Load Balance MME in Pool
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes S10 Configuration and Mobility Management Entity (MME) load balancing. MME runs on Aggregation Services Router (ASR) 5x00 Series.
S10 Interface and Configuration
S10 Interface Description
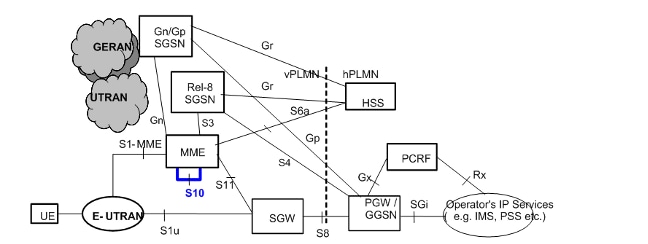
S10 interfaces facilitate user mobility between two MMEs. They provide for transfer of User Equipement (UE) context from one MME to another with GprsTransfer Protocol version2 (GTPv2). This figure shows the role of S10 in EPC architecture.
S10 Call Flows
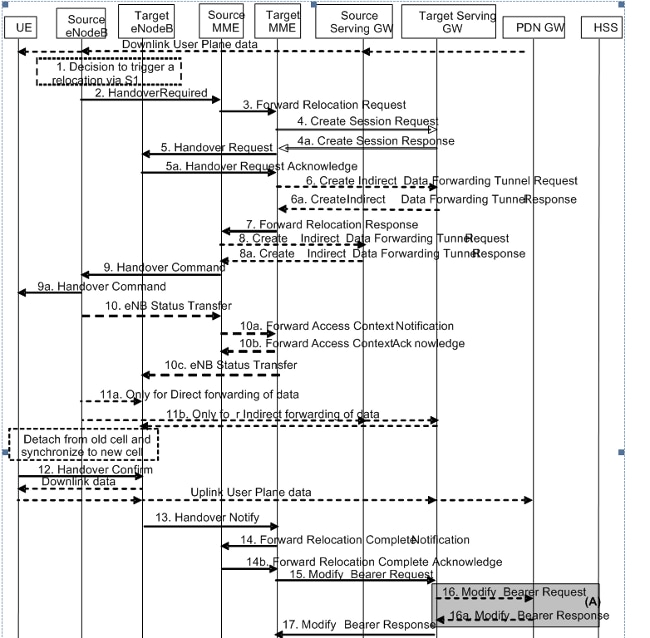
Tracking Area Update Triggered MME Change with Serving GateWay Change
This figure is extracted from Technical Specification 23.401 Ref[1]. Refer to section 5.3.3.1 of [1] for details.

Step 3 - The first arrival of a Tracking Area Update (TAU) request at the new MME with a foreign Globally Unique Temporary ID (GUTI) prompts the new MME to set up a new call. The new MME can look up the old MME's IP addresses with the Globally Unique MME Identifier (GUMMEI) derived from the GUTI.
Steps 4, 5, and 6 - Steps 4 and 5 can be repeated if the integrity protection fails at the new MME. The new MME then performs the authentication, sets the UE validated bit to true, and again requests the old MME to send the Mobility Management (MM) context information via the context response.
Step 7 - Context acknowledge includes a flag in order to indicate a Serving GateWay (SGW) change to the old MME. This helps the old MME to decide whether to send S11 Delete Session Request or not at the end of UE context relocation.
Steps 12, 13, 14, and 15 - Home Subscriber Server (HSS) Interactions
The new MME sets the Update Type in the Update Location Request to MME Only Type. For this Update Type, HSS sends a Cancel Location Request to both the 'old Serving Gprs Support Node (SGSN)' and 'old MME'.
Steps 18 and 19 - MME assigns a new GUTI in response to this TAU trigger. Hence, the UE responds with a TAU Complete message.
After Step 19 - If the Active Flag is set in the TAU request, MME initiates a transition to connected mode in order to establish S1u connections.
TAU Triggered MME Change without SGW Change

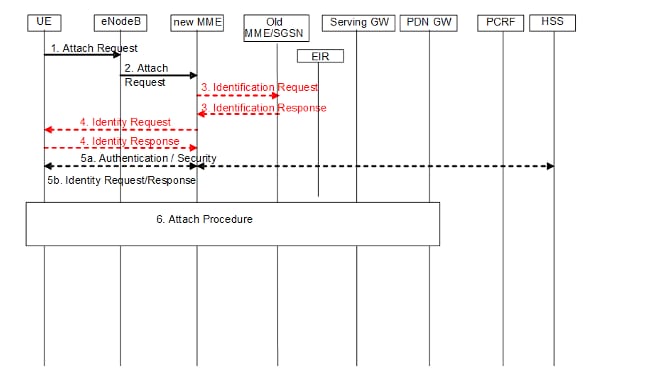
Attach Request with Old MME's GUTI
S1-Based Handover with MME and SGW Change
Domain Name Server Queries
Target MME Selection
When an S1 handover required message arrives at the source MME, the MME first verifies whether the new Tracking Area Identifier (TAI) of the UE is still served by the current MME. If not, a TAI-based Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is constructed (with service tag as MME) and the DNS server is queried for MMEs that serve this TAI. After the IP address of the target MME is determined, an S10 Fwd relocation request is sent to the target MME.
The TAI-FQDN shall be constructed as:
tac-lb<TAC-low-byte>.tac-hb<TAC-high-byte>.tac.epc.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org
Source MME Lookup
Given the GUTI, the new MME needs to know how to reach the old MME. The new MME should query the DNS and obtain the IP address of the old MME for the GUMMEI derived from the GUTI.
For this purpose, MME constructs FQDN with GUMMEI. The DNS query the Application Program Interface (API) first looks into its local cache for the corresponding FQDN entry. If not found, it queries the designated DNS server. The result is the IP address of this MME. If the query fails, MME should request the UE for IMSI and proceed with authentication procedures.
The MME node FQDN shall be constructed as:
mmec<MMEC>.mmegi<MMEGI>.mme.epc.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org
SGW Selection
The new MME is required to select an SGW for the UE that relocates to it. This is done based on a query to the DNS server based on the TAI FQDN (with service tag as SGW).
The TAI FQDN shall be constructed as:
tac-lb<TAC-low-byte>.tac-hb<TAC-high-byte>.tac.epc.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org
Packet GateWay Selection
Packet GateWay (PGW) selection is only completed in the initial attach procedures. In TAU-attach and S1 handover, the existing PGW is retained.
Configuration Around S10
- Configure the S10 interface and VLAN mapping.
- Ensure the common MME group ID is in place, otherwise change it accordingly. Configure the peer MME address.
- Configure the corresponding Evolved GPRS Tunneling Protocol (EGTP) service.
local]# config
[local](config)# context mme
[mme(config-ctx)# interface s10
[mme(config-if-eth)# ip address 192.25.19.13 255.255.255.248
[mme(config-if-eth)#exit
[mme(config-ctx)# mme-service mme_svc
[mme(config-mme-service)# mme-id group-id 61005 mme-code 113
[mme(config-mme-service)# peer-mme gummei mcc 704 mnc 01 group-id 61005
mme-code 114 address 172.25.19.14
[mme] (config-mme-service)#exitThe CLI is required in order to set up the DNS context for the target MME and source MME lookup.
[mme(config-mme-service) dns peer-mme context <ctxt-name>
[mme](config-ctx)# egtp-service mme_s10
[mme](config-egtp-service)# interface-type interface-mme
[mme](config-egtp-service)# gtpc bind ipv4-address 192.25.19.13
[mme](config-egtp-service)# end
[local]# Config
[local](config)# port ethernet 17/1
[local](config-port-17/1)# vlan 166
[local](config-port-17/1-vlan-166)# no shutdown
[local](config-port-17/1-vlan-166)# bind interface s10 mme
[local](config-port-17/1-vlan-166)# end
Load Balancing Between MMEs
The MME load balancing functionality permits UEs that enter into an MME Pool Area to be directed to an appropriate MME in a manner that achieves load balancing between MMEs. In order to achieve this, set a Weight Factor for each MME such that the probability of the eNodeB selecting an MME is proportional to its Weight Factor. The Weight Factor is typically set in accordance with the capacity of an MME node relative to other MME nodes.
The Weight Factor is sent from the MME to the eNodeB via S1-AP messages.
The weight factor of an MME is sent to eNodeB with the Relative MME Capacity S1AP Information Element (IE).
| IE/Group Name | Presence | Range | IE Type and Reference | Semantics Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative MME Capacity | M |
INTEGER (0..255) |
This IE is included in the S1AP S1 SETUP RESPONSE message from MME.
If the relative MME capacity is changed after the S1 interface is already initialized, then the MME CONFIGURATION UPDATE message is used to update this information to the eNodeB.
The MME will have a service level configuration to specify its relative MME capacity.
<mme-service># relative-capacity <0-255><mme-service># default relative-capacity
Default value is "255"
Load Rebalancing
The MME Load Rebalancing functionality permits UEs that are registered on an MME (within an MME Pool Area) to be moved to another MME. Typically, this procedure should not be used when the MME becomes overloaded because the Load Balancing function should have ensured that the other MMEs in the pool area are similarly overloaded.
The eNodeBs might have their Load Balancing parameters adjusted beforehand (such as, the Weight Factor is set to zero if all subscribers are to be removed from the MME, which routes new entrants to the pool area into other MMEs).
In order to offload ECM-CONNECTED mode UEs, the MME initiates the S1 release procedure with release cause "load balancing TAU required".
In order to offload UEs which perform TA updates or attaches initiated in ECM-IDLE mode, the MME completes that procedure and the procedure ends when the MME releases S1 with release cause "load balancing TAU required".
In order to offload UEs in ECM-IDLE state without waiting for the UE to perform a TAU or Service request and become ECM CONNECTED, the MME first pages UE in order to bring it to an ECM-CONNECTED state.
MME provides an executive level command in order to offload UEs for a particular mme-service for load rebalancing amongst MMEs in a MME pool area. If the "stop" option is selected, then the offloading actions are discontinued and calls to this MME service are handled normally.
Perform Load Rebalancing (UE Offloading)
This example rebalances (offloads) 30 percent of all UEs from the specified mme-service (to other mme-services in the MME pool) over the course of 10 minutes.
mme offload mme-service mme_svc time-duration 10 offload-percentage 30 -noconfirm
This command can also be entered with the disable-implicit-detach option. By default, if the UE context is not transferred to another MME within 5 minutes, the UE is implicitly detached. This option disables this implicit detach timer.
mme offload mme-service mme_svc time-duration 10 offload-percentage 30
disable-implicit-detach -noconfirm
In order to stop the offloading process, enter the command with the stop keyword option.
mme offload mme-service mme_svc stop -noconfirm
Verify Load Rebalancing (UE Offloading)
This command shows the offload configuration as well as the status of the rebalancing.
show mme-service name svc_name offload statistics
[local]asr5000# show mme-service name mme1 offload statistics
Current Offload Status: In Progress
Implicit Detach Status: Enabled
Time Duration Requested: 600 secs
Percentage of Subscribers Requested: 30
Total Number of Subscribers: 0
Total Number of Subscribers to be Offloaded: 0
Total Number of Subscribers Offloaded: 0
Total Number of Subscribers Received Context Transfer: 0
Remaining Time: 0 secs
Where the Current Offload Status field will report one of the following:
- None - No UEs marked for offloading and no UEs currently being offloaded.
- Marked - MME has marked UEs for offloading, but is waiting for
offload trigger on timer expiry.
- In Progress - MME is currently offloading marked UEs.
- Done - Offload procedure is completed or has been terminated by operator
using stop keyword.
These counters are reset each time an offload procedure is initiated, or when this command is entered:
clear mme-service statistics offload
Monitor Load Rebalancing
This section describes commands available to monitor load rebalancing on the MME.
Load Rebalancing Show Command(s) and/or Outputs
This section provides information in regards to show commands and their outputs in support of load rebalancing (UE offload). This show command displays current statistics for the Load Rebalancing feature.
show mme-service name <mme_svc_name> offload statistics
This command also provides information in relation to load balancing:
show mme-service session full all
UE Offloading --> Displays the UE offload state.
Possible values are None, Marked, In-Progress and Done.
Additional Commands
show mme-service statistics
show egtpc statistics
show egtpc sessions
show mme-service mme_svc offload statistics
show subscriber mme-only summary
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
19-Jun-2015 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback