Wireless Domain Services Configuration
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document introduces the concept of Wireless Domain Services (WDS). The document also describes how to configure one access point (AP) or the Wireless LAN Services Module (WLSM) as the WDS and at least one other as an infrastructure AP. The procedure in this document guides you to a WDS that is functional and allows clients to associate to either the WDS AP or to an infrastructure AP. This document intends to establish a basis from which you can configure Fast Secure Roaming or introduce a Wireless LAN Solutions Engine (WLSE) into the network, so you can use the features.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Have thorough knowledge of wireless LAN networks and wireless security issues.
-
Have knowledge of current Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) security methods.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
APs with Cisco IOS® Software
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(2)JA2 or later
-
Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless LAN Services Module
The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration and an IP address on interface BVI1, so the unit is accessible from the Cisco IOS Software GUI or the command line interface (CLI). If you work in a live network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Wireless Domain Services
WDS is a new feature for APs in Cisco IOS Software and the basis of the Catalyst 6500 Series WLSM. WDS is a core function that enables other features like these:
-
Fast Secure Roaming
-
WLSE interaction
-
Radio Management
You must establish relationships between the APs that participate in WDS and the WLSM, before any other WDS-based features work. One of the purposes of WDS is to eliminate the need for the authentication server to validate user credentials and reduce the time required for client authentications.
In order to use WDS, you must designate one AP or the WLSM as the WDS. A WDS AP must use a WDS user name and password to establish a relationship with an authentication server. The authentication server can be either an external RADIUS server or the Local RADIUS Server feature in the WDS AP. The WLSM must have a relationship with the authentication server, even though WLSM does not need to authenticate to the server.
Other APs, called infrastructure APs, communicate with the WDS. Before registration occurs, the infrastructure APs must authenticate themselves to the WDS. An infrastructure server group on the WDS defines this infrastructure authentication.
One or more client server groups on the WDS define client authentication.
When a client attempts to associate to an infrastructure AP, the infrastructure AP passes the credentials of the user to the WDS for validation. If the WDS sees the credentials for the first time, WDS turns to the authentication server to validate the credentials. The WDS then caches the credentials, in order to eliminate the need to return to the authentication server when the same user attempts authentication again. Examples of re-authentication include:
-
Re-keying
-
Roaming
-
When the user starts up the client device
Any RADIUS-based EAP authentication protocol can be tunneled through WDS such as these:
-
Lightweight EAP (LEAP)
-
Protected EAP (PEAP)
-
EAP-Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS)
-
EAP-Flexible Authentication through Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST)
MAC address authentication can also tunnel to either an external authentication server or against a list local to a WDS AP. The WLSM does not support MAC address authentication.
The WDS and the infrastructure APs communicate over a multicast protocol called WLAN Context Control Protocol (WLCCP). These multicast messages cannot be routed, so a WDS and the associated infrastructure APs must be in the same IP subnet and on the same LAN segment. Between the WDS and the WLSE, WLCCP uses TCP and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port 2887. When the WDS and WLSE are on different subnets, a protocol like Network Address Translation (NAT) cannot translate the packets.
An AP configured as the WDS device supports up to 60 participating APs. An Integrated Services Router (ISR) configured as the WDS devices supports up to 100 participating APs. And a WLSM-equipped switch supports up to 600 participating APs and up to 240 mobility groups. A single AP supports up to 16 mobility groups.
Note: Cisco recommends that the infrastructure APs run the same version of IOS as the WDS device. If you use an older version of IOS, the APs might fail to authenticate to the WDS device. In addition, Cisco recommends that you use the latest version of the IOS. You can find the latest version of IOS in the Wireless downloads page.
Role of the WDS Device
The WDS device performs several tasks on your wireless LAN:
-
Advertises its WDS capability and participates in electing the best WDS device for your wireless LAN. When you configure your wireless LAN for WDS, you set up one device as the main WDS candidate and one or more additional devices as backup WDS candidates. If the main WDS device goes off line, one of the backup WDS devices takes its place.
-
Authenticates all APs in the subnet and establishes a secure communication channel with each of them.
-
Collects radio data from APs in the subnet, aggregates the data, and forwards it to the WLSE device on your network.
-
Acts as a pass-through for all 802.1x-authenticated client devices associated to participating APs.
-
Registers all client devices in the subnet that use dynamic keying, establishes session keys for them, and caches their security credentials. When a client roams to another AP, the WDS device forwards the client's security credentials to the new AP.
Role of Access Points Using the WDS Device
The APs on your wireless LAN interact with the WDS device in these activities:
-
Discover and track the current WDS device and relay WDS advertisements to the wireless LAN.
-
Authenticate with the WDS device and establish a secure communication channel to the WDS device.
-
Register associated client devices with the WDS device.
-
Report radio data to the WDS device.
Configuration
WDS presents the configuration in an ordered, modular fashion. Each concept builds on the concept that precedes. The WDS omits other configuration items such as passwords, remote access, and radio settings for clarity and focus on the core subject matter.
This section presents the information necessary to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Designate an AP as WDS
The first step is to designate an AP as the WDS. The WDS AP is the only one that communicates with the authentication server.
Complete these steps in order to designate an AP as WDS:
-
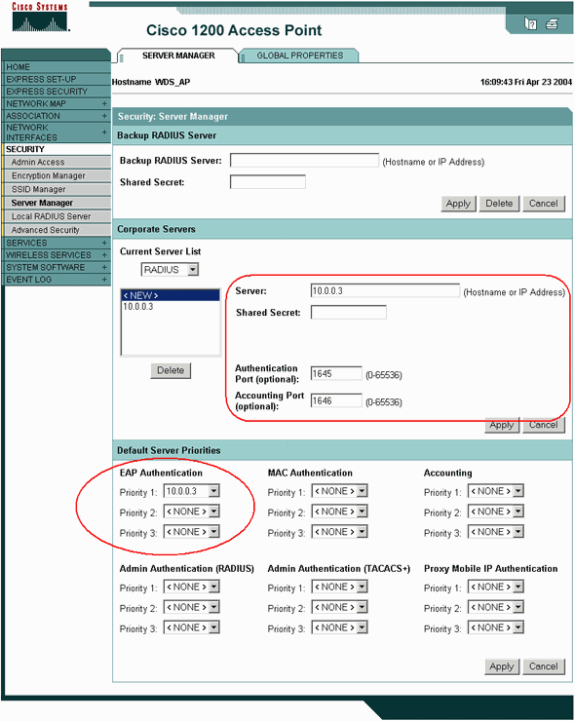
In order to configure the Authentication server on the WDS AP, choose Security > Server Manager to go to the Server Manager tab:
-
Under Corporate Servers, type the IP address of the authentication server in the Server field.
-
Specify the Shared Secret and the ports.
-
Under Default Server Priorities, set the Priority 1 field to that server IP address under the appropriate authentication type.
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. WDS_AP(config)#aaa group server radius rad_eap WDS_AP(config-sg-radius)#server 10.0.0.3 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 WDS_AP(config-sg-radius)#exit WDS_AP(config)#aaa new-model WDS_AP(config)#aaa authentication login eap_methods group rad_eap WDS_AP(config)#radius-server host 10.0.0.3 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key labap1200ip102 !--- This command appears over two lines here due to space limitations. WDS_AP(config)#end WDS_AP#write memory
-
-
The next step is to configure the WDS AP in the authentication server as an authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) client. For this, you need to add the WDS AP as an AAA client. Complete these steps:
Note: This document uses the Cisco Secure ACS server as the authentication server.
-
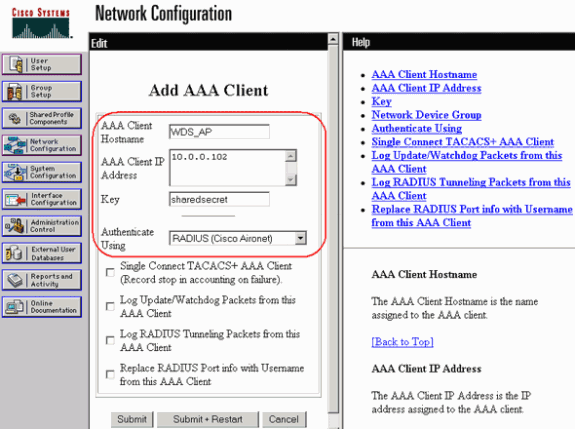
In Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS), this occurs on the Network Configuration page where you define these attributes for the WDS AP:
-
Name
-
IP address
-
Shared secret
-
Authentication method
-
RADIUS Cisco Aironet
-
RADIUS Internet Engineering Task Force [IETF]
-
Click on Submit.
For other non-ACS authentication servers, refer to the documentation from the manufacturer.
-
-
Also, in Cisco Secure ACS, ensure that you configure ACS to perform LEAP authentication on the System Configuration - Global Authentication Setup page. First, click System Configuration, then click Global Authentication Setup.
-
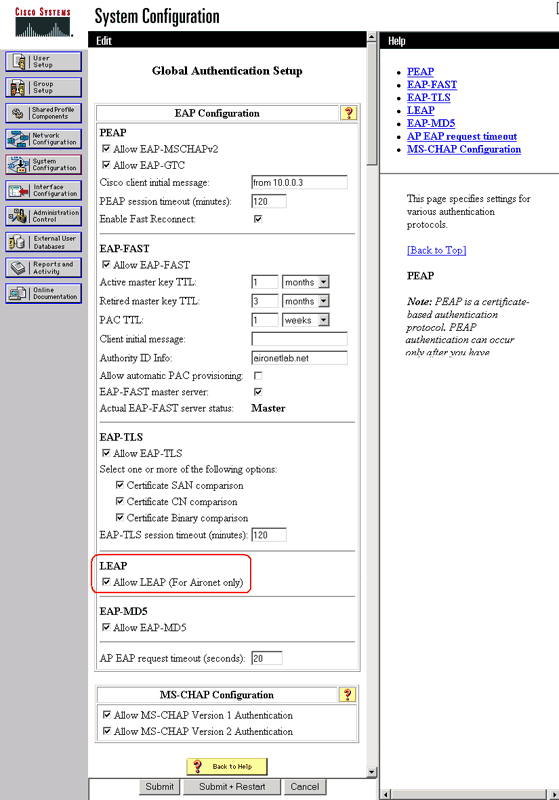
Scroll down the page to the LEAP setting. When you check the box, ACS authenticates LEAP.
-
-
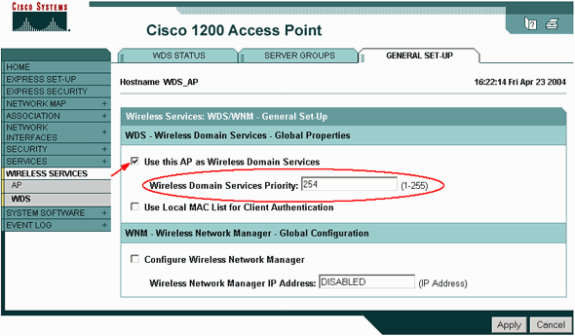
In order to configure the WDS setttings on the WDS AP, choose Wireless Services > WDS on the WDS AP, and click on the General Set-Up tab. Perform these steps:
-
Under WDS-Wireless Domain Services - Global Properties, check Use this AP as Wireless Domain Services.
-
Set the value for the Wireless Domain Services Priority field to a value of approximately 254, because this is the first one. You can configure one or more APs or switches as candidates to provide WDS. The device with the highest priority provides WDS.
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. WDS_AP(config)#wlccp wds priority 254 interface BVI1 WDS_AP(config)#end WDS_AP#write memory
-
-
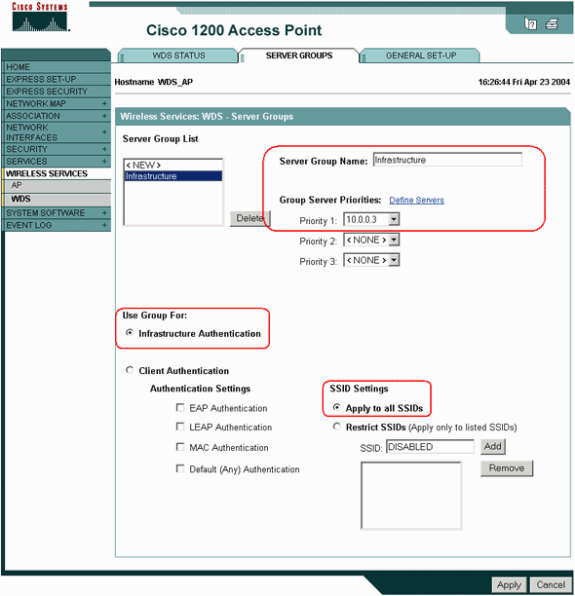
Choose Wireless Services > WDS, and go to the Server Groups tab:
-
Define a Server Group Name that authenticates the other APs, an Infrastructure group.
-
Set Priority 1 to the previously configured authentication server.
-
Click the Use Group For: Infrastructure Authentication radio button.
-
Apply the settings to the relevant Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs).
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. WDS_AP(config)#wlccp authentication-server infrastructure method_Infrastructure WDS_AP(config)#aaa group server radius Infrastructure WDS_AP(config-sg-radius)#server 10.0.0.3 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 WDS_AP(config-sg-radius)#exit WDS_AP(config)#aaa authentication login method_Infrastructure group Infrastructure WDS_AP(config)#end WDS_AP#write memory !--- Some of the commands in this table appear over two lines here due to !--- space limitations. Ensure that you enter these commands in a single line.
-
-
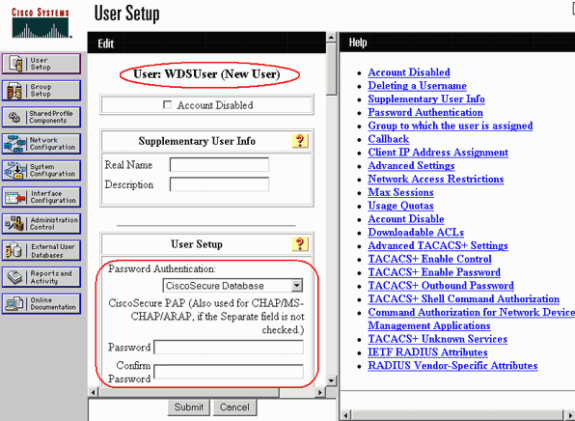
Configure the WDS user name and password as a user in your authentication server.
In Cisco Secure ACS, this occurs on the User Setup page, where you define the WDS user name and password. For other non-ACS authentication servers, refer to the documentation from the manufacturer.
Note: Do not put the WDS user in a group that is assigned many rights and privileges—WDS only requires limited authentication.
-
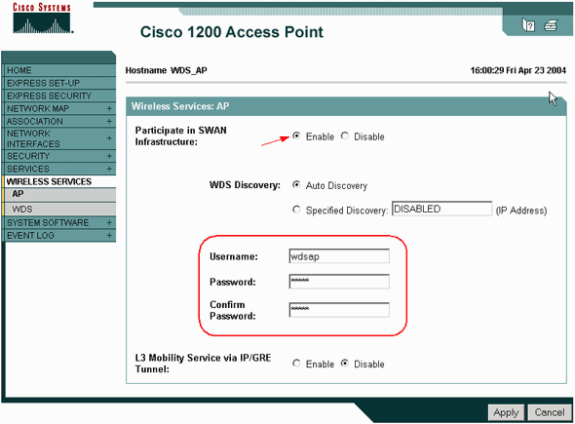
Choose Wireless Services > AP, and click Enable for the Participate in SWAN infrastructure option. Then type the WDS Username and Password.
You must define a WDS user name and password on the authentication server for all devices that you designate members of the WDS.
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. WDS_AP(config)#wlccp ap username wdsap password wdsap WDS_AP(config)#end WDS_AP#write memory
-
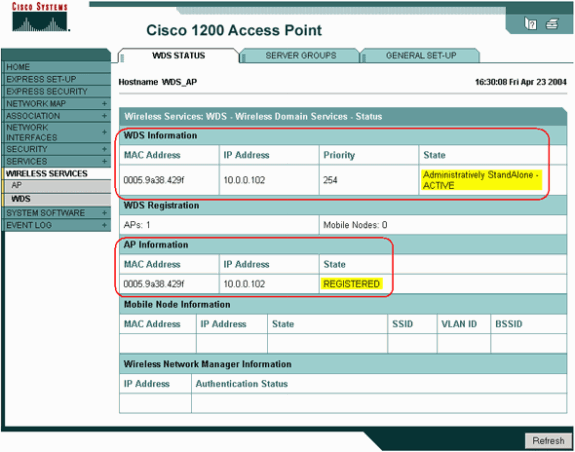
Choose Wireless Services > WDS. On the WDS AP WDS Status tab, check whether the WDS AP appears in the WDS Information area, in the ACTIVE State. The AP must also appear in the AP Information area, with State as REGISTERED.
-
If the AP does not appear REGISTERED or ACTIVE, check the authentication server for any errors or failed authentication attempts.
-
When the AP registers appropriately, add an infrastructure AP to use the services of the WDS.
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#show wlccp wds ap MAC-ADDR IP-ADDR STATE LIFETIME 0005.9a38.429f 10.0.0.102 REGISTERED 261 WDS_AP#show wlccp ap WDS = 0005.9a38.429f, 10.0.0.102 state = wlccp_ap_st_registered IN Authenticator = 10.0.0.102 MN Authenticator = 10.0.0.102 WDS_AP#Note: You cannot test client associations because client authentication does not have provisions yet.
-
Designate a WLSM as WDS
This section explains how to configure a WLSM as a WDS. The WDS is the only device that communicates with the authentication server.
Note: Issue these commands at the enable command prompt of the WLSM, not of the Supervisor Engine 720. In order to get to the command prompt of the WLSM, issue these commands at an enable command prompt in the Supervisor Engine 720:
c6506#session slot x proc 1
!--- In this command, x is the slot number where the WLSM resides.
The default escape character is Ctrl-^, then x.
You can also type 'exit' at the remote prompt to end the session
Trying 127.0.0.51 ... Open
User Access Verification
Username: <username>
Password: <password>
wlan>enable
Password: <enable password>
wlan#
|
Note: In order to troubleshoot and maintain your WLSM more easily, configure Telnet remote access to the WLSM. Refer to Configuring Telnet Remote Access.
In order to designate a WLSM as WDS:
-
From the CLI of the WLSM, issue these commands, and establish a relationship with the authentication server:
wlan#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. wlan(config)#aaa new-model wlan(config)#aaa authentication login leap-devices group radius wlan(config)#aaa authentication login default enable wlan(config)#radius-server host ip_address_of_authentication_server auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 !--- This command needs to be on one line. wlan(config)#radius-server key shared_secret_with_server wlan(config)#end wlan#write memory
Note: There is no priority control in the WLSM. If the network contains multiple WLSM modules, WLSM uses redundancy configuration in order to determine the primary module.
-
Configure the WLSM in the authentication server as an AAA client.
In Cisco Secure ACS, this occurs on the Network Configuration page where you define these attributes for the WLSM:
-
Name
-
IP address
-
Shared secret
-
Authentication method
-
RADIUS Cisco Aironet
-
RADIUS IETF
-
For other non-ACS authentication servers, refer to the documentation from the manufacturer.

-
Also, in Cisco Secure ACS, configure ACS to perform LEAP authentication on the System Configuration - Global Authentication Setup page. First, click System Configuration, then click Global Authentication Setup.

-
Scroll down the page to the LEAP setting. When you check the box, ACS authenticates LEAP.

-
-
On the WLSM, define a method that authenticates the other APs (an infrastructure server group).
wlan#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. wlan(config)#wlccp authentication-server infrastructure leap-devices wlan(config)#end wlan#write memory -
On the WLSM, define a method that authenticates the client devices (a client server group) and what EAP types those clients use.
wlan#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. wlan(config)#wlccp authentication-server client any leap-devices wlan(config)#end wlan#write memoryNote: This step eliminates the need for the Define Client Authentication Method process.
-
Define a unique VLAN between the Supervisor Engine 720 and the WLSM in order to allow the WLSM to communicate with outside entities like APs and authentication servers. This VLAN is unused anywhere else or for any other purpose on the network. Create the VLAN on the Supervisor Engine 720 first, then issue these commands:
-
On the Supervisor Engine 720:
c6506#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. c6506(config)#wlan module slot_number allowed-vlan vlan_number c6506(config)#vlan vlan_number c6506(config)#interface vlan vlan_number c6506(config-if)#ip address ip_address subnet_mask c6506(config-if)#no shut c6506(config)#end c6506#write memory
-
On the WLSM:
wlan#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. wlan(config)#wlan vlan vlan_number wlan(config)#ipaddr ip_address subnet_mask wlan(config)#gateway ip_address_of_vlan_interface_on_Sup720_created_above wlan(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 !--- This is typically the same address as the gateway statement. wlan(config)#admin wlan(config)#end wlan#write memory
-
-
Verify the function of the WLSM with these commands:
-
On the WLSM:
wlan#show wlccp wds mobility LCP link status: up HSRP state: Not Applicable Total # of registered AP: 0 Total # of registered MN: 0 Tunnel Bindings: Network ID Tunnel IP MTU FLAGS ========== =============== ========= ===== <vlan> <ip address> 1476 T Flags: T=Trusted, B=IP Broadcast enabled, N=Nonexistent wlan#
-
On the Supervisor Engine 720:
c6506#show mobility status WLAN Module is located in Slot: 5 (HSRP State: Active) LCP Communication status : up Number of Wireless Tunnels : 0 Number of Access Points : 0 Number of Access Points : 0
-
Designate an AP as Infrastructure Device
Next, you must designate at least one infrastructure AP and relate the AP to the WDS. The clients associate to infrastructure APs. The infrastructure APs request the WDS AP or WLSM to perform authentication for them.
Complete these steps in order to add an infrastructure AP that uses the services of the WDS:
Note: This configuration applies only to the infrastructure APs and not the WDS AP.
-
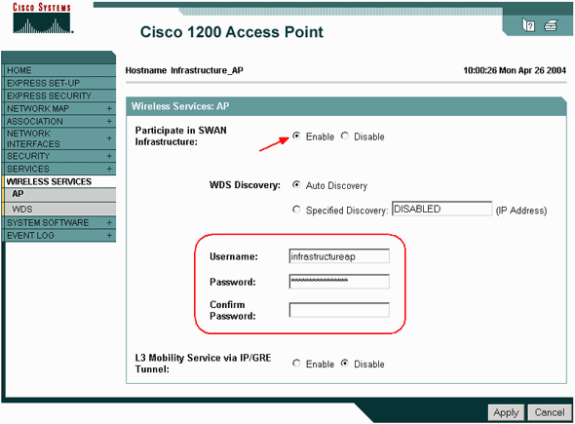
Choose Wireless Services > AP. On the infrastructure AP, select Enable for the Wireless Services option. Then type the WDS Username and Password.
You must define a WDS user name and password on the authentication server for all devices that are to be members of the WDS.
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Infrastructure_AP(config)#wlccp ap username infrastructureap password infrastructureap Infrastructure_AP(config)#end Infrastructure_AP#write memory
-
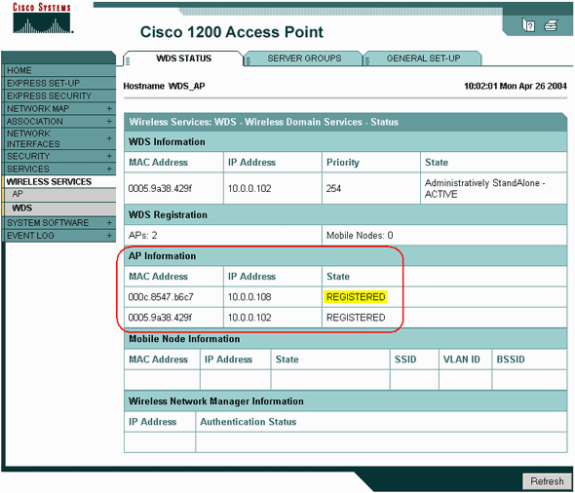
Choose Wireless Services > WDS. On the WDS AP WDS Status tab, the new infrastructure AP appears in the WDS Information area, with State as ACTIVE, and in the AP Information area, with State as REGISTERED.
-
If the AP does not appear ACTIVE and/or REGISTERED, check the authentication server for any errors or failed authentication attempts.
-
After the AP appears ACTIVE and/or REGISTERED, add a client authentication method to the WDS.
Alternatively, issue this command from the CLI:
WDS_AP#show wlccp wds ap MAC-ADDR IP-ADDR STATE LIFETIME 000c.8547.b6c7 10.0.0.108 REGISTERED 194 0005.9a38.429f 10.0.0.102 REGISTERED 76Alternatively, issue this command from the WLSM:
wlan#show wlccp wds ap MAC-ADDR IP-ADDR STATE LIFETIME 000c.8547.b6c7 10.0.0.108 REGISTERED 194 0005.9a38.429f 10.0.0.102 REGISTERED 76 wlan#Then, issue this command on the infrastructure AP:
Infrastructure_AP#show wlccp ap WDS = 0005.9a38.429f, 10.0.0.102 state = wlccp_ap_st_registered IN Authenticator = 10.0.0.102 MN Authenticator = 10.0.0.102 Infrastructure_AP#
Note: You cannot test client associations because client authentication does not have provisions yet.
-
Define Client Authentication Method
Finally, define a method of client authentication.
Complete these steps in order to add a client authentication method:
-
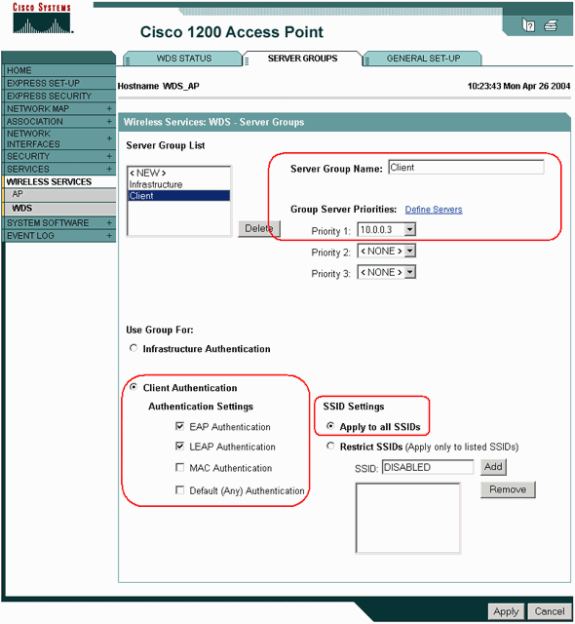
Choose Wireless Services > WDS. Perform these steps on the WDS AP Server Groups tab:
-
Define a server group that authenticates clients (a Client group).
-
Set Priority 1 to the previously configured authentication server.
-
Set the applicable type of authentication (LEAP, EAP, MAC, and so forth).
-
Apply the settings to the relevant SSIDs.
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. WDS_AP(config)#wlccp authentication-server client eap method_Client WDS_AP(config)#wlccp authentication-server client leap method_Client WDS_AP(config)#aaa group server radius Client WDS_AP(config-sg-radius)#server 10.0.0.3 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 WDS_AP(config-sg-radius)#exit WDS_AP(config)#aaa authentication login method_Client group Client WDS_AP(config)#end WDS_AP#write memory
Note: The example WDS AP is dedicated and does not accept client associations.
Note: Do not configure on the infrastructure APs for server groups because infrastructure APs forward any requests to the WDS to be processed.
-
-
On the infrastructure AP or APs:
-
Under the Security > Encryption Manager menu item, click WEP Encryption or Cipher, as required by the authentication protocol you use.
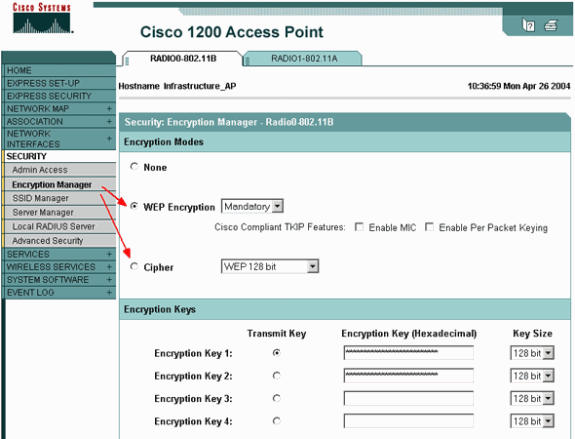
-
Under the Security > SSID Manager menu item, select authentication methods as required by the authentication protocol you use.
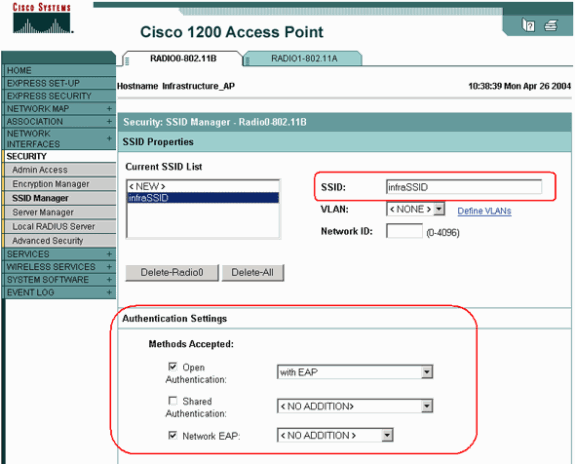
-
-
You can now successfully test whether clients authenticate to infrastructure APs. The AP of the WDS in the WDS Status tab (under the Wireless Services > WDS menu item) indicates that the client appears in the Mobile Node Information area and has a REGISTERED State.
If the client does not appear, check the authentication server for any errors or failed authentication attempts by the clients.
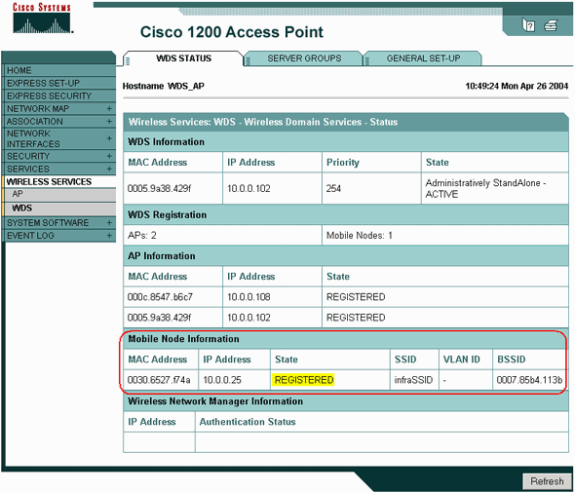
Alternatively, issue these commands from the CLI:
WDS_AP#show wlccp wds MAC: 0005.9a38.429f, IP-ADDR: 10.0.0.102 , Priority: 254 Interface BVI1, State: Administratively StandAlone - ACTIVE AP Count: 2 , MN Count: 1 WDS_AP#show wlccp wds mn MAC-ADDR IP-ADDR Cur-AP STATE 0030.6527.f74a 10.0.0.25 000c.8547.b6c7 REGISTERED WDS_AP#Note: If you need to debug authentication, ensure that you debug on the WDS AP, because the WDS AP is the device that communicates with the authentication server.
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information that you can use to troubleshoot your configuration. This list shows some of the common questions related to the WDS command in order to further clarify the usefulness of these commands:
-
Question: On the WDS AP, what are the recommended settings for these items?
-
radius-server timeout
-
radius-server deadtime
-
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) message integrity check (MIC) Failure Holdoff Time
-
Client Holdoff Time
-
EAP or MAC Reauthentication Interval
-
EAP Client Timeout (optional)
Answer: It is suggested that you keep the configuration with default settings regarding these special settings, and only use them when there is a problem regarding timing.
These are the recommended settings for the WDS AP:
-
Disable radius-server timeout. This is the number of seconds an AP waits for a reply to a RADIUS request before it resends the request. The default is 5 seconds.
-
Disable radius-server deadtime. The RADIUS is skipped by additional requests for the duration of minutes unless all servers are marked dead.
-
TKIP MIC Failure Holdoff Time is enabled by default to 60 seconds. If you enable holdoff time, you can enter the interval in seconds. If the AP detects two MIC failures within 60 seconds, it blocks all TKIP clients on that interface for the holdoff time period specified here.
-
Client Holdoff Time should be disabled by default. If you enable holdoff, enter the number of seconds that the AP should wait after an authentication failure before a subsequent authentication request is processed.
-
EAP or MAC Reauthentication Interval is disabled by default. If you enable reauthentication, you can specify the interval or accept the interval given by the authentication server. If you choose to specify the interval, enter the interval in seconds that the AP waits before it forces an authenticated client to reauthenticate.
-
EAP Client Timeout (optional) is 120 seconds by default. Enter the amount of time the AP should wait for wireless clients to respond to EAP authentication requests.
-
-
Question: In regards to TKIP holdoff time, I read that this should be set to 100 ms and not 60 seconds. I assume it is set to one second from the browser because that is the lowest number you can select?
Answer: There is no specific recommendation to set it to 100 ms unless there is a failure reported where the only solution is to increase this time. One second is the lowest setting.
-
Question: Do these two commands help client authentication in any way and are they needed on the WDS or infrastructure AP?
-
radius-server attribute 6 on-for-login-auth
-
radius-server attribute 6 support-multiple
Answer: These commands do not help the authentication process and they are not needed on the WDS or the AP.
-
-
Question: On the infrastructure AP, I assume that none of the Server Manager and Global Properties settings are needed because the AP receives information from the WDS. Are any of these specific commands needed for the infrastructure AP?
-
radius-server attribute 6 on-for-login-auth
-
radius-server attribute 6 support-multiple
-
radius-server timeout
-
radius-server deadtime
Answer: There is no need to have Server Manager and Global Properties for the infrastructure APs. The WDS takes care of that task and there is no need to have these settings:
-
radius-server attribute 6 on-for-login-auth
-
radius-server attribute 6 support-multiple
-
radius-server timeout
-
radius-server deadtime
The radius-server attribute 32 include-in-access-req format %h setting remains by default and is required.
-
An AP is a Layer 2 device. Therefore, the AP does not support Layer 3 mobility when the AP is configured to act as a WDS device. You can achieve Layer 3 mobility only when you configure the WLSM as the WDS device. Refer to the Layer 3 Mobility Architecture section of Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless LAN Services Module: White Paper for more information.
Therefore, when you configure an AP as a WDS device, do not use the mobility network-id command. This command applies to Layer 3 mobility and you need to have a WLSM as your WDS device in order to properly configure Layer 3 mobility. If you use the mobility network-id command incorrectly, you can see some of these symptoms:
-
Wireless clients cannot associate with the AP.
-
Wireless clients can associate to the AP, but do not receive an IP address from the DHCP server.
-
A wireless phone is not authenticated when you have a voice over WLAN deployment.
-
EAP authentication does not occur. With the mobility network-id configured, the AP tries to build a Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnel to forward EAP packets. If no tunnel is established, the packets do not go anywhere.
-
An AP configured as a WDS device does not function as expected, and the WDS configuration does not work.
Note: You cannot configure the Cisco Aironet 1300 AP/Bridge as a WDS master. The 1300 AP/Bridge does not support this functionality. The 1300 AP/Bridge can participate in a WDS network as an infrastructure device in which some other AP or WLSM is configured as a WDS master.
Troubleshooting Commands
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
-
debug dot11 aaa authenticator all—Shows the various negotiations that a client goes through as the client associates and authenticates through the 802.1x or EAP process. This debug was introduced in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(15)JA. This command obsoletes debug dot11 aaa dot1x all in that and later releases.
-
debug aaa authentication—Shows the authentication process from a generic AAA perspective.
-
debug wlccp ap—Shows the WLCCP negotiations involved as an AP joins a WDS.
-
debug wlccp packet—Shows the detailed information about WLCCP negotiations.
-
debug wlccp leap-client—Shows the details as an infrastructure device joins a WDS.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
19-Oct-2009 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)















 Feedback
Feedback