Access VPDN Dial-in Using IPSec Over L2TP
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Access VPDN Dial-in Using IPSec Over L2TP
Proposed Solution No. 2: IPSec Tunnel Between the Peer and LNS
Overview of Call Establishment
Configuring the Peer for IPSec over VPDN
Configuring the LAC for IPSec over VPDN
Configuring the LNS for IPSec over VPDN
Configuring the LNS TACACS+ Server for VPDN
LNS TACACS+ Server Configuration
Peer Debug Output from Successful IPSec Negotiation
LNS Debug Output From Successful IPSec Negotiation
Access VPDN Dial-in Using IPSec Over L2TP
This document describes how an Internet service provider (ISP) partners with one of its enterprise customers to add Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) encryption to an existing virtual private dial network (VPDN).
VPDNs are networks that extend dial access to users over a shared infrastructure. They use Layer 2 tunneling protocols L2F, L2TP or PPTP to tunnel user calls through the Internet. They are a cost-effective method of establishing long-distance point-to-point connections between remote users and a private network.
However, the Internet is subject to many security threats including loss of privacy, loss of data integrity, identity spoofing, and denial of service. The Layer 2 tunneling protocols do not offer protection from these threats. The goal of IPSec is to minimize all of these threats in the existing network infrastructure itself, without requiring expensive host and application modifications.

Note
Although the network used to document this solution is a fully functioning, end-to-end network and the complete configurations for the devices are included, this document focuses on the IPSec configurations. It does not discuss in detail such features as basic IP connectivity and VPDN configuration.
This document contains the following sections:
•
Proposed Solution No. 2: IPSec Tunnel Between the Peer and LNS
Business Objectives
The ISP has established a VPDN network to offer remote access service to its customers. It now wants to expand this VPDN service to include encryption. The goal of the ISP is to implement this encryption service as quickly, easily, and inexpensively as possible without disrupting the existing network or purchasing new equipment.
The enterprise company has leased VPDN service from the ISP to connect its remote office to its headquarters office. This VPDN service is sufficient for nonsensitive traffic, but now the enterprise wants to be able to securely send sensitive traffic between the remote office and the headquarters. The enterprise determines that only the connection between the remote office and headquarters needs encryption—mobile users that dial-in from laptop PCs need not establish encrypted sessions.
Original Network Topology
The enterprise and ISP have already configured a VPDN network. Figure 1 shows the original VPDN network topology without IPSec.
Figure 1 Original Network Topology

Figure 1 shows the entire end-to-end network topology; however, only the devices described in Table 1 are critical to the VPDN functionality.
Table 1 VPDN Devices
In this network, users at the enterprise remote office are connected to the peer. When users need to connect to the headquarters office, the peer initiates a VPDN session that uses L2TP to tunnel the user session to the headquarters office. First the peer establishes a PPP session with the local LAC of the ISP. The LAC retrieves L2TP tunneling information from the LAC AAA server, and then establishes an L2TP tunnel and session with the LNS at the enterprise headquarters. The LNS forwards the user name and password to the LNS AAA server for authentication and authorization. Once the user is authenticated and authorized, the user has access to the headquarters network.
Business Drivers
The preexisting VPDN network uses L2TP to tunnel PPP traffic over the Internet. Because L2TP does not encrypt traffic, both the control and data packets of the L2TP protocol are vulnerable to the following types of attacks:
•
Discovery of user identities by snooping data packets.
•
Modification packets (both control and data).
•
Hijacking of the L2TP tunnel or the PPP connection inside the tunnel.
•
Denial of service attacks that terminate PPP connections or L2TP tunnels.
•
Disruption of the PPP Encryption Control Protocol (ECP) negotiation in order to weaken or remove confidentiality protection.
•
Disruption of the PPP Link Control Protocol (LCP) authentication negotiation so as to weaken the PPP authentication process or gain access to user passwords.
IPSec addresses these threats in the following ways:
•
Providing authentication, integrity, and replay protection of control packets.
•
Providing integrity and replay protection of data packets.
•
Protecting control packet confidentiality.
•
Providing the option of a scalable approach to key management.
L2TP tunnel authentication provides mutual authentication between the LAC and the LNS at tunnel origination. Therefore, it does not protect control and data traffic on a per-packet basis. PPP authenticates the client to the LNS, but also does not provide per-packet authentication, integrity, or replay protection.
We recommend IPSec as the best method to ensure per-packet authentication, integrity, and replay protection.
Possible Solutions
Possible Solution No. 1: IPSec Tunnel Between the LAC and LNS
The client initiates a PPP session (either by itself or by using a peer) to the LAC. The LAC negotiates an L2TP tunnel with the LNS and forwards the client PPP session to the LNS. The LAC and LNS then negotiate an IPSec tunnel to encrypt the client PPP session. The session is encrypted between the LAC and LNS, which is the segment of the network most susceptible to attack, but it is not encrypted between the client and the LAC.
Possible Solution No. 2: IPSec Tunnel Between the Peer and LNS
The client connects to the peer, and the peer initiates a PPP session to the LAC. The LAC negotiates an L2TP tunnel with the LNS and forwards the client PPP session to the LNS. The peer and LNS then negotiate an IPSec tunnel to encrypt the client PPP session. In this solution, the only segment of the network that is not encrypted is the connection between the client and the peer. But because the client and peer are typically in the same office, this solution usually is not a security risk.
Possible Solution No. 3: IPSec Tunnel Between the Client and LNS
The client initiates a PPP session (either by itself or by using a peer) to the LAC. The LAC negotiates an L2TP tunnel with the LNS and forwards the client PPP session to the LNS. The client and LNS then negotiate an IPSec tunnel to encrypt the client PPP session. In this solution, the entire network is encrypted. This solution is useful when a peer is shared by different parties. It is also useful for mobile users that do not have access to a peer but still need a secure remote connection. The disadvantages of this solution are that it requires that every client be configured for IPSec (instead of just the single peer), and that IPSec negotiation may take longer on clients than on the peer.
Proposed Solution No. 2: IPSec Tunnel Between the Peer and LNS
The enterprise company decides to implement solution no. 2 because it is the simplest solution that provides the encryption it needs: The enterprise requires that the entire session be encrypted—not just the link between the LAC and LNS. The enterprise maintains its own peer at the remote office, so it does not need to encrypt the connections between clients and the peer. The enterprise does not need encryption for its mobile users, so it does not need to configure client-initiated IPSec.
Overview
Adding IPSec to an existing VPDN network is a relatively simple process. Usually, no new equipment is required; the existing VPDN devices can be reconfigured to perform IPSec. The only situation in which you might need to purchase new equipment is if the existing equipment does not have enough CPU power to perform IPSec in addition to its existing responsibilities.
Network Topology
Figure 2 shows the end-to-end IPSec VPDN network.
Figure 2 Postimplementation Network Topology
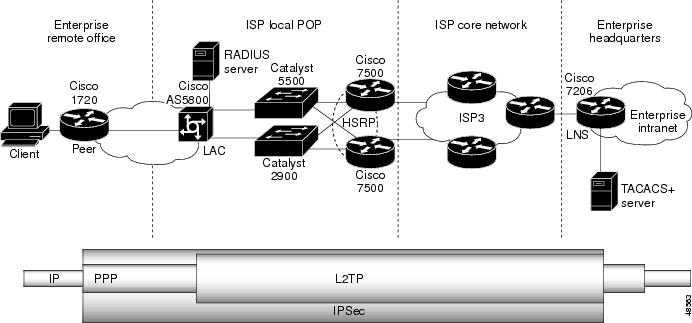
In the new IPSec network, the peer, LAC, and LNS establish L2TP tunnels and sessions exactly as they did in the original network. Once the L2TP tunnel and session are established, the peer initiates IPSec negotiation with the LNS (the LAC is not involved in IPSec). Once the peer and LNS complete IPSec negotiation, the connection is secured from the peer in the remote office to the LNS at the headquarters office.
Benefits
•
Because IPSec is standards-based, the network will be able to interoperate with other non-Cisco IPSec-compliant devices.
•
Because IPSec does not require any additional devices or any changes to the network topology, it is fast, easy, and inexpensive to deploy on an existing VPDN network.
•
Deploying IPSec on the ISDN router instead of on individual PCs eliminates the need to reconfigure every PC in the office.
•
IPSec is a flexible security solution: multiple encryption types are supported
IPSec can be reconfigured for more complex, large-scale service that uses such features as digital certificates, dynamic crypto maps, dynamic tunnel endpoint discovery, wildcard pre-shared keys, multiple certificate authority roots support, and so on.
Functional Description
This section contains the following sections:
•
Overview of Call Establishment
Overview of Call Establishment
Figure 3 shows how an IPSec-encrypted call is established over the VPDN network.
Figure 3 IPSec over VPDN Call Establishment

The following list describes the sequence of events shown in Figure 3:
1.
A user in the enterprise remote office initiates a call to the headquarters office from a PC connected to the peer. The peer places a call over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) to forward the user PPP session to the LAC.
2.
When the LAC receives the PPP session, it negotiates an L2TP tunnel with the LNS at the enterprise headquarters.
3.
After the LAC and LNS establish an L2TP tunnel, the LAC forwards the user information to the LNS. The LNS authenticates the user and establishes an L2TP session for the user.
4.
Once the L2TP tunnel and session are established, the remote user has connectivity to the enterprise headquarters. The peer then initiates IPSec negotiation directly with the LNS (the LAC is not involved in IPSec).
IPSec Negotiation Process
IPSec negotiation is processed by the following three software components: IPSec, Internet Key Exchange (IKE), and the crypto engine.
•
IPSec—Initiates IPSec negotiation, and then verifies and implements the IKE negotiations.
•
IKE—Negotiates the security policies and security associations (SAs).
•
Crypto engine—Performs the actual encryption tasks.
The following list describes how an IPSec session is negotiated by these three software components:
1.
After the L2TP tunnel and session are established, IPSec on the peer initiates IPSec negotiation.
2.
IKE verifies the pre-shared keys.
3.
IKE verifies which SA it is configured to support.
4.
The crypto engine generates ALG parameters for Dh phase 1.
5.
IKE verifies the IKE policy of the other device.
6.
The crypto engine creates the ISAKMP SKEYID, generates HMAC context, and clears the dh number.
7.
IKE compares the incoming transform sets against its allowed transform sets and negotiates the appropriate SAs. IKE first compares the AH protocol transforms, and then the ESP protocol transforms.
8.
IPSec accepts the SAs negotiated by IKE.
9.
IKE creates four SAs:
–
AH protocol inbound
–
AH protocol outbound
–
ESP protocol inbound
–
ESP protocol outbound
10.
IPSec initializes these SAs.
11.
IPSec installs the new SA information into its SA database.
For detailed information about IPSec negotiation, see "Debug Output" later in this document.
Implementation
The following sections describe how the IPSec network is implemented:
Prerequisites
Before IPSec is configured , the ISP and enterprise need to establish VPDN connectivity between the enterprise remote office and the headquarters using the ISP LAC to establish L2TP tunnels with the enterprise LNS.
IPSec uses IP protocols 50 and 51, and IKE traffic passes on protocol 17, port 500 (UDP 500). Before configuring IPSec, you should ensure that these protocols and ports are permitted by access lists.
Before configuring IPSec, you also should ensure that the any keyword is not used in any access lists.
Design Considerations
When designing an IPSec network, you will make a number of decisions. Most involve choosing between increased performance and increased security. The following sections provide details on these decisions:
•
Authentication only, or Authentication and Encryption
•
Diffie-Hellman Group Identifier Options
•
Security Association Lifetimes
Authentication only, or Authentication and Encryption
IPSec can be configured to perform authentication only, or both authentication and encryption.
Decision: The enterprise decides that its data needs to be both authenticated and encrypted.
Encryption Algorithm
IPSec offers the choice of two encryption algorithms: 56-bit DES-CBC or 168-bit DES. 168-bit DES is the more secure of the two encryption algorithms, but it requires more time and processing power than 56-bit DES-CBC. Also, there are international restrictions on 168-bit encryption.
Decision: The enterprise decides that 56-bit DES-CBC encryption is sufficient for its needs.
Hash Algorithm
IPSec offers the choice of two hash algorithms: SHA-1 and MD5. MD5 is slightly faster. There has been a demonstrated successful (but extremely difficult) attack against MD5; however, the HMAC variant used by IKE prevents this attack.
Decision: The enterprise decides to use the SHA-1 hash algorithm.
Authentication Method
IPSec offers three authentication methods:
•
Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman (RSA) signatures—The most secure and the most scalable. However they require the use of a certification authority, which makes RSA signatures the most difficult option to configure.
•
RSA encrypted nonces—Do not require that the peers possess the public keys of each other, but do not require the use of a certification authority. They are easier to configure in a small network, but do not scale well for large-scale networks.
•
Pre-shared keys—The simplest authentication method. They do not scale well for large-scale networks, and are not as secure as RSA signatures.
Decision: The enterprise decides to make its initial IPSec configuration as simple as possible, so it decides to use pre-shared keys.
Diffie-Hellman Group Identifier Options
The Diffie-Hellman identifier is used for deriving key materials between peers. IPSec offers the choice of 768-bit or 1024-bit Diffie-Hellman groups. The 1024-bit Diffie-Hellman group is more secure, but requires more CPU time to execute.
Decision: The enterprise decides that the 768-bit Diffie-Hellman group is sufficient.
Security Association Lifetimes
The lifetimes of IKE security associations can be configured to any desired value. The default value is 86,400 seconds, or one day. When the first IKE negotiation begins, SAs are negotiated. Each peer retains the SAs until the SA lifetime expires. Any subsequent IKE negotiations can reuse these SAs, which speeds future negotiations. Therefore, longer lifetimes can increase performance, but they also increase SAs exposure to attack. The longer an SA is used, the more encrypted traffic can be gathered by an attacker and used in an attack.
Decision: The enterprise decides to use the default value of 86,400-second SA lifetimes.
Ramifications
•
Scaling limitations
Although using pre-shared authentication keys is the simplest way to implement IPSec, it is not a practical solution for large-scale networks. Therefore, if the ISP wants to expand its IPSec service, it should reconfigure IPSec to use digital certificates obtained from a certificate authority.
•
Limitations of initiating IPSec at the ISDN router:
When IPSec is initiated at the ISDN router, the connection between the PC and the ISDN router is not encrypted. Usually, this un-encrypted link is not a security concern because the PC and ISDN router are both located in the same office. However, in some circumstances, the ISDN router may be shared by multiple parties. In this case, the connection between the PC and ISDN router could be subject to attack.
Also, initiating IPSec at the ISDN router limits security for mobile users. The connection between the mobile PC and the ISDN router will not be encrypted. This connection is over the PSTN, which is less susceptible to attack than is the Internet. Therefore it is not a critical security concern, but it is a concern for highly sensitive data.
Device Characteristics
Figure 4 shows added details of the devices critical to performing IPSec over VPDN.
Figure 4 Details of Network Topology

Device Characteristics
Table 2 describes the devices shown in Figure 4.
Configuration Summaries
The following sections contain the sections of the device configurations needed to enable IPSec on an L2TP network:
•
Configuring the Peer for IPSec over VPDN
•
Configuring the LAC for IPSec over VPDN
•
Configuring the LNS for IPSec over VPDN
•
Configuring the LNS TACACS+ Server for VPDN
Configuring the Peer for IPSec over VPDN
The following commands are necessary to enable a peer to dial in to the LAC and negotiate IPSec with the LNS:
!Identifies the version of Cisco IOS software running on the LAC.version 12.1!Includes millisecond timestamps on log and debug entries that are useful for!troubleshooting and optimizing the network.service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezoneservice timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone!Specifies that passwords will not be encrypted in configuration output. This is useful!when first configuring a network, but is a security risk when the network is!operational.no service password-encryption!!Configures the hostname of the router.hostname isdn4!logging buffered 4096 debuggingenable secret 5 $1$r4OC$rE0tf7GTYYZFc80M5SRJL0!username nas2-52 password 0 lab!!memory-size iomem 15!Configures the timezone and Daylight Savings Time adjustment.clock timezone PDT -8clock summer-time PDT recurring!Allows for the configuration of the first subnet in each classfull network.ip subnet-zero!isdn switch-type basic-5essisdn voice-call-failure 0!!!Creates IKE policy 1, which would be given highest priority if there were additional IKE !policies.crypto isakmp policy 1!Specifies that IKE will use pre-shared keys for authentication.authentication pre-share!By default, this IKE policy will use the 56-bit DES-CBC encryption algorithm, the SHA-1 !hash algorithm, the 768-bit Diffie-Hellman group, and 86400 second SA lifetimes.!!Specifies the pre-shared key as cisco123 for negotiation with the LNS at IP address !192.250.3.2. This pre-shared key must also be specified on the LNS for the peer IP !address.crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.250.3.2!By default, the peer's ISAKMP identity is set as its IP address, 192.232.1.25.!!Creates the transform set called e2e. It includes an AH transform, an ESP encryption !transform, and an ESP authentication transform. The transform set on the LNS must !include all three of these transforms for successful negotiation.crypto ipsec transform-set e2e ah-md5-hmac esp-des esp-md5-hmac!!!Creates the crypto map called vpdn-isg, gives it a sequence number (priority) of 10, and !specifies that IKE will be used to establish IPSec security associations.crypto map vpdn-isg 10 ipsec-isakmp!Specifies the IP address of the LNS.set peer 192.250.3.2!Instructs the crypto map to use the e2e transform set.set transform-set e2e!Specifies that extended access list 101 will be used to determine which traffic is to be !protected by IPSec.match address 101!cns event-service server!!interface BRI0description "Lucent BRI # 60153"no ip addressencapsulation pppno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachedialer pool-member 1isdn switch-type basic-5essisdn incoming-voice modemno fair-queueno cdp enable!Specifies that traffic using BRI 0 is to be encrypted by crypto map vpdn-isg.crypto map vpdn-isg!!FastEthernet 0 is the interface that is used for VPDN and IPSec traffic.interface FastEthernet0ip address 192.232.1.25 255.255.255.248speed autohalf-duplexno cdp enable!!Dialer 6 is used to establish the initial PPP connection to the LAC.interface Dialer6description "vpdn dialup to ISP3AC5 192.250.3.0 via NAS5-58-RS"ip unnumbered FastEthernet0encapsulation pppno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachedialer pool 1!Specifies the remote name of the LAC.dialer remote-name isp3ac5-hgw!Specifies the PRI number of the LAC.dialer string 50127dialer-group 1no cdp enableppp authentication chap pap callinppp chap hostname isdn4@isp3-2.comppp chap password 7 09404F0B!Specifies that traffic using dialer 6 is to encrypted by crypto map vpdn-isg.crypto map vpdn-isg!ip classlessip route 192.232.1.24 255.255.255.248 FastEthernet0ip route 192.250.3.2 255.255.255.255 Dialer6ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer6no ip http server!!Specifies that traffic from 192.232.1.24 (the peer) to 192.250.3.0 (the LNS) is to be !permitted. Because this access list is reference in crypto map vpdn-isg, traffic meeting the requirements of this access list will be encrypted by crypto map vpdn-isg.access-list 101 permit ip 192.232.1.24 0.0.0.7 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit!!endFor the complete configuration, see "Peer Configuration."
Configuring the LAC for IPSec over VPDN
The following commands are necessary to enable the LAC to receive calls from the peer and forward them to the LNS using L2TP. The LAC is not involved in IPSec negotiation.
!Identifies the version of Cisco IOS software running on the LACversion 12.1!Includes millisecond timestamps on log and debug entries that are useful for!troubleshooting and optimizing the networkservice timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezoneservice timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone!Specifies that passwords will not be encrypted in configuration output. This is useful!when first configuring a network, but is a security risk when the network is!operational.no service password-encryption!!Configures the hostname for the LAC.hostname NAS5-58-RS!boot system flash c5800-p456i-mz.121-4.0.1.T!Configures AAA and specifies that the LAC will authenticate VPDN tunnels with RADIUS.aaa new-modelaaa authentication ppp default if-needed local group radius!!Configures the usernames and passwords that are used for VPDN tunnel negotiation. These !usernames and passwords are called tunnel secrets.username isp3ac5-hgw password 0 labusername isdn-nas5-isp3 password 0 lab!!!Configures the timezone and Daylight Savings Time adjustment.clock timezone PDT -8clock summer-time PDT recurringdial-tdm-clock priority 1 trunk-slot 0 port 0!!!Allows for the configuration of the first subnet in each classfull network.ip subnet-zeroip cefno ip domain-lookup!!Turns on VPDN.vpdn enableno vpdn logging!Instructs the LAC to tunnel VPDN calls based on the user domain name.vpdn search-order domain!!This is the VPDN group for the enterprise.vpdn-group 1!Configures a request dial-in VPDN subgroup.request-dialin!Configures L2TP as the tunnel protocol.protocol l2tp!Specifies that users with the domain name isp3-2.com will be tunneled by this VPDN!group.domain isp3-2.com!Specifies the IP address of the enterprise LNS.!initiate-to ip 192.250.3.2!Configures the local name that the ISP will use to identify itself for L2TP tunnel!authentication with the service provider LNS. If the ISP expands to a stacked-LAC!environment, it will need to use the same local name on all of the LACs.local name isdn-nas5-isp3!!Configures the telco switch type. When the switch type is configured in global!configuration mode, it is automatically propagated into the individual serial!interfaces.isdn switch-type primary-5ess!!!controller T1 1/0/4!Configures the T1 framing type as super frame (ESF).framing esf!Configures the LAC to gets its primary clocking from T1 controller 0.clock source line primary!Configures the T1 line code type as B8ZS.linecode b8zs!Assigns all 24 T1 timeslots as ISDN PRI channels and creates a D-channel serial!interface (Serial interface 0:23). Individual B-channel serial interfaces are also!created (Serial interfaces 0:0 through 0:22), but they are not shown in the!configuration.pri-group timeslots 1-24!Includes the PRI number that corresponds to this controller in the configuration for !easy reference.description LucentPRInumber = 50127!!interface FastEthernet0/0/0description "This is the IP id for this router"ip address 192.232.0.33 255.255.255.248full-duplex!interface FastEthernet0/5/0description "This is the secondary interface for router"ip address 192.232.0.41 255.255.255.248full-duplex!!!!Serial interface 1/0/4:23 is the D channel that corresponds to controller T1 1/0/4. The !behavior of the B-channel serial interfaces (1/0/4:0 through 1/0/4:22) is controlled by !the configuration of Serial interface 1/0/4:23.interface Serial1/0/4:23!Includes the PRI number that corresponds to this interface in the configuration for !easy reference.description LucentPRInumber = 50127!Specifies that the interface does not require an IP address.no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1!This command is automatically configured on all of the serial interfaces by the isdn!switch-type global configuration mode command.isdn switch-type primary-5ess!!interface Dialer1ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppdialer in-banddialer map ip 192.232.1.25 name isdn4dialer-group 1peer default ip address pool NAS5POOLppp authentication chap pap ms-chap!!ip classlessip route 192.232.1.24 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.25ip route 192.232.1.25 255.255.255.255 Dialer1ip route 192.250.3.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.0.38ip route 192.250.3.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.0.44no ip http server!access-list 10 permit 192.232.0.0 0.0.255.255access-list 101 permit ip 192.232.0.32 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.40 0.0.0.7dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit!!!!Specifies the IP address of the RADIUS server, and the ports that are to be sued for !authorization and accounting.radius-server host 192.232.0.122 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646!Specifies thatradius-server retransmit 5!Configures the password for the RADIUS server.radius-server key <key>!!!endFor the complete LAC configuration, see "LAC Configuration."
Configuring the LNS for IPSec over VPDN
The following commands are necessary to enable the LNS to establish L2TP tunnels and sessions with the LAC and to negotiate IPSec with the peer:
!Identifies the version of Cisco IOS software running on the LAC.version 12.1!Includes millisecond timestamps on log and debug entries that are useful for!troubleshooting and optimizing the network.service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezoneservice timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone!Specifies that passwords will not be encrypted in configuration output. This is useful!when first configuring a network, but is a security risk when the network is!operational.no service password-encryptionservice udp-small-serversservice tcp-small-servers!!Configures the hostname of the router.hostname ISP3AC5!boot system disk0:c7200-jo3s56i-mz.121-3.3!!Configures AAA and specifies that the LAC will authenticate VPDN tunnels with TACACS+.aaa new-modelaaa authentication ppp default local group tacacs+!!!!Configures the usernames and passwords that are used for VPDN tunnel negotiation. These !usernames and passwords are called tunnel secrets.username isdn-nas5-isp3 password 0 labusername isp3ac5-hgw password 0 lab!!!Configures the timezone and Daylight Savings Time adjustment.clock timezone PST -8clock summer-time PST recurring!Allows for the configuration of the first subnet in each classfull network.ip subnet-zerono ip fingerno ip domain-lookup!!Turns on VPDN.vpdn enableno vpdn logging!!!This is the VPDN group that negotiates with the ISP LAC.vpdn-group 2!Configures an accept-dialin VPDN subgroup.accept-dialin!Specifies that this VPDN group will negotiate either L2F or L2TP tunnels.protocol any!Instructs the LNS to clone virtual access interfaces for VPDN sessions from virtual!template 3.virtual-template 3!Specifies that this VPDN group will negotiate L2TP tunnels with LACs that identify!themselves with the local name isdn-nas5-isp3.terminate-from hostname isdn-nas5-isp3local name isp3ac5-hgw!!Creates IKE policy 1, which would be given highest priority if there were additional IKE !policies.crypto isakmp policy 1!Specifies that IKE will use pre-shared keys for authentication.authentication pre-share!By default, this IKE policy will use the 56-bit DES-CBC encryption algorithm, the SHA-1 !hash algorithm, the 768-bit Diffie-Hellman group, and 86400 second SA lifetimes.!!Specifies the pre-shared key as cisco123 for negotiation with the peer at IP address !192.232.1.25. This pre-shared key must also be specified on the peer for the LNS IP !address.!By default, the LNS's ISAKMP identity is set as its IP address, 192.250.3.2.crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.232.1.25!The next two pre-shared keys are for IPSec tunnels to other peers (not shown in this !network) at the IP addresses 192.232.1.33.57, and 192.232.1.57.crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.232.1.33crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.232.1.57!!!Creates the transform set called e2e. It includes an AH transform, an ESP encryption !transform, and an ESP authentication transform. The transform set on the LNS must !include all three of these transforms for successful negotiation.crypto ipsec transform-set e2e ah-md5-hmac esp-des esp-md5-hmac!!Creates the crypto map called vpdn-isg, gives it a sequence number (priority) of 10, and !specifies that IKE will be used to establish IPSec security associations.crypto map vpdn-isg 10 ipsec-isakmp!Specifies the IP address of the peer.set peer 192.232.1.25!Instructs the crypto map to use the e2e transform set.set transform-set e2e!Specifies that extended access list 102 will be used to determine which traffic is to be !protected by IPSec.match address 102!The next two crypto maps are for the IPSec tunnels to other peers not shown in this !network.crypto map vpdn-isg 20 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.232.1.33set transform-set e2ematch address 103crypto map vpdn-isg 30 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.232.1.57set transform-set e2ematch address 104!cns event-service server!!interface FastEthernet0/0description "network to the TACACS+ server - stss-ss20"ip address 192.250.3.9 255.255.255.248full-duplex!!interface FastEthernet3/0description To ISP3DA4, Fa5/1ip address 192.250.3.2 255.255.255.248no ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachehalf-duplex!!!!Creates virtual template 3, which is used to clone virtual access interfaces for!incoming VPDN sessions.interface Virtual-Template3!Specifies that the virtual access interfaces will use the IP address of Fast Ethernet!interface 3/0.ip unnumbered FastEthernet3/0no ip route-cacheno keepalive!Enables CHAP and PAP authentication.ppp authentication chap!Specifies that traffic using virtual-access interfaces cloned from virtual template 3 is !to be encrypted by crypto map vpdn-isg.crypto map vpdn-isg!ip local pool ISP3POOL 192.239.192.1 192.239.199.254ip kerberos source-interface anyno ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.250.3.1ip route 192.232.1.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.1ip route 192.232.1.8 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.9ip route 192.232.1.16 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.17ip route 192.232.1.24 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.25ip route 192.232.1.32 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.33ip route 192.232.1.40 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.41ip route 192.232.1.48 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.49ip route 192.232.1.56 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.57no ip http server!!Specifies that traffic from 192.250.3.0 (the LNS) to 192.232.1.24 (the peer) is to be !permitted. Because this access list is reference in crypto map vpdn-isg, traffic meeting !the requirements of this access list will be encrypted by crypto map vpdn-isg.access-list 102 permit ip 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.24 0.0.0.7!The next two access lists are for the IPSec tunnels to other peers not shown in this !network.access-list 103 permit ip 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.32 0.0.0.7access-list 104 permit ip 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.56 0.0.0.7!!Specifies the IP address of the TACACS+ server.tacacs-server host 223.255.254.254!Configures the password for the TACACS+ server.tacacs-server key cisco12345!!!!endFor the complete LNS configuration, see "LNS Configuration."
Configuring the LNS TACACS+ Server for VPDN
The following user profile enables the LNS TACACS+ server to verify a user who dials in with the username isdn4@isp3-2com and the password lab.
user = isdn4@isp3-2com{password = chap "lab"service=ppp {protocol=lcp {}protocol=ip {}Complete Configuration Files
The following sections contain the complete device configurations:
•
LNS TACACS+ Server Configuration
Peer Configuration
!hostname isdn4!logging buffered 4096 debuggingenable secret 5 $1$r4OC$rE0tf7GTYYZFc80M5SRJL0!username nas2-52 password 0 lab!!!!memory-size iomem 15clock timezone PDT -8clock summer-time PDT recurringip subnet-zerono ip fingerip ftp username anonymousip ftp password cywang@cisco.comno ip domain-lookupip host tftp-ipc 223.255.254.254ip host NAS3-53 192.232.0.17ip host NAS2-52 192.232.0.9!ip audit notify logip audit po max-events 100isdn switch-type basic-5essisdn voice-call-failure 0!!!!!!!crypto isakmp policy 1authentication pre-sharecrypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.250.3.2!!crypto ipsec transform-set e2e ah-md5-hmac esp-des esp-md5-hmac!crypto map vpdn-isg 10 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.250.3.2set transform-set e2ematch address 101!cns event-service server!!!!interface Serial0no ip addressshutdownno fair-queueno cdp enable!interface Serial1no ip addressshutdownno cdp enable!interface BRI0description "Lucent BRI # 60153"no ip addressencapsulation pppno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachedialer pool-member 1isdn switch-type basic-5essisdn incoming-voice modemno fair-queueno cdp enablecrypto map vpdn-isg!interface FastEthernet0ip address 192.232.1.25 255.255.255.248speed autohalf-duplexno cdp enable!interface Dialer1description "dialup to NAS2-52 to I & 192.232.0.8 network"ip unnumbered FastEthernet0encapsulation pppno ip mroute-cachedialer pool 1dialer remote-name NAS2-52dialer idle-timeout 180dialer string 50151dialer-group 1pulse-time 0no cdp enableppp authentication chap pap callinppp chap hostname isdn4!interface Dialer5description "vpdn dialup to local1.com" via NAS5-58ip unnumbered FastEthernet0encapsulation pppdialer pool 1dialer remote-name LOCAL1HGW-45dialer string 50120dialer-group 1no cdp enableppp authentication chap pap callinppp chap hostname isdn4@l2tplocal1.comppp chap password 7 00081204!interface Dialer6description "vpdn dialup to ISP3AC5 192.250.3.0 via NAS5-58-RS"ip unnumbered FastEthernet0encapsulation pppno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachedialer pool 1dialer remote-name isp3ac5-hgwdialer string 50127dialer-group 1no cdp enableppp authentication chap pap callinppp chap hostname isdn4@isp3-2.comppp chap password 7 09404F0Bcrypto map vpdn-isg!ip default-gateway 192.232.0.17ip kerberos source-interface anyip classlessip route 192.232.0.8 255.255.255.248 192.232.0.9ip route 192.232.0.9 255.255.255.255 Dialer1ip route 192.232.3.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.3.1ip route 192.232.3.1 255.255.255.255 Dialer5ip route 192.250.3.0 255.255.255.248 192.250.3.2ip route 192.250.3.2 255.255.255.255 Dialer6ip route 192.255.201.55 255.255.255.255 192.232.0.22ip route 223.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 FastEthernet0no ip http server!access-list 101 permit ip 192.232.1.24 0.0.0.7 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7dialer-list 1 protocol ip permitno cdp run!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0transport input noneline aux 0line vty 0 4exec-timeout 0 0password lablogin!exception protocol ftpexception dump 223.255.254.254sntp server 223.255.254.254no scheduler allocateendLAC Configuration
Current configuration : 20078 bytes!! Last configuration change at 11:13:34 PDT Fri Sep 29 2000! NVRAM config last updated at 17:23:52 PDT Thu Sep 28 2000!version 12.1service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezoneservice timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezoneno service password-encryptionservice compress-config!hostname NAS5-58-RS!boot system flash c5800-p456i-mz.121-4.0.1.Taaa new-modelaaa authentication login NO_Auth noneaaa authentication login VTY local-case group radiusaaa authentication ppp default if-needed local group radiusaaa authorization network default local group radiusaaa accounting suppress null-usernameaaa accounting exec NO_Auth stop-only group radiusaaa accounting network default start-stop group radiusenable secret 5 $1$K7AO$bfpHNfllIAngDnnrC4lAK1!username cisco password 0 labusername nas5-l2tp password 0 labusername local1-hgw password 0 labusername nas5 password 0 labusername nas5-b2b password 0 labusername isp3ac5-hgw password 0 labusername isdn-nas5-isp3 password 0 labusername linux-nas5-isp3 password 0 labusername peer1-58-RS password 0 labusername async4 password 0 labusername CGb000 password 0 lab!!!!shelf-id 0 router-shelfshelf-id 1 dial-shelf!!!resource-pool disable!modem-pool Defaultpool-range 1/3/0-1/3/71,1/4/0-1/4/71,1/5/0-1/5/71,1/6/0-1/6/143,1/7/0-1/7/143!clock timezone PDT -8clock summer-time PDT recurringdial-tdm-clock priority 1 trunk-slot 0 port 0!!!!ip subnet-zeroip rcmd rsh-enableip cefno ip domain-lookup!vpdn enableno vpdn loggingvpdn search-order domain!vpdn-group 1request-dialinprotocol l2tpdomain isp3-1.comdomain isp3-2.cominitiate-to ip 192.250.3.2local name isdn-nas5-isp3!vpdn-group 2request-dialinprotocol l2tpdomain l2tplocal1.cominitiate-to ip 192.232.3.1local name nas5-l2tp!vpdn-group 3request-dialinprotocol l2fdomain l2flocal1.comdomain vpdn1.cominitiate-to ip 192.232.3.1local name nas5!vpdn-group 4request-dialinprotocol l2tpdomain vpdn2.cominitiate-to ip 192.232.3.1local name nas5!vpdn-group 5request-dialinprotocol l2tpdomain isp3-3.cominitiate-to ip 192.250.3.2local name nas5-b2b!isdn switch-type primary-5esschat-script dial ABORT "NO CARRIER" TIMEOUT 30 "" at OK "\datd \T" CONNECT!!!!!!!crypto isakmp policy 1authentication pre-share!crypto isakmp policy 2authentication pre-sharecrypto isakmp key cisco1234 address 192.232.1.41!!crypto ipsec transform-set dial esp-des esp-md5-hmac!crypto map toISDN6 20 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.232.1.41set transform-set dialmatch address 101!!!controller T1 1/0/0framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50120!controller T1 1/0/1framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50121!controller T1 1/0/2framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50122!controller T1 1/0/3framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50126!controller T1 1/0/4framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50127!controller T1 1/0/5framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50128!controller T1 1/0/6framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description LucentPRInumber = 50129!controller T1 1/0/7framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description "btb to callgen router T1-1"!controller T1 1/0/8framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description "btb to callgen router T1-2"!controller T1 1/0/9framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description "btb to callgen router T1-3"!controller T1 1/0/10framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24description "btb to callgen router T1-5"!controller T1 1/0/11framing esflinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-3,24!controller T3 1/1/0framing c-bitclock source linecablelength 224t1 1-24,28 controller!controller T1 1/1/0:1framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:2framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:3framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:4framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:5framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:6framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:7framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:8framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:9framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:10framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:11framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:12framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:13framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:14framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:15framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:16framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:17framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:18framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:19framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:20framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:21framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:22framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:23framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:24framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1/0:28framing esfpri-group timeslots 1-24!!!interface Loopback0ip address 111.111.111.1 255.255.255.0!interface Loopback1ip address 222.222.222.1 255.255.255.0!interface FastEthernet0/0/0description "This is the IP id for this router"ip address 192.232.0.33 255.255.255.248full-duplex!interface FastEthernet0/5/0description "This is the secondary interface for router"ip address 192.232.0.41 255.255.255.248full-duplex!interface Ethernet0/6/0description "temporary connection to e4/0 of tftp-gw1 to tftp-server"ip address 192.232.2.4 255.255.255.248shutdown!interface Ethernet0/6/1description "Network to CG-TERM-5300 ethernet 0"ip address 193.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 secondaryip address 193.0.1.3 255.255.255.0 secondaryip address 193.0.1.1 255.255.255.0no ip mroute-cacheno cdp enable!interface Ethernet0/6/2ip address 131.3.81.58 255.255.255.0!interface Ethernet0/6/3no ip address!interface Serial1/0/0:23description LucentPRInumber = 50120no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemcrypto map toISDN6!interface Serial1/0/1:23description LucentPRInumber = 50121no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/2:23description LucentPRInumber = 50122no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/3:23description LucentPRInumber = 50126no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/4:23description LucentPRInumber = 50127no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/5:23description LucentPRI# = 50128 (huntgroup # = 50199)no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/6:23description LucentPRI# = 50129 (huntgroup # = 50199)no ip addressencapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/7:23description "btb to callgen router T1-1"ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/8:23description "btb to callgen router T1-2"ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer rotary-group 1dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modem!interface Serial1/0/9:23description "btb to callgen router T1-3"no ip addressencapsulation pppno ip route-cache cefip mroute-cachedialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemno peer default ip addressppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/0/10:23no ip addressencapsulation pppno ip route-cache cefip mroute-cachedialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemno peer default ip addressppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/0/11:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cachedialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap!interface Serial1/1/0:1:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:2:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:3:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:4:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:5:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:6:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:7:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:8:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:9:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:10:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:11:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:12:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:13:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:14:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:15:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:16:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:17:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:18:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:19:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:20:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:21:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:22:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:23:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:24:23ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip mroute-cacheload-interval 30dialer-group 1isdn switch-type primary-5essisdn incoming-voice modemppp authentication chap pap!interface Serial1/1/0:28:23no ip addressno ip route-cache cefisdn switch-type primary-5essno cdp enable!interface Group-Async0no ip addressno group-range!interface Group-Async1ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppip tcp header-compression passiveno ip mroute-cachedialer in-banddialer-group 1ntp disableasync default routingasync mode dedicatedpeer default ip address pool NAS5POOLppp authentication chap papgroup-range 1/3/00 1/7/143!interface Dialer1ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0/0encapsulation pppno ip route-cache cefno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachedialer in-banddialer map ip 192.232.1.25 name isdn4dialer map ip 192.232.1.33 name isdn5dialer map ip 192.232.2.33 name async3dialer map ip 192.232.1.41 name isdn6dialer map ip 192.232.1.49 name isdn7dialer map ip 192.232.1.57 name isdn8dialer map ip 192.232.1.1 name isdn1dialer map ip 192.232.2.1 async1dialer map ip 192.232.1.9 name isdn2dialer map ip 192.232.1.17 name isdn3dialer-group 1peer default ip address pool NAS5POOLppp authentication chap pap ms-chapcrypto map toISDN6!interface Dialer2no ip addressno ip route-cache cefno cdp enable!interface Dialer3no ip addressno ip route-cache cefno cdp enable!router ripversion 2redistribute connectedpassive-interface Dialer1network 192.232.0.0network 192.239.224.0network 192.239.225.0network 192.239.226.0network 192.239.227.0no auto-summary!ip local pool NAS5POOL 192.239.224.2 192.239.227.254ip kerberos source-interface anyip classlessip route 112.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.250.3.2ip route 122.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.250.3.2ip route 191.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 131.3.81.61ip route 192.232.1.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.1ip route 192.232.1.8 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.9ip route 192.232.1.16 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.17ip route 192.232.1.24 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.25ip route 192.232.1.32 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.33ip route 192.232.1.40 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.41ip route 192.232.1.40 255.255.255.248 Dialer1ip route 192.232.150.0 255.255.255.0 192.250.3.2ip route 192.236.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.250.3.2ip route 192.236.8.0 255.255.248.0 192.250.3.2ip route 192.236.32.0 255.255.248.0 192.250.3.2ip route 192.236.48.0 255.255.248.0 192.250.3.2ip route 192.250.3.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.0.38ip route 192.250.3.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.0.44 100ip route 223.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 Ethernet0/6/2no ip http server!access-list 10 permit 192.232.0.0 0.0.255.255access-list 10 permit 192.239.0.0 0.0.255.255access-list 101 permit ip 192.232.0.32 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.40 0.0.0.7access-list 102 permit ip 192.232.0.0 0.0.0.255 192.232.1.0 0.0.0.255dialer-list 1 protocol ip permitroute-map FILTER permit 10match ip address 10!!!radius-server host 192.232.0.122 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646radius-server retransmit 5radius-server key ciscolab!voice-port 1/0/0:D!voice-port 1/0/1:D!voice-port 1/0/2:D!voice-port 1/0/3:D!voice-port 1/0/4:D!voice-port 1/0/5:D!voice-port 1/0/6:D!voice-port 1/0/7:D!voice-port 1/0/8:D!voice-port 1/0/9:D!voice-port 1/0/10:D!voice-port 1/0/11:D!voice-port 1/1/0:1:D!voice-port 1/1/0:2:D!voice-port 1/1/0:3:D!voice-port 1/1/0:4:D!voice-port 1/1/0:5:D!voice-port 1/1/0:6:D!voice-port 1/1/0:7:D!voice-port 1/1/0:8:D!voice-port 1/1/0:9:D!voice-port 1/1/0:10:D!voice-port 1/1/0:11:D!voice-port 1/1/0:12:D!voice-port 1/1/0:13:D!voice-port 1/1/0:14:D!voice-port 1/1/0:15:D!voice-port 1/1/0:16:D!voice-port 1/1/0:17:D!voice-port 1/1/0:18:D!voice-port 1/1/0:19:D!voice-port 1/1/0:20:D!voice-port 1/1/0:21:D!voice-port 1/1/0:22:D!voice-port 1/1/0:23:D!voice-port 1/1/0:24:D!voice-port 1/1/0:28:D!dial-peer cor custom!!!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0login authentication NO_Authtransport input noneline aux 0line vty 0 4password lablogin authentication VTYline 1/3/00 1/3/71exec-timeout 0 0activation-character 0disconnect-character 0autoselect during-loginautoselect pppscript dialer dialmodem InOutno modem log rs232transport preferred nonetransport input allescape-character soft 0escape-character 0autohanguphold-character 0line 1/4/00 1/4/71exec-timeout 0 0activation-character 0disconnect-character 0autoselect during-loginautoselect pppscript dialer dialmodem InOutno modem log rs232transport preferred nonetransport input allescape-character soft 0escape-character 0autohanguphold-character 0line 1/5/00 1/5/71exec-timeout 0 0activation-character 0disconnect-character 0autoselect during-loginautoselect pppscript dialer dialmodem InOutno modem log rs232transport preferred nonetransport input allescape-character soft 0escape-character 0autohanguphold-character 0line 1/6/00 1/6/143exec-timeout 0 0activation-character 0disconnect-character 0autoselect during-loginautoselect pppscript dialer dialmodem InOutno modem log rs232transport preferred nonetransport input allescape-character soft 0escape-character 0autohanguphold-character 0line 1/7/00 1/7/143exec-timeout 0 0activation-character 0disconnect-character 0autoselect during-loginautoselect pppscript dialer dialmodem InOutno modem log rs232transport preferred nonetransport input allescape-character soft 0escape-character 0autohanguphold-character 0!ntp clock-period 17180177ntp update-calendarntp server 223.255.254.254 version 1endLNS Configuration
Current configuration : 37589 bytes!! Last configuration change at 13:00:31 PST Tue Oct 3 2000! NVRAM config last updated at 17:15:00 PST Fri Sep 29 2000 by hkonardi!version 12.1service timestamps debug datetime localtime show-timezoneservice timestamps log datetime localtime show-timezoneno service password-encryptionservice udp-small-serversservice tcp-small-servers!hostname ISP3AC5!boot system disk0:c7200-jo3s56i-mz.121-3.3aaa new-modelaaa authentication login default local-case group tacacs+aaa authentication login NO_Auth noneaaa authentication ppp default local group tacacs+aaa authorization network default if-authenticated local group tacacs+aaa accounting exec default start-stop group acacs+enable password lab!!!username isdn-nas5-isp3 password 0 labusername isp3ac5-hgw password 0 lab!!clock timezone PST -8clock summer-time PST recurringip subnet-zerono ip fingerip ftp username dialip ftp password dialno ip domain-lookupip host tftpserv 223.255.254.254!ip multicast-routingvpdn enableno vpdn logging!vpdn-group 1accept-dialinprotocol anyvirtual-template 1terminate-from hostname nas5-to-isp3local name isp3ac5-hgw!vpdn-group 2accept-dialinprotocol anyvirtual-template 3terminate-from hostname isdn-nas5-isp3local name isp3ac5-hgw!vpdn-group 3accept-dialinprotocol anyvirtual-template 3terminate-from hostname nas3local name isp3ac5-hgw!vpdn-group 4accept-dialinprotocol anyvirtual-template 3terminate-from hostname isdn-nas2-isp3local name isp3ac5-hgw!vpdn-group 5accept-dialinprotocol anyvirtual-template 2terminate-from hostname nas5-b2blocal name isp3ac5-hgw!vpdn-group 6accept-dialinprotocol anyvirtual-template 3terminate-from hostname nas1local name isp3ac5-hgw!!!crypto isakmp policy 1authentication pre-sharecrypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.232.1.25crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.232.1.33crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 192.232.1.57!!crypto ipsec transform-set e2e ah-md5-hmac esp-des esp-md5-hmac!crypto map vpdn-isg 10 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.232.1.25set transform-set e2ematch address 102crypto map vpdn-isg 20 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.232.1.33set transform-set e2ematch address 103crypto map vpdn-isg 30 ipsec-isakmpset peer 192.232.1.57set transform-set e2ematch address 104!cns event-service server!!!!!!!!!interface Loopback0ip address 192.232.150.2 255.255.255.0 secondaryip address 192.232.150.230 255.255.255.0 secondaryip address 192.232.150.1 255.255.255.0no ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cacheno logging event link-status!interface FastEthernet0/0description "network to the Radius server - stss-ss20"ip address 192.250.3.9 255.255.255.248full-duplex!interface FastEthernet1/0no ip addressfull-duplexbridge-group 1!interface FastEthernet1/1no ip addressbridge-group 1!interface Ethernet1/2no ip addressbridge-group 1!interface Ethernet1/3no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/4no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/5no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/6no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/7no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/8no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/9no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/10no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/11no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/12no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet1/13no ip addressshutdown!interface FastEthernet3/0description To ISP3DA4, Fa5/1ip address 192.250.3.2 255.255.255.248no ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cachehalf-duplex!interface FastEthernet4/0description "to IXIA 01/07/04, the pair of 01/07/03"ip address 192.236.8.1 255.255.248.0no ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cacheload-interval 30full-duplexno cdp enable!interface Ethernet5/0no ip addressno ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cacheshutdownno cdp enable!interface Ethernet5/1description To BACKDOOR NETWORKip address 223.255.243.128 255.255.240.0no cdp enable!interface Ethernet5/2no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet5/3description "to IXIA 01/08/02, the pair of 01/08/01"ip address 192.236.32.1 255.255.248.0no ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cacheno cdp enable!interface Ethernet5/4description "to IXIA 01/07/01, the pair of 01/07/02"ip address 192.236.48.1 255.255.248.0no ip route-cacheno ip mroute-cacheno cdp enable!interface Ethernet5/5no ip address!interface Ethernet5/6no ip addressshutdown!interface Ethernet5/7ip address 10.10.10.13 255.255.255.0!interface Virtual-Template1ip unnumbered FastEthernet3/0no keepalivepeer default ip address pool ISP3POOLppp authentication chap pap!interface Virtual-Template2ip unnumbered FastEthernet3/0no ip route-cacheload-interval 30no keepalivepeer default ip address pool ISP3POOLppp authentication chap pap!interface Virtual-Template3ip unnumbered FastEthernet3/0no ip route-cacheno keepaliveppp authentication chap papcrypto map vpdn-isg!ip local pool ISP3POOL 192.239.192.1 192.239.199.254ip kerberos source-interface anyno ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.250.3.1ip route 192.232.1.0 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.1ip route 192.232.1.8 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.9ip route 192.232.1.16 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.17ip route 192.232.1.24 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.25ip route 192.232.1.32 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.33ip route 192.232.1.40 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.41ip route 192.232.1.48 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.49ip route 192.232.1.56 255.255.255.248 192.232.1.57no ip http server!access-list 102 permit ip 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.24 0.0.0.7access-list 103 permit ip 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.32 0.0.0.7access-list 104 permit ip 192.250.3.0 0.0.0.7 192.232.1.56 0.0.0.7snmp-server engineID local 00000009020000027D419C00snmp-server community public ROsnmp-server community STSS RWsnmp-server packetsize 2048snmp-server contact Mark Manzanares (mmanzana@cisco.com)snmp-server chassis-id ISP3AC5snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkdown linkup coldstartsnmp-server enable traps casasnmp-server enable traps gtpsnmp-server enable traps isdn call-informationsnmp-server enable traps isdn layer2snmp-server enable traps channelsnmp-server enable traps snasw alertsnmp-server enable traps hsrpsnmp-server enable traps configsnmp-server enable traps entitysnmp-server enable traps envmonsnmp-server enable traps bgpsnmp-server enable traps ipmulticastsnmp-server enable traps rsvpsnmp-server enable traps frame-relaysnmp-server enable traps syslogsnmp-server enable traps rtrsnmp-server enable traps dlswsnmp-server enable traps dialsnmp-server enable traps voice poor-qovsnmp-server enable traps xgcp!tacacs-server host 223.255.254.254tacacs-server key cisco12345bridge 1 protocol ieee!alias exec int_desc show int | include Descriptionalias exec cpu show proc cpu | include CPUalias exec mem show mem free | include Processor!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0login authentication NO_Authtransport input noneline aux 0exec-timeout 0 0line vty 0 4exec-timeout 0 0password labline vty 5 15password lab!exception protocol ftpexception region-size 36864exception flash all disk0:ntp clock-period 17180166ntp update-calendarntp server 223.255.254.254 version 1endLNS TACACS+ Server Configuration
user = isdn4@isp3-2com{password = chap "lab"service=ppp {protocol=lcp {}protocol=ip {}Debug Output
The following sections shows debug output from successful IPSec negotiation between the peer and LNS:
•
Peer Debug Output from Successful IPSec Negotiation
•
LNS Debug Output From Successful IPSec Negotiation
Peer Debug Output from Successful IPSec Negotiation
isdn4#show debugCryptographic Subsystem:Crypto ISAKMP debugging is onCrypto Engine debugging is onCrypto IPSEC debugging is onisdn4#isdn4#*Mar 1 16:22:53 PDT: IPSEC(sa_request): ,(key eng. msg.) src= 192.232.1.25, dest= 192.250.3.2,src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0x87E2ABDD(2279779293), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4004*Mar 1 16:22:53 PDT: IPSEC(sa_request): ,(key eng. msg.) src= 192.232.1.25, dest= 192.250.3.2,src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0x9400618(155190808), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4004*Mar 1 16:22:53 PDT: ISAKMP: received ke message (1/2)*Mar 1 16:22:53 PDT: ISAKMP: local port 500, remote port 500*Mar 1 16:22:53 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): beginning Main Mode exchange*Mar 1 16:22:53 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): sending packet to 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_NO_STATE.*Mar 1 16:22:56 PDT: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface BRI0:1, changed state to up.*Mar 1 16:22:56 PDT: %DIALER-6-BIND: Interface BR0:1 bound to profile Di6...Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)isdn4#*Mar 1 16:23:02 PDT: %ISDN-6-CONNECT: Interface BRI0:1 is now connected to 50127unknown*Mar 1 16:23:02 PDT: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface BRI0:1, changed state to up*Mar 1 16:23:02 PDT: %CRYPTO-4-RECVD_PKT_INV_SPI: decaps: rec'd IPSEC packet hasinvalid spi fordestaddr=192.232.1.25, prot=51, spi=0x1C080522(470287650)*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): retransmitting phase 1 MM_NO_STATE...*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): incrementing error counter on sa: retransmitphase 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): retransmitting phase 1 MM_NO_STATE*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): sending packet to 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_NO_STATE*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): received packet from 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_NO_STATE*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing SA payload. message ID = 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): found peer pre-shared key matching 192.250.3.2*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking ISAKMP transform 1 against priority1 policy*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: encryption DES-CBC*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: hash SHA*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: default group 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: auth pre-share*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable. Next payload is 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate alg parameter*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CRYPTO_ENGINE: Dh phase 1 status: 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CRYPTO_ENGINE: Dh phase 1 status: 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): SA is doing pre-shared key authentication using id type ID_IPV4_ADDR*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): sending packet to 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_SA_SETUP*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): received packet from 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_SA_SETUP*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing KE payload. message ID = 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate alg parameter*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing NONCE payload. message ID = 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): found peer pre-shared key matching 192.250.3.2*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: create ISAKMP SKEYID for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): SKEYID state generated*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing vendor id payload*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): speaking to another IOS box!*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (1): ID payloadnext-payload : 8type : 1protocol : 17port : 500length : 8*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (1): Total payload length: 12*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): sending packet to 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_KEY_EXCH*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): received packet from 192.250.3.2 (I) MM_KEY_EXCH*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. message ID = 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing HASH payload. message ID = 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): SA has been authenticated with 192.250.3.2*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): beginning Quick Mode exchange, M-ID of 211899060*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): sending packet to 192.250.3.2 (I) QM_IDLE*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: clear dh number for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): received packet from 192.250.3.2 (I) QM_IDLE*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing HASH payload. message ID = 211899060*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing SA payload. message ID = 211899060*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: transform 1, AH_MD5*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: encaps is 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: validate proposal 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): Checking IPSec proposal 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: encaps is 1*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life type in seconds*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytes*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: validate proposal 0*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): atts are acceptable.*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: IPSEC(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.250.3.2, src= 192.232.1.25,dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 0s and 0kb,spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: IPSEC(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #2,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.250.3.2, src= 192.232.1.25,dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 0s and 0kb,spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4*Mar 1 16:23:03 PDT: validate proposal request 0*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing NONCE payload. message ID = 211899060*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. message ID = 211899060*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): processing ID payload. message ID = 211899060*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ipsec allocate flow 0*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ipsec allocate flow 0*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): Creating IPSec SAs*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: inbound SA from 192.250.3.2 to 192.232.1.25(proxy 192.250.3.0 to 192.232.1.24)*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: has spi 0x87E2ABDD and conn_id 2000 and flags 4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 3600 seconds*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: outbound SA from 192.232.1.25 to 192.250.3.2(proxy 192.232.1.24 to 192.250.3.0 )*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: has spi -213910971 and conn_id 2001 and flags 4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 3600 seconds*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): Creating IPSec SAs*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: inbound SA from 192.250.3.2 to 192.232.1.25(proxy 192.250.3.0 to 192.232.1.24)*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: has spi 0x9400618 and conn_id 2002 and flags 4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 3600 seconds*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: outbound SA from 192.232.1.25 to 192.250.3.2(proxy 192.232.1.24 to 192.250.3.0 )*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: has spi -1518012306 and conn_id 2003 and flags 4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 3600 seconds*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytes*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): sending packet to 192.250.3.2 (I) QM_IDLE*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: ISAKMP (0:1): deleting node 211899060 error FALSE reason ""*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.232.1.25, src= 192.250.3.2,dest_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0x87E2ABDD(2279779293), conn_id= 2000, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) src= 192.232.1.25, dest= 192.250.3.2,src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0xF33FFA45(4081056325), conn_id= 2001, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.232.1.25, src= 192.250.3.2,dest_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0x9400618(155190808), conn_id= 2002, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) src= 192.232.1.25, dest= 192.250.3.2,src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0xA584F86E(2776954990), conn_id= 2003, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.232.1.25, sa_prot= 51,sa_spi= 0x87E2ABDD(2279779293),sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2000*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.250.3.2, sa_prot= 51,sa_spi= 0xF33FFA45(4081056325),sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2001*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.232.1.25, sa_prot= 50,sa_spi= 0x9400618(155190808),sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2002*Mar 1 16:23:04 PDT: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.250.3.2, sa_prot= 50,sa_spi= 0xA584F86E(2776954990),sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2003isdn4#LNS Debug Output From Successful IPSec Negotiation
ISP3AC5#show debugCryptographic Subsystem:Crypto ISAKMP debugging is onCrypto Engine debugging is onCrypto Key Exchange debugging is onCrypto IPSEC debugging is onISP3AC5#ISP3AC5#Oct 3 13:05:41 PST: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Virtual-Access152, changed state to upOct 3 13:05:47 PST: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Virtual-Access152, changed state to upOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:0): received packet from 192.232.1.25 (N) NEW SAOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: local port 500, remote port 500Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing SA payload. message ID = 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): found peer pre-shared key matching 192.232.1.25Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): Checking ISAKMP transform 1 against priority 1 policyOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: encryption DES-CBCOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: hash SHAOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: default group 1Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: auth pre-shareOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): atts are acceptable. Next payload is 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate alg parameterOct 3 13:05:48 PST: CRYPTO_ENGINE: Dh phase 1 status: 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CRYPTO_ENGINE: Dh phase 1 status: 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): SA is doing pre-shared key authentication using id type ID_IPV4_ADDROct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): sending packet to 192.232.1.25 (R) MM_SA_SETUPOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): received packet from 192.232.1.25 (R) MM_SA_SETUPOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing KE payload. message ID = 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate alg parameterOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing NONCE payload. message ID = 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): found peer pre-shared key matching 192.232.1.25Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: create ISAKMP SKEYID for conn id 1365Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): SKEYID state generatedOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing vendor id payloadOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): speaking to another IOS box!Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): sending packet to 192.232.1.25 (R) MM_KEY_EXCHOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): received packet from 192.232.1.25 (R) MM_KEY_EXCHOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing ID payload. message ID = 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing HASH payload. message ID = 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1365Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): SA has been authenticated with 192.232.1.25Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (1365): ID payloadnext-payload : 8type : 1protocol : 17port : 500length : 8Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (1365): Total payload length: 12Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1365Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: clear dh number for conn id 1Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): sending packet to 192.232.1.25 (R) QM_IDLEOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): received packet from 192.232.1.25 (R) QM_IDLEOct 3 13:05:48 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1365Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing HASH payload. message ID = 211899060Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing SA payload. message ID = 211899060Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): Checking IPSec proposal 1Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: transform 1, AH_MD5Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: encaps is 1Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life type in secondsOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytesOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: validate proposal 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): atts are acceptable.Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): Checking IPSec proposal 1Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DESOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: encaps is 1Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life type in secondsOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life duration (basic) of 3600Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life type in kilobytesOct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: SA life duration (VPI) of 0x0 0x46 0x50 0x0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: validate proposal 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): atts are acceptable.Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: IPSEC(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.250.3.2, src= 192.232.1.25,dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 0s and 0kb,spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: IPSEC(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #2,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.250.3.2, src= 192.232.1.25,dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 0s and 0kb,spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: validate proposal request 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing NONCE payload. message ID = 211899060Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing ID payload. message ID = 211899060Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (1365): ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET src 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248 prot 0 port 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): processing ID payload. message ID = 211899060Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (1365): ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET dst 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248 prot 0 port 0Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): asking for 2 spis from ipsecOct 3 13:05:48 PST: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: IPSEC(spi_response): getting spi 4081056325 for SAfrom 192.232.1.25 to 192.250.3.2 for prot 2Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: IPSEC(spi_response): getting spi 2776954990 for SAfrom 192.232.1.25 to 192.250.3.2 for prot 3Oct 3 13:05:48 PST: ISAKMP: received ke message (2/2)Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1365Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): sending packet to 192.232.1.25 (R) QM_IDLEOct 3 13:05:49 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): received packet from 192.232.1.25 (R) QM_IDLEOct 3 13:05:49 PST: CryptoEngine0: generate hmac context for conn id 1365Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: ipsec allocate flow 0Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: ipsec allocate flow 0Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): Creating IPSec SAsOct 3 13:05:49 PST: inbound SA from 192.232.1.25 to 192.250.3.2(proxy 192.232.1.24 to 192.250.3.0)Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: has spi 0xF33FFA45 and conn_id 2218 and flags 4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 3600 secondsOct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytesOct 3 13:05:49 PST: outbound SA from 192.250.3.2 to 192.232.1.25(proxy 192.250.3.0 to 192.232.1.24 )Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: has spi -2015188003 and conn_id 2219 and flags 4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 3600 secondsOct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytesOct 3 13:05:49 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): Creating IPSec SAsOct 3 13:05:49 PST: inbound SA from 192.232.1.25 to 192.250.3.2(proxy 192.232.1.24 to 192.250.3.0)Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: has spi 0xA584F86E and conn_id 2220 and flags 4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 3600 secondsOct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytesOct 3 13:05:49 PST: outbound SA from 192.250.3.2 to 192.232.1.25(proxy 192.250.3.0 to 192.232.1.24 )Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: has spi 155190808 and conn_id 2221 and flags 4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 3600 secondsOct 3 13:05:49 PST: lifetime of 4608000 kilobytesOct 3 13:05:49 PST: ISAKMP (0:1365): deleting node 211899060 error FALSE reason"quick mode done (await()"Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.250.3.2, src= 192.232.1.25,dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0xF33FFA45(4081056325), conn_id= 2218, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) src= 192.250.3.2, dest= 192.232.1.25,src_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),dest_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= AH, transform= ah-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0x87E2ABDD(2279779293), conn_id= 2219, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) dest= 192.250.3.2, src= 192.232.1.25,dest_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),src_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0xA584F86E(2776954990), conn_id= 2220, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,(key eng. msg.) src= 192.250.3.2, dest= 192.232.1.25,src_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),dest_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,lifedur= 3600s and 4608000kb,spi= 0x9400618(155190808), conn_id= 2221, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.250.3.2, sa_prot= 51,sa_spi= 0xF33FFA45(4081056325),sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2218Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.232.1.25, sa_prot= 51,sa_spi= 0x87E2ABDD(2279779293),sa_trans= ah-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2219Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.250.3.2, sa_prot= 50,sa_spi= 0xA584F86E(2776954990),sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2220Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created,(sa) sa_dest= 192.232.1.25, sa_prot= 50,sa_spi= 0x9400618(155190808),sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2221Oct 3 13:05:49 PST: IPSEC(add_sa): peer asks for new SAs -- expire current in 120 sec.,(sa) sa_dest= 192.232.1.25, sa_prot= 50,sa_spi= 0xE1DAEAC0(3789220544),sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 2213,(identity) local= 192.250.3.2, remote= 192.232.1.25,local_proxy= 192.250.3.0/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4),remote_proxy= 192.232.1.24/255.255.255.248/0/0 (type=4)Related Documents
•
IPSec Overview: http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/cc/techno/protocol/ipsecur/prodlit/ipsec_ov.htm
•
IPSec White Paper: http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/cc/techno/protocol/ipsecur/ipsec/tech/ipsec_wp.htm
•
Securing L2TP Using IPSec: http://search.ietf.org/internet-drafts/draft-ietf-l2tpext-security-01.txt
•
Configuring IPSec Network Security: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/secur_c/scprt4/scdipsec.htm
•
IPSec Network Security Commands: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/secur_r/srprt4/srdipsec.htm
•
Configuring Internet Key Exchange Security Protocol: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/secur_c/scprt4/scdike.htm
•
Internet Key Exchange Security Protocol Commands: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/secur_r/srprt4/srdike.htm
•
L2TP over IPSec configurations for IPSec between the LAC and LNS: http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/24.html
 Feedback
Feedback