IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
Available Languages
Contents
- IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
- IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
- ICMP for IPv6
- How to Configure IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
- Enabling Flow-Label Marking in Packets that Originate from the Device
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
- Example: Displaying IPv6 Interface Statistics
- Additional References
- Feature Information for IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
IPv6 MTU Path Discovery allows a host to dynamically discover and adjust to differences in the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size of every link along a given data path.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
As in IPv4, path MTU discovery in IPv6 allows a host to dynamically discover and adjust to differences in the MTU size of every link along a given data path. In IPv6, however, fragmentation is handled by the source of a packet when the path MTU of one link along a given data path is not large enough to accommodate the size of the packets. Having IPv6 hosts handle packet fragmentation saves IPv6 device processing resources and helps IPv6 networks run more efficiently.
 Note |
In IPv6, the minimum link MTU is 1280 octets. We recommend using an MTU value of 1500 octets for IPv6 links. |
With IPv6 path MTU discovery, a device originating IPv6 traffic has an MTU cache that contains MTU values received in ICMPv6 "toobig" messages. In order to prevent an attacker from filling the MTU cache, the device keeps track of the destinations to which it has originated (sent) traffic, and only accepts toobig ICMPv6 messages that have an inner destination matching one of these tracked destinations.
If a malicious device can learn to which destination the device is originating traffic, it could still send a toobig ICMPv6 message to the device for this destination, even if the attacker is not on the path to this destination, and succeeds in forcing his entry into the MTU cache. The device then starts fragmenting traffic to this destination, which significantly affects device performance.
Enabling flow-label marking for locally generated traffic can mitigate this attack. Originated packets are marked with a flow label (which is randomly generated and changed every minute), and toobig messages received are checked against the values sent. Unless an attacker can snoop traffic, the attacker will not know which flow label to use, and its toobig message will be dropped.
ICMP for IPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) in IPv6 functions the same as ICMP in IPv4. ICMP generates error messages, such as ICMP destination unreachable messages, and informational messages, such as ICMP echo request and reply messages. Additionally, ICMP packets in IPv6 are used in the IPv6 neighbor discovery process, path MTU discovery, and the Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) protocol for IPv6. MLD is used by IPv6 devices to discover multicast listeners (nodes that want to receive multicast packets destined for specific multicast addresses) on directly attached links. MLD is based on version 2 of the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) for IPv4.
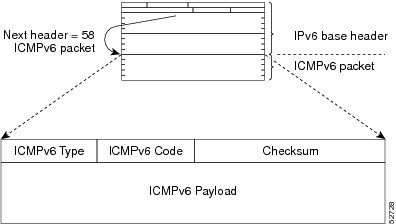
A value of 58 in the Next Header field of the basic IPv6 packet header identifies an IPv6 ICMP packet. ICMP packets in IPv6 are like a transport-layer packet in the sense that the ICMP packet follows all the extension headers and is the last piece of information in the IPv6 packet. Within IPv6 ICMP packets, the ICMPv6 Type and ICMPv6 Code fields identify IPv6 ICMP packet specifics, such as the ICMP message type. The value in the Checksum field is derived (computed by the sender and checked by the receiver) from the fields in the IPv6 ICMP packet and the IPv6 pseudoheader. The ICMPv6 Data field contains error or diagnostic information relevant to IP packet processing. The figure below shows the IPv6 ICMP packet header format.
How to Configure IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
Enabling Flow-Label Marking in Packets that Originate from the Device
This feature allows the device to track destinations to which the device has sent packets that are 1280 bytes or larger.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
Example: Displaying IPv6 Interface Statistics
In the following example, the show ipv6 interface command is used to verify that IPv6 addresses are configured correctly for FastEthernet interface 1/0. Information may also be displayed about the status of IPv6 neighbor redirect messages, IPv6 neighbor discovery messages, stateless autoconfiguration, and MTU size.
Device# show ipv6 interface fastethernet 1/0
Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is stalled, link-local address is FE80::1
Global unicast address(es):
2001:DB8:2000::1, subnet is 2001:DB8:2000::/64
2001:DB8:3000::1, subnet is 2001:DB8:3000::/64
Joined group address(es):
FF02::1
FF02::2
FF02::1:FF00:1
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds
ND advertised reachable time is 0 milliseconds
ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 milliseconds
ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds
ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses.
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
| IPv6 addressing and connectivity |
IPv6 Configuration Guide |
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| IPv6 commands |
Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference |
| Cisco IOS IPv6 features |
Cisco IOS IPv6 Feature Mapping |
MIBs
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for IPv6 MTU Path Discovery |
| Feature Name | Releases | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 MTU Path Discovery |
12.2(2)T 12.2(17a)SX1 12.2(25)SEA 12.2(25)SG 12.2(33)SRA 15.0(2)SG Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1 3.2.0SG |
Path MTU discovery in IPv6 allows a host to dynamically discover and adjust to differences in the MTU size of every link along a given data path. The following commands were introduced or modified: clear ipv6 mtu, ipv6 flowset. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback