Congestion Management Overview
Congestion management features allow you to control congestion by determining the order in which a traffic flow (or packets) is sent out an interface based on priorities assigned to packets. Congestion management entails the creation of queues, assignment of packets to those queues based on the classification of the packet, and scheduling of the packets in a queue for transmission.
 Note |
From Cisco IOS XR Release 7.3.1 onwards, systems with Cisco NC57 line cards running in compatibility mode support QoS over Layer 2 services for:
Starting with Cisco IOS XR Release 7.4.1 systems with Cisco NC57 line cards running in native mode support QoS over Layer 2 services for:
|
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Set Peak Burst Size for Egress Shaping |
Release 7.4.1 |
This feature is now supported on routers that have Cisco NC57 line cards installed and operate in native and compatibility
modes.
With this feature you can configure the burst size along with the existing egress shaper bandwidth, using the "shape average shaper bandwidth burst size burst unit " command. This feature is used to control higher bursts of traffic being transmitted to the devices that have lower queue length configured to receive traffic. For more information, see Configure Traffic Shaping. |
| Absolute Rates for Bundle Interfaces for Traffic Shapers and Traffic Policers |
Release 7.4.1 |
This feature is now supported on routers that have Cisco NC57 line cards installed and operate in native and compatibility modes. For more information, see Configure Traffic Shaping and Configure Traffic Policing (Two-Rate Three-Color). |
|
Ingress Policing on BVI (Bridge Group Virtual Interface) and Low-Latency Queueing (LLQ) |
Release 7.4.1 |
This feature is now supported on routers that have Cisco NC57 line cards installed and operate in native and compatibility modes. For more information, see "Restrictions for QoS on BVI" under Restrictions and Low-Latency Queuing with Strict Priority Queuing |
The types of traffic regulation mechanisms supported are:
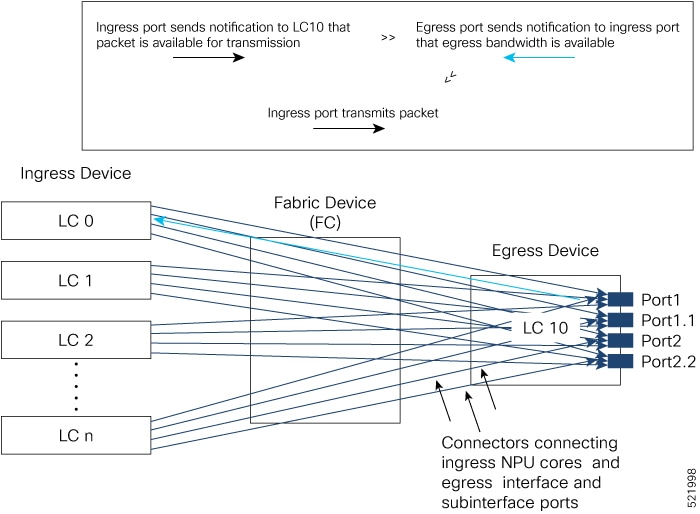


 Feedback
Feedback