Installing Cisco ONS 15454 SONET/SDH 15454 MRC-12 Cards
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Installing Cisco ONS 15454 SONET/SDH 15454 MRC-12 Cards
Slot Compatibility by Cross-Connect Card
15454_MRC-12 Card-Level Indicators
15454_MRC-12 Port-Level Indicators
15454_MRC-12 Card Specifications
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Installing Cisco ONS 15454 SONET/SDH 15454 MRC-12 Cards
Product Name: 15454-MRC-I-12 (SONET); 15454E-MRC-I-12 (SDH)
This document provides card specifications and describes installation and removal procedures for the Cisco ONS 15454 MRC-12 card. As appropriate, use this document in conjunction with the Cisco ONS 15454 Procedure Guide, Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual, and the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide; or the Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Procedure Guide, the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual, or the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide, when working with ONS 15454 SONET and ONS 15454 SDH cards.
This document contains the following sections:
•
"15454_MRC-12 Card Description" section
•
"15454_MRC-12 Card Specifications" section
•
"Install the 15454_MRC-12 Card" section
•
"Related Documentation" section
•
"Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request" section
15454_MRC-12 Card Description
The 15454_MRC-12 multirate card provides up to twelve OC-3/STM-1 ports, twelve OC-12/STM-4 ports, or four OC-48/STM-16 ports using small form-factor pluggables (SFPs), in various combinations of line rates depending on the card slot, port, and cross-connect cards used. (See the "Slot Compatibility by Cross-Connect Card" section and the "Ports and Line Rates" section for more information.) All ports are Telcordia GR-253 compliant. The 15454_MRC-12 card can use the following SFP optics: SR, IR, LR, coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM), and DWDM. See the "Optical Card SFPs and XFPs" section for more information about SFPs.
The ports operate at up to 2488.320 Mbps over a single-mode fiber. The 15454_MRC-12 card has twelve physical connector adapters with two fibers per connector adapter (Tx and Rx). The card supports VT payloads, STS-1 payloads, and concatenated payloads at STS-3c, STS-6c, STS-9c, STS-12c, STS-18c, STS-24c, STS-36c, or STS-48c signal levels. It is fully interoperable with the ONS 15454 G-Series Ethernet cards.
The card supports 1+1 unidirectional and bidirectional facility protection. It also supports 1+1 protection in four-fiber BLSR applications where both span switching and ring switching might occur. You can provision this card as part of a BLSR/MS-SPRing, UPSR/SNCP, or a 1+1 linear configuration.

Note
Longer distances are possible in an amplified system using dispersion compensation.
Figure 1 shows the 15454_MRC-12 faceplate and block diagram.
Figure 1 15454_MRC-12 Card Faceplate and Block Diagram

Slot Compatibility by Cross-Connect Card
You can install 15454_MRC-12 cards in Slots 1 through 6 and 12 through 17 with the following cross-connect cards in SONET (ANSI) and SDH (ETSI) applications:
•
SONET: XCVT, XC10G, or XC-VXC-10G
•
SDH: XC-VXL-2.5G, XC-VXL-10G, or XC-VXC-10G

Note
The 15454_MRC-12 card supports an errorless software-initiated cross-connect card switch when used in a shelf equipped with XC-VXC-10G and TCC2/TCC2P cards.
The maximum bandwidth of the 15454_MRC-12 card is determined by the cross-connect card. Table 1 shows the maximum bandwidth for different cross-connect configurations in an ANSI shelf. Table 2 shows the maximum bandwidth for different cross-connect configurations in an ETSI shelf.
Ports and Line Rates
Each port on the 15454_MRC-12 card can be configured as OC-3/STM-1, OC-12/STM-4, or OC-48/STM-16, depending on the available bandwidth and existing provisioned ports. Based on the cross-connect card and slot limitations shown in Table 1, the following rules apply for various synchronous transport signal (STS) available bandwidths. (Table 3 shows the same information in tabular format.)
•
STS-12
–
Port 1 is the only port that is usable as an OC-12/STM-4. If Port 1 is used as an OC-12/STM-4, all other ports are disabled.
–
Ports 1, 4, 7, and 10 are the only ports usable as OC-3/STM-1. If any of these ports is used as an OC-3/STM-1, Ports 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, and 12 are disabled.
•
STS-48
–
Port 1 is the only port usable as an OC-48. If Port 1 is used as an OC-48, all other ports are disabled.
–
Ports 1, 4, 7, and 10 are the only ports usable as OC-12/STM-4.
–
If Port 4 is used as an OC-12/STM-4, Ports 2 and 3 are disabled.
–
If Port 7 is used as an OC-12/STM-4, Ports 5, 6, and 8 are disabled.
–
If Port 10 is used as an OC-12/STM-4, Ports 9, 11, and 12 are disabled.
–
Any port can be used as an OC-3/STM-1 as long as all of the above rules are followed.
•
STS-192
–
Ports 1, 4, 7, and 10 are the only ports usable as OC-48.
–
If Port 4 is used as an OC-48, Ports 2 and 3 are disabled.
–
If Port 7 is used as an OC-48, Ports 5, 6, and 8 are disabled.
–
If Port 10 is used as an OC-48, Ports 9, 11, and 12 are disabled.
–
If Port 4 is used as an OC-12/STM-4, Ports 2 and 3 can be used as an OC-12/STM-4 or OC-3/STM-1.
–
If Port 7 is used as an OC-12/STM-4, Ports 5, 6, and 8 can be used as an OC-12/STM-4 or OC-3/STM-1.
–
If Port 10 is as used as an OC-12/STM-4, Ports 9, 11, and 12 can be used as an OC-12/STM-4 or OC-3/STM-1.
–
If Port 4 is used as an OC-3/STM-1, Ports 2 and 3 can be used as an OC-3/STM-1 or OC-12/STM-4.
–
If Port 7 is used as an OC-3/STM-1, Ports 5, 6, and 8 can be used as an OC-3/STM-1 or OC-12/STM-4.
–
If Port 10 is used as an OC-3/STM-1, Ports 9, 11, and 12 can be used as an OC-3/STM-1 or OC-12/STM-4.
–
Any port can be used as an OC-12/STM-4 or OC-3/STM-1, as long as all of the above rules are followed.
Table 3 shows the 15454_MRC-12 port availability and OC-N line rate for each port, based on total available bandwidth. To use the table, go to the rows for the bandwidth that you have available, as determined in Table 1. Each row indicates what line rate can be provisioned for each port (identified in the MCR-12 Port Number row). The Ports Used column shows the total number of ports that can be used with each bandwidth scheme.
Table 3 Line Rate Configurations Per 15454_MRC-12 Port, Based on Available Bandwidth in an ONS 15454 ANSI Shelf
OC-3
OC-12
OC-48OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12
OC-48OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12
OC-48OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12
OC-48OC-3
OC-12OC-3
OC-12—
—
STS-12 Available Bandwidth
12
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
1
12
3
—
—
3
—
—
3
—
—
3
—
—
4
12
STS-48 Available Bandwidth
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
12
36
3
—
—
12
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
10
39
3
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
3
3
3
3
7
39
3
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
—
4
39
12
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
12
45
12
—
—
12
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
10
48
12
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
3
3
3
3
7
48
12
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
—
4
48
12
3
3
3
—
—
12
—
3
3
3
3
9
45
12
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
—
12
—
—
9
45
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
—
12
—
—
9
36
3
3
3
3
—
—
12
—
—
12
—
—
6
36
48
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
1
48
STS-192 Available Bandwidth
(when installing additional SFPs from the top port to the bottom port)1
48
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
12
81
48
12
12
12
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
12
108
48
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
3
3
3
3
12
144
48
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
180
48
3
3
3
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
153
48
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
12
12
12
12
12
117
48
—
—
48
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
10
120
48
—
—
48
12
12
12
12
3
3
3
3
10
156
48
—
—
48
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
10
192
48
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
3
3
3
3
7
156
48
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
12
12
12
12
7
192
48
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
4
192
STS-192 Available Bandwidth (when installing additional SFPs from the bottom port to the top port)1
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
—
48
—
—
9
72
3
3
3
3
12
12
12
12
—
48
—
—
9
108
3
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
—
48
—
—
9
135
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
—
48
—
—
9
144
12
12
12
12
3
3
3
3
—
48
—
—
9
108
12
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
—
48
—
—
9
81
3
3
3
3
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
6
108
3
12
12
12
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
6
135
12
12
12
12
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
6
144
12
3
3
3
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
6
117
3
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
4
147
12
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
48
—
—
4
156
1 If the MRC-12 card is initially populated with OC-3/12 on all its 12 ports, you can later add OC-48 SFPs on that card from top port to bottom port or from bottom port to top port. The maximum available bandwidth usage is different for these two cases.
Table 4 shows the 15454_MRC-12 port availability and STM-N line rate for each port, based on total available bandwidth. To use the table, go to the rows for the bandwidth that you have available, as determined in Table 2. Each row indicates what line rate can be provisioned for each port (identified in the MCR-12 Port Number row). The Ports Used column shows the total number of ports that can be used with each bandwidth scheme.
Table 4 Line Rate Configurations Per 15454_MRC-12 Port, Based on Available Bandwidth in an ONS 15454 ETSI Shelf
STM-1
STM-4
STM-16STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4
STM-16STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4
STM-16STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4
STM-16STM-1
STM-4STM-1
STM-4—
—
STS-12 Available Bandwidth
4
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
1
12
1
—
—
1
—
—
1
—
—
1
—
—
4
12
STS-48 Available Bandwidth
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
36
1
—
—
4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
39
1
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
1
1
1
1
7
39
1
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
—
4
39
4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
45
4
—
—
4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
48
4
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
1
1
1
1
7
48
4
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
—
4
48
4
1
1
1
—
—
4
—
1
1
1
1
9
45
4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
—
4
—
—
9
45
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
—
4
—
—
9
36
1
1
1
1
—
—
4
—
—
4
—
—
6
36
16
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
1
48
STS-192 Available Bandwidth
(when installing additional SFPs from the top port to the bottom port)1
16
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
81
16
12
12
12
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
108
16
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
1
1
1
1
12
144
16
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
180
16
1
1
1
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
153
16
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12
12
12
12
12
117
16
—
—
16
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
120
16
—
—
16
12
12
12
12
1
1
1
1
10
156
16
—
—
16
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
10
192
16
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
1
1
1
1
7
156
16
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
12
12
12
12
7
192
16
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
4
192
STS-192 Available Bandwidth (when installing additional SFPs from the bottom port to the top port)1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
—
16
—
—
9
72
1
1
1
1
12
12
12
12
—
16
—
—
9
108
1
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
—
16
—
—
9
135
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
—
16
—
—
9
144
12
12
12
12
1
1
1
1
—
16
—
—
9
108
12
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
—
16
—
—
9
81
1
1
1
1
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
6
108
1
12
12
12
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
6
135
12
12
12
12
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
6
144
12
1
1
1
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
6
117
1
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
4
147
12
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
16
—
—
4
156
1 If the MRC-12 card is initially populated with STM-1/STM-4 on all its 12 ports, you can later add STM-16 SFPs on that card from top port to bottom port or from bottom port to top port. The maximum available bandwidth usage is different for these two cases.
15454_MRC-12 Card-Level Indicators
Table 5 describes the three card-level LEDs on the 15454_MRC-12 card.
15454_MRC-12 Port-Level Indicators
Each port has a port-level LED. The LED flashes green if the port is transmitting or receiving a signal, and it flashes red when there is a signal failure.
You can also find the status of the 15454_MRC-12 card ports by using the LCD screen on the ONS 15454 fan-tray assembly. Use the LCD to view the status of any port or card slot; the screen displays the number and severity of alarms for a given port or slot. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide or Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Troubleshooting Guide for a complete description of the alarm messages.
Optical Card SFPs and XFPs
The ONS 15454 and ONS 15454 SDH optical cards use industry-standard SFPs and XFP modular receptacles.
Currently, the only optical cards that use SFPs and XFPs are the 15454_MRC-12, OC192SR1/STM64IO Short Reach, and OC192/STM64 Any Reach cards.
For all optical cards, the type of SFP or XFP plugged into the card is displayed in CTC and TL1. Cisco offers SFPs and XFPs as separate orderable products.
Compatibility by Card
Table 6 lists the compatible SFPs for the 15454_MRC-12 card.

CautionOnly use SFPs and XFPs certified for use in Cisco Optical Networking Systems (ONSs). The qualified Cisco SFP pluggable module's top assembly numbers (TANs) are provided in Table 6.
15454_MRC-12 Card Specifications
The 15454_MRC-12 card has the following specifications.

Note
For compatible SFP specifications, see the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual or the Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Reference Manual.
•
Line
–
Bit rate: up to OC-48/STM-16 (2488.320 Mbps), depending on SFP

Note
Each optical interface on the card can be configured as OC-3/STM-1, OC-12/STM-4, or OC-48/STM-16, depending on the available backplane bandwidth and existing provisioned lines. In general, the card supports all different rates on the line side as long as the accumulated bandwidth does not exceed the total backplane allowed bandwidth.
–
Fiber: 1550-nm single-mode
–
Connectors: LC duplex connector for each SFP
–
Compliance: Telcordia GR-253-CORE
•
Transmitter
–
Maximum transmitter output power: Depends on SFP
–
Minimum transmitter output power: Depends on SFP
–
Center wavelength: See wavelength plan
–
Center wavelength accuracy: 1 nm to 4 nm, depending on SFP
–
Transmitter: FP and DFB laser
•
Receiver
–
Maximum receiver level: Depends on SFP
–
Minimum receiver level: Depends on SFP
–
Receiver: PIN PD
–
Receiver input wavelength range: Depends on SFP
•
Environmental
–
Operating temperature: -40 to +149 degrees Fahrenheit (-40 to +65 degrees Celsius)
–
Operating humidity: 5 to 95 percent, noncondensing
–
Power consumption: 38.00 W, 0.79 A at -48 V, 129.66 BTU/hr
•
Dimensions
–
Height: 12.650 in. (321.3 mm)
–
Width: 0.716 in. (18.2 mm)
–
Depth: 9.000 in. (228.6 mm)
–
Depth with backplane connector: 9.250 in. (235 mm)
–
Weight not including clam shell: 3.1 lb (1.3 kg)
•
Wavelength plan. Currently available wavelengths and versions of the 15454_MRC-12 card:
–
For ONS-SC-2G-30.3 through ONS-SC-2G-60.0 SFPs: 1530.33 nm to 1560.61 nm
(32 distinct wavelengths at 100 GHz spacing)–
For ONS-SE-622-1470 through ONS-SE-622-1610 SFPs: 1470 to 1610 nm
(eight distinct wavelengths at 2500 GHz spacing)–
For ONS_SE-155-1470 through ONS-SE-155-1610 SFPs: 1470 to 1610 nm
(eight distinct wavelengths at 2500 GHz spacing)•
For compliance information, refer to the Cisco Optical Transport Products Safety and Compliance Information.
Install the 15454_MRC-12 Card
Use this section if you are installing the 15454_MRC-12 card for the first time. After you become familiar with ONS 15454 card installation and boot up, use this section as a reference. For more information, see the Cisco ONS 15454 Procedure Guide or the Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Procedure Guide.
WarningClass I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products. Statement 291

CautionAlways use the supplied ESD wristband when working with a powered ONS 15454 SDH. Plug the wristband cable into the ESD jack located on the lower-right outside edge of the shelf assembly.

Note
To simplify subnetwork connection protection (SNCP) to multiplex section-shared protection ring (MS-SPRing) conversion and node addition, install optical cards according to an east (Slots 12 and 13) and west (Slots 5 and 6) configuration. This configuration is not mandatory.

Note
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.

Note
If you are installing optical cards, Cisco recommends that you install these before you install electrical cards, as applicable.

Note
To simplify unidirectional path switched ring (UPSR) to bidirectional line switched ring (BLSR) conversion and node addition, install optical cards according to a high-speed east (Slots 12 and 13) and west (Slots 5 and 6) configuration. This configuration is not mandatory.

Note
During the boot process, an Out-of-Service (OOS) OC-N/STM-N port will output a Line Alarm Indication Signal (AIS-L) to any In-Service (IS) far-end receivers. See the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide or Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Troubleshooting Guide for further information about the AIS-L condition.

Note
Install higher-capacity cards first; for example, install an OC-192/STM-64 card before installing an OC-48/STM-12 card. Let each card completely boot before installing the next card.
15454_MRC-12 cards have electrical plugs that plug into electrical connectors on the shelf assembly backplane. When the ejectors are fully closed, the card plugs into the shelf assembly backplane. Figure 2 shows general card installation in an ONS 15454 SONET shelf. (Installation is similar in an ONS 15454 SDH shelf.)
Figure 2 Installing an ONS 15454 Card in a SONET Shelf
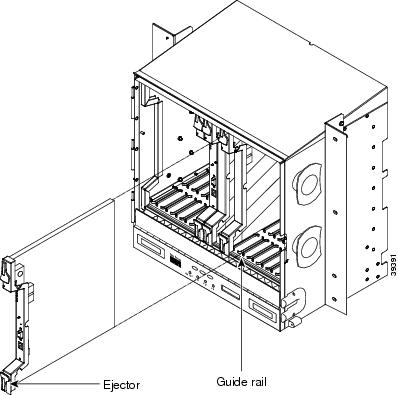

CautionBecause all other cards boot from the active TCC2/TCC2P card, at least one TCC2/TCC2P card must be installed in order to boot the 15454_MRC-12 card. Cisco strongly recommends that you always install and boot two TCC2/TCC2P cards before running any live traffic over an ONS 15454 node.
Step 1
Verify that power is applied to the shelf assembly.
Step 2
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 3
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Step 4
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 5
Verify the LED activity:
•
The red FAIL LED turns on for 10 to 15 seconds.
•
The red FAIL LED blinks for 30 to 40 seconds.
•
All LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
•
The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.

Note
The booting OC-N/STM-N card will send an AIS-L to the far-end receiver as long as it is Locked-enabled, disabled.
Step 6
If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 5, check the following:
•
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
•
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 1 to 5.
Step 7
When you have displayed Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) on your workstation, verify that the card appears in the correct slot on the CTC node view. See the Cisco ONS 15454 Procedure Guide for CTC information and provisioning instructions.
Related Documentation
•
Cisco ONS 15454 Procedure Guide
•
Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Procedure Guide
•
Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual
•
Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Reference Manual
•
Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide
•
Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Troubleshooting Guide
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)

 Feedback
Feedback