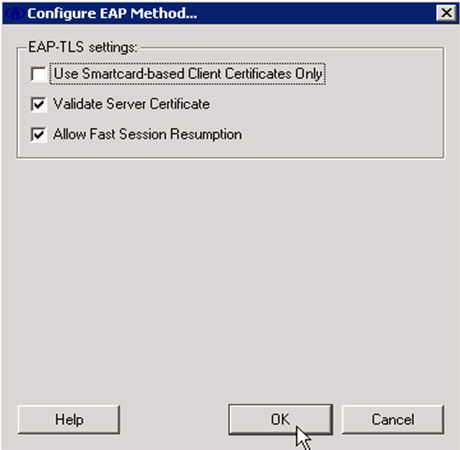
In order to have a secured EAP-TLS configuration you need to check the RADIUS server certificate. In order to do this, check Validate Server Certificate.
-
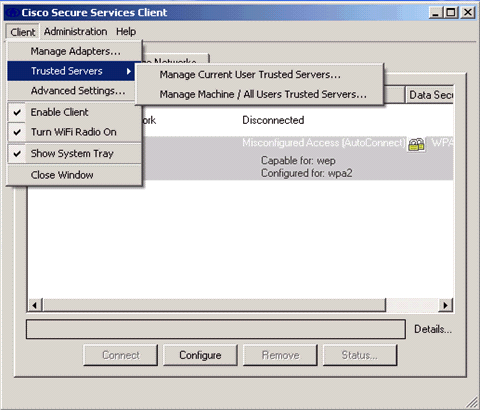
In order to validate the RADIUS server certificate, you need to give Cisco Secure Services Client information in order to accept only the right certificate. Choose Client > Trusted Servers > Manage Current User Trusted Servers.
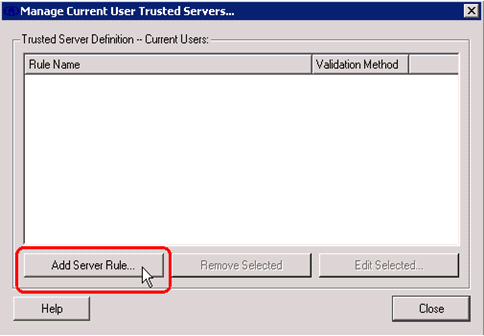
-
Give a name for the rule and check the name of the server certificate.
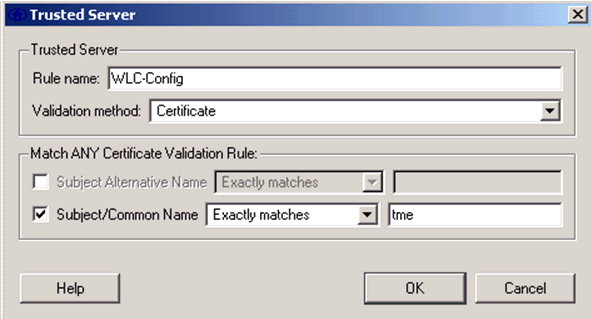
The EAP-TLS configuration is finished.
-
Connect to the Wireless network profile. The Cisco Secure Services Client asks for the user login:
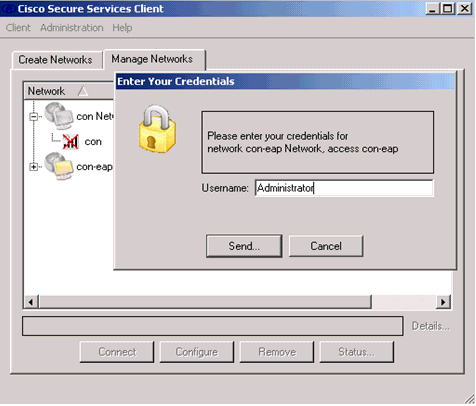
The Cisco Secure Services Client receives the server certificate and checks it (with the rule configured and the Certification Authority installed). It then asks for the certificate to use for the user.
-
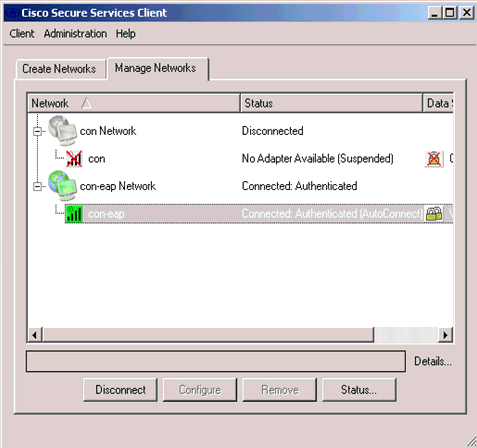
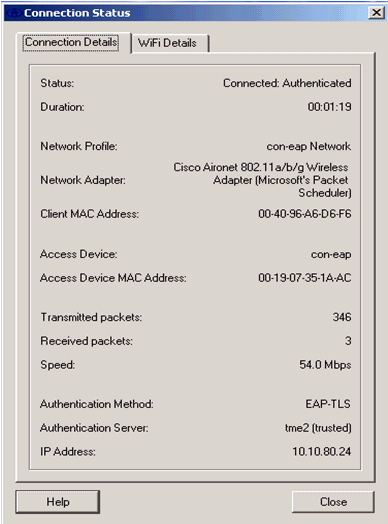
After the client authenticates, choose SSID under the Profile in the Manage Networks tab and click Status to query connection details.
The Connection Details window provides information on the client device, connection status and statistics, and authentication method. The WiFi Details tab provides details on the 802.11 connection status, which includes the RSSI, 802.11 channel, and authentication/encryption.
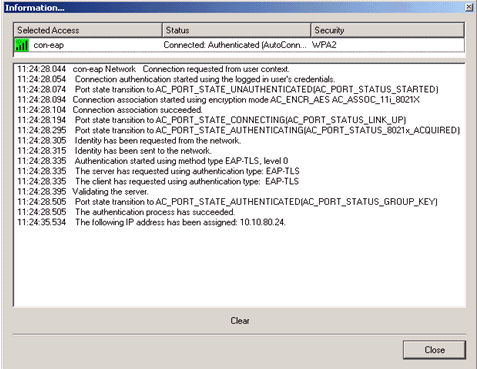
Debug Commands
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
These debug commands can be employed at the WLC to monitor progress of the authentication exchange:
-
debug aaa events enable
-
debug aaa detail enable
-
debug dot1x events enable
-
debug dot1x states enable
-
debug aaa local-auth eap events enable
OR
-
debug aaa all enable
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
03-May-2007 |
Initial Release |







































 Feedback
Feedback