Cisco Transport Controller Operation, Information, and Shortcuts
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
PCTC Operation, Information, and Shortcuts
CTC Software Installed on the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card
CTC Software Installed on the PC or UNIX Workstation
PC and UNIX Workstation Requirements
Node View (Multishelf Mode), Node View (Single-Shelf Mode), and Shelf View (Multishelf Mode)
Multishelf View Card Shortcuts
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Card Shortcuts
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Port Shortcuts
Card View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Port Shortcuts
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Tabs
Using the CTC Launcher Application to Manage Multiple ONS Nodes
TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card Reset
TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card Database
Multishelf and Single-Shelf Modes
Node Icons on the Network View Map
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) and Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Shortcuts
PCTC Operation, Information, and Shortcuts
Last Updated: July 30, 2012, OL-25021-01This document describes operations of the Cisco Transport Controller (CTC), the software interface for Cisco ONS 15454, Cisco ONS 15454 M2, and Cisco ONS 15454 M6 shelf assemblies. For CTC setup and login information, refer to the "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI" document.
This document also describes the CTC views, menus options, tool options, shortcuts, table display options, and the shelf inventory data presented in CTC.

Note
This document is applicable to software R9.4 and earlier releases. For software R9.6.x and later releases, see the CTC Enhancements, Operations, and Shortcuts document.

Note
Unless otherwise specified, ONS 15454, ONS 15454 M2, and ONS 15454 M6 refers to both ANSI and ETSI shelf assemblies.

Note
If network discovery is enabled on the node, CTC searches each node in the network for more recent versions of the CTC software. If a more recent version is discovered, CTC gives you the option of downloading the Java archive (JAR) files to your PC.

Note
The LBAND cards are not supported in ONS 15454 M2 and ONS 15454 M6 chassis.
Document topics include:
•
CTC Software Delivery Methods
•
PC and UNIX Workstation Requirements
•
Using the CTC Launcher Application to Manage Multiple ONS Nodes
•
TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card Reset
•
TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card Database
•
Multishelf and Single-Shelf Modes
•
Node Icons on the Network View Map
CTC Software Delivery Methods
ONS 15454, ONS 15454 M2, and ONS 15454 M6 provisioning and administration is performed using the CTC software. CTC is a Java application that resides on the control cards: TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE. CTC is downloaded to your workstation the first time you log into 15454-DWDM, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 shelf assemblies with a new software release using the web interface. You can also log into CTC using the CTC launcher application (StartCTC.exe). Refer to the "Using the CTC Launcher Application to Manage Multiple ONS Nodes" section for more information.
CTC Software Installed on the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card
The CTC software is preloaded on the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE cards; therefore, you do not need to install software on these cards. When a new CTC software version is released, use the release-specific software upgrade document to upgrade the ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 software on the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE cards.
When you upgrade the CTC software, the control cards store the new CTC version as the protect CTC version. When you activate the new CTC software, the control cards store the older CTC version as the protect CTC version, and the newer CTC release becomes the working version. You can view the software versions that are installed on an ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 shelf assemblies by selecting the Maintenance > Software tabs in node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode).
Select the Maintenance > Software tabs in network view to display the software versions installed on all the network nodes.
CTC Software Installed on the PC or UNIX Workstation
CTC software is downloaded from the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE cards and installed on your computer automatically after you connect to the ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 with a new software release for the first time. Downloading the CTC software files automatically ensures that your computer is running the same CTC software version as the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE cards you are accessing. The CTC files are stored in the temporary directory designated by your computer operating system. Click the Delete CTC Cache button to remove files stored in the temporary directory. If the files are deleted, they download the next time you connect to ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6. Downloading the Java archive (JAR) files for CTC takes several minutes depending on the bandwidth of the connection between your workstation and ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6. For example, JAR files downloaded from a modem or a data communications channel (DCC) network link require more time than JAR files downloaded over a LAN connection.
During network topology discovery, CTC polls each node in the network to determine which one contains the most recent version of the CTC software. If CTC discovers a node in the network that has a more recent version of the CTC software than the version you are currently running, CTC generates a message stating that a later version of the CTC has been found in the network and offers to install the CTC software upgrade. After the node view appears, you can upgrade CTC by using the Tools > Update CTC menu option. If you have network discovery disabled, CTC will not seek more recent versions of the software. Unreachable nodes are not included in the upgrade discovery.

Note
Upgrading the CTC software will overwrite your existing software. You must restart CTC after the upgrade is complete.
CTC Installation Overview
To connect to ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 using CTC, you enter the IP address in the URL field of Microsoft Internet Explorer. After connecting to ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6, the following occurs automatically:
1.
A CTC launcher applet is downloaded from the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card to your computer.
2.
The launcher determines whether your computer has a CTC release matching the release on the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card.
3.
If the computer does not have CTC installed, or if the installed release is older than the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card's version, the launcher downloads the CTC program files from the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card.
4.
The launcher starts CTC. The CTC session is separate from the web browser session, so the web browser is no longer needed. Always log into nodes having the latest software release. If you log into an ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 that is connected with older versions of CTC, or to Cisco ONS 15327s or Cisco ONS 15600s, CTC files are downloaded automatically to enable you to interact with those nodes. The CTC file download occurs only when necessary, such as during your first login. You cannot interact with nodes on the network that have a software version later than the node that you used to launch CTC.
Each ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 can handle up to five concurrent CTC sessions. CTC performance can vary, depending upon the volume of activity in each session, network bandwidth, and TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card load.

Note
You can also use TL1 commands to communicate with ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 through VT100 terminals and VT100 emulation software, or you can telnet to ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 using TL1 ports 2361 and 3083. Refer to the Cisco ONS SONET TL1 Command Guide or Cisco ONS SDH TL1 Command Guide for a comprehensive list of TL1 commands.
PC and UNIX Workstation Requirements
To use CTC for ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6, your computer must have a web browser with the correct Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installed. The correct JRE for each CTC software release is included on the ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 software CD. If you are running multiple CTC software releases on a network, the JRE installed on the computer must be compatible with the different software releases.
When you change the JRE version on the JRE tab, you must exit and restart CTC for the new JRE version to take effect. Table 1 shows JRE compatibility with ONS 15454 software releases.

Note
To avoid network performance issues, Cisco recommends managing a maximum of 50 nodes concurrently with CTC. The 50 nodes can be on a single DCC or split across multiple DCCs. Cisco does not recommend running multiple CTC sessions when managing two or more large networks.
To manage more than 50 nodes, Cisco recommends using Cisco Transport Manager (CTM). If you do use CTC to manage more than 50 nodes, you can improve performance by adjusting the heap size; see the "General Troubleshooting" chapter of the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Troubleshooting Guide. You can also create login node groups; see the "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI" document.
Table 2 lists the requirements for PCs and UNIX workstations. In addition to the JRE, the Java plug-in is also included on the ONS 15454 software CD.
ONS 15454 Connections
You can connect to the ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 shelf assemblies in multiple ways.
(ONS 15454) You can connect your PC directly to the ONS 15454 shelf using the RJ-45(LAN) port on the faceplate of TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3 card or using the backplane RJ-45 LAN port.
(ONS 15454 M6) You can connect your PC directly to the ONS 15454 M6 shelf using the RJ-45(LAN) port on the faceplate of TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card or using the EMS RJ-45 port or using the RJ-45 Craft port. The EMS RJ-45 port and RJ-45 Craft port are present on the external connection unit (ECU).
(ONS 15454 M2) You can connect your PC directly to the ONS 15454 M2 shelf using the RJ-45(LAN) port on the faceplate of TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card or using the EMS RJ-45 port on the power module.
For the ANSI shelf, you can connect using the LAN pins on the backplane (the ETSI shelf provides a LAN connection through the RJ-45 jack on the MIC-T/C/P Front Mount Electrical Connection [FMEC]). Alternatively, you can connect your PC to a hub or switch that is connected to the ONS 15454, connect to the ONS 15454 through a LAN or modem, or establish TL1 connections from a PC or TL1 terminal. Table 3 lists the connection methods and requirements for ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 shelves.

Note
The TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card supports multi-shelf connections through three FE RJ45 connections on the ECU. The TNC and TNCE cards support one GE connection for CRS-1 router through the SFP port on the card. This SFP port can act as a secondary OSC supporting only FE and GE interfaces.
The TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card in ONS 15454 M6 shelf can connect to CTC through the EMS RJ-45 port or Craft port on the ECU. The TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card in ONS 15454 M2 shelf can connect to CTC through the EMS RJ-45 port on the power module.
CTC Window
When you log into a single-shelf ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6, the CTC window appears in node view (Figure 1). When you log into a multishelf ONS 15454 or 15454-M6, meaning that two or more ONS 15454 or 15454-M6 shelves are configured to operate as one node, the multishelf view (Figure 2) appears in the CTC window. The window includes a menu bar, a toolbar, and a top and bottom pane. The top pane provides status information about the selected objects and a graphic of the current view. The bottom pane provides tabs and subtabs to view ONS 15454 information and perform ONS 15454 provisioning and maintenance tasks. From the CTC window, you can display the other ONS 15454 views. In single-shelf mode, these are the network, node, and card views. In multishelf mode, these are the network, multishelf, shelf, and card views.
Figure 1 Node View (Default Login View for Single-Shelf Mode)

Figure 2 Multishelf View (Default Login View for Multishelf Mode)

Summary Pane
The Summary pane on the left has the following fields:
•
Node Addr—IP address of the node.
•
Booted—The Booted field indicates one of the following:
–
Date and time of the node reboot. The node reboot is caused by complete power cycle, software upgrade, or software downgrade.
–
Date and time of reset of the control cards one after the other.
•
User—Login user name.
•
Authority—Security level of users. The possible security levels are Retrieve, Maintanence, Provisioning, and Superuser.
•
SW Version—CTC software version.
•
Defaults—Name provided to identify the defaults list.
Node View (Multishelf Mode), Node View (Single-Shelf Mode), and Shelf View (Multishelf Mode)
Node view, shown in Figure 1, is the first view that appears after you log into a single-shelf ONS 15454. Multishelf view, shown in Figure 2, is the first view that appears after you log into a multishelf ONS 15454. The login node is the first node shown, and it is the "home view" for the session. Multishelf view and node view allow you to manage one ONS 15454 node. The status area shows the node name; IP address; session boot date and time; number of Critical (CR), Major (MJ), and Minor (MN) alarms; name and security level of the current logged-in user; software version; and network element default setup.
(ONS 15454 and ONS 15454-M6 only) In a multishelf mode, up to 30 shelves operate as a single node.

Note
The reason for extending the number of subtending shelves to 30 is to accommodate and manage the new optical and DWDM cards that operate in the even band frequency grid.
When you open a shelf from multishelf view, shelf view appears, which looks similar to node view but does not contain the tabs and subtabs that are used for node-level operations.
CTC Card Colors
The graphic area of the CTC window depicts the ONS 15454 shelf assembly. The colors of the cards in the graphic reflect the real-time status of the physical card and slot (Table 4).
On the ONS 15454 ETSI, the colors of the FMEC cards reflect the real-time status of the physical FMEC cards. Table 5 lists the FMEC card colors. The FMEC ports shown in CTC do not change color.

Note
You cannot preprovision FMECs.
The wording on a card in node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode) shows the status of a card (Active, Standby, Loading, or Not Provisioned). Table 6 lists the card statuses.
Port color in card view, node view (single-shelf mode), and shelf view (multishelf mode) indicates the port service state. Table 7 lists the port colors and their service states. For more information about port service states, see Administrative and Service States.
Table 7 Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Card Port Colors and Service States
Cyan (blue)
Out-of-Service and Management, Loopback (OOS-MA,LPBK) (ANSI)
Locked-enabled,loopback (ETSI)
Port is in a loopback state. On the card in node or shelf view, a line between ports indicates that the port is in terminal or facility loopback (see Figure 3 and Figure 4). Traffic is carried and alarm reporting is suppressed. Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command.
Cyan (blue)
Out-of-Service and Management, Maintenance (OOS-MA,MT) (ANSI)
Locked-enabled,maintenance (ETSI)
Port is out-of-service for maintenance. Traffic is carried and loopbacks are allowed. Alarm reporting is suppressed. Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command. Use this service state for testing or to suppress alarms temporarily. Change the state to IS-NR/Unlocked-enabled; OOS-MA,DSBLD/Locked-enabled,disabled; or OOS-AU,AINS/Unlocked-disabled,automaticInService when testing is complete.
Gray
Out-of-Service and Management, Disabled (OOS-MA,DSBLD) (ANSI)
Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI)
The port is out-of-service and unable to carry traffic. Loopbacks are not allowed in this service state.
Green
In-Service and Normal (IS-NR) (ANSI)
Unlocked-enabled (ETSI)
The port is fully operational and performing as provisioned. The port transmits a signal and displays alarms; loopbacks are not allowed.
Violet
Out-of-Service and Autonomous, Automatic In-Service (OOS-AU,AINS) (ANSI)
Unlocked-disabled,automaticInService (ETSI)
The port is out-of-service, but traffic is carried. Alarm reporting is suppressed. The node monitors the ports for an error-free signal. After an error-free signal is detected, the port stays in this service state for the duration of the soak period. After the soak period ends, the port service state changes to IS-NR/Unlocked-enabled.
Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command. The AINS port will automatically transition to IS-NR/Unlocked-enabled when a signal is received for the length of time provisioned in the soak field.
Figure 3 Terminal Loopback Indicator

Figure 4 Facility Loopback Indicator

Multishelf View Card Shortcuts
If you move your mouse over cards in the multishelf view graphic, popups display additional information about the card including the card type; the card status (active or standby); the type of alarm, such as Critical, Major, or Minor (if any); the alarm profile used by the card; and for transponder (TXP) or muxponder (MXP) cards, the wavelength of the dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) port.
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Card Shortcuts
If you move your mouse over cards in the node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode) graphic, pop-ups display additional information about the card including the card type; the card status (active or standby); the type of alarm, such as Critical, Major, or Minor (if any); the alarm profile used by the card; and for TXP or MXP cards, the wavelength of the DWDM port. Right-click a card to reveal a shortcut menu, which you can use to open, reset, delete, or change a card. Right-click a slot to preprovision a card (that is, provision a slot before installing the card).
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Port Shortcuts
If you move your mouse over the ports in the node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), the popup message displays information about the port type, service state, and the alarm profile used by the port. For example, the popup message displays "((EXP-RX-1-4) Service State: IS-NR, Alarm Profile: Inherited)".
Card View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Port Shortcuts
If you right-click the ports in the card view (single-shelf mode or multishelf mode), the popup message displays the side information along with shelf, slot, and port information. For example, the popup message displays "Shelf 1, Slot 3 (40 SMR2 C), Port EXP-TX 1-1, Side C".
Multishelf View Tabs
Table 8 lists the tabs and subtabs available in the multishelf view. The actions on these tabs apply to the multishelf node and its subtending shelves.
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) or Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Tabs
Table 9 lists the tabs and subtabs available in node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode).
Network View
Network view allows you to view and manage ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 that have DCC connections to the node that you logged into and any login node groups you have selected (Figure 5).
Figure 5 Network in CTC Network View


Note
Nodes with DCC connections to the login node do not appear if you checked the Disable Network Discovery check box in the Login dialog box.
The graphic area displays a background image with colored ONS 15454 icons. A Superuser can set up the logical network view feature, which enables each user to see the same network view.
Network View Tabs
Table 10 lists the tabs and subtabs available in network view.
CTC Node Colors
The color of a node in network view, shown in Table 11, indicates the node alarm status.
DCC Links
The lines show DCC connections between the nodes (Table 12). DCC connections can be green (active) or gray (fail). The lines can also be solid (circuits can be routed through this link) or dashed (circuits cannot be routed through this link). Circuit provisioning uses active/routable links. Selecting a node or span in the graphic area displays information about the node and span in the status area.
Link Consolidation
CTC provides the ability to consolidate the DCC, generic communications channel (GCC), optical transmission section (OTS), and PPC links shown in the network view into a more streamlined view. Link consolidation allows you to condense multiple inter-nodal links into a single link. The link consolidation sorts links by class, meaning that all DCC links are consolidated together, for example.You can access individual links within consolidated links using the right-click shortcut menu.Each link has an associated icon (Table 13).

Note
Link consolidation is only available on non-detailed maps. Non-detailed maps display nodes in icon form instead of detailed form, meaning that the nodes appear as rectangles with ports on the sides. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Configuration Guide for more information about consolidated links.
Card View
The card view provides information about individual ONS 15454 cards. Use this window to perform card-specific maintenance and provisioning. A graphic showing the ports on the card is shown in the graphic area. The status area displays the node name, slot, number of alarms, card type, equipment type, card status (active or standby), card service state if the card is present, and port service state (described in Table 7). The information that appears and the actions that you can perform depend on the card. For more information about card service states, refer to Administrative and Service States.

Note
CTC provides a card view for all cards except the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TSC/TSCE cards.
Use the card view tabs and subtabs shown in Table 14 to provision and manage the ONS 15454. The subtabs, fields, and information shown under each tab depend on the card type selected.
Using the CTC Launcher Application to Manage Multiple ONS Nodes
The CTC Launcher application is an executable file, StartCTC.exe, that is provided on Software Release 9.2.1 CDs for Cisco ONS products. You can use CTC Launcher to log into multiple ONS nodes that are running CTC Software Release 3.3 or higher, without using a web browser. The CTC launcher application provides an advantage particularly when you have more than one NE version on the network, because it allows you to pick from all available CTC software versions. It also starts more quickly than the browser version of CTC and has a dedicated node history list.
CTC Launcher provides two connection options. The first option is used to connect to ONS NEs that have an IP connection to the CTC computer. The second option is used to connect to ONS NEs that reside behind third party, OSI-based GNEs. For this option, CTC Launcher creates a TL1 tunnel to transport the TCP traffic through the OSI-based GNE.
The TL1 tunnel transports the TCP traffic to and from ONS ENEs through the OSI-based GNE. TL1 tunnels are similar to the existing static IP-over-CLNS tunnels, GRE, and Cisco IP, that can be created at ONS NEs using CTC. (Refer to the Cisco ONS product documentation for information about static IP-over-CLNS tunnels.) However, unlike the static IP-over-CLNS tunnels, TL1 tunnels require no provisioning at the ONS ENE, the third-party GNE, or DCN routers. All provisioning occurs at the CTC computer when the CTC Launcher is started.
Figure 6 shows examples of two static IP-over-CLNS tunnels. A static Cisco IP tunnel is created from ENE 1 through other vendor GNE 1 to a DCN router, and a static GRE tunnel is created from ONS ENE 2 to the other vender, GNE 2. For both static tunnels, provisioning is required on the ONS ENEs. In addition, a Cisco IP tunnel must be provisioned on the DCN router and a GRE tunnel provisioned on GNE 2.
Figure 6 Static IP-Over-CLNS Tunnels
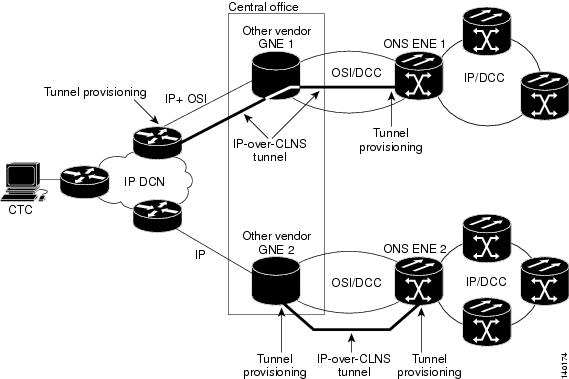
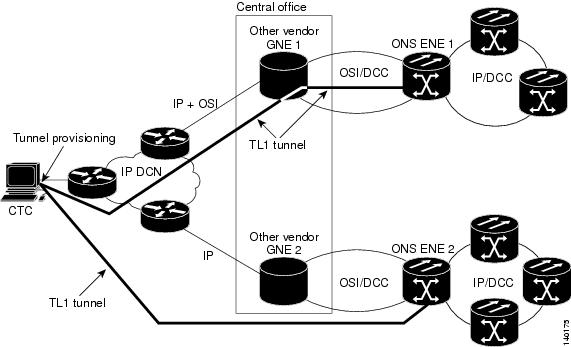
Figure 7 shows the same network using TL1 tunnels. Tunnel provisioning occurs at the CTC computer when the tunnel is created with the CTC Launcher. No provisioning is needed at ONS NEs, GNEs, or routers.
Figure 7 TL1 Tunnels
TL1 tunnels provide several advantages over static IP-over-CLNS tunnels. Because tunnel provisioning is needed only at the CTC computer, they are faster to set up. Because they use TL1 for TCP transport, they are more secure. TL1 tunnels also provide better flow control. On the other hand, IP over CLNS tunnels require less overhead and usually provide a slight performance edge over TL1 Tunnels (depending on network conditions). TL1 tunnels do not support all IP applications such as SNMP and RADIUS Authentication. Table 15 shows a comparison between the two types of tunnels.
TL1 tunnel specifications and general capabilities include:
•
Each tunnel generally supports between six to eight ENEs, depending on the number of tunnels at the ENE.
•
Each CTC session can support up to 32 tunnels.
•
The TL1 tunnel database is stored locally in the CTC Preferences file available in the user's HOME directory. The filename is CTC.ini (Windows PC) and .ctcrc (Linux, Apple MAC, and Solaris).
•
Automatic tunnel reconnection when the tunnel goes down.
•
Each ONS NE can support at least 16 concurrent tunnels.
TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card Reset
You can soft reset the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card by using CTC or by physically resetting the card (a hard reset). A soft reset reboots the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card and reloads the operating system and the application software. Additioncrally, a hard reset temporarily removes power from the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card and clears all the buffer memory.
You can apply a soft reset from CTC to either an active or standby TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card without affecting traffic. If you need to perform a hard reset on an active TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card, put the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card into standby mode first by performing a soft reset.

Note
Hard reset can also be performed on the TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card through CTC and TL1 interface. Before performing the hard reset, bring the TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card to maintenance mode.
When you reset the standby TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card, the system traffic is not affected. When you reset the active TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card, traffic switches to the standby card if the standby card is present and in the ready standby state. If the standby card is not in the ready standby state, traffic does not switch, and results in loss of system traffic and management connectivity until the card reboots completely.

CautionWhen you reset the TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card on the ONS 15454 or 15454-M6 shelves in simplex control mode, loss of management connectivity happens until the card reboots. The system traffic loss may occur depending on the line card and traffic type.

Note
(Cisco ONS 15454 shelf) When a CTC reset is performed on an active TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3 card, the AIC-I card goes through an initialization process and also resets because it is controlled by the active TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3 card.
The active and standby TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE cards provisioned in a multishelf node is automatically reset every 100 days. The traffic is not affected due to this reset.
It is possible for all the TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE cards on a node to automatically reset simultaneously. To avoid the automatic reset, manually reset the TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE cards every 90 to 95 days. It is recommended that the reset of the TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE cards of a node be staggered. The user must reset a TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE card, confirm proper recovery, and wait 15 minutes before resetting the next TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE card. It is recommended to reset all the standby TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE cards before resetting the active TNC/TSC/TNCE/TSCE cards.
See the "Reset the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card" procedure to perform a manual reset.
TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE Card Database
When dual TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE cards are installed in the ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 shelves, each TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card hosts a separate database; therefore, the protect card database is available if the database on the working TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card fails. You can also store a backup version of the database on the workstation running CTC. This operation should be part of a regular ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 maintenance program at approximately weekly intervals, and should also be completed when preparing ONS 15454, 15454-M2, or 15454-M6 for a pending natural disaster, such as a flood or fire.
The TNC and TNCE cards provide 4GB of nonvolatile database storage for communication, provisioning, and system control. This allows full database recovery during power failure.
The configuration details are stored in the database of the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card. The database restore from a TNC and TNCE cards to a TSC and TSCE cards or vice versa is not supported.

Note
The following parameters are not backed up and restored: node name, IP address, mask and gateway, and Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) port. If you change the node name and then restore a backed up database with a different node name, the circuits map to the new node name. We recommend keeping a record of the old and new node names.
Software Revert
When you click the Activate button after a software upgrade, the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card copies the current working database and saves it in a reserved location in the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE card flash memory. If later during the upgrade you need to revert to the original working software load from the protect software load, the saved database installs automatically. You do not need to restore the database manually or recreate circuits.
The revert feature is useful if the maintenance window in which you were performing an upgrade closes while you are still upgrading CTC software. You can revert to the protect software load without losing traffic. During the next maintenance window, you can complete the upgrade and activate the new software load.
Circuits created or provisioning done after you activate a new software load (upgrade to a higher release) will be lost with a revert. The database configuration at the time of activation is reinstated after a revert. (This does not apply to maintenance reverts, such as Software R5.0.1 to Software R5.0.2, because maintenance releases retain the database during activation.)

CautionCisco does not recommend reverting after changing provisioning on the node. Depending upon the particular provisioning, reverting in this case can be traffic affecting.
To perform a supported (non-service-affecting) revert from a software release that you have just activated, the release you revert to must have been working at the time you first activated the new software on that node. Because a supported revert automatically restores the node configuration at the time of the previous activation, any configuration changes made after activation will be lost when you revert the software. Downloading the software release that you are upgrading to a second time after you have activated the new load ensures that no actual revert to a previous load can take place (the TCC2/TCC2P/TCC3/TNC/TNCE/TSC/TSCE resets, but it does not affect the traffic and does not change your database).

Note
To perform a supported software upgrade or revert, you must consult the specific upgrade document and release notes for the release you are upgrading to (or reverting from).
Multishelf and Single-Shelf Modes
In a DWDM configuration, CTC views can be displayed in one of two modes. If a node contains only one shelf, the possible views are network view, node view, and card view. This is known as single-shelf mode. In multishelf mode, a control node and subtending shelves are configured to operate as a single node. In this mode, four views are possible: network view, multishelf view, shelf view, and card view. Multishelf view is the home view for nodes that are configured in multishelf mode. Multishelf view displays all of the shelves in the node. When you open a shelf from multishelf view, shelf view appears, which looks similar to node view but does not contain the tabs and subtabs that are used for node-level operations.
Display CTC Views
CTC provides four views of the ONS 15454, ONS 15454-M6, and the ONS network:
•
If the login ONS 15454 or ONS 15454-M6 node is in multishelf mode, the multishelf view appears when you first log into the node. This view shows a graphic of the ONS 15454 or ONS 15454-M6 racks and provides access to tabs and subtabs that you use to manage the multishelf node and its subtending shelves.
•
If the login ONS 15454 or ONS 15454-M6 node is in single-shelf mode, node view appears when you first log into an ONS 15454 or ONS 15454-M6. This view shows a graphic of the ONS 15454 or ONS 15454-M6 shelf and provides access to tabs and subtabs that you use to manage the node. When you open a shelf from multishelf view, shelf view appears, which looks similar to node view but does not contain the tabs and subtabs that are used for node operations.
•
Card view provides access to individual ONS 15454 or ONS 15454-M6 cards. This view provides a graphic of the card and provides access to tabs and subtabs that you use to manage the card.
•
Network view shows all the nodes in a ring and provides access to tabs and subtabs that you use to manage the network. A Superuser can create a network view that is identical for all users who log into the network or users can create custom views with maps.
Users can group a subset of nodes into a domain, which is used to isolate nodes or groups of nodes for easier maintenance and a more streamlined network view. Double-clicking a domain displays all the nodes that are members of the domain.Nodes connected to the domain nodes are grayed out.
Table 16 lists different actions for changing CTC views.
Node Icons on the Network View Map
Table 17 lists the node icons on the network view map.

Note
In the mixed configuration node with ONS 15454 and ONS 15454-M6 cards, only the node controller icon will be displayed in the network view.
Manage the CTC Window
Different navigational methods are available within the CTC window to access views and perform management actions. You can double-click and right-click objects in the graphic area and move the mouse over nodes, cards, and ports to view popup status information.
CTC Menu and Toolbar Options
The CTC window menu bar and toolbar provide primary CTC functions. Table 18 shows the actions that are available from the CTC menu and toolbar.
Table 18 CTC Menu and Toolbar Options
File
Add Node

Adds a node to the current session. See the "DLP-G49 Add a Node to the Current Session or Login Group" task.
Delete Selected Node

Deletes a node from the current session.
Lock CTC

Locks CTC without closing the CTC session. A user name and password are required to open CTC.

Prints CTC data. See the "DLP-G113 Print CTC Data" task.
Export

Exports CTC data. See the "DLP-G114 Export CTC Data" task.
Exit

Closes the CTC session.
Edit
Preferences

Displays the Preferences dialog box, which shows the following tabs:
•
General—Allows you to change event defaults and manage preferences.
•
Login Node Groups—Allows you to create login node groups. See the "DLP-G48 Create Login Node Groups" task.
•
Map—Allows you to customize the network view. See the "DLP-G168 Change the Network View Background Color" task and the "DLP-G170 Apply a Custom Network View Background Map" task.
•
Circuit—Allows you to change the color of circuit spans. This task is not applicable on DWDM-only nodes.
•
Firewall—Sets the Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) listener ports for access to the ONS 15454 through a firewall. See the "NTP-G27 Set Up the ONS 15454 for Firewall Access" task in the chapter "Turn Up a Node" of the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Configuration Guide.
•
JRE—Allows you to select another Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version. See the "DLP-G52 Change the JRE Version" task.
View
Go To Previous View

Displays the previous CTC view. Available only after you navigate to a next view.
Go To Next View

Displays the next CTC view. Go to Previous View and Go to Next View are similar to forward and backward navigation in a web browser.
Go To Parent View

References the CTC view hierarchy: network view, multishelf view (multishelf mode), node view (single-shelf mode), shelf view (multishelf mode), and card view. In card view, this command displays the node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode); in node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), the command displays network view. Not available in network view. In shelf view (multishelf mode), this command displays multishelf view.
Go To Selected Object View

Displays the object selected in the CTC window.
Go To Home View

Displays the login node in node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode). If the login node is a multishelf node controller, the multishelf view displays.
Go To Network View

Displays the network view.
Go To Other Node

Displays a dialog box allowing you to type in the node name or IP address of a a network node that you want to view.
Show Status Bar
—
Click this item to display or hide the status bar at the bottom of the CTC window.
Show Tool Bar
—
Click this item to display or hide the CTC toolbar.
Tools
Circuits
—
Displays the following options:
•
Repair Circuits—Repairs incomplete circuits following replacement of the ONS 15454 alarm interface panel (AIP). Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Troubleshooting Guide for more information.
•
Reconfigure Circuits—Allows you to reconfigure circuits. Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
•
Set Path Selector Attributes—Allows you to edit path protection or subnetwork connection protection (SNCP) circuit path selector attributes. Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
•
Set Circuit State—Allows you to change a circuit state. Not applicable on DWDM nodes.
•
Roll Circuit—Allows you to reroute live traffic without interrupting service.
•
Delete Rolls—Removes rolls that are not deleted by CTC after a roll has been completed.
•
Upgrade OCHNC—(ONS 15454 only) Upgrades OCHNCs created in earlier software releases to OCHCCs. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Configuration Guide for more information.
•
Show RPR Circuit Ring—Shows the RPR ring for the circuit selected on the Circuits window.
Overhead Circuits
—
(SONET and SDH only) Displays the Repair IP Tunnels option, which fixes circuits that are in the PARTIAL status as a result of node IP address changes.
Links
—
Displays the following options:
•
Repair PPCs option that launches the PPC Repair wizard. The PPC Repair wizard fixes PPC termination in cases where the IP address changes for one node connected by one link. It will also discover the IP address change based on information stored by the PPC terminations.
•
Repair server trails that launches the Server Trail Repair wizard. The repair server trails option repairs server trail terminations in cases where the IP address changes for a node connected by a Server Trail link.
Topology Upgrade
—
Displays the following options:
•
Convert Path Protection to BLSR (or Convert SNCP to MS-SPRing)—Converts a path protection configuration to a bidirectional line switch ring (BLSR) or an SNCP to a multiplex section-shared protection ring (MS-SPRing). Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
•
Convert Unprotected to Path Protection (or SNCP)—Converts a point-to-point or linear add/drop multiplexer (ADM) to path protection or SNCP. Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
Manage IPoDWDM
—
Displays the following options:
•
SRLG Report
–
Consolidated SRLG Report
–
Detailed SRLG Report
•
Manage SRLGs
Manage VLANs
—
Displays a list of VLANs that have been created and allows you to delete VLANs. Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
Open TL1 Connection

Displays the TL1 session dialog box so you can create a TL1 session to a specific node. Refer to the Cisco ONS SONET TL1 Reference Guide and the Cisco ONS SDH TL1 Reference Guide.
Manage TL1 Tunnels
—
Creates, edits, deletes, opens, and closes TL1 tunnels that transports the TCP traffic to and from ONS ENEs through the OSI-based GNE.
Open IOS Connection

Displays the Cisco IOS command line interface (CLI) dialog box if a Cisco IOS capable card (ML-Series card) is installed in the node. Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
Manage TL1 Tunnels
—
Displays existing TL1 tunnels; allows you to create, edit, and delete the tunnels.
Open IOS Connection
Image present. Descrption?
Open Pseudo IOS Connection
—
Displays the simulated Cisco IOS command line interface (CLI) on a DWDM node.
Functional View
Image present. Descrption?
Update CTC
—
Allows you to update CTC to a newer version, if a newer version was found during network discovery.
Window
Reset to Default

Restores the default view position. This option can be accesed from any perspective to go back to the default initial position of any added view. After deleting a customized view, the view goes back to default position.
Perspective

Add Perspective—Opens the add perspective dialogue box to create a new custom perspective. Is it possible to add views for those network elements only on the networks that support perspective feature.

Remove Perspectives—Opens a remove perspectives dialog box, where you can choose the perspective you want to delete. You can not delete the active default CTC view.

Remove Active Perspectives—Deletes the current customized perspective. you cannot delete the active default CTC perspective.
Show Network Explorer
—
Displays the network explorer pane.
Show Summary
—
Displays the summary pane.
Show Main Tabbed View
—
Displays the pane with all tabs.
Help
Contents and Index
—
Displays the online help window.
User Manuals
—
Displays the Cisco ONS 15454 documentation.
About CTC
—
Displays the software version and the nodes in the CTC session.
—
Network Scope
—
Displays the selected network scope. The network scope drop-down list has three options: DWDM, TDM, or All. If you choose DWDM, DWDM and hybrid nodes appear on the network view map. If you choose TDM, TDM and hybrid nodes appear on the network view map. If you choose All, every node on the network appears on the network view map.
—
Link Filter

Opens the Link Filter dialog box, which allows you to choose which link classes appear on the nondetail network map. The available classes vary according to the selected network scope.
•
ALL—DCC, GCC, OTS, PPC
•
DWDM—GCC, OTS, PPC
•
TDM—DCC, PPC
—
—

(Toolbar only) Zooms out the network view area.
—
—

(Toolbar only) Zooms in the network view area.
—
—

(Toolbar only) Zooms in a selected network view area.
—
—


Opens the CTC Alerts dialog box, which shows the status of certain CTC background tasks. When the CTC Alerts toolbar icon contains a red triangle, unread notifications exist. When there are no unread notifications, the CTC Alerts toolbar icon contains a gray triangle (see the icons in the Toolbar column for comparison). Notifications include:
•
Network disconnection.
•
Send-PDIP inconsistency—CTC discovers a new node that does not have a SEND-PDIP setting consistent with the login node.
•
Circuit deletion status—Reports when the circuit deletion process completes if you chose "Notify when complete" as described in the "DLP-G106 Delete Optical Channel Network Connections" task and the "DLP-G347 Delete Optical Channel Client Connections" task in the chapter "Create Optical Channel Circuits and Provisionable Patchcords" of the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Configuration Guide. The CTC Alerts window always reports circuit deletion errors.
•
Conditions retrieval error.
•
Software download failure.
You can save a notification by clicking the Save button in the CTC Alerts dialog box and navigating to the directory where you want to save the text file.
By default, the CTC Alerts dialog box appears automatically. To disable automatic popup, see the "DLP-G53 Configure the CTC Alerts Dialog Box for Automatic Popup" task.
—
—

Changes between fixed and floating panes.
—
—

Click Toggle auto-hide to hide the pane.
—
—

Closes the pane.
CTC Mouse Options
In addition to the CTC menu bar and toolbar, you can invoke actions by double-clicking CTC window items with your mouse, or by right-clicking an item and selecting actions from shortcut menus. Table 19 lists the CTC window mouse shortcuts.
Multishelf View Shortcuts
Table 20 shows actions on ONS 15454 cards that you can perform by moving your mouse over the CTC window in multishelf view (multishelf mode).
Node View (Single-Shelf Mode) and Shelf View (Multishelf Mode) Shortcuts
Table 21 shows actions that you can perform by moving your mouse in the CTC window in node (single-shelf mode) or shelf (multishelf mode) view.
Network View Tasks
Right-click the network view graphic area or a node, span, or domain to display shortcut menus. Table 22 lists the actions that are available from the network view.
Table 22 Network Management Tasks in Network View
Open a node
Any of the following:
•
Double-click a node icon.
•
Right-click a node icon and choose Open Node from the shortcut menu.
•
Click a node and choose Go To Selected Object View from the View menu.
•
From the View menu, choose Go To Other Node. Choose a node from the Select Node dialog box.
•
Double-click a node alarm or event in the Alarms or History tab.
Move a node icon
Press and hold the left mouse button to drag the node icon to a new location.
Reset node icon position
Right-click a node and choose Reset Node Position from the shortcut menu. The node icon moves to the position defined by the longitude and latitude fields on the Provisioning > General tab in node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode).
Consolidate links
Right-click on a link and choose Collapse OTS Links from the shortcut menu. For more detailed instructions, refer to Manage the Node.
Provision a circuit
•
Right-click a node. From the shortcut menu, choose Provision Circuit To and choose the node where you want to provision the circuit. For circuit creation procedures, see the chapter "Create Optical Channel Circuits and Provisionable Patchcords" in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Configuration Guide.
Update circuits with new node
Right-click a node and choose Update Circuits With New Node from the shortcut menu. Use this command when you add a new node and want to pass circuits through it.
Display a link end point
Right-click a span. From the shortcut menu, choose Go To {<node> | <port> | <slot>} for the drop port you want to view. CTC displays the card in card view.
Display span properties
Do any of the following:
•
Move the mouse over a span; the properties appear near the span.
•
Click a span; the properties appear in the upper left corner of the window.
•
Right-click a span; the properties appear at the top of the shortcut menu.
Perform a Path Protection (ANSI) or SNCP (ETSI) protection switch for an entire span
Right-click a network span and click Circuits. In the Circuits on Span dialog box, switch options appear in the Path Protection (or SNCP) Span Switching field.
Display DWDM span properties
Right-click a DWDM network span and choose Circuits from the shortcut menu. The optical channel network connection (OCHNC), optical direction, and circuit appear.
Upgrade a span
Right-click a span and choose Upgrade Span from the shortcut menu. Not applicable to DWDM nodes.
Table Display Options
Right-clicking a table column displays a shortcut menu. Table 23 shows table display options, which include rearranging or hiding CTC table columns and sorting table columns by primary or secondary keys.
Equipment Inventory
In node view (single-shelf mode) and multishelf view (multishelf mode), the Inventory tab displays information about the ONS 15454 equipment, including:
•
Location—Identifies where the equipment is installed, either chassis or slot number.
•
Eqpt Type—Displays the type of equipment.

Note
CTC lists the 12 passive inventory ports for the M6 chassis in the format
USBP_SIDE_PORT (for example, CTC displays USBP_A_1 for port 1 on the left side of the chassis, and USBP_B_1 for port 1 on the right side of the chassis). These are labeled on the M6 chassis from 1-12.
•
Actual Eqpt Type—Displays the specific card name.
•
Admin State—Changes the card service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about card administrative states, refer to the "Administrative and Service States" document.
–
IS (ANSI) or Unlocked (ETSI)—Puts the card in the In-Service and Normal (IS-NR [ANSI]) or Unlocked-enabled (ETSI) service state.
–
OOS,MA (ANSI) or Locked,maintenance (ETSI)—Puts the card in the Out-of-Service and Autonomous, Maintenance (OOS-AU,MT [ANSI]) or Unlocked-disabled,maintenance (ETSI) service state.
•
Service State—Displays the current card service state, which is an autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the card. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about card service states, refer to the "Administrative and Service States" document.
•
HW Part #—Displays the hardware part number; this number is printed on the top of the card or equipment piece.
•
HW Rev—Displays the hardware revision number.
•
Serial #—Displays the equipment serial number; this number is unique to each card.
•
CLEI Code—Displays the Common Language Equipment Identifier code.
•
Bootroom Rev—Displays the boot read-only memory (ROM) revision number.
•
Product ID—Displays the manufacturing product identifier for a hardware component, such as a fan tray, chassis, or card. The Product ID column displays "N/A" for equipment existing before Software Release 4.6.
•
Version ID—Displays the manufacturing version identifier for a fan tray, chassis, or card. The Version ID column displays "N/A" for equipment existing before Software Release 4.6.
Buttons at the bottom of the Inventory tab are used to delete or reset a card when a card is selected, or to delete a PPM if a PPM is selected on the table.

Note
After the card is upgraded using the boot code upgrade procedure, the bootstrap version is displayed in the Inventory tab in CTC. However, the boot code version is not displayed.
Facilities View
In node view (single-shelf mode), shelf view (multishelf mode), and multishelf view (multishelf mode), the Maintenance > DWDM > All Facilities tab displays facility information for all facilities on the ONS 15454 equipment:
•
Marked—Displays a check mark if you have designated the facility for logical grouping. For information on marking a facility to group it with others, see the "NTP-G166 View the Facilities" task in the chapter "Maintain the Node" of the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Configuration Guide.
•
Location—Displays the slot number, slot type, port number, and port type of the facility.
•
Admin State—Displays the administrative state of the facility.
•
Service State—Displays the service state of the facility.
•
Power—Displays the power level of the facility.
Additional References
Table 24 references related documents of different releases.











 Feedback
Feedback