Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4
What's New in this Release
Related Documentation
Console Access to CNSIE-2110-K9 System
Console Access to CNSIE-2115-K9 System
Serial Connection Settings
Troubleshooting the Serial Port
Cabling an ASM Interconnect Network
Cisco IOS Dependences
Installation Notes
XML Transform Tool for Users Migrating from Release 1.3 to 1.4
Router Configuration
Limitations and Restrictions
New Event Subject Names
For Cisco IOS
For IMGW Device Module Development Toolkit
Legacy Subject Names
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.3
Open Caveats - Release 1.3
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.3.1
Open Caveats - Release 1.3.1
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.3.2
Open Caveats - Release 1.3.2
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.4
Open Caveats Release 1.4
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4
The Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 is a network management application that acts as a configuration service for automating the deployment and management of network devices and services. The Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 runs on the Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine (CNS 2100 Series system) hardware platform.
Each Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 manages a group of Cisco IOS devices (routers) and services they deliver, storing their configurations and Cisco IOS images, then delivering them as needed. The Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 automates initial configurations, configuration and image updates, dynamically generating the device-specific configuration or image on-demand, and logs the results.
The CNS Image Service is an automated, scalable, and secure mechanism designed to distribute Cisco IOS images and related software updates to Cisco IOS devices that have Cisco Intelligence Agents (CIAs).
For those devices that do not have a CIA, non-Cisco IOS devices, and non-Cisco devices, you can use the IMGW Toolkit to create scripts that support SSH sessions between these devices and the CNS Configuration Engine 1.4.
What's New in this Release
This section highlights the new features found in this release:
• Support for PIX devices in auto-update mode
Support for PIX devices in auto-update mode
• IMGW Device Module Development Toolkit
IMGW Device Module Development Toolkit
• CNS Image Service
CNS Image Service
• This release supports Cisco IOS 12.3.
This release supports Cisco IOS 12.3.
• The base element of the CNS event subject namespace has been changed from cisco.cns.* to cisco.mgmt.cns.* in support of Cisco IOS 12.3.
The base element of the CNS event subject namespace has been changed from cisco.cns.* to cisco.mgmt.cns.* in support of Cisco IOS 12.3.
The CNS event subject namespace has been modified in accordance with the new Cisco subject naming conventions. In order to keep up with the new subject naming convention, CNS agents in Cisco IOS have been modified and released with the 12.3 Cisco IOS train. The change affects the subject names that the CNS agents subscribe to and publish on.
For the smooth transition of existing applications from the old subject namespace, the Namespace Mapping service (NSM) has been updated with a new mechanism that maps old subjects to the new ones.
There are no code or configuration changes required in applications written using the NSM API since the API interfaces have not been modified. However, upgrading to Cisco CNS SDK 1.5.4 is a required procedure for the transition.
Applications that are written without the use of the Namespace Mapper have to be modified to accommodate the change in CNS event subjects. For example, the subject cisco.cns.config.load has been modified to cisco.mgmt.cns.config.load.
We recommend that all applications use the Namespace Mapper in order to maintain the separation between design-time and deployment-time subjects.
For a complete list of the new event subject names, see "New Event Subject Names" section.
• The none mode under Event Services Setting in the Setup program is not supported from the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 user interface for updates made from the user interface to devices that use the old CNS event subject names. This is because NSM is not invoked in the none mode. NSM has been modified to translate subject names in support of devices not running Cisco IOS 12.3.
The none mode under Event Services Setting in the Setup program is not supported from the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 user interface for updates made from the user interface to devices that use the old CNS event subject names. This is because NSM is not invoked in the none mode. NSM has been modified to translate subject names in support of devices not running Cisco IOS 12.3.
• Refer to the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Administrator Guide for more information about these features.
Refer to the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Administrator Guide for more information about these features.
Related Documentation
Other documentation related to this product include:
• Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Installation & Setup Guide For Linux
Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Installation & Setup Guide For Linux
• Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Administrator Guide
Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Administrator Guide
• Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine Installation Guide
Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine Installation Guide
• Release Notes for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine
Release Notes for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine
• Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine Machine Code License
Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine Machine Code License
• Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine
• Cisco CNS Software Development Kit API Reference and Programmer Guide
Cisco CNS Software Development Kit API Reference and Programmer Guide
Console Access to CNSIE-2110-K9 System
Normal terminal login to the CNSIE-2110-K9 (x330) system is supported by way of the system serial port. The CNS 2100 Series system redirects and supports console login at the serial port.
For more information about console access to the CNSIE-2110-K9 (x330) system, refer to the Release Notes for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine, Release 1.3.
Console Access to CNSIE-2115-K9 System
Normal terminal login to the CNSIE-2115-K9 (x335) system is supported by way of the system serial port (See Figure 1, callout-7).
Timesaver  For immediate console access to the server, use two DB9 connectors and a rollover cable to connect your laptop computer to the server serial port.
For immediate console access to the server, use two DB9 connectors and a rollover cable to connect your laptop computer to the server serial port.
Figure 1 CNSIE-2115-K9 (x335)Rear Panel
1.  Power connector: Connect the power cable here.
Power connector: Connect the power cable here.
2.  Ethernet 2 connector: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
Ethernet 2 connector: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
3.  USB 3 connector: Connect to a Universal Serial Bus here.
USB 3 connector: Connect to a Universal Serial Bus here.
4.  Ethernet 1 connector: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
Ethernet 1 connector: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
5.  ISM connector: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector.
ISM connector: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector.
6.  C2T OUT connector: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
C2T OUT connector: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
7.  Serial connector: Connect a 9-pin serial device to this connector.
Serial connector: Connect a 9-pin serial device to this connector.
8.  C2T IN connector: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
C2T IN connector: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
9.  Power connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the power cable for Remote Service Adapter here.
Power connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the power cable for Remote Service Adapter here.
10.  RS-485 on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the ASM Interconnect Module to this connector.
RS-485 on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the ASM Interconnect Module to this connector.
11.  Serial connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect a 9-pin serial device to this connector.
Serial connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect a 9-pin serial device to this connector.
12.  Ethernet connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
Ethernet connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
The CNS 2100 Series system redirects and supports console login at the serial port. It is a more desirable feature because you can perform daily or emergency administrative tasks remotely, by way of the serial port.
Serial Connection Settings
The serial connection settings are as follows:
9600 baud
8 data bit
N (No)parity
1 stop bit
Troubleshooting the Serial Port
The serial port is enabled by default. If there is a connection problem, verify that it is enabled by accessing the Remote Console Redirection menu during system start as follows:
Step 1  Press F1, then go to: Configuration/Setup Utility (menu) -> Devices and I/O ports (menu) -> Remote Console Redirection (menu)
Press F1, then go to: Configuration/Setup Utility (menu) -> Devices and I/O ports (menu) -> Remote Console Redirection (menu)
Step 2  Make sure the Remote Console Active parameter is enabled.
Make sure the Remote Console Active parameter is enabled.
Cabling an ASM Interconnect Network
An Advanced System Management (ASM) bus is integrated into the C2T interconnect cables, so by adding one or more Remote Supervisor Adapters to a C2T chain of servers, you can create an Advanced System Management (ASM) interconnect network. For information about using a Remote Supervisor Adapter for remote server management, see the documentation that comes with the adapter.
Before cabling the ASM interconnect network, review the following information:
• The cables in an ASM interconnect network are hot-swappable.
The cables in an ASM interconnect network are hot-swappable.
• Make sure that the firmware for the Remote Supervisor Adapter, ASM processor, and integrated system management processor (ISMP) are at the latest level.
Make sure that the firmware for the Remote Supervisor Adapter, ASM processor, and integrated system management processor (ISMP) are at the latest level.
• The servers in an ASM interconnect network are referred to by their assigned addresses, not by their positions in the rack.
The servers in an ASM interconnect network are referred to by their assigned addresses, not by their positions in the rack.
An ASM interconnect network can have up to 24 RS-485 connections, depending on the configuration. The connections can include Remote Supervisor Adapters, ASM processors, ASM PCI adapters, and ISMPs. Use the following information to determine the number of servers and connections that you can have on your ASM interconnect network:
• Each Remote Supervisor Adapter, ASM processor, ASM PCI adapter, and ISMP in a server that is connected to the network uses one connection. For example, if a server that is connected to the network has a Remote Supervisor Adapter and an integrated ASM processor, the server uses two connections on the network.
Each Remote Supervisor Adapter, ASM processor, ASM PCI adapter, and ISMP in a server that is connected to the network uses one connection. For example, if a server that is connected to the network has a Remote Supervisor Adapter and an integrated ASM processor, the server uses two connections on the network.
• The network must include at least one server with a Remote Supervisor Adapter (either installed as an option or pre-installed in the server).
The network must include at least one server with a Remote Supervisor Adapter (either installed as an option or pre-installed in the server).
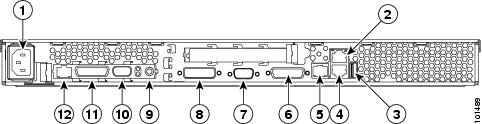
You can connect up to 23 xSeries 335 servers into an ASM interconnect network using one Remote Supervisor Adapter. However, if you use both xSeries 335 and xSeries 330 servers in the network, the xSeries 330 servers must be the lowest-numbered servers in the chain. Figure 2 shows an ASM interconnect network with three servers.
Figure 2 ASM Interconnect Network of Three Servers
1.  IN: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
IN: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
2.  OUT: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
OUT: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
3.  ISM: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector in the first (A) server.
ISM: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector in the first (A) server.
4.  ASM link cable: Connect this cable to the ISM connector (3) in the first server.
ASM link cable: Connect this cable to the ISM connector (3) in the first server.
5.  Mouse: Connect a mouse to this connector.
Mouse: Connect a mouse to this connector.
6.  Keyboard: Connect a keyboard to this connector.
Keyboard: Connect a keyboard to this connector.
7.  Video: Connect a monitor to this line.
Video: Connect a monitor to this line.
8.  ASM interconnect module: Connect this module to the RS-485 connector (9) on the Remote Supervisor Adapter in the first server.
ASM interconnect module: Connect this module to the RS-485 connector (9) on the Remote Supervisor Adapter in the first server.
9.  RS-485 on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the ASM Interconnect Module to this connector.
RS-485 on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the ASM Interconnect Module to this connector.
You can add up to 23 more servers to the network by installing a Remote Supervisor adapter in the 24th server, creating a second ASM bus. Figure 3 shows an ASM interconnect network with 46 servers.
Figure 3 ASM Interconnect Network of 46 Servers
1.  IN: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
IN: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
2.  OUT: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
OUT: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
3.  ISM: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector in the first (A) server.
ISM: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector in the first (A) server.
4.  ASM link cable: Connect this cable to the ISM connector (3) in the first server.
ASM link cable: Connect this cable to the ISM connector (3) in the first server.
5.  Mouse: Connect a mouse to this connector.
Mouse: Connect a mouse to this connector.
6.  Keyboard: Connect a keyboard to this connector.
Keyboard: Connect a keyboard to this connector.
7.  Video: Connect a monitor to this line.
Video: Connect a monitor to this line.
8.  Second ASM bus: Connect servers 24 through 46 on this bus.
Second ASM bus: Connect servers 24 through 46 on this bus.
9.  First ASM bus: Connect servers 1 through 23 on this bus.
First ASM bus: Connect servers 1 through 23 on this bus.
To cable an ASM interconnect network, complete the following steps:
Step 1  Follow the instructions for cabling a C2T chain.
Follow the instructions for cabling a C2T chain.
Step 2  Connect an ASM interconnect module (which comes with the Remote Supervisor Adapter) to the RS-485 connector on the Remote Supervisor Adapter in the first server. If the network contains more than 23 servers, do the same on the 24th server.
Connect an ASM interconnect module (which comes with the Remote Supervisor Adapter) to the RS-485 connector on the Remote Supervisor Adapter in the first server. If the network contains more than 23 servers, do the same on the 24th server.
Connect an ASM link cable (which comes with the Remote Supervisor Adapter) from the ASM interconnect module to the ISM connector in the first server. Insert a terminator into the second connector on the ASM interconnect module. If the network contains more than 23 servers, do the same on the 24th server.
Cisco IOS Dependences
Table 1 lists Cisco IOS versions with corresponding versions of CNS Configuration Engine including feature limitations associated with each version.
Table 1 CNS Configuration Engine and Cisco IOS Dependencies
|
Cisco IOS
|
CNS Configuration Engine
|
Limitations
|
12.3 |
1.3.2 or later |
|
12.2(11)T |
1.2 or later |
|
12.2(2)T |
1.2 or later with no authentication. |
Applications will be unable to use exec commands or point-to-point messaging. |
Installation Notes
To be able to monitor the installation activity and run the Setup program, you should have a local keyboard-mouse and serial port connected to your system (refer to the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Installation & Setup Guide For Linux).
The software installs automatically. During the install sequence, the install script pauses at the Red Hat screen. Press Enter to continue.
XML Transform Tool for Users Migrating from Release 1.3 to 1.4
An XML transformation script has been added to DAT for automating the XML file conversion of IMGW data because the optional attribute device-type in Release 1.3 IMGW schema is now mandatory. The script assigns an type of UNKNOWN to the IMGW devices without device type defined.
For IMGW XML file conversion, run the following shell script in the /opt/CSCOdat/XMLTransform/ directory on the CNS IE2100 Series console:
./datxmltransformer.sh <imgw-device-data.xml> _dat_xml_transformer_1_3.xsl
The system generates an IMGW XML file conforming to 1.4 DTD with the same data.
The shell script takes two input arguments. The first argument specifies the absolute pathname to the old (1.3) IMGW XML file whose name must end with an xml extension. The file should contain only IMGW device data, enclosed between the <imgw-device> tags, because unrelated data are not parsed and removed.
The second argument specifies the XSL style-sheet that describes the rules for transforming the IMGW data.
For example, given an XML file of imgw-data-1.3.xml in release 1.3 DTD format, here is the list of steps for the conversion:
Step 1  Login to the CNS 2100 Series system console.
Login to the CNS 2100 Series system console.
Step 2  Change directories to: /opt/CSCOdat/XMLTransform/.
Change directories to: /opt/CSCOdat/XMLTransform/.
Step 3  Issue the following commands:
Issue the following commands:
./datxmltransformer.sh ./imgw-data-1.3.xml _dat_xml_transformer_1_3.xsl
The XML that is to be converted (imgw-data-1.3.xml) must be present on the CNS 2100 Series system. The script creates a new file with the name imgw-data-1.3-new.xml in the same directory as the old file. This file conforms to release 1.4 DTD and can be imported into Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 using the bulk upload function.
Router Configuration
For a router to pick up its initial configuration from the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4, install the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 software before installing a router. Then, establish a connection between the router and the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4.
For information about Cisco CNS Flow-Through Provisioning, refer to:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1839/products_feature_guide09186a0080087d2a.html.
Limitations and Restrictions
• For this release, ConfigID, ImageID, and DeviceName must have the same value (see CSCec08478).
For this release, ConfigID, ImageID, and DeviceName must have the same value (see CSCec08478).
• Provider mode is not supported in the Image Server (see CSCec51936). However, you can do group-level operations through the GUI. You will not be able to map CNS subjects to subjects specific to their application's namespace.
Provider mode is not supported in the Image Server (see CSCec51936). However, you can do group-level operations through the GUI. You will not be able to map CNS subjects to subjects specific to their application's namespace.
• If you download a configuration that changes username, password, enable password, or IP address for a non-agent-enabled device, you need to modify the corresponding IMGW hop information for the device to update it with the new username, password, enable password, and IP address.
If you download a configuration that changes username, password, enable password, or IP address for a non-agent-enabled device, you need to modify the corresponding IMGW hop information for the device to update it with the new username, password, enable password, and IP address.
• External directory is not supported for IMGW.
External directory is not supported for IMGW.
• SFTP - An SFTP server is permanently enabled which can be used for administrative tasks such as placing images securely into the FTP directory [ /tftp/CSCOcnsis/images/ ] for image download by devices over FTP or TFTP. Any regular system account may login to SFTP.
SFTP - An SFTP server is permanently enabled which can be used for administrative tasks such as placing images securely into the FTP directory [ /tftp/CSCOcnsis/images/ ] for image download by devices over FTP or TFTP. Any regular system account may login to SFTP.
• FTP - FTP service is READ-ONLY.
FTP - FTP service is READ-ONLY.
• TFTP:
TFTP:
– No new files can be created and files cannot be deleted. However, existing files can be overwritten ONLY if they are publicly writeable. The permissions of the files placed into the ftp directory can be controlled by the SFTP user managing files in the ftp directory.
No new files can be created and files cannot be deleted. However, existing files can be overwritten ONLY if they are publicly writeable. The permissions of the files placed into the ftp directory can be controlled by the SFTP user managing files in the ftp directory.
– The TFTP service does not require an account or password on the server system. Due to the lack of authentication information, TFTPD allows only publicly readable files (o+r) to be accessed. Files may be written only if they already exist and are publicly writable.
The TFTP service does not require an account or password on the server system. Due to the lack of authentication information, TFTPD allows only publicly readable files (o+r) to be accessed. Files may be written only if they already exist and are publicly writable.
• All password values in Setup must contain alphanumeric characters only. Special characters have different meanings in the UNIX shell and should not be used for passwords.
All password values in Setup must contain alphanumeric characters only. Special characters have different meanings in the UNIX shell and should not be used for passwords.
• Device Name values may contain only: period (.), underscore (_), hyphen (-), and alphanumeric characters.
Device Name values may contain only: period (.), underscore (_), hyphen (-), and alphanumeric characters.
• Group Name values may contain only: underscore (_) and alphanumeric characters.
Group Name values may contain only: underscore (_) and alphanumeric characters.
New Event Subject Names
This section lists the new event subject names that are associated with Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4.
For Cisco IOS
This section lists the new event subject names that are associated with Cisco IOS 12.3.
CNS Event Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.event.boot
cisco.mgmt.cns.event.id-changed
CNS Image Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.image.* - Events related to the image distribution agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.image.checkServer
cisco.mgmt.cns.image.inventoryRequest
cisco.mgmt.cns.image.upgradeRequest
cisco.mgmt.cns.image.status
CNS Exec Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.exec.* - Events related to exec command-like functions.
cisco.mgmt.cns.exec.cmd
cisco.mgmt.cns.exec.rsp
cisco.mgmt.cns.exec.reload
CNS Config Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.config.complete
cisco.mgmt.cns.config.failure
cisco.mgmt.cns.config.warning
cisco.mgmt.cns.config.sync-status
cisco.mgmt.cns.config.reboot - deprecated. Use cisco.mgmt.cns.exec.reload instead. cisco.mgmt.cns.config.load
cisco.mgmt.cns.config.id-changed
cisco.mgmt.cns.config-changed
cisco.mgmt.cns.config-changed.lost
CNS Inventory Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.inventory.get
cisco.mgmt.cns.inventory.device-details
cisco.mgmt.cns.inventory.oir
CNS Syslog Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.emerg
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.alert
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.crit
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.err
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.warning
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.notice
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.info
cisco.mgmt.cns.log.debug
CNS MIB Access Agent
cisco.mgmt.cns.mibaccess.request
cisco.mgmt.cns.mibaccess.response
cisco.mgmt.cns.mibaccess.notification
cisco.mgmt.cns.snmp.rqst
cisco.mgmt.cns.snmp.resp
cisco.mgmt.cns.snmp.trap
CNS Event Gateway
cisco.mgmt.cns.device.connect
cisco.mgmt.cns.device.disconnect
For IMGW Device Module Development Toolkit
This section lists the new event subject names that are associated the IMGW Device Module Development Toolkit.
cisco.mgmt.cns.imgw.devicemodule.request.register
cisco.mgmt.cns.imgw.devicemodule.request.deregister
cisco.mgmt.cns.imgw.devicemodule.response.register
cisco.mgmt.cns.imgw.devicemodule.response.deregister
Legacy Subject Names
The following is a list of all the subject names in use in Cisco IOS releases prior to 12.3, and CNS Configuration Engine Release 1.3.2. Starting with Release 12.3 of Cisco IOS and Release 1.3.2 of the CNS Configuration Engine, the prefix for all of the subjects listed below will be modified from cisco.cns to cisco.mgmt.cns.
Here is the list of subjects names in use prior to IOS 12.3:
cisco.cns.config.complete
cisco.cns.config.failure
cisco.cns.config.warning
cisco.cns.config.sync-status
cisco.cns.config.reboot
cisco.cns.config.load
cisco.cns.config.id-changed
cisco.cns.exec.cmd
cisco.cns.exec.rsp
cisco.cns.inventory.get
cisco.cns.inventory.device-details
cisco.cns.inventory.oir
cisco.cns.config-changed
cisco.cns.config-changed.lost
cisco.cns.event.boot
cisco.cns.event.id-changed
SYSLOG
cisco.cns.log.emerg
cisco.cns.log.alert
cisco.cns.log.crit
cisco.cns.log.err
cisco.cns.log.warning
cisco.cns.log.notice
cisco.cns.log.info
cisco.cns.log.debug
SAA
cisco.cns.slm
cisco.cns.customtrap
MIB Access
cisco.cns.mibaccess.request
cisco.cns.mibaccess.response
cisco.cns.mibaccess.notification
cisco.cns.snmp.rqst
cisco.cns.snmp.resp
cisco.cns.snmp.trap
CNS Event Gateway
cisco.cns.device.connect
cisco.cns.device.disconnect
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.3
This section lists caveats that were resolved for the CNS 2100 Series platform (see Table 2) and Release 1.3 of the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine software application (see Table 3).
.
Table 2 CNS 2100 Series Platform
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdu77514 |
ldaputil.properties shows groupOfNames as Group object class. In general, groupOfNames is used by LDAP servers as a method of grouping. The Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 uses groupOfNames ObjectClass in its grouping mechanism. If it is necessary, you can use your own group object class as long as two multi-value attributes exist in that object class: member (this can be changed as well) and seealso. |
CSCdw31205 |
If the serial port is not connected, reboot or shutdown -r now does not reboot the system. This condition can also cause problems (hard disk corruption) when powering off the system using spoff 50 because file-system buffers are not flushed. |
CSCdw46662 |
In the Setup program, the prompt Enter the Event Gateway Debug Log does not adequately explain what the Setup program is asking for. |
CSCdw65776 |
If you configure the CNS 2100 Series for External Directory mode and you do not use the sample schema, you will be prompted for the elements of your schema. It is important when setting up your own schema to put the Namespace Mapper group context under the CNS context. No checking is done for this requirement, but if this requirement is not satisfied, you will not be able to view or update any devices in the user interface. |
CSCdw84222 |
The command show version was used for displaying the software versions on the system in the previous releases. This command is not yet removed from the system, but it is obsolete. The output should be ignored. |
CSCdw85170 |
When you change the Admin account, then run relocate or reinitialize, the Admin account is corrupted. This occurs because of a problem in redefining the Linux administrator account username in Setup. |
Table 3 Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.3
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdu85243 |
The Search functionality is inconsistent. |
CSCdv05930 |
Tools->Directory Manager->Edit Schema The Unique ID for this attribute is editable. Any value can be given to this attribute. Since this value is OID for this attribute it should follow the standards used for creating OIDs. |
CSCdw37706 |
All users can be deleted using Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 user interface. |
CSCdw83530 |
No warning given to user when reverting back to original schema. |
CSCdw84916 |
Device update fails when the uniquedeviceid and uniqueconfigid of the device are different. |
CSCdw89165 |
DAT allows addition of device with same cn= in different containers. |
CSCdw89291 |
Inconsistent behavior in View and Update screen when template is invalid. |
CSCdx01553 |
The Event Gateway debugging log exhausts available disk space within two days of turning on the debugging option. |
Open Caveats - Release 1.3
This section lists known caveats that are open for the CNS 2100 Series platform (see Table 4) and Release 1.3 of the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine software application (see Table 5).
Table 4 CNS 2100 Series Platform
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdw58345 |
The current version of LDAP directory is unable to handle attributes more than 64 characters, which causes internal processes to fail. |
When running the Setup program on the CNS 2100 Series, do not create any user-specified identifiers that are longer than 64 characters. |
CSCdv70366 |
The directory API does not support special characters in device names, such as < & etc. The API does not accept special characters in username or password fields. |
When using the Intelligent Modular Gateway feature of the CNS 2100 Series to configure a device by means of Telnet or SSH, it is not possible to use punctuation characters in the username or password for the target device. |
CSCdv85666 |
When setting up the CNS 2100 Series with the Setup program, if you enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, you are not re-prompted to enter a correct one. This invalid IP address causes network connectivity problems for the unit. |
If you accidentally enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, proceed through the rest of Setup program, but do not commit the changes. Then log in as setup again (if the unit has never been configured before) or run the Setup program (if you are updating a previous configuration) and enter the correct values. |
CSCdv90816 |
In the Linux operating system, the two Ethernet interfaces are defined as Ethernet0 and Ethernet1. The user is presented with this nomenclature when configuring and using these two interfaces. The labelling on the IBM x330 hardware shows the two Ethernet interfaces as Ethernet1 and Ethernet2. |
In the CNS 2100 Series, the hardware is labeled with ports Ethernet 1 and Ethernet 2. The software identifies these ports as Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 1. Ethernet 1 on the hardware label refers to Ethernet 0 in the software. Ethernet 2 on the hardware label refers to Ethernet 1 in the software. |
Table 5 Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.3
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdv04599 |
TibGate getting killed after fetching large number of mappings. When using the Namespace Mapper feature, there is a limitation of 150 mappings per subject name. If more than 150 mappings are provided, the CNS Event Gateway stops functioning. |
Limit the number of mappings per subject name to 150. |
CSCdy15293 |
The reload button in the web-based user interface might not work properly when reload is pressed number of times. |
To clear this problem, close and restart the web browser. |
CSCdy48492 |
When there are about 5,000 devices to be displayed in the Update or Delete Device screens it takes about 10 minutes to display all the devices in the screen. |
When you click on the Update or Delete Device links in the Devices menu please wait for sometime for the browser to display all the devices and the corresponding check boxes. |
CSCdy48788 |
When the Bulkupload data contains invalid attributes, DAXMLservelet stops working and logs invalid errors. This is a problem in the current LDAP directory version. |
Validate that there are no invalid attributes in the Bulkupload data. If for some reason the system goes into this state, then reload the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 software. |
CSCdy53209 |
The Event Gateway (TibGate) is unable to allocate memory. This problem is noticed in stress cases only. |
Reduced usage of memory should help the problem. |
CSCdy61014 |
Currently due to resource constraints, it is not possible to have all 5,000 devices connect to the Event Gateway (TibGate) all at once. |
The workaround is to stagger device connection in multiple waves of 500 devices per wave. |
CSCdy62870 |
Authentication server may become unresponsive when many events (2000 or so) are sent (via event bus) to the IMGW devices. |
There is no workaround. Httpd would have to be restarted to restore the authentication server. |
CSCdy63149 |
When more than 500 simultaneous connections come in, the configuration service can leave a spinning java thread utilizing CPU cycles. However, this thread is scheduled whenever other threads come in. |
Currently, the only workaround is to reload Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 software to get rid of the thread. |
CSCdy68363 |
This is a known problem when over loading the Webserver. |
When NSM provider mode (algorithmic) was tested by bringing up 100 clients at a time with 1,000 seconds delay before another set of 100 clients, all 5,000 clients were able to establish connection with TibGate successfully. |
CSCdy72661 |
Event Gateway (TibGate) authentication request timeout option not set to support 5,000 devices. |
None. This parameter is set automatically by the setup program. |
CSCdy80613 |
Currently due to limited resources, it takes a long time for all 5,000 devices to receive configuration updates. |
Issue updates in staggered waves of 500 devices per wave. |
CSCdy83389 |
When 5000 devices try to post their inventory information and connect to Event Gateway upon receiving their configurations, it may take up to an hour before the last configuration is received. During this period, most of the device authentication requests are queued and timeout due to the default authentication timeout value of 180 seconds. |
The devices will retry automatically and will ultimately get authenticated. |
CSCdz14956 |
Under stress conditions over a period of weeks it has been noticed that the EventMonitor on the GUI stops logging the events. |
To restart the EventMonitor log, restart the CNS 2100 Series system. |
CSCdz20043 |
GUI: Tools -> Data Manager -> UpdateProductList, the option on the UpdateProductList page Download from Cisco Web site does not work. This is because the default URL specified in the properties is incorrect. |
Specified URL option and enter the URL explicitly. |
CSCdz33665 |
When SSL is turned on and 5,000 devices post their configurations, then connect to the Event Gateway (TibGate) upon receiving their configurations, all 5,000 successfully connect to the Event Gateway. But, if all 5,000 disconnect from the Event Gateway and reconnect, the CNS 2100 Series system experiences out of memory failures and the number of devices that successfully reconnect to the Event Gateway is reduced. The problem gets worse for each subsequent 5,000 disconnect and reconnect sequence. |
The number of devices using SSL, either connecting to Apache configuration server or connecting to the Event Gateway (TibGate, should be limited to 3,000 or less. |
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.3.1
This section lists caveats that were resolved in Release 1.3.1 (see Table 6).
Table 6 Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.3.1
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdw58345 |
The current version of LDAP directory is unable to handle attributes more than 64 characters, which causes internal processes to fail. |
CSCdy48492 |
When there are about 5,000 devices to be displayed in the Update or Delete Device screens it takes about 10 minutes to display all the devices in the screen. |
CSCdy61014 |
Currently due to resource constraints, it is not possible to have all 5,000 devices connect to the Event Gateway (TibGate) all at once. |
CSCdy63149 |
When more than 500 simultaneous connections come in, the configuration service can leave a spinning java thread utilizing CPU cycles. However, this thread is scheduled whenever other threads come in. |
CSCdy72661 |
Event Gateway (TibGate) authentication request timeout option not set to support 5,000 devices. |
CSCdz20043 |
GUI: Tools -> Data Manager -> UpdateProductList, the option on the UpdateProductList page Download from Cisco Web site does not work. This is because the default URL specified in the properties is incorrect. |
Open Caveats - Release 1.3.1
This section lists known caveats that are open for the CNS 2100 Series third-party software (see Table 7), CNS 2100 Series platform (see Table 8), and Release 1.3.1 of the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine software application (see Table 9).
Table 7 CNS 2100 Series Third-Party Software
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdv70366 |
The directory API does not support special characters in device names, such as < & etc. The API does not accept special characters in username or password fields. |
When using the Intelligent Modular Gateway feature of the CNS 2100 Series to configure a device by means of Telnet or SSH, it is not possible to use punctuation characters in the username or password for the target device. |
Table 8 CNS 2100 Series Platform
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdv85666 |
When setting up the CNS 2100 Series with the Setup program, if you enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, you are not re-prompted to enter a correct one. This invalid IP address causes network connectivity problems for the unit. |
If you accidentally enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, proceed through the rest of Setup program, but do not commit the changes. Then log in as setup again (if the unit has never been configured before) or run the Setup program (if you are updating a previous configuration) and enter the correct values. |
CSCdv90816 |
In the Linux operating system, the two Ethernet interfaces are defined as Ethernet0 and Ethernet1. The user is presented with this nomenclature when configuring and using these two interfaces. The labelling on the IBM x330 hardware shows the two Ethernet interfaces as Ethernet1 and Ethernet2. |
In the CNS 2100 Series, the hardware is labeled with ports Ethernet 1 and Ethernet 2. The software identifies these ports as Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 1. Ethernet 1 on the hardware label refers to Ethernet 0 in the software. Ethernet 2 on the hardware label refers to Ethernet 1 in the software. |
CSCdz76673 |
The following new Event Gateway prompts have been added:
Enter log file rotation timer
(minutes, 0 = no rotation): [15]
Enter max log file size (Kbytes):
Enter the max versions of log file
These prompt changes are not reflected in the internaldir.pl and externaldir.pl files in the /opt/CSCOcnsie/bin directory. These are sample scripts to run the user's non-interactive setup prompts. Without these prompts, it is possible to run non-interactive setup. However, the drawback is that the values for the above prompts default to its existing values. Users cannot set these values using non interactive setup script. |
None. |
CSCdz78340 |
In NSM default mode, when 5,000 devices pull down their initial configuration of size 64 KB with 27 LDAP attributes and establish connection with Event Gateway, they will succeed at the very first time after a fresh reboot of CNS 2100 Series. If all the devices go down and come back again, they encounter memory allocation failure and not all the connections are established with Event Gateway. |
If you reduce the size of the initial configuration file to 20 KB, the problem will not be seen. |
CSCdz81426 |
Setup can fail and pause indefinitely when a numeric hostname, such as 2110, is used and entered at the network-parameter prompt. The log file /var/log/appliance-setup.log contains errors similar to the followings: 2003-01-10 21:05:50 rvrd: unable to resolve network specification (2110) 2003-01-10 21:05:50 rvrd: unable to resolve network specification (2110) It shows that Tibco fails to resolve the numeric hostname for an IP address. |
Name the appliance with an alpha-numeric value beginning with an alpha value. |
CSCdz83000 |
When IMGW starts, it generates a debug messages. It displays the debug messages a number of times recursively. [root@infystorm2 tools]# /etc/rc.d/init.d/Imgw stop Stopping IMGW [ OK ] [root@infystorm2 tools]# /etc/rc.d/init.d/Imgw start Done [root@infystorm2 tools]# perl: warning: Setting locale failed. perl: warning: Please check that your locale settings: LANGUAGE = (unset), LC_ALL = (unset), LANG = "en_US.iso885915" are supported and installed on your system. perl: warning: Falling back to the standard locale ("C"). perl: warning: Setting locale failed. perl: warning: Please check that your locale settings: LANGUAGE = (unset), LC_ALL = (unset), LANG = "en_US.iso885915" are supported and installed on your system. perl: warning: Falling back to the standard locale ("C"). |
None. |
CSCeb76924 |
httpd (Apache web server) is not running or cannot be started due to a out-of-space problem. The following error message is seen in /var/log/appliance-setup.log: Waiting for tomcat to initialize...
........Starting httpd:fopen:No
space left on device httpd:could not open error log file
/etc/httpd/logs/error_log.[FAILED] There are many (thousands) mgetty.log files generated in the /var/log directory. This large number of log files uses up all file system resources and the file system is not able to accommodate any more new file. Once the log files are removed, the system can function normally. After inspecting the logrotate configuration file (/etc/logrotate.d/mgetty) that comes with mgetty, it was found that there is a mis-configuration in the file: /var/log/mgetty.log.tty* {
nocompress
missingok
} The wide-card asterisk commands logrotate to rotate not only the mgetty.log.ttyS0 file, but all the files that are created in each of the subsequent rotation. Eventually, all the file system resources are used up. |
This is a two-step workaround: First, remove existing mgetty log files with the command:
find /var/log -name 'mgetty.log.ttyS0.*' -print | xargs rm -fr Second, correct the mgetty logrotate configuration (/etc/logrotate.d/mgetty) as follows: /var/log/mgetty.log.ttyS0 {
nocompress
missingok
} |
Table 9 Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.3.1
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdv04599 |
TibGate getting killed after fetching large number of mappings. When using the Namespace Mapper feature, there is a limitation of 150 mappings per subject name. If more than 150 mappings are provided, the CNS Event Gateway stops functioning. |
Limit the number of mappings per subject name to 150. |
CSCdy15293 |
The reload button in the web-based user interface might not work properly when reload is pressed number of times. |
To clear this problem, close and restart the web browser. |
CSCdy48788 |
When the Bulkupload data contains invalid attributes, DAXMLservelet stops working and logs invalid errors. This is a problem in the current LDAP directory version. |
Validate that there are no invalid attributes in the Bulkupload data. If for some reason the system goes into this state, then reload the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 software. |
CSCdy68363 |
In NSM Provider mode, if 5,000 devices try to establish connection with Event Gateway at a time, NSM Server is stressed and takes longer time to resolve the original subject. If the keepalive timeout on the devices is set less than the resolve time period (which depends on the load at that time), Event Gateway fails to send keepalive messages back to the devices. This causes the devices to time out and retry for a new connection. |
1.  Set a keepalive timeout that is longer than the time required for NSM server to resolve the original subject. Testing has been done with 3,500 seconds and 5 retries, and the problem was not observed. Set a keepalive timeout that is longer than the time required for NSM server to resolve the original subject. Testing has been done with 3,500 seconds and 5 retries, and the problem was not observed. 2.  Bring up the 5,000 devices in batches: a set of 100 with 1,000 seconds delay before another set of 100. All 5,000 devices will establish connection with Event Gateway successfully. The same thing applies to configuration update also. Bring up the 5,000 devices in batches: a set of 100 with 1,000 seconds delay before another set of 100. All 5,000 devices will establish connection with Event Gateway successfully. The same thing applies to configuration update also. |
CSCdy80613 |
Currently due to limited resources, it takes a long time for all 5,000 devices to receive configuration updates. |
Issue updates in staggered waves of 500 devices per wave. |
CSCdy83389 |
When 5000 devices try to post their inventory information and connect to Event Gateway upon receiving their configurations, it may take up to an hour before the last configuration is received. During this period, most of the device authentication requests are queued and timeout due to the default authentication timeout value of 180 seconds. |
The devices will retry automatically and will ultimately get authenticated. |
CSCdz14956 |
Under stress conditions over a period of weeks it has been noticed that the EventMonitor on the GUI stops logging the events. |
To restart the EventMonitor log, restart the CNS 2100 Series system. |
CSCdz33665 |
When SSL is turned on and 5,000 devices post their configurations, then connect to the Event Gateway (TibGate) upon receiving their configurations, all 5,000 successfully connect to the Event Gateway. But, if all 5,000 disconnect from the Event Gateway and reconnect, the CNS 2100 Series system experiences out of memory failures and the number of devices that successfully reconnect to the Event Gateway is reduced. The problem gets worse for each subsequent 5,000 disconnect and reconnect sequence. |
The number of devices using SSL, either connecting to Apache configuration server or connecting to the Event Gateway (TibGate, should be limited to 3,000 or less. |
CSCdz84489 |
If you configure the Event ID and Config ID using the cns id command before the event agent is started, you will not receive any config/event changed events even after the event agent is enabled. |
In order for the notification to be sent out, it is necessary that the event and config agent are up and running prior to the execution of the cns id command. |
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.3.2
This section lists caveats that were resolved in Release 1.3.2 (see Table 10 through Table 11).
Table 10 Security
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCea75440 |
Disable TRACE and/or TRACK methods in Apache. |
CSCeb13752 |
Keeping the Tibco Web Admin port open all the time, is potential security risk. So, by default the http port of the Tibco Web Admin GUI should be closed and it should be opened only when the user runs an open-tibco-web-admin-port script. After the user completes web admin task by accessing the GUI, the http port of the Tibco Web Admin GUI is closed again by running a close-tibco-web-a dmin-port script. This facility enables the user to open the Tibco Web Admin port, only when it is needed and reduces the security risk. |
Table 11 NSM
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCea76581 |
Since Cisco IOS has changed its subject names from cisco.cns.* to cisco.mgmt.cns.*, NSM has to be changed to accommodate backward compatibility for the agents in old Cisco IOS images. |
Table 12 General
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdv04599 |
TibGate getting killed after fetching large number of mappings. |
CSCdw58345 |
The current version of LDAP directory is unable to handle attributes more than 64 characters, which causes internal processes to fail. |
CSCdy48788 |
When the Bulkupload data contains invalid attributes, DAXMLservelet stops working and logs invalid errors. This is a problem in the current LDAP directory version. |
CSCdy83389 |
When 5000 devices try to post their inventory information and connect to Event Gateway upon receiving their configurations, it may take up to an hour before the last configuration is received. |
CSCdz76673 |
The following prompts added to the Setup program for non-interactive setup: Enter log file rotation timer (minutes, 0 = no rotation): [15]
Enter max log file size (Kbytes): [3072]
Enter the max versions of log file (0-99): [1] |
CSCdz81426 |
Setup can fail and pause indefinitely when a numeric hostname, such as 2110, is used and entered at the network-parameter prompt. The log file /var/log/appliance-setup.log contains errors similar to the followings: 2003-01-10 21:05:50 rvrd: unable to resolve network specification ('2110') 2003-01-10 21:05:50 rvrd: unable to resolve network specification ('2110') It shows that Tibco fails to resolve the numeric hostname for an IP address. |
CSCea08252 |
CNS 2100 Series system should not hard code port numbers (Apache, Tomcat, Tibco). |
CSCea80575 |
Need TACACS+ support. |
CSCea81390 |
No carriage return on multi-line banner when configuration server sent configuration. |
CSCea88624 |
IMGW expect script does not support 6400 NRP2 connection. [Duplicate of CSCea09168] |
CSCea89886 |
If the relocate script is run, the parent attribute of the device, DemoRouter, is not updated with group information. |
CSCea09168 |
IMGW expect script does not support 6400 NRP2 connection. |
CSCea92657 |
LDAP server listening on non-standard port causes NSM problems. |
CSCeb01588 |
Cache should update when directory is updated by means of external applications. |
CSCeb11255 |
IMGW should use port numbers in all its http requests. |
CSCeb16858 |
Update Cisco IOS packages for security updates. |
Open Caveats - Release 1.3.2
This section lists known caveats that are open for the CNS 2100 Series third-party software (see Table 13), CNS 2100 Series platform (see Table 14), and Release 1.3.2 of the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine software application (see Table 15).
Table 13 CNS 2100 Series Third-Party Software
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdv70366 |
The directory API does not support special characters in device names, such as < & etc. The API does not accept special characters in username or password fields. |
When using the Intelligent Modular Gateway feature of the CNS 2100 Series to configure a device by means of Telnet or SSH, it is not possible to use punctuation characters in the username or password for the target device. |
Table 14 CNS 2100 Series Platform
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdv85666 |
When setting up the CNS 2100 Series with the Setup program, if you enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, you are not re-prompted to enter a correct one. This invalid IP address causes network connectivity problems for the unit. |
If you accidentally enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, proceed through the rest of Setup program, but do not commit the changes. Then log in as setup again (if the unit has never been configured before) or run the Setup program (if you are updating a previous configuration) and enter the correct values. |
Table 15 Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.3.2
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdy15293 |
The reload button in the web-based user interface might not work properly when reload is pressed number of times. |
To clear this problem, close and restart the web browser. |
CSCdy68363 |
Under more stressful load where both Event Gateway and Webserver are contending for directory searches (5000 modular router devices each with 5 subdevices), NSM resolve takes a long time to return. During this time, NO keepalive is sent from the Event Gateway to the affected devices. This is a function of the keepalive value configured on the device, which may cause the device to timeout, terminate the current connection, and retry with a new connection. |
Configure the device keepalive interval to a value greater than the delay described to prevent devices from prematurely terminating connections. |
CSCdy80613 |
Currently due to limited resources, it takes a long time for all 5,000 devices to receive configuration updates. |
Issue updates in staggered waves of 500 devices per wave. |
CSCdz14956 |
Under stress conditions over a period of weeks it has been noticed that the EventMonitor on the GUI stops logging the events. |
To restart the EventMonitor log, restart the CNS 2100 Series system. |
CSCdz33665 |
When SSL is turned on and 5,000 devices post their configurations, then connect to the Event Gateway (TibGate) upon receiving their configurations, all 5,000 successfully connect to the Event Gateway. But, if all 5,000 disconnect from the Event Gateway and reconnect, the CNS 2100 Series system experiences out of memory failures and the number of devices that successfully reconnect to the Event Gateway is reduced. The problem gets worse for each subsequent 5,000 disconnect and reconnect sequence. |
The number of devices using SSL, either connecting to Apache configuration server or connecting to the Event Gateway (TibGate), should be limited to 3,000 or less. |
CSCdz78340 |
Memory allocation failure: 293 clients could not establish connection with Event Gateway. |
None. |
CSCdz83000 |
When IMGW starts, it generates a debug messages. It displays the debug messages a number of times recursively. |
None. |
CSCdz90247 |
Not all required property files are backed up during a backup operation. As a result, a subsequent restore operation could fail if the directory password is changed after a backup, by re-running setup. |
Do not change the directory password between backup and restore operations. |
Resolved Caveats - Release 1.4
This section lists caveats that have been resolved in Release 1.4 of Cisco CNS Configuration Engine (see Table 16 through Table 18).
Table 16 CNS 2100 Series Third-Party Software
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdv70366 |
The directory API does not support special characters in device names, such as < & and so forth. The API does not accept special characters in username or password fields. |
Table 17 CNS 2100 Series Platform
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdv85666 |
When setting up the CNS 2100 Series with the Setup program, if you enter an invalid IP address for the Ethernet0 interface, you are not re-prompted to enter a correct one. This invalid IP address causes network connectivity problems for the unit. |
CSCdy80613 |
Updating large number of devicesÞ—say 5000—in provider mode takes around 3 hours to send events to all the devices. This may be a function of NSM resolve method taking time to get the mappings from directory. |
CSCdz76673 |
The following new Event Gateway prompts have been added:
Enter log file rotation timer (minutes, 0 = no rotation): [15]
Enter max log file size (Kbytes): [3072]
Enter the max versions of log file (0-99): [1]
These prompt changes are not reflected in the internaldir.pl and externaldir.pl files in the /opt/CSCOcnsie/bin directory. These are sample scripts to run the user's non-interactive setup prompts. Without these prompts, it is possible to run non-interactive setup. However, the drawback is that the values for the above prompts default to its existing values. Users cannot set these values using non interactive setup script. |
CSCdz80791 |
Thread Pooling Reduces the over head on OS for creating and destroying threads especially during high stress conditions rendering more stability to Event Gateway process. |
CSCdz81426 |
Setup can fail and pause indefinitely when a numeric hostname, such as 2110, is used and entered at the network-parameter prompt. The log file /var/log/appliance-setup.log contains errors similar to the followings: 2003-01-10 21:05:50 rvrd: unable to resolve network specification ('2110') 2003-01-10 21:05:50 rvrd: unable to resolve network specification ('2110') It shows that Tibco fails to resolve the numeric hostname for an IP address. |
CSCeb76924 |
httpd (Apache web server) is not running or cannot be started due to a out-of-space problem. The following error message is seen in /var/log/appliance-setup.log: Waiting for tomcat to initialize... ........Starting httpd:fopen:No space left on device httpd:could not open error log file /etc/httpd/logs/error_log. [FAILED] There are many (thousands) mgetty.log files generated in the /var/log directory. This large number of log files uses up all file system resources and the file system is not able to accommodate any more new file. Once the log files are removed, the system can function normally. After inspecting the logrotate configuration file (/etc/logrotate.d/mgetty) that comes with mgetty, it was found that there is a mis-configuration in the file: /var/log/mgetty.log.tty* {
nocompress
missingok
} The wide-card asterisk commands logrotate to rotate not only the mgetty.log.ttyS0 file, but all the files that are created in each of the subsequent rotation. Eventually, all the file system resources are used up. |
Table 18 Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4
|
ID
|
Problem
|
CSCdv04599 |
TibGate getting killed after fetching large number of mappings. When using the Namespace Mapper feature, there is a limitation of 150 mappings per subject name. If more than 150 mappings are provided, the CNS Event Gateway stops functioning. |
CSCdy48788 |
When the Bulkupload data contains invalid attributes, DAXMLservelet stops working and logs invalid errors. This is a problem in the current LDAP directory version. |
CSCdy83389 |
When 5000 devices try to post their inventory information and connect to Event Gateway upon receiving their configurations, it may take up to an hour before the last configuration is received. During this period, most of the device authentication requests are queued and timeout due to the default authentication timeout value of 180 seconds. |
CSCdz14956 |
Under stress conditions over a period of weeks it has been noticed that the EventMonitor on the GUI stops logging the events. |
CSCdz33665 |
When SSL is turned on and 5,000 devices post their configurations, then connect to the Event Gateway (TibGate) upon receiving their configurations, all 5,000 successfully connect to the Event Gateway. But, if all 5,000 disconnect from the Event Gateway and reconnect, the CNS 2100 Series system experiences out of memory failures and the number of devices that successfully reconnect to the Event Gateway is reduced. The problem gets worse for each subsequent 5,000 disconnect and reconnect sequence. |
CSCdz90247 |
Not all required property files are backed up during a backup operation. As a result, a subsequent restore operation could fail if the directory password is changed after a backup, by re-running setup. |
CSCeb74266 |
The relocate command will not correctly backup all directory data. |
CSCeb83743 |
GUI device delete of large group does not work. |
CSCec43672 |
IMGW configures non-agent enabled device by means of Telnet expect scripts, which are TTY-oriented. Logging messages output to the console interfere with the data handling of the expect scripts. |
CSCec44377 |
After running setup, no IMGW devices are correctly subscribed to CNS events, so IMGW fails to contact IMGWDevice servlet. |
CSCec44849 |
Changing ConfigID from device causes GUI to lose ImageID information. |
CSCec45289 |
In external directory mode, the following two prompts are part of the schema prompts that appear when you choose to define your own schema values by entering n to the Use sample schema (y/n)? prompt:
Enter container name under which group objects are stored:
Enter container name under which application objects are stored:
Once they are changed, and you run Setup again later where you enter y to the Use sample schema (y/n)? prompt, there is a problem resetting these values to the internal default values: ou=CNSGroups
ou=CNSApplications |
CSCec45413 |
Image server needs to check the correct running information version string. |
Open Caveats Release 1.4
This section lists known caveats that are open for the Release 1.4 of the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine software application (see Table 19).
Table 19 CNS Configuration Engine 1.4
|
ID
|
Problem
|
Workaround
|
CSCdx70042 |
An Operator (user that is not an Administrator) can create an order entry (under Order Entry -> New Order) but cannot delete it once created. Only a user with administrative privileges can delete an order entry, but only by means of the Devices -> Delete Devices menu. |
Have an administrative user delete the order entry by means of the Devices -> Delete Devices menu. |
CSCdy15293 |
The reload button in the web-based user interface might not work properly when reload is pressed number of times. |
To clear this problem, close and restart the web browser. |
CSCec08478 |
Currently, you cannot use unique values for ConfigID, ImageID, and DeviceName. |
Please use the same values for ImageID, ConfigID, and DeviceName. |
CSCec08483 |
ImageID must be changed on receiving image-id-changed event. |
If the imageID is changed from the console of the device, you must manually go to the server GUI and update this value for the same device. NOTE: DeviceName, ConfigID and ImageID must all be the same at all times. |
CSCec17163 |
If during setup you enter for the internal FTP server prompt a username that already exists, Setup will accept this value and during processing you will see the following error message in the output:
Processing internal ftp
parameters... Error: Internal ftp
username is an existing system
account! Please rerun setup to
reconfigure FTP.
|
Rerun Setup and disable FTP, then run Setup again and enter a valid username for the FTP user. |
CSCec17900 |
GUI: Edit Device -> Image ID cannot be unique. |
If you modify the value for ImageID during Edit Device, you must also use this new value for DeviceName and ConfigID. NOTE: DeviceName, ConfigID and ImageID must all be the same at all times. |
CSCec20018 |
FTP user password shows as clear text in Image Locations. |
None. |
CSCec20359 |
While creating or editing an image (from main menu select Image Service -> Images -> Create Image or Edit Image) it is possible to enter a value for an image location that is not a valid URL. Trying to distribute the image from this location would fail since the image would not be locatable. |
Use only valid URL values for image locations. |
CSCec25286 |
Case One: Image server log files are rolled over, thus "View Log" only displays the latest log file. In the case of a large job, the logged information for the first (and some subsequent) devices may be in a rolled-over log file and may not be visible via the GUI. Case Two: When a job completes successfully, it is removed from the status queue. Thus, the status cannot be viewed for a completed job any more. Note that jobs that fail (i.e. at least one device fails) then the job is retained in the status queue. |
Case One: To see full log details, go to Tools --> Log Manager --> Export Logs, select the "Image Server Log" and download it to the client filesystem. The Log Manager will concatenate all rolled over files into the single exported file, thus delivering the entire log history. For cases where the job falls within the last log and is viewable in its entirety by the GUI, simply view the log via Tools --> Log Manager --> View Logs. A filter string is helpful which will display lines that have the filter string present [i.e. use the device's ImageId or job id]. Case Two: The status of the job can be obtained by viewing the image server log under Tools --> Log Manager --> View Logs. If part of the job log is not viewable (because the log has rolled-over) then follow the workaround for Case One. Tip: The log-rotation file-size limit can be set during setup. Setting it to the maximum value can help alleviate log rollover frequency. For example, enter max log file size (Kbytes): 2097152 (or enter an invalid choice such as -1 to see the allowable limits). |
CSCec31261 |
Editing the image information of a device in an existing job gives an exception error. |
Ensure that the device being edited is not part of any of the currently executing jobs. |
CSCec40033 |
GUI: Query job - Stopped jobs are listed as executing jobs. |
None. |
CSCec40266 |
Inventory response from the device does not report the alias file systems. |
Use the actual file system names in the destination field. |
CSCec44849 |
Changing ConfigID from device causes GUI to lose ImageID information. |
Do not directly change the configID of the device from the console. |
CSCec47838 |
There is a limitation on batchsize value to be [<= 500] for SYSTEM WIDE. |
Total batchsize value of executing jobs must not exceed this limitation. |
CSCec50180 |
If there exists a device [DeviceA] which has been submitted to a job and it is in the process of updating its image; then DeviceA can be deleted by the user from the Devices->Delete Device menu. This does not cause any problems on the server side. Once the job has been submitted the server will try to complete it. The deletion of the device does not affect the job. |
None. |
CSCec51936 |
Image Server does not support NSM provider mode. For example, though the NSM server is setup in provider mode, Image Server still sends out individual checkServer events to the devices instead of checkServer.<group-name> events. |
None. |
CSCec57645 |
For an IMGW device, the following attributes cannot be modified: Device name, Device Type, Gateway-Id and Agent Type. Hop Information can be modified. |
Delete the IMGW device, and re-create it with desired attributes. |
CSCec65247 |
Symptom: Template Editor applet fails to load when Java Plug-in is used. Conditions: When Sun Java Plug-in 1.3.1 is enabled in browser (Netscape 4.76 and IE 5.0). |
Use Sun Java Plug-in 1.4. |
CSCec66822 |
Uniqueness of device name is not enforced while creating the device in different Device containers through the DAT create-device screen. |
Ensure the device name is unique while adding the device in different containers through DAT. |
CSCec67971 |
Job status page requires one page per device in a job. Jobs with a large number of devices in them have a lengthy Job Status page. |
Limit the number of devices per job. |
CSCec71143 |
Tomcat ports 8009 got into CLOSE_WAIT state. This is a known bug on Tomcat version 4.1.18. which is the version currently used. |
None. |
CSCec74859 |
The following special characters have special meaning in the request commands sent to IMGW devices: \ $ " [ |
Users should avoid using these special characters in the filename for images. |
CSCec75172 |
When creating an image for AP352 on the Configuration Engine since, the version string is not a mandatory field, you may create an image without this field. If such an image is associated with an AP device, and the device is submitted in a job the Image Server will return a failure message for this job. |
Enter a version string while creating an image for AP devices. In the case of the AP device, the only valuable information obtained from the inventory report is the version string which is used to evaluate whether the device is running the image we want or not. If this version string is not provided on the Image Server, the server can not verify what image the device is running on the device. |
CSCec75653 |
The GUI filter is expected to function like the UNIX limited regular expression pattern but is currently functioning like a RE expression. According to RE syntax and usage quantifiers (?*+{}) are considered repeating operators and as such can not be at position one in regular expression pattern and must have a preceding token. According to the UNIX limited regular expression quantifiers such as ? * may be expressions by themselves. |
The quantifiers such as ? * must be preceded with a "." For example: * will now be .* |
CSCec78144 |
Activation only fails if overwrite and erase flags are selected. |
Un-check overwrite and erase flags when update image with activation only option. |
CSCec81609 |
Images can be created without specifying any image location. When editing a device all images on the system are displayed in the drop down list. Selecting and image without any image location could cause null pointer exceptions or failed jobs for this device. |
Create images with at least one valid image location. Always make sure the image associated with a device has at least one valid image location. |
CSCec82012 |
NullPointer Exception occurs when any XML element is empty. |
Do not submit a XML file with an empty XML element. If no value has to be provided for a XML tag, remove it from the XML file |
CSCec82014 |
IBM directory dies on adding an object with invalid attribute name. |
Use only a -z, A-Z. |
CSCec82048 |
With validate-data flag turned on, the bulk upload operation will verify if the image associated with a device in the XML file already exists in the directory before actually creating the device. If the image does not exist in the directory, the device will not be created, and an error will be reported to the user. |
Make sure that all the image objects associated with a device in the XML file have been created in the directory. Create the images first, followed by the devices. |
CSCec84928 |
IMGW: Inconsistent behavior in http mode. |
None. |
CSCec85550 |
GUI: Edit image takes more than 20 minutes to display the status. |
An image can be associated with more than one device. The performance of the Edit Image operation is directly related to the number of devices managed by the Configuration Engine. The devices that reference this image might need to be updated as part of the Edit Image operation. |
CSCec86703 |
Error messages returned to the device are irrelevant. When given an incorrect/non-existing object name in the directory reports: com.cisco.cns.cfgsrv.Invalid ParameterException: Invalid Attribute Name. When given invalid/non-existing Attribute name, the device reports config failure messages: CNS_INVALID_CLI_CMD and IMGW Device reports: Incomplete command. When given invalid credentials for the directory Server reports: com.cisco.cns.cfgsrv.Invalid ParameterException: Invalid Attribute Name. |
Perform manual verifications to prevent the following conditions: For incorrect/non-existing object name in the directory, check if given object exists in LDAP server. For invalid/non-existing Attribute name, verify all attributes in the template exist in LDAP server. For invalid credentials for the directory, verify LDAP server credentials using ldapsearch tool. |
CSCec87203 |
If the image to be activated exists on the flash of device, and job is to distribute the same image with ERASE flag selected but OVERWRITE flag not selected, then distribution does not take place. |
The OVERWRITE flag must be selected in order to have the image distributed in such a case. |
CSCec88061 |
The status indicator LED on the Device icon does NOT reflect the connect/disconnect status. The connect/disconnect events do NOT work in NSM Provider Mode. They only work in default mode. Hence, the status LED on the device icons do not reflect the status. |
Use default NSM mode. If this status LED is essential in your deployment process, there is a manual workaround available only through TAC support. |
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
Copyright © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Support for PIX devices in auto-update mode
IMGW Device Module Development Toolkit
CNS Image Service
This release supports Cisco IOS 12.3.
The base element of the CNS event subject namespace has been changed from cisco.cns.* to cisco.mgmt.cns.* in support of Cisco IOS 12.3.
The none mode under Event Services Setting in the Setup program is not supported from the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 user interface for updates made from the user interface to devices that use the old CNS event subject names. This is because NSM is not invoked in the none mode. NSM has been modified to translate subject names in support of devices not running Cisco IOS 12.3.
Refer to the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Administrator Guide for more information about these features.
Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Installation & Setup Guide For Linux
Cisco CNS Configuration Engine 1.4 Administrator Guide
Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine Installation Guide
Release Notes for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine
Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine Machine Code License
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine
Cisco CNS Software Development Kit API Reference and Programmer Guide
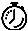
For immediate console access to the server, use two DB9 connectors and a rollover cable to connect your laptop computer to the server serial port.
Power connector: Connect the power cable here.
Ethernet 2 connector: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
USB 3 connector: Connect to a Universal Serial Bus here.
Ethernet 1 connector: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
ISM connector: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector.
C2T OUT connector: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
Serial connector: Connect a 9-pin serial device to this connector.
C2T IN connector: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
Power connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the power cable for Remote Service Adapter here.
RS-485 on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the ASM Interconnect Module to this connector.
Serial connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect a 9-pin serial device to this connector.
Ethernet connector on Remote Service Adapter: Connect an Ethernet cable here.
Press F1, then go to: Configuration/Setup Utility (menu) -> Devices and I/O ports (menu) -> Remote Console Redirection (menu)
Make sure the Remote Console Active parameter is enabled.
The cables in an ASM interconnect network are hot-swappable.
Make sure that the firmware for the Remote Supervisor Adapter, ASM processor, and integrated system management processor (ISMP) are at the latest level.
The servers in an ASM interconnect network are referred to by their assigned addresses, not by their positions in the rack.
Each Remote Supervisor Adapter, ASM processor, ASM PCI adapter, and ISMP in a server that is connected to the network uses one connection. For example, if a server that is connected to the network has a Remote Supervisor Adapter and an integrated ASM processor, the server uses two connections on the network.
The network must include at least one server with a Remote Supervisor Adapter (either installed as an option or pre-installed in the server).
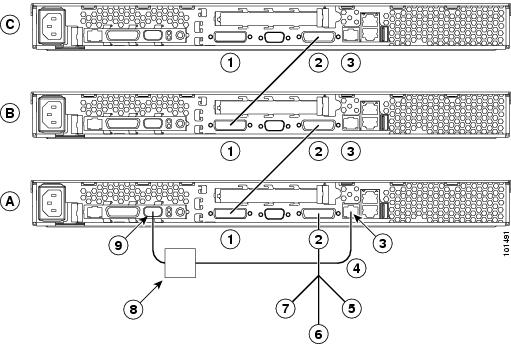
IN: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
OUT: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
ISM: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector in the first (A) server.
ASM link cable: Connect this cable to the ISM connector (3) in the first server.
Mouse: Connect a mouse to this connector.
Keyboard: Connect a keyboard to this connector.
Video: Connect a monitor to this line.
ASM interconnect module: Connect this module to the RS-485 connector (9) on the Remote Supervisor Adapter in the first server.
RS-485 on Remote Service Adapter: Connect the ASM Interconnect Module to this connector.
IN: Connect the cable from the output connector of another server to this connector.
OUT: Connect the cable from this connector to the input connector of another server.
ISM: Connect an ASM link cable from the ASM interconnect module to this connector in the first (A) server.
ASM link cable: Connect this cable to the ISM connector (3) in the first server.
Mouse: Connect a mouse to this connector.
Keyboard: Connect a keyboard to this connector.
Video: Connect a monitor to this line.
Second ASM bus: Connect servers 24 through 46 on this bus.
First ASM bus: Connect servers 1 through 23 on this bus.
Follow the instructions for cabling a C2T chain.
Connect an ASM interconnect module (which comes with the Remote Supervisor Adapter) to the RS-485 connector on the Remote Supervisor Adapter in the first server. If the network contains more than 23 servers, do the same on the 24th server.
Login to the CNS 2100 Series system console.
Change directories to: /opt/CSCOdat/XMLTransform/.
Issue the following commands:
For this release, ConfigID, ImageID, and DeviceName must have the same value (see CSCec08478).
Provider mode is not supported in the Image Server (see CSCec51936). However, you can do group-level operations through the GUI. You will not be able to map CNS subjects to subjects specific to their application's namespace.
If you download a configuration that changes username, password, enable password, or IP address for a non-agent-enabled device, you need to modify the corresponding IMGW hop information for the device to update it with the new username, password, enable password, and IP address.
External directory is not supported for IMGW.
SFTP - An SFTP server is permanently enabled which can be used for administrative tasks such as placing images securely into the FTP directory [ /tftp/CSCOcnsis/images/ ] for image download by devices over FTP or TFTP. Any regular system account may login to SFTP.
FTP - FTP service is READ-ONLY.
TFTP:
No new files can be created and files cannot be deleted. However, existing files can be overwritten ONLY if they are publicly writeable. The permissions of the files placed into the ftp directory can be controlled by the SFTP user managing files in the ftp directory.
The TFTP service does not require an account or password on the server system. Due to the lack of authentication information, TFTPD allows only publicly readable files (o+r) to be accessed. Files may be written only if they already exist and are publicly writable.
All password values in Setup must contain alphanumeric characters only. Special characters have different meanings in the UNIX shell and should not be used for passwords.
Device Name values may contain only: period (.), underscore (_), hyphen (-), and alphanumeric characters.
Group Name values may contain only: underscore (_) and alphanumeric characters.

 Feedback
Feedback