Introduction
This document describes how to detect and locate a rogue access point or a rogue client with the use of the 9800 wireless controller.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- IEEE 802.11 Fundamentals.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Cisco Wireless 9800-L Controller IOS® XE 17.12.1
- Cisco Catalyst 9130AXI Series Access Point.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
A Cisco rogue access point refers to an unauthorized wireless access point that has been installed on a network without the knowledge or approval of the network administrator. These rogue access points can pose security risks to a network, and attackers can use them to gain unauthorized access, intercept sensitive information, or launch other malicious activities. Cisco Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) is a solution designed to identify and manage rogue access points.
A Cisco rogue client, also known as a rogue station or rogue device, refers to an unauthorized and potentially malicious wireless client device connected to a rogue access point. Similar to rogue access points, rogue clients pose security risks because an attacker can connect to a network without proper authorization. Cisco provides tools and solutions to help detect and mitigate the presence of rogue clients to maintain network security.
Scenarios
Scenario 1: Detect And Locate A Rogue Access Point
The next steps show you how to use the 9800 wireless controllers to help detect a rogue client or an access point that is not managed by the user network:
- Use the wireless controller to find which of your access points detected the rogue device:
You can view the rogue access points or the rogue clients via GUI or CLI; for the GUI, go to Monitoring tab, then Wireless, and choose Rogue, then you can use the filters to find your rogue device, and for the CLI, you can use the command show wireless wps rogue ap summary to view all detected rogue devices, or you can use the command show wireless wps rogue ap detailed <mac-addr> to view the details on a specific rogue device.
Here is the result from the CLI to view the list of the rogue devices via the command show wireless wps rogue ap summary:
9800L#show wireless wps rogue ap summary
Rogue Location Discovery Protocol : Disabled
Validate rogue APs against AAA : Disabled
Rogue Security Level : Custom
Rogue on wire Auto-Contain : Disabled
Rogue using our SSID Auto-Contain : Disabled
Valid client on rogue AP Auto-Contain : Disabled
Rogue AP timeout : 1200
Rogue init timer : 180
Total Number of Rogue APs : 137
MAC Address Classification State #APs #Clients Last Heard Highest-RSSI-Det-AP RSSI Channel Ch.Width GHz
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0014.d1d6.a6b7 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:09 1416.9d7f.a220 -85 1 20 2.4
002a.10d3.4f0f Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:17:39 1416.9d7f.a220 -54 36 80 5
002a.10d4.b2e0 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:17:39 1416.9d7f.a220 -60 36 40 5
0054.afca.4d3b Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:26:29 1416.9d7f.a220 -86 1 20 2.4
00a6.ca8e.ba80 Unclassified Alert 1 2 01/31/2024 21:27:20 1416.9d7f.a220 -49 11 20 2.4
00a6.ca8e.ba8f Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:50 1416.9d7f.a220 -62 140 80 5
00a6.ca8e.bacf Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:50 1416.9d7f.a220 -53 140 40 5
00f6.630d.e5c0 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:09 1416.9d7f.a220 -48 1 20 2.4
00f6.630d.e5cf Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:40 1416.9d7f.a220 -72 128 20 5
04f0.212d.20a8 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:19 1416.9d7f.a220 -81 1 20 2.4
04f0.2148.7bda Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:24:19 1416.9d7f.a220 -82 1 20 2.4
0c85.259e.3f30 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:21:30 1416.9d7f.a220 -63 11 20 2.4
0c85.259e.3f32 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:21:30 1416.9d7f.a220 -63 11 20 2.4
0c85.259e.3f3c Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:30 1416.9d7f.a220 -83 64 20 5
0c85.259e.3f3d Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:30 1416.9d7f.a220 -82 64 20 5
0c85.259e.3f3f Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:30 1416.9d7f.a220 -82 64 20 5
12b3.d617.aac1 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:09 1416.9d7f.a220 -72 1 20 2.4
204c.9e4b.00ef Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:40 1416.9d7f.a220 -59 116 20 5
22ad.56a5.fa54 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:09 1416.9d7f.a220 -85 1 20 2.4
4136.5afc.f8d5 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:27:30 1416.9d7f.a220 -58 36 20 5
5009.59eb.7b93 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:09 1416.9d7f.a220 -86 1 20 2.4
683b.78fa.3400 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:00 1416.9d7f.a220 -69 6 20 2.4
683b.78fa.3401 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:00 1416.9d7f.a220 -69 6 20 2.4
683b.78fa.3402 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:00 1416.9d7f.a220 -72 6 20 2.4
683b.78fa.3403 Unclassified Alert 1 0 01/31/2024 21:28:00 1416.9d7f.a220 -72 6 20 2.4
...
2. You can filter on one of the WLANs configured on your 9800 controller to see if you have any rogue devices that broadcasts the same WLANs, next figure is shows the result where my C9130 detected this rogue on both bands:
 GUI Rogue List
GUI Rogue List
3. List the access points that detected the rogue device.
You can view the APs which detected the rogue device, the next figure shows the AP that detected this rogue, channel, RSSI value, and more information:
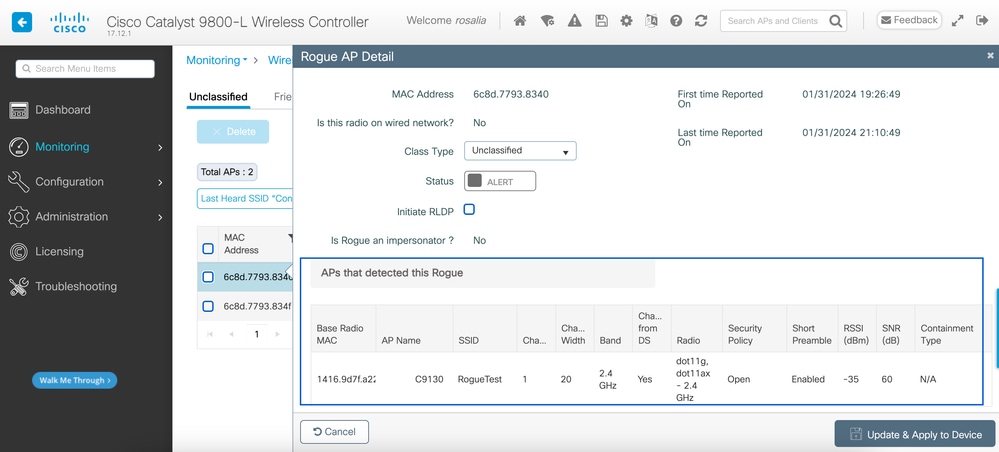 GUI Rogue AP Details
GUI Rogue AP Details
From the CLI you can view this information via the command show wireless wps rogue ap detailed <mac-addr>.
4. Find the closest access point to the rogue device based on the closest RSSI value.
Based on the results of how many access points detected the rogue device, you have to look for the closest AP based on the RSSI value displayed on the wireless controller, in the next example only one AP detected the rogue, however with a high RSSI value, which means the rogue device is very nearby my AP.
The next is the output of command show wireless wps rogue ap detailed <mac-addr> to view the channel the AP/WLC heard this rogue device on, plus the RSSI value:
9800L#show wireless wps rogue ap detailed 6c8d.7793.834f
Rogue Event history
Timestamp #Times Class/State Event Ctx RC
-------------------------- -------- ----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ----
01/31/2024 22:45:39.814917 1154 Unc/Alert FSM_GOTO Alert 0x0
01/31/2024 22:45:39.814761 1451 Unc/Alert EXPIRE_TIMER_START 1200s 0x0
01/31/2024 22:45:39.814745 1451 Unc/Alert RECV_REPORT 1416.9d7f.a220/34 0x0
01/31/2024 22:45:29.810136 876 Unc/Alert NO_OP_UPDATE 0x0
01/31/2024 19:36:10.354621 1 Unc/Pend HONEYPOT_DETECTED 0x0
01/31/2024 19:29:49.700934 1 Unc/Alert INIT_TIMER_DONE 0xab98004342001907 0x0
01/31/2024 19:26:49.696820 1 Unk/Init INIT_TIMER_START 180s 0x0
01/31/2024 19:26:49.696808 1 Unk/Init CREATE 0x0
Rogue BSSID : 6c8d.7793.834f
Last heard Rogue SSID : RogueTest
802.11w PMF required : No
Is Rogue an impersonator : No
Is Rogue on Wired Network : No
Classification : Unclassified
Manually Contained : No
State : Alert
First Time Rogue was Reported : 01/31/2024 19:26:49
Last Time Rogue was Reported : 01/31/2024 22:45:39
Number of clients : 0
Reported By
AP Name : C9130
MAC Address : 1416.9d7f.a220
Detecting slot ID : 1
Radio Type : dot11ax - 5 GHz
SSID : RogueTest
Channel : 36 (From DS)
Channel Width : 20 MHz
RSSI : -43 dBm
SNR : 52 dB
ShortPreamble : Disabled
Security Policy : Open
Last reported by this AP : 01/31/2024 22:45:39
5. Collect over-the-air capture on the same channel to locate the rogue.
Now the channel where this rogue AP broadcasts is found, and based on the RSSI value, the 9130 access point heard this rogue at -35dBm, which is considered very close, this gives you an idea on which area this rogue is located, the next step is to collect an over-the-air capture.
Next figure shows an over-the-air capture on channel 36, from the OTA, you can see the rogue AP performs a containment de-authentication attack to the managed access point:
 Rogue AP OTA Capture
Rogue AP OTA Capture
You can use the information from the previous figure to understand how close this rogue is, and at least you can have an idea where physically this rogue access point is located. You can filter via the rogue AP radio mac address, you would be able to see if the rogue is currently active or not if you check if you have beacon packets over the air.
Scenario 2: Detect and Locate a Rogue Client that sends an De-authentication Flood
The next steps show you how to use the 9800 wireless controller to find a rogue client connected to a rogue access point that is not managed by the user network or a rogue client who does an de-authentication attack:
1.Use the wireless controller to find the rogue client.
From the wireless controller GUI, navigate to the Monitoring tab, Wireless, then choose Rogue Clients, or you can use the command show wireless wps rogue client summary from the CLI to list down the rogue clients detected on the controller:
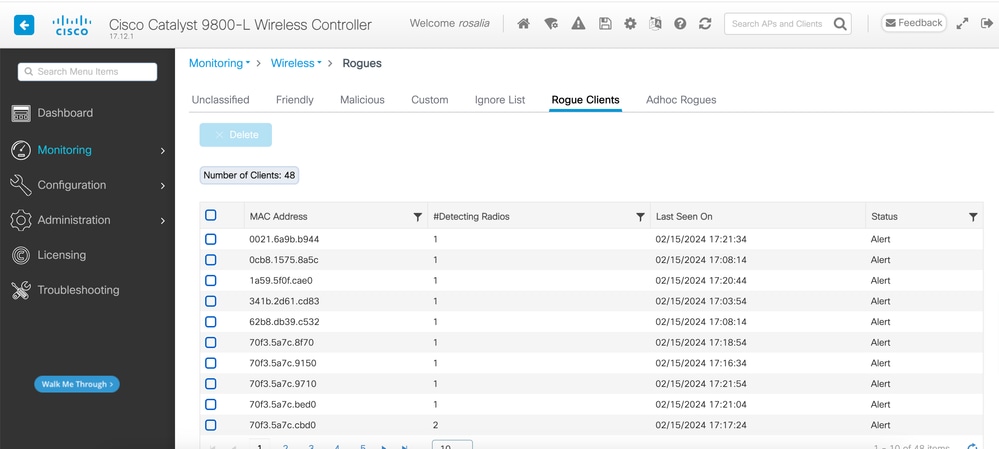 Rogue Client List GUI
Rogue Client List GUI
Next output shows the CLI result:
9800L#show wireless wps rogue client summary
Validate rogue clients against AAA : Disabled
Validate rogue clients against MSE : Disabled
Number of rogue clients detected : 49
MAC Address State # APs Last Heard
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
0021.6a9b.b944 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:22:44
0cb8.1575.8a5c Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:08:14
1a59.5f0f.cae0 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:20:44
341b.2d61.cd83 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:03:54
62b8.db39.c532 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:08:14
70f3.5a7c.8f70 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:18:54
70f3.5a7c.9150 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:23:04
70f3.5a7c.9710 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:22:34
70f3.5a7c.bed0 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:22:54
70f3.5a7c.cbd0 Alert 2 02/15/2024 17:17:24
70f3.5a7c.d030 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:20:44
70f3.5a7c.d050 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:20:44
70f3.5a7c.d0b0 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:16:54
70f3.5a7c.d110 Alert 2 02/15/2024 17:18:24
70f3.5a7c.d210 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:20:24
70f3.5a7c.d2f0 Alert 2 02/15/2024 17:23:04
70f3.5a7c.f850 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:19:04
70f3.5a7f.8971 Alert 1 02/15/2024 17:16:44
...
2. The next output example shows the details about rogue client with mac address 0021.6a9b.b944, that was detected by a managed AP 9130 on channel 132, next output is shows more details:
9800L#show wireless wps rogue client detailed 0021.6a9b.b944
Rogue Client Event history
Timestamp #Times State Event Ctx RC
-------------------------- -------- ----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ----
02/15/2024 17:22:44.551882 5 Alert FSM_GOTO Alert 0x0
02/15/2024 17:22:44.551864 5 Alert EXPIRE_TIMER_START 1200s 0x0
02/15/2024 17:22:44.551836 5 Alert RECV_REPORT 0x0
02/15/2024 17:15:14.543779 1 Init CREATE 0x0
Rogue BSSID : 6c8d.7793.834f
SSID : Testing-Rogue
Gateway : 6c8d.7793.834f
Rogue Radio Type : dot11ax - 5 GHz
State : Alert
First Time Rogue was Reported : 02/15/2024 17:15:14
Last Time Rogue was Reported : 02/15/2024 17:22:44
Reported by
AP : C9130
MAC Address : 1416.9d7f.a220
Detecting slot ID : 1
RSSI : -83 dBm
SNR : 12 dB
Channel : 132
Last reported by this AP : 02/15/2024 17:22:44
3. After you collect an over-the-air capture on the same channel, you can see that you have a de-authenticated flood, where the rogue client uses one of the managed access point BSSID to disconnect clients:
 De-authentication OTA
De-authentication OTA
The RSSI value for the packets is high, which means the rogue client is physically near the managed access point.
4. After you remove the rogue client from the network, the next figure shows a clean network and a healthy environment over-the-air:
 Healthy OTA
Healthy OTA
Related Information







 Feedback
Feedback