IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ) and L2PT on L2
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ) and L2PT on L2 Ports
Prerequisites for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Restrictions for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Information About QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Benefits of QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Port-based EoMPLS over GRE with Static Pseudowire Provisioning
Customizable Tunneling MAC Address
How to Implement QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Configuring QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Configuration Examples for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Example: EoMPLS Pseudowire over GRE with Static Label
Example: EoMPLS xconnect on SVI
Example: QinQ and L2PT on L2 ports with Dual-Homed Topology
l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point
Feature Information for QinQ and L2PT
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ) and L2PT on L2 Ports
Revised: July 27, 2012 OL-20468-02First Published: November 11, 2011Last Updated: July 27, 2012This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QinQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT) on Integrated Services Router Generation 2 (ISR G2). User interface will be aligned with the service provider module or switch to support QinQ and L2PT on ISR G2 Layer 2 Port. This enables service providers to run Layer 2 Ethernet services and provide transparent LAN services over a metropolitan Ethernet infrastructure to customers.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for QinQ and L2PT" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Restrictions for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Information About QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
How to Implement QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Configuration Examples for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Feature Information for QinQ and L2PT
Prerequisites for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Ensure that you have the appropriate Cisco routers and switches. This feature supports the following Integrated Series Router Generation 2 (ISR G2) platforms:
–
Cisco 89x and 888EA ISR G2
–
Cisco 19xx ISR G2
–
Cisco 29xx ISR G2
–
Cisco 39xx ISR G2
•
Ensure that you have the appropriate ether-switch modules installed in ISR G2:
–
HWIC-4ESW, HWIC-4ESW-PO
–
HWIC-D-9ESW, HWIC-D-9ESW-POE
–
EHWIC-4ESG, EHWIC-4ESG-P
–
EHWIC-D-8ESG, EHWIC-D-8ESG-P

Note
You cannot use the EHWIC switch in conjunction with the HWICs.

Note
This feature supports Release 15.2(2)T and later releases.
Restrictions for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Configuration through SNMP/MIB is not supported.
•
The following dual-attached topology will not be supported where two links from the switch are connected to the same PE:

Although 802.1Q tunneling works well for Layer 2 packet switching, incompatibilities exist between some Layer 2 features and Layer 3 switching:
•
A tunnel port cannot be a routed port.
•
IP routing is not supported on a VLAN that includes 802.1Q ports. Packets received from a tunnel port are forwarded based only on Layer 2 information. If routing is enabled on a switch virtual interface (SVI) that includes tunnel ports, untagged IP packets received from the tunnel port are recognized and routed by the switch. Customers can access the Internet through the native VLAN.
•
If this access is not needed, you should not configure SVIs on VLANs that include tunnel ports.
•
Tunnel ports do not support IP access control lists (ACLs).
•
Layer 3 quality of service (QoS) ACLs and other QoS features related to Layer 3 information are not supported on tunnel ports. MAC-based QoS is supported on tunnel ports.
Information About QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Customers are connected across a service-provider network that are connected to various Layer 2 customer premises equipments (CPEs). Cisco devices will be configured to work with third-party CPEs. All configurations will be done at the Provider Edge (PE).
Service providers can take advantage of ISR G2 support for xconnect over Multiprotocol Label Switching (SVIEoMPLS) over generic routing encapsulation (GRE) with Static Pseudowire Provisioning and L2PT on Layer 2 ports, dot1Q tunnel mode support on Layer 2 ports, customizable L2PT tunneling MAC address, and other Layer 2 Ethernet services.
Benefits of QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Simpler Architecture and Lower Operational Cost
Layer 2 Ethernet services are offered as a specific service based on pure Ethernet access. End-to-end Ethernet services have simpler architecture with lower operational cost.
Scalability
The objectives of these enhancements are to enable service providers to extend Layer 2 Ethernet services over any access technology and provide transparent LAN services over a metropolitan Ethernet infrastructure to customers.
Because QinQ uses a double-tagged frame technique, it doubles the theoretical frame size limit of the IEEE 802.1Q, which is sufficient to accommodate network growth for several years.
Efficiency
These enhancements will also enable service providers to run both IP and non-IP traffic under the same CPE.
Features
The following concepts will help you understand how to implement QinQ and L2PT, which are the focus of this documentation:
•
Port-based EoMPLS over GRE with Static Pseudowire Provisioning
•
Virtual Private Network
•
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
•
QinQ Support on Layer 2 Ports
•
Customizable Tunneling MAC Address
Port-based EoMPLS over GRE with Static Pseudowire Provisioning
Ethernet over multiprotocol label switching (EoMPLS) is a tunneling mechanism that allows you to tunnel Layer 2 traffic through a Layer 3 MPLS network. EoMPLS is also known as Layer 2 tunneling.
EoMPLS effectively facilitates the Layer 2 extension over long distances. EoMPLS over GRE helps create the GRE tunnel as a hardware-based switch and encapsulates EoMPLS frames within the GRE tunnel with high performance. The GRE connection is established between the two core routers and then the MPLS label switch path (LSP) is tunneled over.
The following are the required features:
•
EoMPLS pseudowire over GRE with static label
•
EoMPLS xconnect on SVI
•
Allow set dscp/prec tunnel for policy-maps output on tunnel interfaces
•
Port-based pseudowire on Layer 3 ports

Note
Port-based pseudowire on Layer 3 ports and allow set dscp/prev tunnel for policy-maps output on tunnel interfaces are supported on IOS Release 15.2(4)M and later releases.
For more information about EoMPLS over GRE, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/interface/configuration/guide/ir_impl_tun.html#wp1139016.
Virtual Private Network
Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security, prioritization, reliability, and manageability requirements of private networks.
VPNs provide security through encryption tunneling, and the Cisco routers support hardware-based Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) IP Security (IPsec), Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), and Secure Sockets Layer VPN (SSL VPN). Encryption features can be enabled on the routers with the Advanced Security or any later feature set of the Cisco IOS Software.
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling allows Layer 2 protocol data units (PDUs) (CDP, STP, LACP, PAgP, UDLD, and VTP) to be tunneled through a network.
For more information about L2PT, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SXF/native/configuration/guide/l2pt.html.
The following are the required features:
•
Customizable Tunneling MAC Address
•
Port-based PW on Layer 2 ports
•
L2PT on Layer 2 ports
•
L2PT on Layer 3 ports

Note
L2PT on Layer 3 Ports is supported in 15.2 (4)M.
QinQ Support on Layer 2 Ports
QinQ or QnQ is short for 802.1Q-in-802.1Q. The original 802.1Q specification allows a single VLAN header to be inserted into an Ethernet frame. QinQ enables service providers to use a single VLAN to support customers who have multiple VLANs, while preserving customer VLAN IDs and keeping traffic in different customer VLANs segregated.
For more information about QinQ, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SXF/native/configuration/guide/dot1qtnl.html.
The following is the required feature:
•
Switchport mode dot1q-tunnel QinQ on Layer 2 Ethernet port
Customizable Tunneling MAC Address
Because customers are connected across a service-provider network that are connected to various Layer 2 third-party CPEs, they do not use the same MAC address, which can cause conflicts to Cisco devices. To resolve this, Cisco L2PT destination MAC address will be configurable and will be set as the default MAC address.
Customizable Tunneling MAC Address is a sub-feature of L2PT.
How to Implement QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Configuring QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
Configuring QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface interface-id
4.
switchport mode access
or
switchport mode dot1q-tunnel
5.
l2protocol-tunnel [cdp | stp | vtp | lacp | pagp | udld]
6.
end
7.
show l2protocol
8.
copy running-config startup-config (Optional)
DETAILED STEPS
Example
The following is a sample output from the show l2protoclol-tunnel command on PE1:
Router# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5l2protocol-tunnel mac-address: 0100.0ccd.cdd0Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encaps Decaps DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter Counter---- -------- --------- --------- ------- ------- -------Fa0 cdp ---- ---- 995 952 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----stp ---- ---- 28416 0 0vtp ---- ---- 0 0 0pagp ---- ---- 0 0 0lacp ---- ---- 2063 2054 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----Troubleshooting Tips
Use the following verification commands on CE:
•
show cdp neighbor
•
show spanning tree vlan vlan-id
•
show vtp status
•
show udld neighbor
•
show etherchannel channel-group-number summary
Configuring xconnect on SVI
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface interface-id
4.
no ip address
5.
xconnect peer-ip-address vcid pseudowire-parameters
6.
mpls local-pseudowire-label remote-pseudowire-label
DETAILED STEPS
Example
The following is a sample output fromt the show xconnect all command on PE:
Router# show xconnect allLegend: XC ST=Xconnect State S1=Segment1 State S2=Segment2 StateUP=Up DN=Down AD=Admin Down IA=InactiveSB=Standby RV=Recovering NH=No HardwareXC ST Segment 1 S1 Segment 2 S2------+---------------------------------+--+---------------------------------+--UP ac Vl10:10(Eth VLAN) UP mpls 2.2.2.2:10 UPDN ac Vl20:20(Eth VLAN) DN mpls 2.2.2.2:20 DNThe following is a sample output from the show l2protocol-tunnel command on PE:Router# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5l2protocol-tunnel mac-address: 0100.0ccd.cdd0Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encaps Decaps DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter Counter---- -------- --------- --------- ------- ------- -------Fa0 cdp --- --- 953 952 0lldp --- --- 0 0 0stp --- --- 45 30 0vtp --- --- 0 0 0--- --- --- ---- ---- ----lacp --- --- 2058 2061 0--- --- --- ---- ---- ----Troubleshooting Tips
Use the following verification commands on PE:
•
show mpls l2transport vc
•
show xconnect all
•
show l2protocol-tunnel
Configuration Examples for QinQ and L2PT on L2 Ports
•
Example: EoMPLS Pseudowire over GRE with Static Label
•
Example: EoMPLS xconnect on SVI
•
Example: QinQ and L2PT on L2 ports with Dual-Homed Topology
Example: EoMPLS Pseudowire over GRE with Static Label
The following example shows how to configure L2PT over GRE:
Sample Topology

CE1 Configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0PE1 Configuration
mpls label range 2000 16000 static 16 1999mpls label protocol ldppseudowire-class testencapsulation mplsprotocol noneinterface Loopback1description *** Loopback Interface ***ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255interface Tunnel1description *** Tunnel Interface to PE2 ***ip unnumbered Loopback1interface FastEthernet3description * PW Attachment Circuit, connected to CE1 *switchport access vlan 100switchport mode dot1q-tunnelno ip addressload-interval 30l2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel lldpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpno cdp enableinterface GigabitEthernet0ip address 21.0.0.1 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autointerface Vlan100description **L2VPN Customer**xconnect 1.1.1.2 100 encapsulation mpls manual pw-class testmpls label 100 150router ospf 1network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0network 21.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0ip route 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 Tunnel1mpls ldp router-id Loopback1IP Core Configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/0ip address 22.0.0.1 255.255.255.0interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 21.0.0.2 255.255.255.0router ospf 1network 21.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0network 22.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0PE2 Configuration
mpls label range 2000 16000 static 16 1999mpls label protocol ldppseudowire-class testencapsulation mplsprotocol noneinterface Loopback1description ***loopback interface***ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255interface Tunnel1description ***Tunnel Int to PE1***bandwidth 10ip unnumbered Loopback1load-interval 30mpls iptunnel source GigabitEthernet0/0tunnel destination 21.0.0.1interface GigabitEthernet0/0description *** BB interface ***ip address 22.0.0.2 255.255.255.0load-interval 30duplex autospeed autointerface GigabitEthernet0/1/3description * PW Attachment Circuit, connected to CE1switchport access vlan 100no ip addressl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel lldpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpno cdp enable!interface Vlan100description **L2VPN Customer**no ip addressload-interval 30mpls label protocol ldpxconnect 1.1.1.1 100 encapsulation mpls manual pw-class testmpls label 150 100!router ospf 1network 1.1.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0network 22.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0!ip forward-protocol nd!ip route 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 Tunnel1!mpls ldp router-id Loopback1CE2 Configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0Example: EoMPLS xconnect on SVI
The following example shows the relevant configuration for EoMPLS under SVI for a single PE:
mpls label range 2000 16000 static 16 1999mpls label protocol ldp!pseudowire-class testencapsulation mplsprotocol none!interface Loopback1description *** Loopback Interface ***ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255!interface FastEthernet3description * PW Attachment Circuit *switchport access vlan 100switchport mode dot1q-tunnel!interface Vlan100description **L2VPN Customer**no ip addressxconnect 1.1.1.2 100 encapsulation mpls manual pw-class testmpls label 100 150!mpls ldp router-id Loopback1!endExample: QinQ and L2PT on L2 ports with Dual-Homed Topology
The following example shows how to configure QinQ and L2PT on Layer 2 ports using a Dual-Homed Topology:
Physical Topology
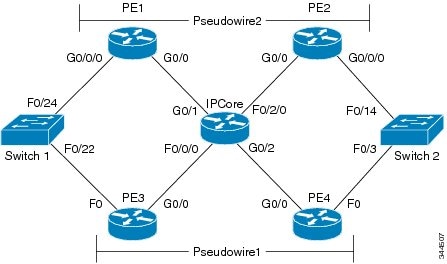
Logical

Topology
Switch-1 Configuration
interface FastEthernet0/22switchport access vlan 20switchport mode accesschannel-group 48 mode activeendinterface FastEthernet0/24switchport access vlan 20switchport mode accesschannel-group 48 mode activeendinterface Port-channel48switchport access vlan 20switchport mode accessendinterface Vlan20ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0endSWITCH-1# ping 10.0.0.2Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 msSWITCH-1#show spanning-tree vlan 20VLAN0020Spanning tree enabled protocol ieeeRoot ID Priority 20Address 000d.28fd.e100This bridge is the rootHello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 secBridge ID Priority 20 (priority 0 sys-id-ext 20)Address 000d.28fd.e100Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 secAging Time 300Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------Po48 Desg FWD 12 128.67 P2pSWITCH-1# show cdp neighborsCapability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route BridgeS - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - PhoneDevice ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port IDSWITCH-2 Fas 0/24 136 R S I SM-ES3-24-Fas 0/14SWITCH-2 Fas 0/22 149 R S I SM-ES3-24-Fas 0/13SWITCH-1#show etherchannel 48 summaryFlags: D - down P - in port-channelI - stand-alone s - suspendedH - Hot-standby (LACP only)R - Layer3 S - Layer2u - unsuitable for bundlingU - in use f - failed to allocate aggregatord - default portNumber of channel-groups in use: 3Number of aggregators: 3Group Port-channel Protocol Ports------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------48 Po48(SU) LACP Fa0/22(P) Fa0/24(P)PE1 Configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0switchport access vlan 10no ip addressl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpno cdp enableendinterface Vlan10no ip addressxconnect 5.5.5.5 10 encapsulation mplsendinterface Loopback0ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0duplex autospeed autointerface GigabitEthernet0/0/0switchport access vlan 10no ip addressl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldno cdp enableinterface Vlan10no ip addressxconnect 5.5.5.5 10 encapsulation mplsrouter ospf 100mpls ldp autoconfig area 0network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0 area 0network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0PE 1# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5l2protocol-tunnel mac-address: 0100.0ccd.cdd0Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encaps Decaps DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter Counter------------------- ----------- --------- --------- --------- --------- ---------Gi0/0/0 cdp ---- ---- 955 952 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----stp ---- ---- 28416 0 0vtp ---- ---- 0 0 0pagp ---- ---- 0 0 0lacp ---- ---- 2063 2054 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----PE-3 Configuration
PE 3# show running-configinterface Loopback0ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255interface FastEthernet0switchport access vlan 10switchport mode dot1q-tunnelno ip addressl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel lldpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldno cdp enableinterface FastEthernet1no ip addressshutdowninterface FastEthernet2switchport access vlan 10no ip addressshutdownl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldno cdp enableinterface GigabitEthernet0ip address 30.0.0.2 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autointerface Vlan10no ip addressxconnect 2.2.2.2 10 encapsulation mplsrouter ospf 100mpls ldp autoconfig area 0network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0network 30.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0PE 3# show xconnect allLegend: XC ST=Xconnect State S1=Segment1 State S2=Segment2 StateUP=Up DN=Down AD=Admin Down IA=InactiveSB=Standby RV=Recovering NH=No HardwareXC ST Segment 1 S1 Segment 2 S2------+---------------------------------+--+---------------------------------+--UP ac Vl10:10(Eth VLAN) UP mpls 2.2.2.2:10 UPDN ac Vl20:20(Eth VLAN) DN mpls 2.2.2.2:20 DNPE 3# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5l2protocol-tunnel mac-address: 0100.0ccd.cdd0Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encaps Decaps DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter Counter------------------- ----------- --------- --------- --------- --------- ---------Fa0 cdp ---- ---- 953 952 0lldp ---- ---- 0 0 0stp ---- ---- 45 30 0vtp ---- ---- 0 0 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----lacp ---- ---- 2058 2061 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----IP-CORE Configuration
interface Loopback0ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0!interface Loopback1no ip addressshutdowninterface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0duplex autospeed autono keepalive!interface GigabitEthernet0/2ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autono keepalive!interface FastEthernet0/0/0ip address 20.0.0.2 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/2/0ip address 50.0.0.1 255.0.0.0duplex autospeed autorouter ospf 100mpls ldp autoconfig area 0network 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0network 20.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0network 30.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0network 50.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0default-information originatePE-2 Configurationinterface Loopback0ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255!interface GigabitEthernet0/0ip address 50.0.0.2 255.0.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 110.0.0.2 255.0.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface GigabitEthernet0/2no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0switchport access vlan 10switchport mode dot1q-tunnelno ip addressl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldno cdp enable!interface Vlan10no ip addressxconnect 6.6.6.6 10 encapsulation mplsrouter ospf 100mpls ldp autoconfig area 0network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 area 0network 50.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0PE 2# show xconnect allLegend: XC ST=Xconnect State S1=Segment1 State S2=Segment2 StateUP=Up DN=Down AD=Admin Down IA=InactiveSB=Standby RV=Recovering NH=No HardwareXC ST Segment 1 S1 Segment 2 S2------+---------------------------------+--+---------------------------------+--UP ac Vl10:10(Eth VLAN) UP mpls 6.6.6.6:10 UPPE 2# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5l2protocol-tunnel mac-address: 0100.0ccd.cdd0Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encaps Decaps DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter Counter------------------- ----------- --------- --------- --------- --------- ---------Gi0/0/0 cdp ---- ---- 965 959 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----stp ---- ---- 0 28647 0vtp ---- ---- 0 0 0pagp ---- ---- 0 0 0lacp ---- ---- 2077 2074 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----===========================================================================PE 4:-======interface Loopback0ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255!interface FastEthernet0switchport access vlan 10switchport mode dot1q-tunnelno ip addressl2protocol-tunnel cdpl2protocol-tunnel stpl2protocol-tunnel vtpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point udldl2protocol-tunnel point-to-point pagpno cdp enableinterface GigabitEthernet0ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autointerface Vlan10no ip addressxconnect 4.4.4.4 10 encapsulation mplsrouter ospf 100mpls ldp autoconfig area 0network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0network 20.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0!router ospf 500PE 4# show xconnect allLegend: XC ST=Xconnect State S1=Segment1 State S2=Segment2 StateUP=Up DN=Down AD=Admin Down IA=InactiveSB=Standby RV=Recovering NH=No HardwareXC ST Segment 1 S1 Segment 2 S2------+---------------------------------+--+---------------------------------+--UP ac Vl10:10(Eth VLAN) UP mpls 4.4.4.4:10 UPDN ac Vl20:20(Eth VLAN) DN mpls 4.4.4.4:20 DNPE 4# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5l2protocol-tunnel mac-address: 0100.0ccd.cdd0Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encaps Decaps DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter Counter------------------- ----------- --------- --------- --------- --------- ---------Fa0 cdp ---- ---- 961 962 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----stp ---- ---- 30 45 0vtp ---- ---- 0 0 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----lacp ---- ---- 2080 2077 0--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----SWITCH-2 Configurationinterface FastEthernet0/13switchport access vlan 20switchport mode accesschannel-group 48 mode activeendinterface FastEthernet0/14switchport access vlan 20switchport mode accesschannel-group 48 mode activeendinterface Port-channel48switchport access vlan 20switchport mode accessend!interface Vlan20ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0endSWITCH-2# ping 10.0.0.1Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.1, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/3/8 msSWITCH-2# show spanning-tree vlan 20VLAN0020Spanning tree enabled protocol ieeeRoot ID Priority 20Address 000d.28fd.e100Cost 12Port 432 (Port-channel48)Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 secBridge ID Priority 32788 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 20)Address 5475.d016.1e80Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 secAging Time 300 secInterface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------Po48 Root FWD 12 128.432 P2pSWITCH-2# show cdp neighborsCapability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route BridgeS - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac RelayDevice ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port IDSWITCH-1 Fas 0/14 170 R S I WS-C3550- Fas 0/24SWITCH-1 Fas 0/13 170 R S I WS-C3550- Fas 0/22Command Reference
This section documents the new and existing commands that you can use in this release.
•
debug l2protocol-tunnel (new)
•
l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point (new)
debug l2protocol-tunnel
To configure the debugging option of Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT), use the debug l2protocol-tunnel command in EXEC mode.
debug l2protocol-tunnel [error | event | misc | packet]
Syntax Description
error
(Optional) Displays L2PT errors.
event
(Optional) Displays L2PT events.
misc
(Optional) Displays L2PT miscellaneous.
packet
(Optional) Displays L2PT activities.
Command Default
If you do not specify a debugging option, all options are enabled.
Command Modes
User EXEC (>)
Command History
Examples
The following example shows how to debug the l2protocol-tunnel command:
Router# debug l2protocol-tunnel errorRelated Commands
l2protoco-tunnel
Enables Layer 2 protocol tunneling for CDP, STP, or VTP packets on an interface.
show l2protocol-tunnel
Displays information about L2PT ports.
l2protocol-tunnel
To enable the protocol tunneling on an interface and specify the type of protocol to be tunneled, use the l2protocol-tunnel command in global or interface configuration mode. To disable protocol tunneling, use the no form of this command.
Global Configuration
l2protocol-tunnel [cos cos-value | global | mac-address]
no l2protocol-tunnel
Interface Configuration
l2protocol-tunnel [cdp | lldp | stp | vtp]
no l2protocol-tunnel
Syntax Description<
Defaults
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Global configuration (config)
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
On all the service provider edge switches, you must enable PortFast BPDU filtering on the 802.1Q tunnel ports by entering these commands:
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree bpdufilter enableRouter(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
Note
PortFast BPDU filtering is enabled automatically on tunnel ports.
If you do not specify a protocol, all protocols are tunneled.
You can configure protocol tunneling on VLAN and trunk interfaces.
You must enter the switchport command once without any keywords to configure the LAN port as a Layer 2 interface before you can enter additional switchport commands with keywords. This action is required only if you have not entered the switchport command for the interface.
Examples
This example shows how to enable a tunneling protocol on an interface:
Router> enableRouter# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/0Router(config-if)# l2protocol-tunnel cdpThis example shows how to disable a tunneling protocol on an interface:
Router> enableRouter# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface FastEthernet 4/1Router(config-if)# no l2protocol-tunnelProtocol tunneling disabled on interface fastEthernet 4/1Related Commands
l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point
To enable point-to-point protocol tunneling, use the l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point command in interface configuration mode. To disable, use the no form of this command.
l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point [pagp | lacp | udld]
no l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point [pagp | lacp | udld]
Syntax Description
Command Default
If no keyword is selected, tunneling is enabled for all three protocols.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
To avoid a network failure, make sure that the network is a point-to-point topology before you enable tunneling for PAgP, LACP, or UDLD packets.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable link aggregation on a point-to-point protocol tunneling:
Router(config-if)# l2protocol-tunnel point-to-point lacpRelated Commands
show l2protocol-tunnel
To display the protocols that are tunneled on an interface or on all interfaces, use the show l2protocol-tunnel command in the user EXEC or priveleged EXEC mode.
show l2protocol-tunnel [{interface interface-id mod/port} | summary | vlan vlan]
Syntax Description
Command Default
This command has no default settings.
Command Modes
User EXEC (>)
Privileged EXEC (#)Command History
Usage Guidelines
After enabling Layer 2 protocol tunneling on an access or IEEE 802.1Q tunnel port by using the l2protocol-tunnel interface configuration command, you can configure some or all of these parameters:
•
Protocol type to be tunneled
•
Shutdown threshold
•
Drop threshold
The show l2protocol-tunnel command displays only the ports that have protocol tunneling enabled.
The show l2protocol-tunnel summary command displays the ports that have protocol tunneling enabled, regardless of whether the port is down or currently configured as a trunk.
The show l2protocol-tunnel [interface interface-id] command shows only the information about the active ports in which all the parameters are configured.
Examples
The following example is an output from the show l2protocol-tunnel command:
Router# show l2protocol-tunnelCOS for Encapsulated Packets: 5Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop Encapsulation Decapsulation DropThreshold Threshold Counter Counter CounterFa0/3 --- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----pagp ---- ---- 0 242500lacp ---- ---- 24268 242640udld ---- ---- 0 897960Fa0/4 --- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----pagp 1000 ---- 24249 242700lacp ---- ---- 24256 242660udld ---- ---- 0 1344820Gi0/3 cdp ---- ---- 134482 1344820--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----pagp 1000 ---- 0 242500lacp 500 ---- 0 485320udld 300 ---- 44899 448980Gi0/3 cdp ---- ---- 134482 1344820--- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----pagp ---- 1000 0 242700lacp ---- ---- 0 485220udld 300 ---- 44899 448980This example shows how to display a summary of Layer 2-protocol tunnel ports:
Router# show l2protocol-tunnel summaryCOS for Encapsulated Packets:5Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets:0Port Protocol Shutdown Drop StatusThreshold Threshold(cdp/stp/vtp) (cdp/stp/vtp)------- ----------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------Fa9/1 --- stp --- ----/----/---- ----/----/---- downFa9/9 cdp stp vtp ----/----/---- ----/----/---- upFa9/47 --- --- --- ----/----/---- 1500/1500/1500 down(trunk)Fa9/48 cdp stp vtp ----/----/---- ----/----/---- down(trunk)This example shows how to display Layer 2-protocol tunnel information on interfaces for a specific VLAN:
Router# show l2protocol-tunnel vlan 1COS for Encapsulated Packets: 5Drop Threshold for Encapsulated Packets: 0Protocol Drop Counter-------- -------------cdp 0lldp 0stp 0vtp 0Port Protocol Thresholds CountersShutdown Drop Encap Decap Drop------------------- -------- --------- --------- --------- --------- ---------Related Commands
switchport mode
To set the interface type, use the switchport mode command in interface configuration mode. Use the appropriate no form of this command to reset the mode to the appropriate default mode for the device.
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
switchport mode {access | trunk}
no switchport mode
Cisco Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Switches
switchport mode {access | dot1q-tunnel | dynamic {auto | desirable} | trunk}
no switchport mode
Cisco 7600 Series Routers
switchport mode {access | dot1q-tunnel | dynamic {auto | desirable} | private-vlan | trunk}
no switchport mode
switchport mode private-vlan {host | promiscuous}
no switchport mode private-vlan
Syntax Description
Defaults
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
The default is access mode.
Cisco Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches
The default mode is dependent on the platform; it should be either dynamic auto for platforms that are intended as wiring closets or dynamic desirable for platforms that are intended as backbone switches. The default for PVLAN ports is that no mode is set.
Cisco 7600 Series Routers
The defaults are as follows:
•
The mode is dependent on the platform; it should either be dynamic auto for platforms that are intended for wiring closets or dynamic desirable for platforms that are intended as backbone switches.
•
No mode is set for PVLAN ports.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
If you enter a forced mode, the interface does not negotiate the link to the neighboring interface. Ensure that the interface ends match.
The no form of the command is not supported on the Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and Cisco 3700 series routers.
Cisco Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches and Cisco 7600 Series Routers
If you enter access mode, the interface goes into permanent nontrunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a nontrunk link even if the neighboring interface does not agree to the change.
If you enter trunk mode, the interface goes into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link even if the neighboring interface does not agree to the change.
If you enter dynamic auto mode, the interface converts the link to a trunk link if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode.
If you enter dynamic desirable mode, the interface becomes a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk, desirable, or auto mode.
If you configure a port as a promiscuous or host-PVLAN port and one of the following applies, the port becomes inactive:
•
The port does not have a valid PVLAN association or mapping configured.
•
The port is a SPAN destination.
If you delete a private-port PVLAN association or mapping, or if you configure a private port as a SPAN destination, the deleted private-port PVLAN association or mapping or the private port that is configured as a SPAN destination becomes inactive.
If you enter dot1q-tunnel mode, PortFast Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) filtering is enabled and Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is disabled on protocol-tunneled interfaces.
Examples
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
The following example shows how to set the interface to access desirable mode:
Router(config-if)#switchport mode accessThe following example shows how to set the interface to trunk mode:
Router(config-if)#switchport mode trunkCisco Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches and Cisco 7600 Series Routers
The following example shows how to set the interface to dynamic desirable mode:
Router(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic desirableThe following example shows how to set a port to PVLAN-host mode:
Router(config-if)#switchport mode private-vlan hostThe following example shows how to set a port to PVLAN-promiscuous mode:
Router(config-if)#switchport mode private-vlan promiscuousIntegrated Series Routers Generation 2 (ISR G2) Platforms
The following example shows how to configure tunneling on port 4/1 and verify the configuration:
Router# configure terminalRouter (config)# interface fastethernet 4/1Router (config-if)# switchport mode dot1q-tunnelRouter (config-if)# endRelated Commands
Additional References
Related Documents
Cisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS MPLS commands
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HIWIC-D-9ESW EthernetSwitch Interface Cards
Cisco Integrated Services Routers Generation 2
Standards
—
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
MIBs
RFCs
—
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature.
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for QinQ and L2PT
Table 1 lists the release history for this feature.

Note
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Glossary
ACL—access control list
CDP—Cisco Discovery Protocol
DTP—Dynamic Trunking Protocol
L2PT—Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
PAgP—Port Aggregation Protocol
VTP—VLAN Trunking Protocol
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback