MPLS VPN--Carrier Supporting Carrier
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
MPLS VPN—Carrier Supporting Carrier
Providing a Backbone Network to a Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
Establishing a Route Between the Backbone Carrier and the Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
Transporting a Packet Through a Network of a Backbone Carrier and Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
Providing a Backbone Network to a Customer Carrier Who Is a BGP/MPLS VPN Service Provider
Related Features and Technologies
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Configuring the Backbone Carrier PE Router
Configuring the Customer Carrier CE Routers
Verifying the Carrier Supporting Carrier Configuration
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Is an ISP
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Is an MPLS VPN Provider
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network That Contains Route Reflectors
Backbone Carrier Configuration
Customer Carrier Site 1 Configuration
Customer Carrier Site 2 Configuration
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Has VPNs at the Network's Edge
Backbone Carrier Configuration
Customer Carrier Site 1 Configuration
Customer Carrier Site 2 Configuration
MPLS VPN—Carrier Supporting Carrier
The carrier supporting carrier feature enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider to allow other service providers to use a segment of its backbone network.
Feature History
12.0(14)ST
This feature was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(14)ST.
12.0(16)ST
Support for the Cisco 12000 series routers (Engine 0) for the Cisco IOS 12.0 ST release was added.
12.2(8)T
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T. Support was added for the Cisco 12.2 T release for the following platforms: Cisco 3640 series, Cisco 3660 series, Cisco 4500 series, Cisco uBR7200 series, and the Cisco MGX Route Processor Module.
12.0(21)ST
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(21)ST. Support for the Cisco 12000 series routers was added (for specific line cards supported, see Table 5).
12.0(22)S
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S. Support for the Cisco 12000 series routers was added (for specific line cards supported, see Table 5).
12.0(23)S
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(23)S. Support was added for the Cisco 12000 Series Eight-Port OC-3c/STM-1c ATM Line Card (8-Port OC-3 ATM) and the Cisco 12000 Series Three-Port Gigabit Ethernet Line Card (3-Port GbE).
12.2(14)S
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S and implemented on Cisco 7200 and Cisco 7500 series routers.
12.2(28)SB
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB and implemented on the Cisco 10000 series routers
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
This document includes the following sections:
•
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Feature Overview
Carrier supporting carrier is a term used to describe a situation where one service provider allows another service provider to use a segment of its backbone network. The service provider that provides the segment of the backbone network to the other provider is called the backbone carrier. The service provider that uses the segment of the backbone network is called the customer carrier.
This feature module focuses on a backbone carrier that offers Border Gateway Protocol and Multiprotocol Label Switching (BGP/MPLS) VPN services. The customer carrier can be either
•
An Internet service provider (ISP)
•
A BGP/MPLS VPN service provider
This feature module describes both types of customer carrier.
Providing a Backbone Network to a Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
This section explains how a BGP/MPLS VPN service provider (backbone carrier) can provide a segment of its backbone network to a customer who is an ISP.
Consider the following example:
An ISP has two sites: one in California, the other in Maine. Each site is a point of presence (POP). The ISP wants to connect these sites using a VPN service provided by a backbone carrier. Figure 1 illustrates this situation.
Figure 1 Sample BGP/MPLS Backbone Carrier Supporting an ISP


Note
The CE routers in the figures in this feature module are CE routers to the backbone carrier. However, they are PE routers to the customer carrier.

Note
This document uses the following abbreviations:
CE router: A customer edge router is part of a customer network and interfaces to a provider edge (PE) router. In this document, the CE router sits on the edge of the customer carrier network.
PE router: A provider edge router is part of a service provider's network connected to a customer edge (CE) router. In this document, the PE routers sits on the edge of the backbone carrier network.
ASBR: In this document, an autonomous system boundary router connects one autonomous system to another.
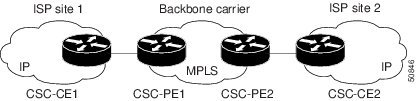
In this example, only the backbone carrier uses MPLS. The customer carrier (ISP) uses only IP. As a result, the backbone carrier must carry all the Internet routes of the customer carrier, which could be as many as 100,000 routes. This poses a scalability problem for the backbone carrier. To solve the scalability problem, the backbone carrier is configured as follows:
•
The backbone carrier allows only internal routes of the customer carrier (IGP routes) to be exchanged between the CE routers of the customer carrier and the PE routers of the backbone carrier.
•
MPLS is enabled on the interface between the CE router of the customer carrier and the PE router of the backbone carrier.
Internal and external routes are differentiated this way:
•
Internal routes go to any of the routers within the ISP.
•
External routes go to the Internet.
The number of internal routes is much smaller than the number of external routes. Restricting the routes between the CE routers of the customer carrier and the PE routers of the backbone carrier significantly reduces the number of routes that the PE router needs to maintain.
Since the PE routers do not have to carry external routes in the VRF routing table, they can use the incoming label in the packet to forward the customer carrier Internet traffic. Adding MPLS to the routers provides a consistent method of transporting packets from the customer carrier to the backbone carrier. MPLS allows the exchange of an MPLS label between the PE and the CE routers for every internal customer carrier route. The routers in the customer carrier have all the external routes either through IBGP or route redistribution to provide Internet connectivity. Figure 2 shows how information is exchanged when the network is configured in this manner.
Figure 2 Backbone Carrier Exchanging Routing Information with a Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP

Establishing a Route Between the Backbone Carrier and the Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
In the example shown in Figure 3, routes are created between the backbone carrier and the customer carrier sites. ASBR2 receives an Internet route that originated outside the network. All routers in the ISP sites have all the external routes through IBGP connections among them.
Figure 3 Establishing a Route Between a Backbone Carrier and a Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP

Table 1 describes the process of establishing the route, which can be divided into two distinct steps:
•
The backbone carrier propagates the IGP information of the customer carrier, which enables the customer carrier routers to reach all the customer carrier routers in the remote sites.
•
Once the routers of the customer carriers in different sites are reachable, external routes can be propagated in the customer carrier sites, using IBGP without using the backbone carrier routers.
Transporting a Packet Through a Network of a Backbone Carrier and Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
Table 2 explains each step in the process of transporting a packet. The following conventions are used in Table 2:
•
The D in the Label Stack and Destination Address column represents an address that is outside the network, such as an Internet address.
•
The notation X(Y) means "the label distributed by Y, which represents the route to X."
•
In the Label Stack and Destination Address column, when a label stack is present, the top label is listed first; the destination address is listed last.
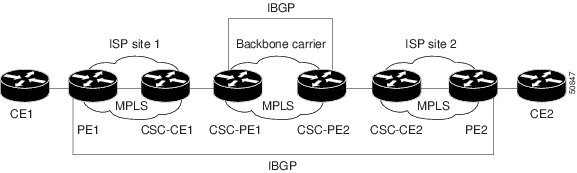
Providing a Backbone Network to a Customer Carrier Who Is a BGP/MPLS VPN Service Provider
When a backbone carrier and the customer carrier both provide BGP/MPLS VPN services, the method of transporting data is different from when a customer carrier provides only ISP services. The following list highlights those differences.
•
When a customer carrier provides BGP/MPLS VPN services, its external routes are VPN-IPv4 routes. When a customer carrier is an ISP, its external routes are IP routes.
•
When a customer carrier provides BGP/MPLS VPN services, every site within the customer carrier must use MPLS. When a customer carrier is an ISP, the sites do not need to use MPLS.
Figure 4 shows how information is exchanged when MPLS VPN services reside on all customer carrier sites and on the backbone carrier.
Figure 4 Backbone Carrier Exchanging Information with a Customer Carrier Who Is an MPLS VPN Service Provider

Establishing a Route Between the Backbone Carrier and the Customer Carrier Who Is an MPLS VPN Service Provider
In the example shown in Figure 5, routes are created between the backbone carrier and the customer carrier sites.
Figure 5 Establishing a Route Between a Backbone Carrier and a Customer Carrier Who Is an MPLS VPN Service Provider
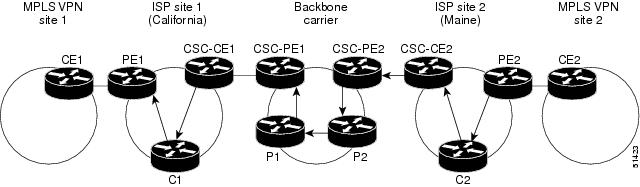
Table 3 describes the process of establishing the route.
Transporting a Packet Through a Network of a Backbone Carrier and Customer Carrier Who Is an MPLS VPN Service Provider
Table 4 explains each step in the process of transporting the packet. The following conventions are used in Table 4:
•
The D in the Label Stack and Destination Address column represents an address that is outside the network, such as an Internet address.
•
The notation X(Y) means "the label distributed by Y, which represents the route to X."
•
In the Label Stack and Destination Address column, when a label stack is present, the top label is listed first; the destination address is listed last.
Benefits
The MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature provides the benefits listed in the following paragraphs to service providers who are backbone carriers and customer carriers.
Benefits to the Backbone Carrier
Implementing the MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature enables the backbone carrier to realize the following benefits:
•
The backbone carrier can accommodate many customer carriers and give them access to its backbone. The backbone carrier does not need to create and maintain separate backbones for its customer carriers. Using one backbone network to support multiple customer carriers simplifies the backbone carrier's VPN operations. The backbone carrier uses a consistent method for managing and maintaining the backbone network. This is also cheaper and more efficient than maintaining separate backbones.
•
The MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature is scalable. Carrier supporting carrier can change the VPN to meet changing bandwidth and connectivity needs. The feature can accommodate unplanned growth and changes. The carrier supporting carrier feature enables tens of thousands of VPNs to be set up over the same network, and it allows a service provider to offer both VPN and Internet services.
•
The MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature is a flexible solution. The backbone carrier can accommodate many types of customer carriers. The backbone carrier can accept customer carriers who are ISPs or VPN service providers or both. The backbone carrier can accommodate customer carriers that require security and various bandwidths.
Benefits to the Customer Carrier
Implementing the MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature enables the customer carrier to realize the following benefits:
•
The MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature removes from the customer carrier the burden of configuring, operating, and maintaining its own backbone. The customer carrier uses the backbone network of a backbone carrier, but the backbone carrier is responsible for network maintenance and operation.
•
Customer carriers who use the VPN services provided by the backbone carrier receive the same level of security that Frame Relay or ATM-based VPNs provide. Customer carriers can also use IPSec in their VPNs for a higher level of security; it is completely transparent to the backbone carrier.
•
Customer carriers can use any link layer technology (SONET, DSL, Frame Relay, and so on) to connect the CE routers to the PE routers and the PE routers to the P routers. The MPLS VPN carrier supporting carrier feature is link layer independent. The CE routers and PE routers use IP to communicate, and the backbone carrier uses MPLS.
•
The customer carrier can use any addressing scheme and still be supported by a backbone carrier. The customer address space and routing information are independent of the address space and routing information of other customer carriers or the backbone provider.
Requirements
The carrier supporting carrier feature includes the following requirements:
•
The PE routers of the backbone carrier require 128 MB of memory.
•
The backbone carrier must enable the PE router to check that the packets it receives from the CE router contain only the labels that the PE router advertised to the CE router. This prevents data spoofing, which occurs when a packet from an unrecognized IP address is sent to a router.
•
A routing protocol is required between the PE and CE routers that connect the backbone carrier to the customer carrier. The routing protocol enables the customer carrier to exchange IGP routing information with the backbone carrier. Use the same routing protocol that the customer carrier uses. You can choose RIP, OSPF, or static routing as the routing protocol. BGP is not supported.
•
Label distribution protocol (LDP) is required between the PE and CE routers that connect the backbone carrier to the customer carrier. LDP is also required on the PE to CE interface for VPN routing/forwarding (VRF). LDP is available on Cisco IOS Release 12.0(10)ST or later.
•
All PE routers that link the backbone carrier to the customer carrier must run this IOS software image. Other PE routers, CE routers, and P routers do not need to run this software image, but, they must run a version of Cisco IOS software that supports MPLS VPNs (Cisco IOS Release 12.0(5)T or later).
•
Every packet that crosses the backbone carrier must be encapsulated, so that the packet includes MPLS labels. To ensure that the packets are encapsulated, issue the following command on the PE routers that connect to CE routers:
(config-if)# mpls ipFor more information, see the IOS Command Reference Guide.
The following features are not supported in the carrier supporting carrier feature:
•
ATM MPLS
•
Carrier supporting carrier traffic engineering
•
Carrier supporting carrier class of service (CoS)
•
RSVP aggregation
•
VPN Multicast between the customer carrier and the backbone carrier network
Related Features and Technologies
The carrier supporting carrier feature is used with the VPN capabilities of MPLS. (MPLS VPNs were introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(5)T.)
Related Documents
•
MPLS Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
•
MPLS Virtual Private Network Enhancements
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.0 Network Protocols Configuration Guide, Part I
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.0 Network Protocols Command Reference, Part I
Supported Platforms
The following router platforms are supported on the edge:
•
Cisco 7200 series
•
Cisco 7500 series
•
Cisco 12000 series
See Table 5 for Cisco 12000 series line card support added for Cisco IOS Releases.
Determining Platform Support Through Cisco Feature Navigator
Cisco IOS software is packaged in feature sets that are supported on specific platforms. To get updated information regarding platform support for this feature, access Cisco Feature Navigator. Cisco Feature Navigator dynamically updates the list of supported platforms as new platform support is added for the feature.
Cisco Feature Navigator is a web-based tool that enables you to determine which Cisco IOS software images support a specific set of features and which features are supported in a specific Cisco IOS image. You can search by feature or release. Under the release section, you can compare releases side by side to display both the features unique to each software release and the features in common.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, you must have an account on Cisco.com. If you have forgotten or lost your account information, send a blank e-mail to cco-locksmith@cisco.com. An automatic check will verify that your e-mail address is registered with Cisco.com. If the check is successful, account details with a new random password will be e-mailed to you. Qualified users can establish an account on Cisco.com by following the directions found at this URL:
Cisco Feature Navigator is updated regularly when major Cisco IOS software releases and technology releases occur. For the most current information, go to the Cisco Feature Navigator home page at the following URL:
Availability of Cisco IOS Software Images
Platform support for particular Cisco IOS software releases is dependent on the availability of the software images for those platforms. Software images for some platforms may be deferred, delayed, or changed without prior notice. For updated information about platform support and availability of software images for each Cisco IOS software release, refer to the online release notes or, if supported, Cisco Feature Navigator.
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature.
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature.
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/MIBS/servlet/index
If Cisco MIB Locator does not support the MIB information that you need, you can also obtain a list of supported MIBs and download MIBs from the Cisco MIBs page at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
To access Cisco MIB Locator, you must have an account on Cisco.com. If you have forgotten or lost your account information, send a blank e-mail to cco-locksmith@cisco.com. An automatic check will verify that your e-mail address is registered with Cisco.com. If the check is successful, account details with a new random password will be e-mailed to you. Qualified users can establish an account on Cisco.com by following the directions found at this URL:
RFCs
•
RFC 1171, A Border Gateway Protocol 4
•
RFC 1164, Application of the Border Gateway Protocol in the Internet
•
RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP-4
•
RFC 2547, BGP/MPLS VPNs
Prerequisites
The backbone carrier must be properly configured for MPLS VPN operation before the customer carriers can access the backbone network. Refer to the MPLS Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and the MPLS Virtual Private Network Enhancements feature modules.
Configuration Tasks
See the following sections to enable a backbone carrier to share its backbone network with a customer carrier. Each task entry in the list indicates if the task is optional or required.
•
Configuring the Backbone Carrier PE Router (required)
•
Configuring the Customer Carrier CE Routers (required)
•
Verifying the Carrier Supporting Carrier Configuration (optional)
Configuring the Backbone Carrier PE Router
To configure the backbone carrier PE route that links to the edge router of the customer carrier, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
Configuring the Customer Carrier CE Routers
To configure the CE router on the customer carrier that links to the edge router of the backbone carrier, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
Verifying the Carrier Supporting Carrier Configuration
The following commands helps to verify the status of LDP sessions that were configured between the backbone carrier and customer carrier. Now the customer carrier ISP sites appear as a VPN customer to the backbone carrier.
This command shows the LDP sessions in VRF VPN1 of the PE router of the backbone carrier.
Router# show mpls ldp discovery vrf vpn1Local LDP Identifier:139.0.0.0:0Discovery Sources:Interfaces:Ethernet1/0 (ldp): xmit/recvLDP Id: 55.0.0.1:0POS6/0 (ldp): xmitThis command list all LDP sessions in a router.
Router# show mpls ldp discovery allLocal LDP Identifier:141.141.141.141:0Discovery Sources:Interfaces:Ethernet1/5 (ldp): xmit/recvLDP Id: 5.5.5.5:0VRF vpn1: Local LDP Identifier:139.0.0.1:0Discovery Sources:Interfaces:Ethernet1/0 (ldp): xmit/recvLDP Id: 55.0.0.1:0POS6/0 (ldp): xmitThe Local LDP Identifier field shows the LDP identifier for the local label switching router for this session. The Interfaces field displays the interfaces engaging in LDP discovery activity:
•
xmit indicates that the interface is transmitting LDP discovery hello packets.
•
recv indicates that the interface is receiving LDP discovery hello packets.
Configuration Examples
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Is an ISP
•
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Is an MPLS VPN Provider
•
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network That Contains Route Reflectors
•
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Has VPNs at the Network's Edge
Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Is an ISP
Figure 6 shows a carrier supporting carrier network configuration where the customer carrier is an ISP. The customer carrier has two sites, each of which is a point of presence (POP). The customer carrier connects these sites using a VPN service provided by the backbone carrier. The backbone carrier uses MPLS. The ISP sites use IP. To enable packet transfer between the ISP sites and the backbone carrier, the CE routers that connect the ISPs to the backbone carrier run MPLS.
Figure 6 Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Carrier Who Is an ISP
The following configuration examples show the configuration of each router in the carrier supporting carrier network. OSPF is the protocol used to connect the customer carrier to the backbone carrier.
CSC-CE1 Configuration
mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 14.14.14.14 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 46.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM2/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM2/0.1 point-to-pointip address 38.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 14.14.14.14 0.0.0.0 area 200network 38.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200network 46.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200CSC-PE1 Configuration
ip cef distributed!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:0route-target export 100:0route-target import 100:0mpls label protocol ldpno mpls aggregate-statistics!interface Loopback0ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Loopback100ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 19.19.19.19 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM1/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 33.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 46.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changespassive-interface ATM3/0/0.1passive-interface Loopback100network 11.11.11.11 0.0.0.0 area 100network 33.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router ospf 200 vrf vpn1log-adjacency-changesredistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 19.19.19.19 0.0.0.0 area 200network 46.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200!router bgp 100bgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 12.12.12.12 remote-as 100neighbor 12.12.12.12 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 12.12.12.12 activateneighbor 12.12.12.12 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 12.12.12.12 activateneighbor 12.12.12.12 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 200 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCSC-PE2 Configuration
ip cef distributed!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:0route-target export 100:0route-target import 100:0mpls label protocol ldpno mpls aggregate-statistics!interface Loopback0ip address 12.12.12.12 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Loopback100ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM0/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM0/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 33.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 47.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changespassive-interface ATM3/0/0.1passive-interface Loopback100network 12.12.12.12 0.0.0.0 area 100network 33.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router ospf 200 vrf vpn1log-adjacency-changesredistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 20.20.20.20 0.0.0.0 area 200network 47.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200!router bgp 100bgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 11.11.11.11 remote-as 100neighbor 11.11.11.11 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 11.11.11.11 activateneighbor 11.11.11.11 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 11.11.11.11 activateneighbor 11.11.11.11 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 200 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCSC-CE2 Configuration
ip cef!mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 16.16.16.16 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 47.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 43.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 16.16.16.16 0.0.0.0 area 200network 43.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200network 47.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Is an MPLS VPN Provider
Figure 7 shows a carrier supporting carrier network configuration where the customer carrier is an MPLS VPN provider. The customer carrier has two sites. The backbone carrier and the customer carrier use MPLS. The IBGP sessions exchange the external routing information of the ISP.
Figure 7 Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Carrier Who Is an MPLS VPN Provider
The following configuration examples show the configuration of each router in the carrier supporting carrier network. OSPF is the protocol used to connect the customer carrier to the backbone carrier.
CE1 Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 17.17.17.17 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/1ip address 37.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router ospf 300log-adjacency-changesredistribute bgp 300 subnetspassive-interface Ethernet0/1network 17.17.17.17 0.0.0.0 area 300!router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30redistribute connectedredistribute ospf 300 match internal external 1 external 2neighbor 37.0.0.1 remote-as 200neighbor 37.0.0.1 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryPE1 Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf vpn2rd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 13.13.13.13 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 38.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/0ip vrf forwarding vpn2ip address 37.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cache!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetspassive-interface Ethernet3/0network 13.13.13.13 0.0.0.0 area 200network 38.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200!router bgp 200no bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 15.15.15.15 remote-as 200neighbor 15.15.15.15 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 15.15.15.15 activateneighbor 15.15.15.15 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 15.15.15.15 activateneighbor 15.15.15.15 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2neighbor 37.0.0.2 remote-as 300neighbor 37.0.0.2 activateneighbor 37.0.0.2 as-overrideneighbor 37.0.0.2 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCSC-CE1 Configuration
mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 14.14.14.14 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 46.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM2/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM2/0.1 point-to-pointip address 38.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 14.14.14.14 0.0.0.0 area 200network 38.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200network 46.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200CSC-PE1 Configuration
ip cef distributed!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:0route-target export 100:0route-target import 100:0mpls label protocol ldpno mpls aggregate-statistics!interface Loopback0ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Loopback100ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 19.19.19.19 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM1/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 33.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 46.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changespassive-interface ATM3/0/0.1passive-interface Loopback100network 11.11.11.11 0.0.0.0 area 100network 33.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router ospf 200 vrf vpn1log-adjacency-changesredistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 19.19.19.19 0.0.0.0 area 200network 46.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200!router bgp 100bgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 12.12.12.12 remote-as 100neighbor 12.12.12.12 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 12.12.12.12 activateneighbor 12.12.12.12 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 12.12.12.12 activateneighbor 12.12.12.12 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 200 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCSC-PE2 Configuration
ip cef distributed!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:0route-target export 100:0route-target import 100:0mpls label protocol ldpno mpls aggregate-statistics!interface Loopback0ip address 12.12.12.12 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Loopback100ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM0/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM0/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 33.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 47.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changespassive-interface ATM3/0/0.1passive-interface Loopback100network 12.12.12.12 0.0.0.0 area 100network 33.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router ospf 200 vrf vpn1log-adjacency-changesredistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 20.20.20.20 0.0.0.0 area 200network 47.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200!router bgp 100bgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 11.11.11.11 remote-as 100neighbor 11.11.11.11 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 11.11.11.11 activateneighbor 11.11.11.11 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 11.11.11.11 activateneighbor 11.11.11.11 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 200 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCSC-CE2 Configuration
ip cef!mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 16.16.16.16 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 47.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 43.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 16.16.16.16 0.0.0.0 area 200network 43.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200network 47.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200PE2 Configuration
ip cefip cef accounting non-recursive!ip vrf vpn2rd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 15.15.15.15 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet3/0ip vrf forwarding vpn2ip address 42.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 43.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetspassive-interface Ethernet3/0network 15.15.15.15 0.0.0.0 area 200network 43.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 200!router bgp 200no bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 13.13.13.13 remote-as 200neighbor 13.13.13.13 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 13.13.13.13 activateneighbor 13.13.13.13 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 13.13.13.13 activateneighbor 13.13.13.13 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2neighbor 42.0.0.2 remote-as 300neighbor 42.0.0.2 activateneighbor 42.0.0.2 as-overrideneighbor 42.0.0.2 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCE2 Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 18.18.18.18 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/1ip address 42.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router ospf 300log-adjacency-changesredistribute bgp 300 subnetspassive-interface Ethernet0/1network 18.18.18.18 0.0.0.0 area 300!router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30redistribute connectedredistribute ospf 300 match internal external 1 external 2neighbor 42.0.0.1 remote-as 200neighbor 42.0.0.1 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryConfiguring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network That Contains Route Reflectors
Figure 8 shows a carrier supporting carrier network configuration that contains route reflectors. The customer carrier has two sites.
Figure 8 Carrier Supporting Carrier Network that Contains Route Reflectors


Note
A connection between route reflectors (RR) is not necessary.
The following configuration examples show the configuration of each router in the carrier supporting carrier network. Note the following:
•
The router IP addresses are abbreviated for ease of reading. For example, the loopback address for PE 1 is 25, which is equivalent to 25.25.25.25.
•
The following list shows the loopback addresses for the CSC-PE routers:
–
CSC-PE1 (75K-37-3): loopback 0 = 15.15.15.15, loopback 1 = 18.18.18.18
–
CSC-PE2 (75K-38-3): loopback 0 = 16.16.16.16, loopback 1 = 20.20.20.20
Backbone Carrier Configuration
Route Reflector 1 (72K-37-1) Configuration
interface Loopback0ip address 13.13.13.13 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 mplsip address 51.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!interface ATM1/1no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/1.1 mplsip address 52.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!router ospf 100auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000network 13.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 51.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 52.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router bgp 100no synchronizationno bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp cluster-id 1redistribute staticneighbor 15.15.15.15 remote-as 100neighbor 15.15.15.15 update-source Loopback0neighbor 16.16.16.16 remote-as 100neighbor 16.16.16.16 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 15.15.15.15 activateneighbor 15.15.15.15 route-reflector-clientneighbor 15.15.15.15 send-community extendedneighbor 16.16.16.16 activateneighbor 16.16.16.16 route-reflector-clientneighbor 16.16.16.16 send-community extendedbgp scan-time import 5exit-address-familyRoute Reflector 2 (72K-38-1) Configuration
interface Loopback0ip address 14.14.14.14 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 mplsip address 53.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!interface ATM1/1no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/1.1 mplsip address 52.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!router ospf 100auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000network 14.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 52.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 53.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router bgp 100no synchronizationno bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp cluster-id 1redistribute staticneighbor 15.15.15.15 remote-as 100neighbor 15.15.15.15 update-source Loopback0neighbor 16.16.16.16 remote-as 100neighbor 16.16.16.16 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 15.15.15.15 activateneighbor 15.15.15.15 route-reflector-clientneighbor 15.15.15.15 send-community extendedneighbor 16.16.16.16 activateneighbor 16.16.16.16 route-reflector-clientneighbor 16.16.16.16 send-community extendedbgp scan-time import 5exit-address-familyCSC-PE1 (75K-37-3) Configuration
ip cef distributed!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:1route-target export 100:1route-target import 100:1!interface Loopback0ip address 15.15.15.15 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Loopback1ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 18.18.18.18 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/0/1ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 55.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM1/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/1/0.1 mplsip address 56.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 50.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 6 32 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/1/0.1 mplsip address 51.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!router ospf 100auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000network 15.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 51.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 55.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 56.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router ospf 1 vrf vpn1redistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 17.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 18.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 55.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 100no bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp log-neighbor-changesneighbor 13.13.13.13 remote-as 100neighbor 13.13.13.13 update-source Loopback0neighbor 14.14.14.14 remote-as 100neighbor 14.14.14.14 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4redistribute staticno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 13.13.13.13 activateneighbor 13.13.13.13 send-community extendedneighbor 14.14.14.14 activateneighbor 14.14.14.14 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 1 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCSC-PE2 (75K-38-3) Configuration
ip cef distributed!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:1route-target export 100:1route-target import 100:1!interface Loopback0ip address 16.16.16.16 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Loopback1ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM0/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM0/1/0.1 mplsip address 56.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!interface ATM2/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM2/1/0.1 mplsip address 53.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls atm vpi 2-5mpls ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 54.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 6 32 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/1/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 57.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 6 33 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 100auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000network 16.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 53.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 54.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 56.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100network 57.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 100!router ospf 1 vrf vpn1redistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 19.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 20.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 54.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 57.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 100no bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp log-neighbor-changesneighbor 13.13.13.13 remote-as 100neighbor 13.13.13.13 update-source Loopback0neighbor 14.14.14.14 remote-as 100neighbor 14.14.14.14 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4redistribute staticno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 13.13.13.13 activateneighbor 13.13.13.13 send-community extendedneighbor 14.14.14.14 activateneighbor 14.14.14.14 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 1 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCustomer Carrier Site 1 Configuration
PE1 (72K-36-8) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf vpn2rd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1no mpls ip propagate-ttl!interface Loopback0ip address 25.25.25.25 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 66.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/0ip vrf forwarding vpn2ip address 70.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cache!interface Ethernet3/1ip address 67.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/2ip address 64.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1network 25.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 64.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 66.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 67.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 200neighbor 22.22.22.22 remote-as 200neighbor 22.22.22.22 update-source Loopback0neighbor 23.23.23.23 remote-as 200neighbor 23.23.23.23 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2redistribute connectedneighbor 70.0.0.2 remote-as 300neighbor 70.0.0.2 activateneighbor 70.0.0.2 as-overrideno auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 22.22.22.22 activateneighbor 22.22.22.22 send-community extendedneighbor 23.23.23.23 activateneighbor 23.23.23.23 send-community extendedexit-address-familyCSC-CE1 (72K-36-9) Configuration
ip cefno ip domain-lookup!interface Loopback0ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 50.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 6 32 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM2/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM2/0.1 point-to-pointip address 66.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/0ip address 65.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/1ip address 55.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1network 11.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 55.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 65.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 66.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101PE2 (72K-36-7) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf vpn2rd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1no mpls ip propagate-ttl!interface Loopback0ip address 24.24.24.24 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Ethernet3/0ip address 65.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/1ip vrf forwarding vpn2ip address 71.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cache!interface Ethernet3/2ip address 67.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet3/3ip address 63.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1network 24.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 63.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 65.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 67.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 200neighbor 22.22.22.22 remote-as 200neighbor 22.22.22.22 update-source Loopback0neighbor 23.23.23.23 remote-as 200neighbor 23.23.23.23 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2neighbor 71.0.0.2 remote-as 300neighbor 71.0.0.2 activateneighbor 71.0.0.2 as-overrideno auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 22.22.22.22 activateneighbor 22.22.22.22 send-community extendedneighbor 23.23.23.23 activateneighbor 23.23.23.23 send-community extendedexit-address-familyRoute Reflector 3 (36K-38-4) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 23.23.23.23 255.255.255.255!interface Ethernet1/1ip address 64.0.0.1 255.0.0.0mpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface Ethernet1/2ip address 63.0.0.1 255.0.0.0mpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM3/0no ip addressno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm scrambling cell-payloadno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0.1 point-to-pointip address 62.0.0.2 255.0.0.0atm pvc 100 0 55 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1log-adjacency-changesnetwork 23.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 62.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 63.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 64.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 200no synchronizationno bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp cluster-id 2redistribute staticneighbor 21.21.21.21 remote-as 200neighbor 21.21.21.21 update-source Loopback0neighbor 24.24.24.24 remote-as 200neighbor 24.24.24.24 update-source Loopback0neighbor 25.25.25.25 remote-as 200neighbor 25.25.25.25 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 21.21.21.21 activateneighbor 21.21.21.21 route-reflector-clientneighbor 21.21.21.21 send-community extendedneighbor 24.24.24.24 activateneighbor 24.24.24.24 route-reflector-clientneighbor 24.24.24.24 send-community extendedneighbor 25.25.25.25 activateneighbor 25.25.25.25 route-reflector-clientneighbor 25.25.25.25 send-community extendedexit-address-familyCE1 (36K-36-1) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 28.28.28.28 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/1ip address 70.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/2ip address 71.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router bgp 300network 28.0.0.0network 70.0.0.0network 71.0.0.0neighbor 70.0.0.1 remote-as 200neighbor 71.0.0.1 remote-as 200Customer Carrier Site 2 Configuration
CSC-CE3 (72K-36-6) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 12.12.12.12 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 54.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 6 32 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface POS2/0ip address 58.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastencapsulation pppmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 59.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 40 aal5snapmpls ip!router ospf 1network 12.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 54.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 58.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 59.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101PE3 (72K-36-4) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf vpn2rd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1!!interface Loopback0ip address 21.21.21.21 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet3/0ip vrf forwarding vpn2ip address 80.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet3/1ip vrf forwarding vpn2ip address 81.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet3/2ip address 61.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 59.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 40 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM6/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM6/0.1 point-to-pointip address 60.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 20 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1network 21.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 59.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 60.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 61.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 200neighbor 22.22.22.22 remote-as 200neighbor 22.22.22.22 update-source Loopback0neighbor 23.23.23.23 remote-as 200neighbor 23.23.23.23 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2redistribute connectedneighbor 80.0.0.2 remote-as 300neighbor 80.0.0.2 activateneighbor 80.0.0.2 as-overrideneighbor 81.0.0.2 remote-as 300neighbor 81.0.0.2 activateno auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 22.22.22.22 activateneighbor 22.22.22.22 send-community extendedneighbor 23.23.23.23 activateneighbor 23.23.23.23 send-community extendedexit-address-familyCSC-CE4 (72K-36-5) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface POS4/0ip address 58.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastencapsulation pppmpls label protocol ldpmpls ipclock source internal!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 60.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 20 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM6/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM6/0.1 point-to-pointip address 57.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 6 33 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 57.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 58.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 60.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101Route Reflector 4 (36K-38-5) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255!interface Ethernet0/1ip address 61.0.0.2 255.0.0.0mpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!interface ATM2/0no ip addressno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm scrambling cell-payloadno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM2/0.1 point-to-pointip address 62.0.0.1 255.0.0.0atm pvc 100 0 55 aal5snapmpls label protocol ldpmpls ip!router ospf 1log-adjacency-changesnetwork 22.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 61.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101network 62.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 101!router bgp 200no synchronizationno bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp cluster-id 2redistribute staticneighbor 21.21.21.21 remote-as 200neighbor 21.21.21.21 update-source Loopback0neighbor 24.24.24.24 remote-as 200neighbor 24.24.24.24 update-source Loopback0neighbor 25.25.25.25 remote-as 200neighbor 25.25.25.25 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 21.21.21.21 activateneighbor 21.21.21.21 route-reflector-clientneighbor 21.21.21.21 send-community extendedneighbor 24.24.24.24 activateneighbor 24.24.24.24 route-reflector-clientneighbor 24.24.24.24 send-community extendedneighbor 25.25.25.25 activateneighbor 25.25.25.25 route-reflector-clientneighbor 25.25.25.25 send-community extendedexit-address-familyCE2 (36K-36-2) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 26.26.26.26 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/1ip address 80.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/2ip address 82.0.0.1 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router ospf 300redistribute bgp 300network 26.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 300network 82.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 300!router bgp 300network 26.0.0.0network 80.0.0.0network 82.0.0.0neighbor 80.0.0.1 remote-as 200CE3 (36K-36-3) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 27.27.27.27 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet1/1ip address 81.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet1/2ip address 82.0.0.2 255.0.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router ospf 300redistribute bgp 300network 27.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 300network 82.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 300!router bgp 300network 27.0.0.0network 81.0.0.0network 82.0.0.0neighbor 81.0.0.1 remote-as 200Configuring a Carrier Supporting Carrier Network with a Customer Who Has VPNs at the Network's Edge
Figure 9 shows a carrier supporting carrier network configuration where the customer carrier has VPNs at the network's edge.
Figure 9 Carrier Supporting Carrier Network
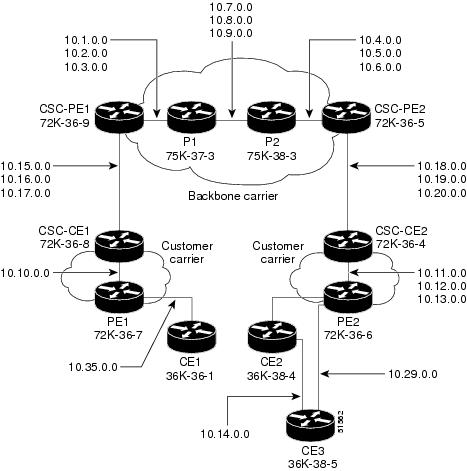
Backbone Carrier Configuration
CSC-PE1 (72K-36-9) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:0route-target export 100:0route-target import 100:0mpls label protocol ldp!!interface Loopback0ip address 14.14.14.14 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Loopback100ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.1.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM1/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.2.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM1/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.3.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM2/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM2/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 30.15.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM2/0.2 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 30.16.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM2/0.3 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 30.17.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetspassive-interface ATM2/0.1passive-interface ATM2/0.2passive-interface ATM2/0.3passive-interface Loopback100network 14.14.14.14 0.0.0.0 area 100network 30.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.2.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.3.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100!router ospf 200 vrf vpn1log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsredistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 22.22.22.22 0.0.0.0 area 200network 30.15.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200!router bgp 100bgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 11.11.11.11 remote-as 100neighbor 11.11.11.11 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 11.11.11.11 activateneighbor 11.11.11.11 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 11.11.11.11 activateneighbor 11.11.11.11 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 200 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyP1 (75K-37-3) Configuration
ip cef distributed!mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 12.12.12.12 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALno atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.7.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 103 0 53 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM1/1/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.8.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 104 0 54 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM1/1/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.9.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 105 0 55 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM3/0/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/0/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.1.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldpmpls accounting experimental inputtag-switching ip!interface ATM3/0/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.2.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM3/0/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.3.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 12.12.12.12 0.0.0.0 area 100network 30.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.2.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.3.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.7.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.8.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.9.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100P2 (75K-38-3) Configuration
ip cef distributed!mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 13.13.13.13 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM0/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM0/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.7.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 103 0 53 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM0/1/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.8.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 104 0 54 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM0/1/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.9.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 105 0 55 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM3/1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastip route-cache distributedatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM3/1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.4.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM3/1/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.5.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM3/1/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.6.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 13.13.13.13 0.0.0.0 area 100network 30.4.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.5.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.6.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.7.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.8.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.9.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100!CSC-PE2 (72K-36-5) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf vpn1rd 100:0route-target export 100:0route-target import 100:0mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Loopback100ip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 23.23.23.23 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 30.18.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM5/0.2 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 30.19.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM5/0.3 point-to-pointip vrf forwarding vpn1ip address 30.20.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM6/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM6/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.4.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM6/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.5.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM6/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.6.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 100log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetspassive-interface ATM5/0.1passive-interface ATM5/0.2passive-interface ATM5/0.3passive-interface Loopback100network 11.11.11.11 0.0.0.0 area 100network 30.4.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.5.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100network 30.6.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 100!router ospf 200 vrf vpn1log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsredistribute bgp 100 metric-type 1 subnetsnetwork 23.23.23.23 0.0.0.0 area 200network 30.18.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.19.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.20.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200!router bgp 100bgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 14.14.14.14 remote-as 100neighbor 14.14.14.14 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 14.14.14.14 activateneighbor 14.14.14.14 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 14.14.14.14 activateneighbor 14.14.14.14 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1redistribute ospf 200 match internal external 1 external 2no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCustomer Carrier Site 1 Configuration
CSC-CE1 (72K-36-8) Configuration
ip cef!mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 15.15.15.15 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface ATM1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM1/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.15.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM1/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.16.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM1/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.17.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface Ethernet3/1ip address 30.10.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 15.15.15.15 0.0.0.0 area 200network 30.10.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.15.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200PE1 (72K-36-7) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf customersiterd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 16.16.16.16 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Ethernet3/1ip vrf forwarding customersiteip address 30.35.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cache!interface Ethernet3/2ip address 30.10.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachempls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetspassive-interface Ethernet3/1network 16.16.16.16 0.0.0.0 area 200network 30.10.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200!router bgp 200no bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 18.18.18.18 remote-as 200neighbor 18.18.18.18 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 18.18.18.18 activateneighbor 18.18.18.18 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 18.18.18.18 activateneighbor 18.18.18.18 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf customersiteneighbor 30.35.0.1 remote-as 300neighbor 30.35.0.1 activateneighbor 30.35.0.1 as-overrideneighbor 30.35.0.1 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCE1 (36K-36-1) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 19.19.19.19 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/2ip address 30.35.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router ospf 300log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsredistribute bgp 300 subnetspassive-interface Ethernet0/2network 19.19.19.19 0.0.0.0 area 300!router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30redistribute connectedredistribute ospf 300 match internal external 1 external 2neighbor 30.35.0.2 remote-as 200neighbor 30.35.0.2 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryCustomer Carrier Site 2 Configuration
CSC-CE2 (72K-36-4) Configuration
ip cef!mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 17.17.17.17 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.11.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM5/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.12.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM5/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.13.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM6/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM6/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.18.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM6/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.19.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM6/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.20.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsnetwork 17.17.17.17 0.0.0.0 area 200network 30.11.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.12.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.13.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.18.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.19.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.20.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200PE2 (72K-36-6) Configuration
ip cef!ip vrf customersiterd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1mpls label protocol ldp!interface Loopback0ip address 18.18.18.18 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcastno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cache!interface Ethernet3/0ip vrf forwarding customersiteip address 30.29.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet3/1ip vrf forwarding customersiteip address 30.30.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface ATM5/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheatm clock INTERNALatm sonet stm-1no atm enable-ilmi-trapno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM5/0.1 point-to-pointip address 30.11.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 100 0 50 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM5/0.2 point-to-pointip address 30.12.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 101 0 51 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!interface ATM5/0.3 point-to-pointip address 30.13.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcastatm pvc 102 0 52 aal5snapno atm enable-ilmi-trapmpls label protocol ldptag-switching ip!router ospf 200log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetspassive-interface Ethernet3/0passive-interface Ethernet3/1network 18.18.18.18 0.0.0.0 area 200network 30.11.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.12.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200network 30.13.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 200!router bgp 200no bgp default ipv4-unicastbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30neighbor 16.16.16.16 remote-as 200neighbor 16.16.16.16 update-source Loopback0!address-family ipv4neighbor 16.16.16.16 activateneighbor 16.16.16.16 send-community extendedno synchronizationexit-address-family!address-family vpnv4neighbor 16.16.16.16 activateneighbor 16.16.16.16 send-community extendedexit-address-family!address-family ipv4 vrf customersiteneighbor 30.29.0.1 remote-as 300neighbor 30.29.0.1 activateneighbor 30.29.0.1 as-overrideneighbor 30.29.0.1 advertisement-interval 5neighbor 30.30.0.1 remote-as 300neighbor 30.30.0.1 activateneighbor 30.30.0.1 as-overrideneighbor 30.30.0.1 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-familyCE2 (36K-38-4) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 21.21.21.21 255.255.255.255!interface Ethernet1/3ip address 30.29.0.1 255.255.0.0!interface Ethernet5/0ip address 30.14.0.1 255.255.0.0!router ospf 300log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsredistribute bgp 300 subnetspassive-interface Ethernet1/3network 21.21.21.21 0.0.0.0 area 300network 30.14.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 300!router bgp 300no synchronizationtimers bgp 10 30redistribute connectedredistribute ospf 300 match internal external 1 external 2neighbor 30.29.0.2 remote-as 200neighbor 30.29.0.2 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryCE3 (36K-38-5) Configuration
ip cef!interface Loopback0ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.255no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/2ip address 30.30.0.1 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Ethernet0/3ip address 30.14.0.2 255.255.0.0no ip directed-broadcast!router ospf 300log-adjacency-changesredistribute connected subnetsredistribute bgp 300 subnetspassive-interface Ethernet0/2network 20.20.20.20 0.0.0.0 area 300network 30.14.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 300!router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changestimers bgp 10 30redistribute connectedredistribute ospf 300 match internal external 1 external 2neighbor 30.30.0.2 remote-as 200neighbor 30.30.0.2 advertisement-interval 5no auto-summaryCommand Reference
This feature requires no new or modified commands. All commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2 command reference publications.
Glossary
AS—autonomous system. A collection of networks under a common administration sharing a common routing strategy.
ASBR—autonomous system boundary router. An edge router located between an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) autonomous system and a non-OSPF network. ASBRs run both OSPF and another routing protocol, such as RIP.
BGP—Border Gateway Protocol. A routing protocol that exchanges network reachability information with other BGP systems, which may be within the same autonomous system or between multiple autonomous systems.
CE router—customer edge router. A router that is part of a customer network and that interfaces to a provider edge (PE) router.
EBGP—External Border Gateway Protocol. A Border Gateway Protocol between routers located in different autonomous systems.
IBGP—Internal Border Gateway Protocol. A Border Gateway Protocol between routers within the same autonomous system.
LDP—label distribution protocol. A standard protocol used by MPLS-enabled routers to assign the labels (addresses) used to forward packets.
LSP—label-switched path. A sequence of hops in which a packet travels from one router to another router by means of label switching mechanisms. A label-switched path can be established dynamically, based on normal routing mechanisms, or through configuration.
LSR—label switching router. An LSR forwards packets in an MPLS network by looking only at the fixed-length label.
MPLS—Multiprotocol Label Switching. MPLS is a method for forwarding packets (frames) through a network. It enables routers at the edge of a network to apply labels to packets (frames). ATM switches or existing routers in the network core can switch packets according to the labels.
Multihop BGP—A Border Gateway Protocol between two routers in different autonomous systems that are more than one hop away from each other.
NLRI—Network Layer Reachability Information. BGP routers exchange network layer reachability information, which includes the full route (BGP AS numbers) to reach the destination network.
PE router—provider edge router. A router that is part of a service provider's network connected to a customer edge (CE) router. All MPLS VPN processing occurs in the PE router.
POP—point of presence. An access point to the Internet. A POP has a unique IP address. The ISP or online service provider (such as AOL) has one or more POPs on the Internet. ISP users dial into the POP to connect to the Internet. A POP can reside in rented space owned by the telecommunications carrier (such as Sprint) to which the ISP is connected. A POP usually includes routers, digital/analog call aggregators, servers, and frequently frame relay or ATM switches.
RD—route distinguisher. An 8-byte value that is concatenated with an IPv4 prefix to create a unique VPN-IPv4 prefix.
RIP—Routing Information Protocol. An internal gateway protocol used to exchange routing information within an autonomous system. RIP uses hop count as a routing metric.
VPN—Virtual Private Network. VPNs connect branch offices and remote users through a shared or public network, such as the Internet, and provide the same security and availability as a private network. Because VPNs use an existing shared WAN infrastructure, costs are lower and deployment is faster than is the case with traditional private networks. A VPN can consist of sites (or systems) that are all from the same enterprise (intranet) or from different enterprises (extranet); it can consist of sites (or systems) that all attach to the same service provider backbone or to different service provider backbones.
VPN-IPv4—A prefix that consists of a customer VPN address that has been made unique by the addition of an 8-byte route distinguisher.
VRF table—VPN routing/forwarding table. A VRF table includes the routing information that defines a customer VPN site that is attached to a PE router. A VRF table consists of the following elements:
•
An IP routing table
•
A derived forwarding table
•
A set of interfaces that use the forwarding table
•
A set of rules and routing protocols that determine what goes into the forwarding table
CCSP, CCVP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0601R)
Copyright © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback