Use Case: Intra-tenant Firewall with Policy-based Routing
Refer the figure given below for topology details.
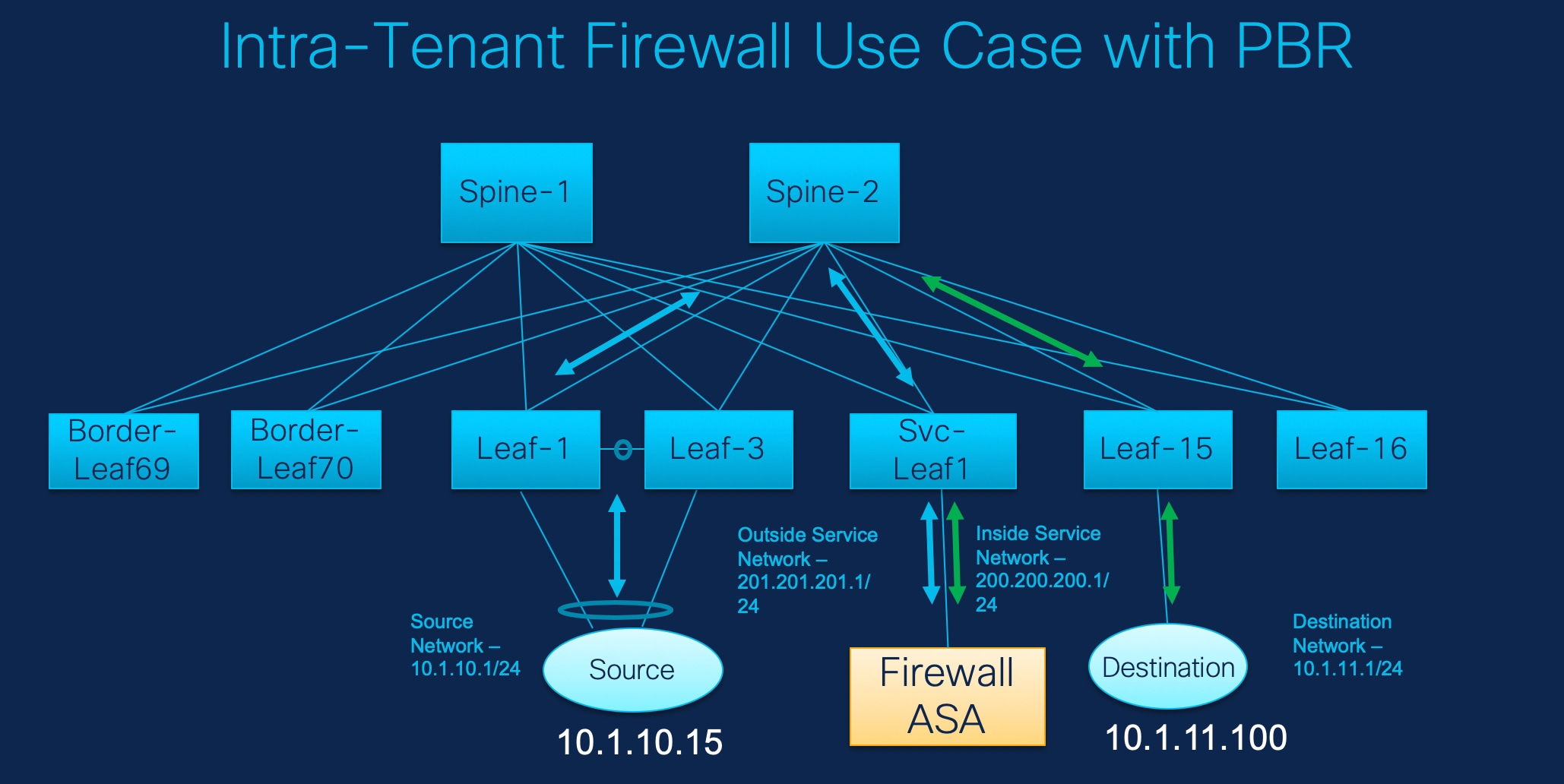
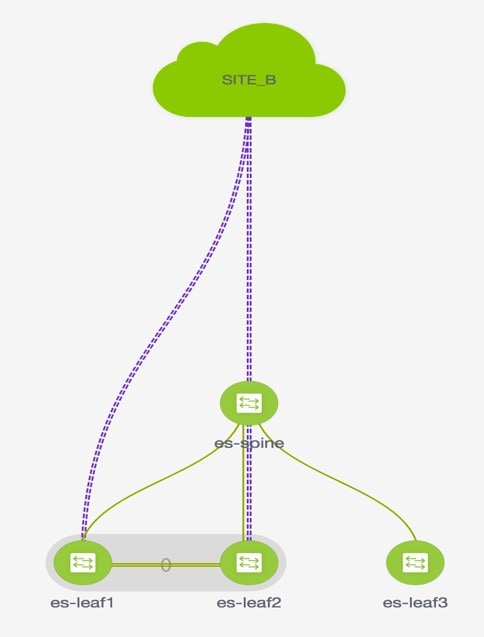
In this topology, Leaf1 and Leaf3 are a vPC pair and they are connected to Source (10.1.10.15) with the Source Network (10.1.10.1/24). The service leaf is connected to the virtual Firewall ASA and Leaf-15 is connected to Destination (10.1.11.100). In this use case, the source network refers to ‘client’ and the destination refers to ‘server’.
Any traffic that is traversing from Source to Destination must go to the outside service network, and the firewall performs its function by allowing or denying traffic. This traffic is then routed to the inside service network and on to the Destination network. Since the topology is stateful, the traffic coming back from the destination to the source follows the same path.
Now, let us see how to perform service redirection in NDFC.
 Note |
|
You can navigate to Services tab by one of the following below mentioned paths:
1. Create Service Node
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Navigate . 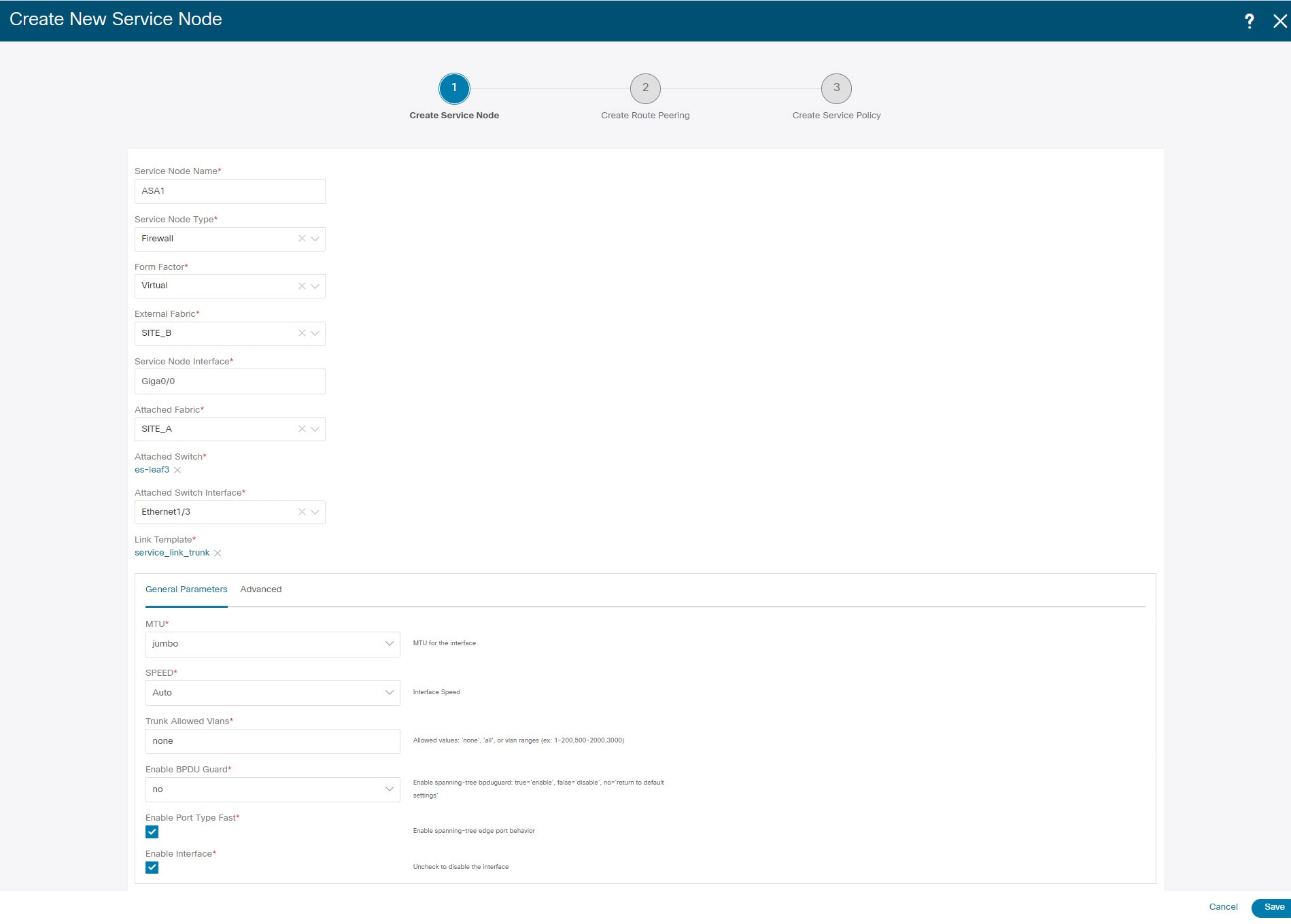 |
||
| Step 2 |
On Services tab, choose . |
||
| Step 3 |
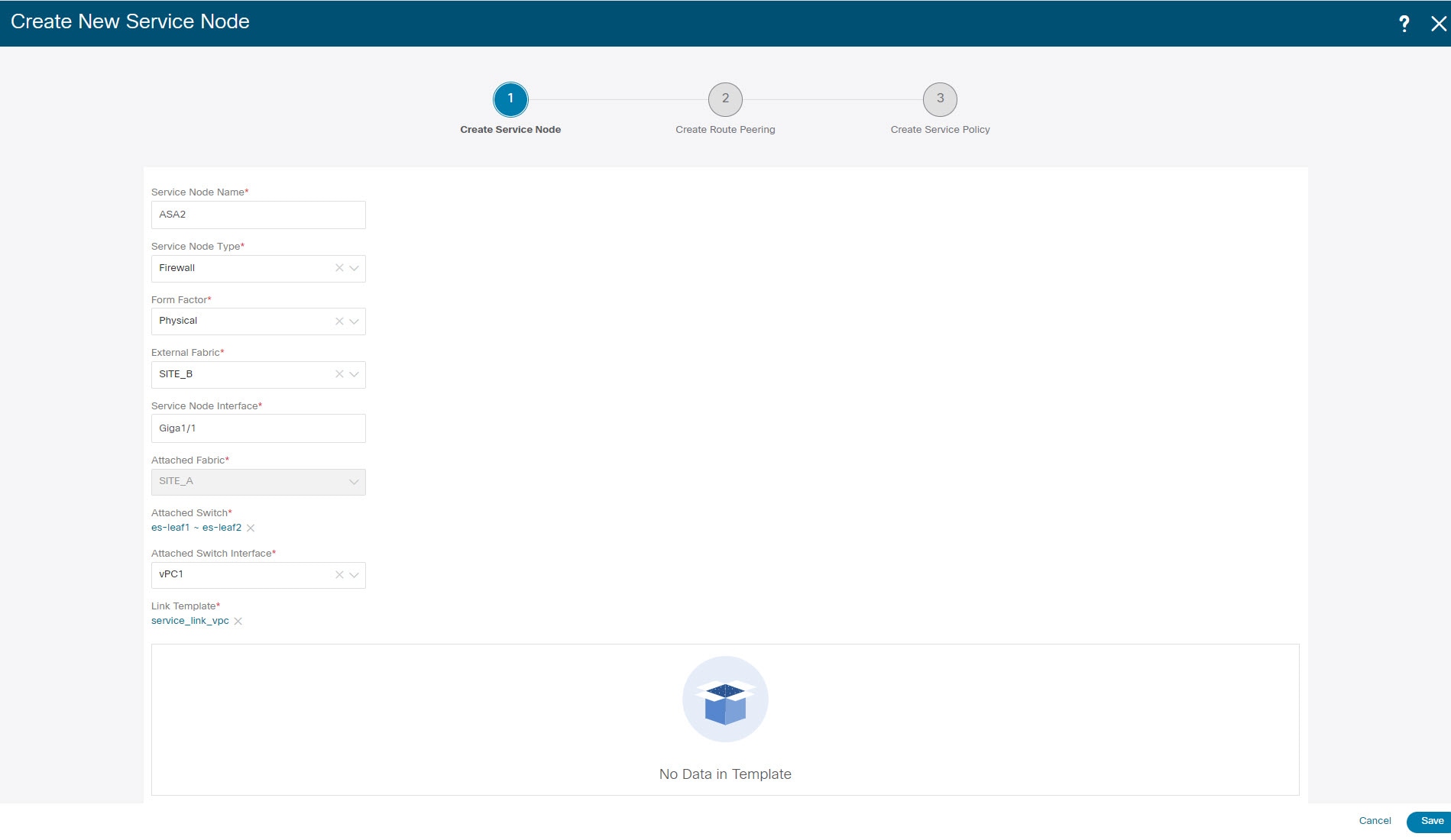
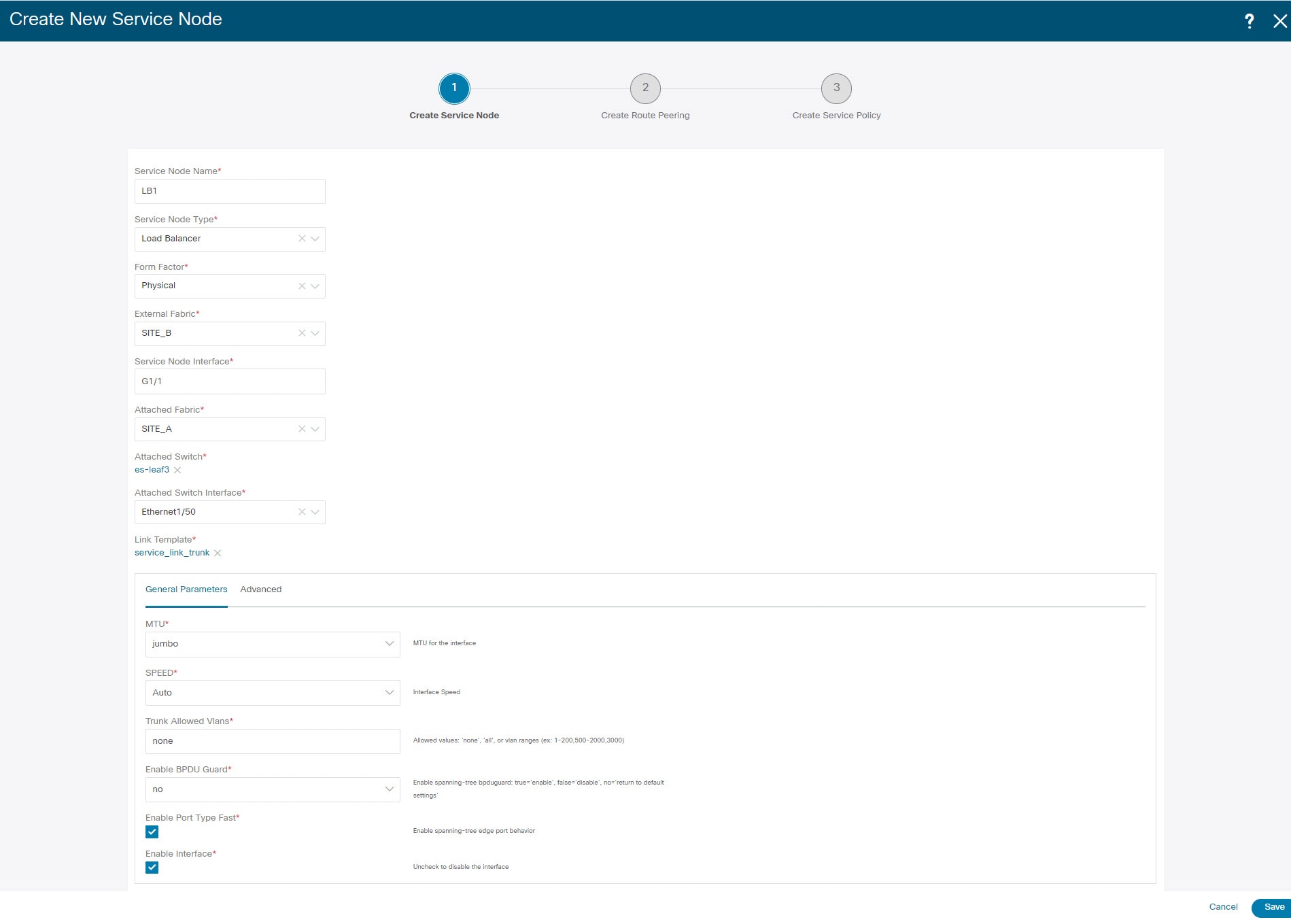
Enter the Service Node Name and specify Firewall in the Service Node Type dropdown box. The Service Node Name must be unique. |
||
| Step 4 |
From the Form Factor drop-down list, select Virtual. |
||
| Step 5 |
Choose External Fabric from drop-down list, select the external fabric in which the service node (for example, ASA firewall) is located.
|
||
| Step 6 |
Enter the interface name of the service node that connects to the service leaf. |
||
| Step 7 |
Select the attached switch that is the service leaf, and the respective interface on the service leaf. |
||
| Step 8 |
Choose service_link_trunk template. NDFC supports trunk, port channel, and vPC link templates. The available link templates in the Link Template drop-down list are filtered based on the selected Attached Switch Interface type. |
||
| Step 9 |
Specify the General Parameters and Advanced parameters, if required. Some parameters are pre-filled with the default values. |
||
| Step 10 |
Click Save to save the created service node. |
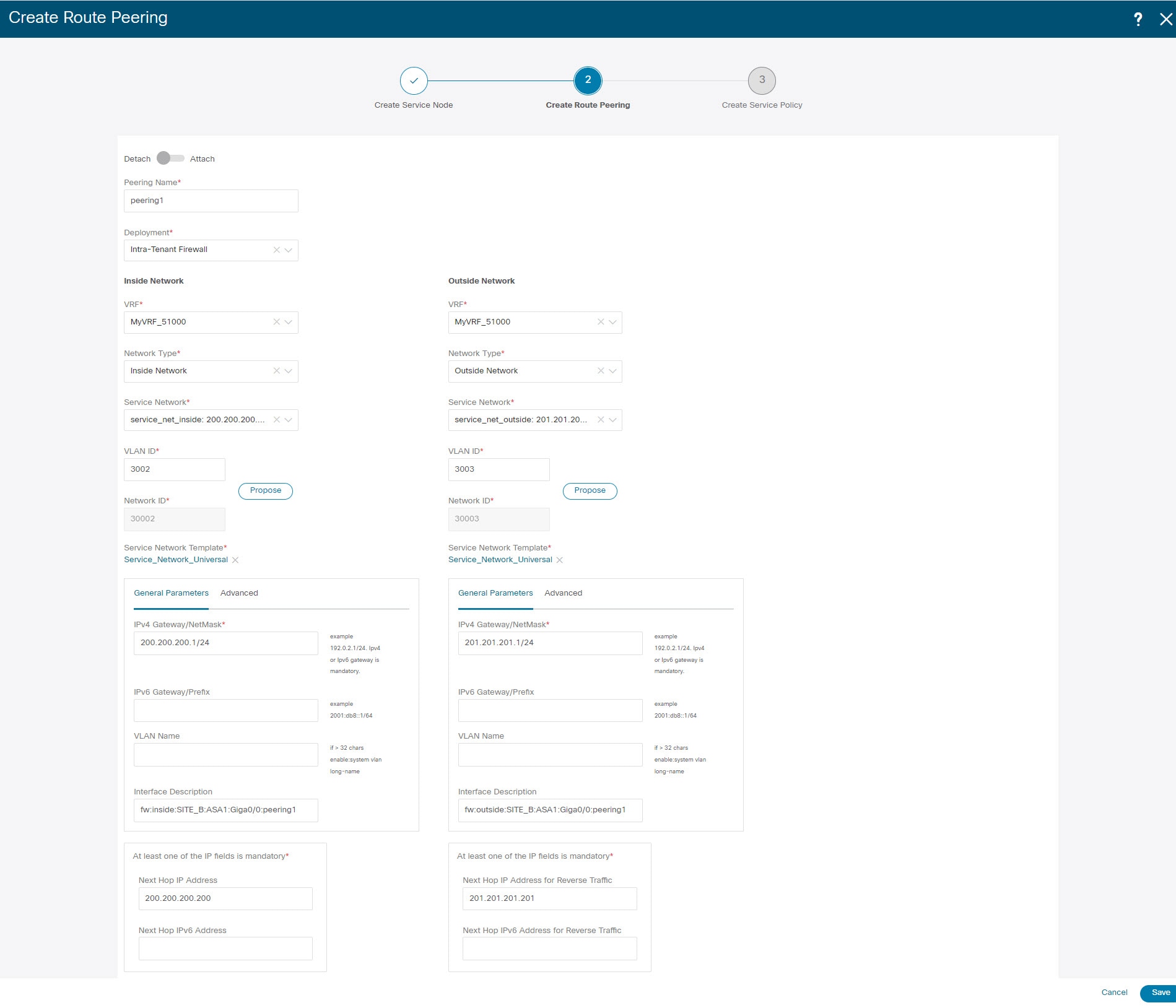
2. Create Route Peering
Let us now configure the peering between a service leaf and a service node.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
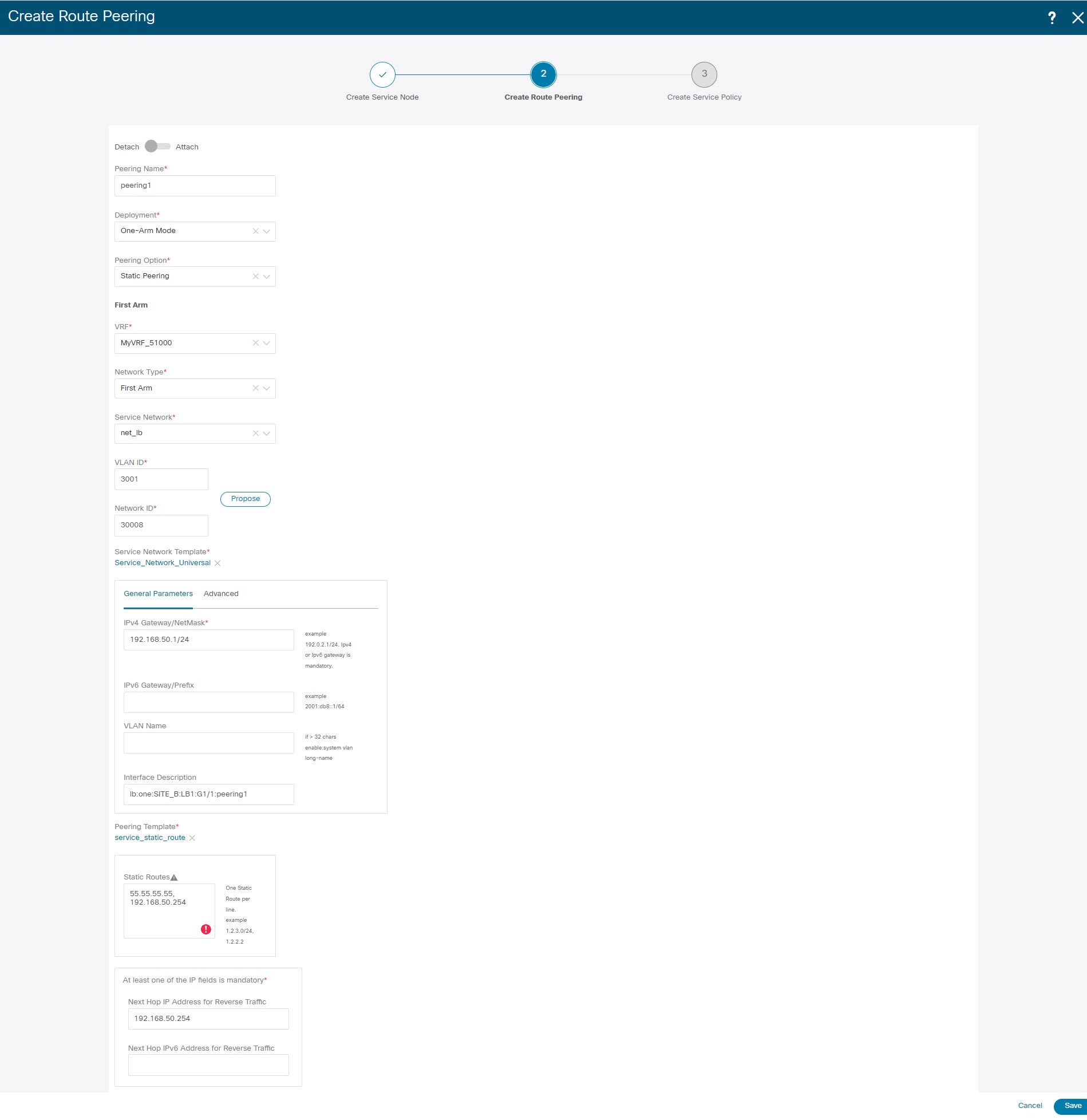
Enter the peering name and select Intra-Tenant Firewall from the Deployment drop-down list. |
| Step 2 |
Under Inside Network, from the VRF drop-down list, select a VRF that exists and select Inside Network under Network Type. Enter the name of the Service Network and specify the Vlan ID. You can also click Propose to allow NDFC to fetch the next available VLAN ID from the specified service network VLAN ID range in the fabric settings. The default Service Network Template is Service_Network_Universal. Under the General Parameters tab, specify the gateway address for the service network. Specify the Next Hop IP Address. This next hop address has to be within the ‘inside service network’ subnet. Under the Advanced tab, the default Routing Tag value is 12345. |
| Step 3 |
Specify the required parameters under Outside Network and specify the Next Hop IP Address for Reverse Traffic. This next hop address for reverse traffic needs to be within the ‘outside service network’ subnet. |
| Step 4 |
Click Save to save the created route peering. |
3. Create Service Policy
Procedure
| Step 1 |
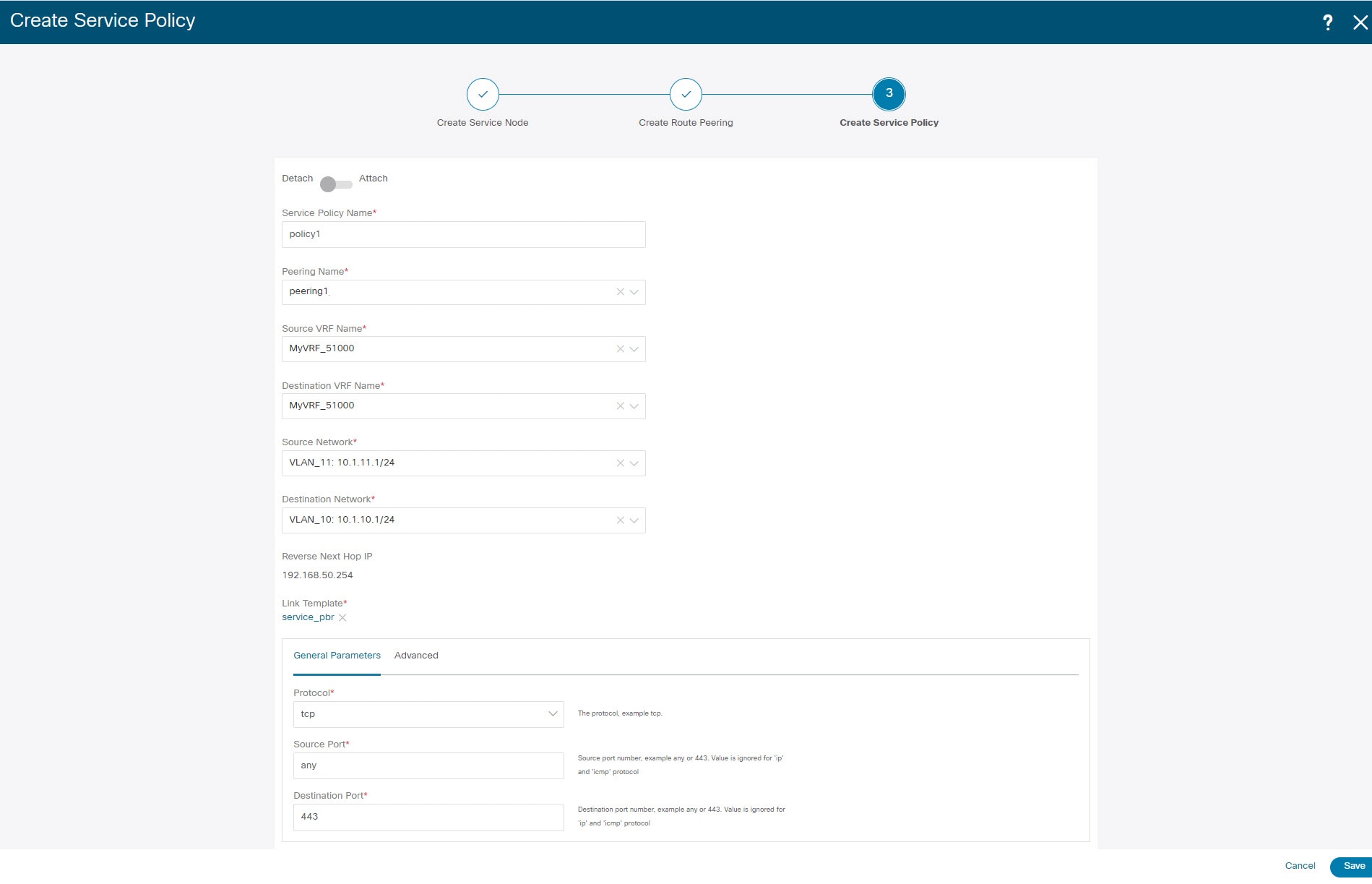
Specify a name for the policy and select the route peering from the Peering Name drop-down list. 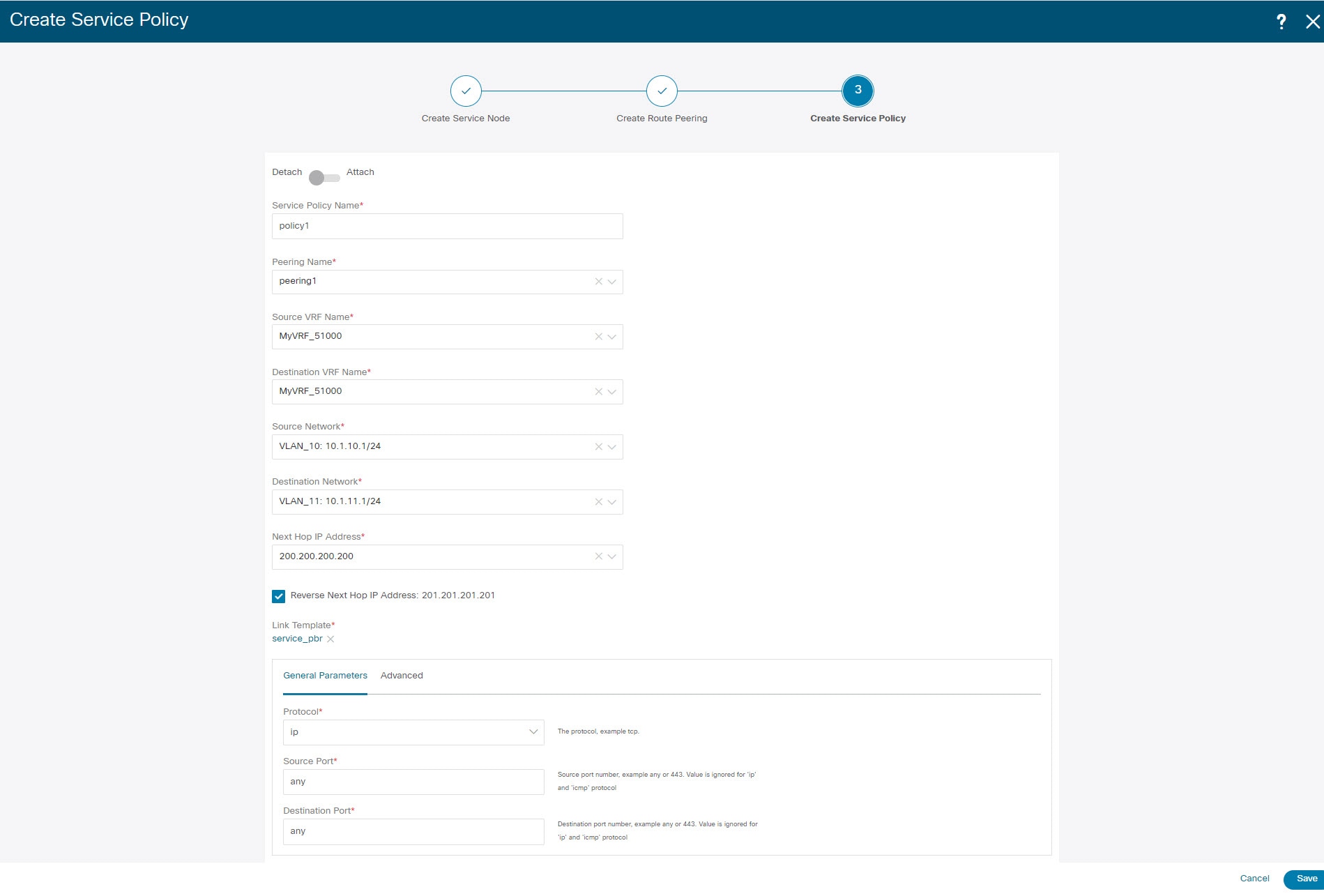 |
||
| Step 2 |
Select the source and destination VRFs from Source VRF Name and Destination VRF Name drop-down lists. The source and destination VRFs for an intra-tenant firewall deployment have to be the same. |
||
| Step 3 |
Select the source and destination networks from Source Network and Destination Network drop-down lists, or specify the source or destination network that is within the network subnets defined in window. |
||
| Step 4 |
The next hop and reverse next hop fields are populated based on the values entered while creating the route peering. Select the check box next to Reverse Next Hop IP Address field to enable policy enforcement on reverse traffic. |
||
| Step 5 |
Under the General Parameters tab in the policy template, select ip from Protocol dropdown list, and specify any in Source Port and Destination Port fields.
|
||
| Step 6 |
Under Advanced tab, by default permit is selected for Route Map Action and none is selected for Next Hop Option. You can change these values, and customize the ACL name and route map match sequence number, if required. For more information, refer Templates in the Layer 4-Layer 7 Service configuration guide. |
||
| Step 7 |
Click Save to save the created service policy. This completes procedures to perform and specify the flows for redirection. |
5. Deploy Service Policy
-
On Services tab, on the Service Policy window choose the required peering.
-
Choose .
The Deploy Service Policy window appears.
-
Click Deploy to confirm deployment.
4. Deploy Route Peering
-
On Services tab, on the Route Peering window choose the required peering.
-
Choose .
The Deploy Route Peering window appears.
-
Click Deploy to confirm deployment.
6. View Stats
Now that the respective redirection policies are deployed, the corresponding traffic will be redirected to the firewall.
To visualize this scenario in NDFC, click the service policy, a slide-in pane appears.
You can view the cumulative statistics for a policy in a specified time range.
Statistics are displayed for:
-
Forwarding traffic on the source switch
-
Reversed traffic on the destination switch
-
Traffic in both directions on the service switch
7. View Traffic Flow in Fabric Builder
The service node in the external fabric is attached to the service leaf, and this external fabric shown as a cloud icon in NDFC topology.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Click the service leaf, a slide-in pane appears and click Show more flows. You can see the flows that are redirected. |
| Step 2 |
Click Details in the Service Flows window to display attachment details. |
8. Visualize Redirected Flows to Destination in the Topology window
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Click Topology and click on leafs to visualize the redirected flows to destination. |
| Step 2 |
Select Redirected Flows from the drop-down list. |
| Step 3 |
Select a policy from the drop-down list or initiate a search by entering a policy name, source network, and destination network in the search field. The search field is autopopulated based on your input. The switches, on which the source and destination network is attached and the flows are redirected and highlighted. |
| Step 4 |
The service node is shown as connected by a dotted line to the leaf switch on the topology window. Hover over the dotted line to get more information about the interface. The traffic from Source traverses to the service leaf where the firewall is configured. Based on firewall rules, traffic is allowed to reach the destination, Leaf 15. |


 Feedback
Feedback