Configure Licenses and Throughput for Catalyst 8000 Series Physical Platforms
Available licenses
This document provides information about the licenses that are available for Cisco Catalyst 8200, 8300, and 8500 Edge Platforms, the supported throughput options, and how you can configure the license and the throughput.
The information applies predominantly to a device operating in the autonomous mode. References to the controller mode are included in certain sections for the sake of comparison and completeness. Where the information applies to controller mode, this has been called-out categorically.
For a more detailed overview on Cisco Licensing, go to https://cisco.com/go/licensingguide.
What's new and changed
The following table provides a summary of license related changes applicable to the Cisco Catalyst 8200, 8300, and 8500 Edge platforms. The table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
|
Feature name |
Release |
Feature information |
|---|---|---|
|
500 Mbps aggregate for Tier 1 and 250 Mbps throughput configuration in autonomous mode |
Cisco IOS XE 17.14.1a |
When you configure a throughput of 250 Mbps or T1, if an HSECK9 license is available on the device, then aggregate throughput throttling is effective. Throughput is capped at 500 Mbps and any distribution of traffic in the upstream and downstream direction is allowed. In earlier releases, bidirectional throughput throttling was applicable to T1 and 250 Mbps. Throughput was capped at 250 Mbps in each direction. For more information, see Release-wise changes in throttling behavior. |
|
Aggregate throughput throttling - physical platforms |
Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.8.1a |
For throughput levels greater than 250 Mbps and Tier 2 and higher tiers, when you configure the bidirectional throughput value on the device, aggregate throughput throttling is effective. This means that traffic is throttled in an aggregate manner irrespective of the distribution of the traffic in the upstream and downstream direction. Bidirectional throughput is represented in the license PID. For example, in DNA-C-500M-E-3Y and DNA-C-T2-E-3Y, the aggregate throughput is double the bidirectional throughput. For more information, see Release-wise changes in throttling behavior. |
|
Tier-based licenses |
Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1a |
Support for tier-based throughput configuration was introduced in addition to existing bandwidth-based (numeric) throughput configuration. Starting with the lowest throughput level, the available tiers are Tier 0 (T0), Tier 1 (T1), Tier 2 (T2), and Tier3 (T3). Each tier represents a throughput level. If the license PID for a product is tier-based, the license is displayed with the tier value in the CSSM Web UI. For a product with a tier-based license, you can configure a tier-based throughput value, and you can also convert to a tier-based throughput value. For more information, see Throughput and Numeric and tier-based throughput. |
|
Cisco Digital Network Architecture (DNA) licenses |
Cisco IOS XE Amsterdam 17.3.2 |
Support for Cisco DNA licenses was introduced. Cisco DNA Licenses are categorised into network-stack licenses and a DNA-stack add-on licenses. For more information, see Cisco DNA license. |
|
High Security license (HSECK9) |
Cisco IOS XE Amsterdam 17.3.2 |
Support for the HSECK9 license was introduced. For more information, see High Security license. |
|
Cisco Unified Border Element license (Cisco UBE license) Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express license (Cisco Unified CME license) Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony license (Cisco Unified SRST license) |
Cisco IOS XE Amsterdam 17.3.2 |
Support for Cisco UBE, Cisco Unified CME, Cisco Unified SRST licenses was introduced. For more information, see Cisco Unified Border Element license, Cisco Unified CME license, and Cisco Unified SRST license. |
Use the Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access the Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Cisco DNA license
A Cisco Digital Network Architecture (DNA) software license is a subscription-based licensing model that combines several feature-specific licenses. A Cisco DNA license includes all feature licenses except the following: High Security (HSECK9), Cisco Unified Border Element (Cisco UBE), Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (Cisco Unified CME), and Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony (Cisco Unified SRST).
Cisco DNA licenses are categorized into network-stack licenses and DNA-stack add-on licenses. See the lists in this section that specify the Cisco DNA Licenses that are available on Cisco Catalyst 8200, 8300, and 8500 Edge platforms.
Cisco DNA Licenses Available on Catalyst 8200 and 8300 Series Edge Platforms:
Network-stack licenses:
-
Network Essentials
-
Network Advantage: Includes features that are available with Network Essentials, and more.
-
Network Premier: Includes features that are available with Network Essentials, Network Advantage, and more.
DNA-stack add-on licenses:
-
Cisco DNA Essentials: Add-on license that is available only with Network Essentials.
-
Cisco DNA Advantage: Add-on license that's available only with Network Advantage. Includes features available with DNA Essentials and more.
-
Cisco DNA Premier: Add-on license that's available only with Network Premier. Includes features available with DNA Essentials, DNA Advantage and more.
Cisco DNA Licenses Available on Catalyst 8500 Series Edge Platforms:
Network-stack licenses:
-
Network Advantage
-
Network Premier: Includes features available with Network Advantage, and more.
DNA-stack add-on licenses:
-
Cisco DNA Advantage
-
Cisco DNA Premier: Add-on license that's available only with Network Premier. Includes features available with DNA Advantage and more.
Guidelines for using a Cisco DNA license
-
A network-stack license is a perpetual or permanent license and has no expiration date.
-
A DNA-stack add-on license is a subscription or a term license that is valid only until a certain date. A 3-year and a 5-year option is available for all DNA-stack add-on licenses. A 7-year subscription option is also available for certain DNA-stack add-on licenses.
-
Tier 3 (T3) or higher tiers are not supported with the Network Essentials and DNA Essentials licenses. If you have configured T3 or higher tiers as the throughput, you cannot change the boot level license to Network Essentials and DNA Essentials. For information about the various tiers available with Cisco DNA Licenses, see Tier and numeric throughput mapping.
-
The DNA-stack add-on license that is available with each network-stack license is optional. You can configure a network-stack license without a DNA-stack add-on license, but you cannot configure DNA-stack add-on license without the corresponding network-stack license.
-
If you use a DNA-stack add-on license, renew the license before term expiry to continue using it, or deactivate the DNA-stack add-on license and then reload the device to continue operating with the network-stack license capabilities.
Ordering considerations for a Cisco DNA license
-
A Cisco DNA license subsumes all performance, boost, and technology package licenses (securityk9, uck9, and appxk9). Thus, when you order a Cisco DNA network-stack license, or a Cisco DNA-stack add-on license, if a performance, boost, and technology package license is required or applicable, it is automatically added to the order.
-
The license Product ID (PID) you purchase can only be a DNA-stack add-on license PID.
-
Even if you order a Cisco DNA license along with a new hardware, the license is not preconfigured on the device. You must configure the boot level license and then the throughput on the device.
-
When ordering a Cisco DNA license, you must also specifiy a throughput value. If the throughput you order is greater than 250 Mbps, an HSECK9 license is required on all variants of Cisco Catalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family except for Catalyst 8500 and 8500L Series Edge Platforms. For more information, see High Security license.
-
When you order a license PID with a tier-based throughput value of T1, an HSECK9 license is automatically added to the order.
Configure a boot level license
If you've purchased a Cisco DNA license for a new device, or if you have an existing device and you want to upgrade, downgrade, add, or remove the currently configured license on your device, perform these steps.
This task sets a boot level license and requires a reload before the configured changes are effective.
Step 1 | show version Displays the currently set boot level license. In the accompanying example, Network Advantage and DNA Advantage licences are configured on the device. Example: |
Step 2 | configure terminal Enters global configuration mode. Example: |
Step 3 | [no] license boot level {network-advantage [addon dna-advantage] | network-essentials [addon dna-essentials] | network-premier [addon dna-premier] } Sets a boot level license. First, configure a network-stack license and then configure the corresponding add-on license. In the command syntax, the configuration of a DNA-stack add-on license is optional. The accompanying example shows configuration on a C8300-1N1S-4T2X router. The network-stack license, Network Premier, and the corresponding add-on license: DNA-Premier, are configured. Example: |
Step 4 | exit Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. Example: |
Step 5 | copy running-config startup-config Saves your entries in the configuration file. Example: |
Step 6 | reload Reloads the device. The license levels you previously configured are effective and displayed only after this reload. Example: |
Step 7 | show version Displays the currently set boot level license. In the accompanying example, the output confirms that Network Premier and DNA-Premier licenses are configured. Example: |
Step 8 | show license summary Displays a summary of license usage which includes information about licenses being used, the count, and the status. Example: |
What's next
Configure the throughput based on your license. For more information, see Throughput
High Security license
The High Security license (HSECK9 license) is an export-controlled license and is restricted by U.S. export control laws. This license is required for the use of full cryptographic functionality. That is, for throughput greater than 250 Mbps and tunnel count over and above a certain number. Note that this requirement applies to all devices of Cisco Catalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family except for Catalyst 8500 and 8500L Series Edge Platforms.
On Cisco Catalyst 8500 and 8500L Series Edge Platforms, the throughput and tunnel scale are not impacted by the non-availability of the HSECK9 license. On these platforms, the HSECK9 license is required only for compliance purposes. On all the remaining models of Cisco Catalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family, the supported tunnel count and throughput are restricted in the absence of an HSECK9 license.
This table specifies the supported tunnel count and supported throughput without the HSECK9 license:
|
PID |
No. of tunnels without HSECK9 license |
Supported throughput without HSECK9 license |
|---|---|---|
|
C8200-1N-4T |
1000 |
T0, T1 |
|
C8200L-1N-4T |
1000 |
T0, T1 |
|
C8300-1N1S-4T2X |
1000 |
T0, T1 |
|
C8300-1N1S-6T |
1000 |
T0, T1 |
|
C8300-2N2S-4T2X |
1000 |
T0, T1 |
|
C8300-2N2S-6T |
1000 |
T0, T1 |
|
C8500-12X4QC |
N/A |
N/A |
|
C8500-12X |
N/A |
N/A |
|
C8500-20X6C |
N/A |
N/A |
|
C8500L-8S4X |
N/A |
N/A |
The term throughput refers to encrypted and unencrypted throughput, combined.
By using an HSECK9 license, the tunnel count restriction is lifted and you can configure throughput greater than 250 Mbps. For detailed information about the available throughput options, see Tier and numeric throughput mapping.
Verify HSECK9 license usage
To know if an HSECK9 license is being used on your device, enter the show license summary command in privileged EXEC mode. The HSECK9 license as displayed as: Router US Export Lic. for DNA (DNA_HSEC).
Device# show license summary
Account Information:
Smart Account: Eg-SA As of Dec 03 15:26:02 2021 UTC
Virtual Account: Eg-VA
License Usage:
License Entitlement Tag Count Status
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
network-advantage_T2 (NWSTACK_T2_A) 1 IN USE
dna-advantage_T2 (DSTACK_T2_A) 1 IN USE
Router US Export Lic... (DNA_HSEC) 1 IN USE
Guidelines for using an HSECK9 license
An HSECK9 license is tied to a chassis. Therefore, one HSECK9 license is required for each chassis UDI where you want to use cryptographic functionality.
An HSECK9 license requires authorization before you can use it. This authorisation is provided by a Smart Licensing Authorization Code (SLAC). Generate and obtain an SLAC from the Cisco SSM portal before you install the SLAC for each HSECK9 license you use.
The method of obtaining an SLAC from the Cisco SSM portal depends on the topology you have implemented. For more information, see Install SLAC for an HSECK9 license.
Verify HSECK9 status
To know if SLAC is installed, enter the show license authorization command in privileged exec mode. If SLAC is installed, the status field displays: SMART AUTHORIZATION INSTALLED on <timestamp>.
Device# show license authorization
Overall status:
Active: PID:C8300-1N1S-4T2X,SN:FDO2250A0J5
Status: SMART AUTHORIZATION INSTALLED on Dec 03 08:24:35 2021 UTC
Last Confirmation code: 418b11b3
Authorizations:
Router US Export Lic. for DNA (DNA_HSEC):
Description: U.S. Export Restriction Compliance license for DNA based Routers
Total available count: 1
Enforcement type: EXPORT RESTRICTED
Term information:
Active: PID:C8300-1N1S-4T2X,SN:FDO2250A0J5
Authorization type: SMART AUTHORIZATION INSTALLED
License type: PERPETUAL
Term Count: 1
Purchased Licenses:
No Purchase Information Available
Ordering considerations for an HSECK9 license
If you place an order for your Cisco Catalyst 8000 platform and your DNA licenses together, the HSECK9 license is automatically added to the order, if applicable. For example, in case of Catalyst 8500 Series Edge Platforms, when you order the hardware, an HSECK9 license is automatically added to the order because throughput support starts at greater than 250 Mbps on these platforms. Further, the requisite SLAC for the HSECK9 license is also factory-installed on the device.
If you order your DNA license separately, the HSECK9 license is not added automatically to your oder. You must separately order the HSECK9 license, if required.
If you plan to use an HSECK9 license with your hardware, provide your Smart Account and Virtual Account information along with the hardware order. This enables Cisco to factory-install SLAC for the HSECK9 license on the hardware. You must still configure throughput on the device before you start using it.
If you order the HSECK9 license separately and not with the hardware, SLAC cannot be factory-installed.
Install SLAC for an HSECK9 license
A Smart Licensing Authorization Code (SLAC) is generated in and obtained from Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) portal.
To obtain the SLAC, there are multiple ways in which a product may be connected to the Cisco SSM portal. Each way of connecting to Cisco SSM is called as a topology. You must implement one of the supported topologies before you can install SLAC.
For information about all the methods, see the Supported Topologies section in the Smart Licensing Using Policy for Cisco Enterprise Routing Platforms document.
Ensure that a boot level license is already configured on the device. To know how to configure a boot license, see Configure a boot level license.
In the output of the show version privileged EXEC command, ensure that a license is mentioned in the License Level field.
Required tasks after installing SLAC
Complete the following required tasks after installing SLAC - only if applicable to the platform:
|
Platform |
Required Tasks After Installing SLAC |
|---|---|
|
For Cisco Catalyst 8200 and 8300 Series Edge Platforms |
Enter the license feature hseck9 command in global configuration mode. This enables the HSECK9 license on these platforms. |
|
For Cisco Catalyst 8500L Series Edge Platforms |
Reload the device after installing SLAC. |
Where to go next:
Configure the throughput based on your license. For more information, see Throughput.
Cisco Unified SRST license
A Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony License (Cisco Unified SRST license) does not require any boot level configuration before you enable it.
In the context of this licensing model, a Unified SRST license is an unenforced license. You must order a Cisco Unified SRST license separately, if required. It is not automatically included with any other license.
Additional references
-
To configure the available Unified SRST features, refer to the configuration guide. For information about the features available with a Cisco Unified SRST license, see the Cisco Unified SCCP and SIP SRST System Administrator Guide (All Versions).
-
For information about supported platforms and about purchasing a Cisco Unified SRST license, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/unified-communications/unified-communications-manager-express/datasheet-c78-744069.html.
-
For information about how to report usage of a Unified SRST license, see Smart Licensing Using Policy for Cisco Enterprise Routing Platforms.
What to do next:
After you purchase this license, configure the throughput. For more information, see Throughput.
Cisco Unified Border Element license
A Cisco Unified Border Element (Cisco UBE) license does not require any boot level configuration before you enable it. After purchase, you can refer to the configuration guide to configure the available Cisco UBE features.
You must order a Cisco UBE license separately, if required. Cisco UBE license is not automatically included with any other license.
Additional References
-
For information about the features available with a Cisco UBE license, see the Cisco Unified Border Element Configuration Guide.
-
For release-based information, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/unified-border-element/products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html.
-
For information about supported platforms and about purchasing a Cisco UBE license, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/unified-communications/unified-border-element/data-sheet-c78-729692.html.
-
For information about how to report usage of a Cisco UBE license, see Smart Licensing Using Policy for Cisco Enterprise Routing Platforms. In the context of this document, a Cisco UBE license is an unenforced license.
What to do next:
After you enable your license, configure the throughput. For more information, see Throughput.
Cisco Unified CME license
A Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express License (Cisco Unified CME license) does not require any boot level configuration before you enable it. After purchase, you can refer to the configuration guide to configure the available features.
Additional references
-
For information about the features available with a Cisco Unified CME license, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide.
-
For information about supported platforms and about purchasing a Cisco Unified CME license, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/unified-communications/unified-communications-manager-express/datasheet-c78-744069.html. You must order a Cisco Unified CME license separately, if required. It is not automatically included with any other license.
-
For information about how to report usage of a Cisco Unified CME license, see Smart Licensing Using Policy for Cisco Enterprise Routing Platforms. In the context of this document, a Cisco Unified CME license is an unenforced license.
What to do next:
After you enable your license, configure the throughput. For more information, see Throughput.
Throughput
Throughput is a measure of the data that is transmitted through a network in a given amount of time. In the context of licensing, throughput tells you how much data is allowed to be transferred through a device.
You must first configure the throughput value in the autonomous mode before data can be transmitted (Tx) and received (Rx) at the configured rate. If you don’t explicitly configure a throughput value, the default throughput is effective.
To know the configured throughput of a device, enter the show platform hardware throughput level command in privileged EXEC mode.
The following sections provide information about how a throughput value is represented, whether the throughput on a device refers to encrypted or unencrypted throughput and what this means, and if and how a limit may be enforced on a device throughput.
Numeric and tier-based throughput
Your Cisco DNA license product ID or PID contains the throughput you are entitled to. The throughput value is either represented by a number or by a tier in the PID. The same value is configured on the device.
Numeric throughput value
When throughput is represented by a number, it is called a numeric throughput value. For example, DNA-C-10M-E-3Y is a license PID with a numeric throughput value of 10M or 10 Mbps.
Depending on the device, some of the other available numeric throughput values are: 15M, 25M, 50M, 100M, 250M, 500M, 1G, 2.5G, 5G, 10G, and so on. Throughput greater than 250 Mbps requires an HSECK9 license.
Tier-Based throughput value
When throughput is represented by a tier, it is called a tier-based throughput value. A tier represents a throughput level and is mapped to a numeric throughput value. For example, DNA-C-T0-E-3Y is a license PID with a tier-based throughput value of T0. The numeric equivalent it is mapped to is a throughput of up to 25 Mbps.
Tier-based throughput configuration is supported starting with Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1a. From this release onwards, tier-based throughput configuration is also the recommended way of configuring throughput on the device.
Starting with the lowest throughput level, the available tiers are Tier 0 (T0), Tier 1 (T1), Tier 2 (T2), Tier 3 (T3), Tier 4 (T4), and Tier 5 (T5). T2 and higher tiers require an HSECK9 license.
Notes about tiers
-
Not all tiers are available with all Cisco DNA licenses. For example, T3 and higher tiers are not available with the Network Essentials and DNA-Essentials licenses. This also means that if you have T3 as the configured throughput, you cannot change the boot level license to Network Essentials and DNA Essentials.
-
Each tier maps to or means a different numeric value for different platforms.
The different platforms in the Cisco Catalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family support different maximum throughput levels. For example, T2 means 1G throughput for C8300-2N2S-4T2X, 500M for C8200-1N-4T, and 250M for C8200L-1N-4T.
Additional references
-
To know which tiers are available with a particular DNA License and to know the numeric equivalent of each tier for a particular platform and see the Tier and numeric throughput mapping section.
-
To know when to configure a numeric throughput value and when to configure tier-based throughput on your device, see the Numeric vs. tier-based throughput configuration section.
Numeric vs. tier-based throughput configuration
With the introduction of tier-based throughput configuration in Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1a, you can configure both numeric and tier-based throughput on your device. This section provides information about when to configure a numeric throughput value and when to configure tier-based throughput.
Identifying whether you have tier-based or numeric licenses
Cisco Smart Software Manager (Cisco SSM) is a portal that enables you to manage all your Cisco software licenses. All the license PIDs you purchase are listed in the Cisco SSM Web UI at: https://software.cisco.com → Manage licenses.
To identify whether you have a tier-based license or a numeric license, log in to the portal and in the corresponding Smart Account and Virtual Account, navigate to Inventory > Licences. The UI displays the throughput type. See this sample screenshot that shows you how tier-based and numeric licenses are displayed:

Configure a numeric or tier-based throughput value
-
If you purchase a numeric license PID, the license is displayed with the numeric throughput value and tier-based value in the Cisco SSM Web UI. For such a license, we recommend that you configure only a numeric throughput value. For more information, see Configure numeric throughput.
-
If you purchase a tier-based license PID, the license is displayed with only the tier value in the Cisco SSM Web UI. For such a license, you can either configure a tier-based throughput value to match the display in the CSSM Web UI, or you can configure a numeric throughput value. For more information, see Configure Tier-Based Throughput or Configure a Numeric Throughput.
Convert a numeric throughput to tier-based and vice versa
This table specifies when you can convert from numeric to tier-based throughput configuration, or vice versa, when this conversion is required, and when it is optional.
|
If you... |
then... |
|---|---|
|
configure a numeric throughput value on the device and the license PID is a numeric license, |
do not convert to tier-based throughput value. |
|
configure a numeric throughput value on the device and the license PID is a tier-based license, |
you can convert the throughput configuration to tier-based value. There is no functional impact if you do not convert to a tier-based throughput value. For more information, see Convert a numeric throughput value to tier-based. |
|
upgrade to a release where tier-based throughput values are supported and the license PID is tier-based, |
you can convert the throughput to tier-based value after upgrade.There is no functional impact if you do not convert to a tier-based throughput value. For more information, see Upgrade from numeric throughput to tier-based throughput. |
|
upgrade to a release where tier-based throughput values are supported, and your license PID is numeric, |
do not convert to a tier-based throughput value. |
| downgrade to a release where only numeric throughput values are supported and your license PID and throughput configuration are tier-based, |
change the configuration to a numeric throughput value before you downgrade. For more information, see Downgrade tier-based throughput to numeric throughput. |
Tier and numeric throughput mapping
This section provides information about the numeric equivalent of each tier and the DNA licenses that each tier is available with.
Tier and numeric throughput mapping for Cisco Catalyst 8000 physical platforms

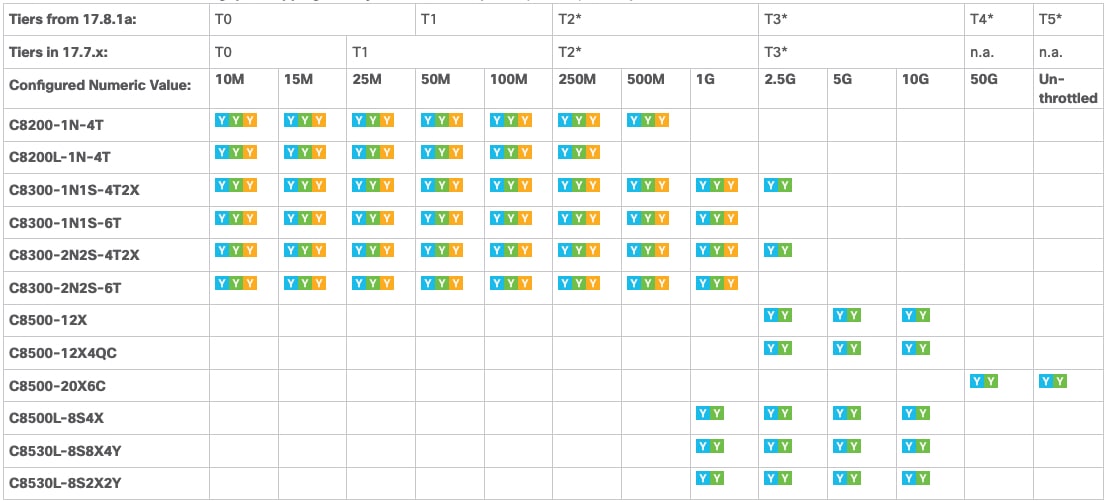
The mapping table in these images clarify only the numeric equivalent of a tier. This mapping does not reflect the final throughput that you are entitled to. The entitled throughput depends on the device’s capability, the software version running on the device, and the throttling behavior for that version. For more information, see Entitled Throughput and Throttling Specifications in the Autonomous Mode.
When you purchase a license PID with a tier-based throughput value of T1, an HSECK9 license is automatically provided.
Encrypted and unencrypted throughput
Encrypted throughput, also known as crypto throughput, is throughput that is protected by a cryptographic algorithm.
Unencrypted throughput on the other hand, is in plain text. Unencrypted throughput is also referred to as Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) traffic.
All references to throughput in this document refer to cryptographic throughput.
Throttled and unthrottled throughput
Throttled throughput, is throughput on which a limit has been enforced. When you configure a throughput value, you are throttling device throughput to the configured extent.
Unthrottled throughput means that no limit is enforced, and the device throughput is at the maximum capability of the device.
Unencrypted throughput (Tx and Rx), is unthrottled by default.
Types of throttling behavior: aggregate and bidirectional
The system can impose throttling in a bidirectional manner or an aggregate manner.
Bidirectional throughput throttling
Here, the system throttles data in each direction. When bidirectional throttling is effective, Tx and Rx data are capped at the bidirectional throughput value separately.
For example, if the bidirectional throughput value is 25 Mbps or T0, and bidirectional throughput throttling is effective, Tx data is capped at 25 Mbps and Rx data is capped at 25 Mbps.
The value that you see in a license PID (whether numeric or tier-based) represents a bidirectional throughput value.
Aggregate throughput throttling
Here, the system doubles the configured value and throttles throughput at this aggregate limit. When aggregate throughput throttling is effective, traffic is not throttled separately in each direction.
For example, if the bidirectional throughput value that is configured is 500 Mbps and aggregate throughput throttling is effective, the traffic in the upstream and downstream direction can be any ratio within the 1 Gbps aggregate limit. For instance, 800 Mbps Tx and 200 Mbps Rx, or, 300 Mbps Tx and 700 Mbps Rx.
Release-wise changes in throttling behavior
To know if the throughput on your device will be throttled in a bidirectional manner or in an aggregate manner, check the software version running on the device. Refer to the release-wise changes in throttling behavior described in this table to identify the throttling behavior.
|
Cisco IOS XE release |
Throttling behavior |
|---|---|
|
Starting with Cisco IOS XE 17.14.1a |
When you configure a throughput of 250 Mbps or T1, aggregate throughput throttling is effective as long as an HSECK9 license is available on the device. This means an aggregate limit of 500 Mbps is available for use in any Tx and Rx ratio. If an HSECK9 license is not available on the device and you configure a throughput value of 250 Mbps, or T1, then bidirectional throughput throttling is effective. The throughput is throttled at 250 Mbps in each direction. |
|
Starting with Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.8.1a |
When you configure a throughput value greater than 250 Mbps or T2 and higher tiers, aggregate throughput throttling is effective. On C8200L-1N-4T, if you configure a numeric value of 250 Mbps, bidirectional throughput throttling is effective and a maximum of 250 Mbps is available in each direction. But if you configure tier T2, aggregate throttling is effective and 500 Mbps is available for use in any Tx and Rx ratio. |
|
Until Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.x |
Only bidirectional throughput throttling is effective. |
Entitled throughput and throttling specifications in the autonomous mode
These tables tell you about the throughput you are entitled to. This is based on the device, the throughput value, which can be aggregate or numeric, and the release, which determines if throttling is imposed in an aggregate or bidirectional manner.
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput * HSECK9 license is required. |
||||
|
Supported throughput values (default 10M) |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.4.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.7.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.8.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.14.1a |
|
10M |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
|
15M |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
|
25M |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
50M |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
|
100M |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
|
250M |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
500M* |
500M bidirectional |
500M bidirectional |
1G aggregate |
1G aggregate |
|
T0 |
- |
15M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
T1 |
- |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
T2 |
- |
500M bidirectional |
1G aggregate |
1G aggregate |
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput * HSECK9 license is required. |
||||
|
Supported throughput values (default 10M) |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= >= 17.5.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.7.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.8.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.14.1a |
|
10M |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
|
15M |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
|
25M |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
50M |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
|
100M |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
|
250M |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
T0 |
- |
15M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
T1 |
- |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
T2* |
- |
250M bidirectional |
500M aggregate |
500M aggregate |
| - |
From 17.8.1a, On C8200-1N-4T-L, if you configure a numeric value of 250 Mbps, a maximum of 250 Mbps is available in each direction. But if you configure tier-based value T2, which requires an HSECK9 license, 500 Mbps is available for use in any Tx and Rx ratio. |
|||
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput * HSECK9 license is required. |
||||
|
Supported throughput values (default 10M) |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.3.2 |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.7.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.8.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.14.1a |
|
10M |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
|
15M |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
|
25M |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
50M |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
|
100M |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
|
250M |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
500M* |
500M bidirectional |
500M bidirectional |
1G aggregate |
1G aggregate |
|
1G* |
1G bidirectional |
1G bidirectional |
2G aggregate |
2G aggregate |
|
2.5G* |
2.5G bidirectional |
2.5G bidirectional |
5G aggregate |
5G aggregate |
|
T0 |
- |
15M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
T1 |
- |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
T2* |
- |
1G bidirectional |
2G aggregate |
2G aggregate |
|
T3* |
- |
10G bidirectional |
20G aggregate |
20G aggregate |
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput * HSECK9 license is required. |
||||
|
Supported throughput values (default 10M) |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.3.2 |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.7.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.8.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.14.1a |
|
10M |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
10M bidirectional |
|
15M |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
15M bidirectional |
|
25M |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
50M |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
50M bidirectional |
|
100M |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
|
250M |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
250M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
500M* |
500M bidirectional |
500M bidirectional |
1G aggregate |
1G aggregate |
|
1G* |
1G bidirectional |
1G bidirectional |
2G aggregate |
2G aggregate |
|
T0 |
- |
15M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
25M bidirectional |
|
T1 |
- |
100M bidirectional |
100M bidirectional |
With HSECK9: 500M aggregate Without HSECK9: 250M bidirectional |
|
T2* |
- |
1G bidirectional |
2G aggregate |
2G aggregate |
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput *HSECK9 license required for compliance purposes only. |
|||
|
Supported throughput values (default 10M) |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.3.2 |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.7.1a |
Entitled throughput & throttling in >= 17.8.1a |
|
2.5G* |
2.5G bidirectional |
2.5G bidirectional |
5G aggregate |
|
5G* |
5G bidirectional |
5G bidirectional |
10G aggregate |
|
10G* |
10G bidirectional |
10G bidirectional |
20G aggregate |
|
T3* |
- |
10G bidirectional |
20G aggregate |
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput *HSECK9 license required for compliance purposes only. |
|||
|
Supported Throughput Values (default 10M) |
Entitled Throughput & Throttling in >= 17.4.1a |
Entitled Throughput & Throttling in >= 17.7.1a |
Entitled Throughput & Throttling in >= 17.8.1a |
|
1G* |
1G Bidirectional |
1G Bidirectional |
2G Aggregate |
|
2.5G* |
2G Bidirectional |
2G Bidirectional |
5G Aggregate |
|
5G* |
5G Bidirectional |
5G Bidirectional |
10G Aggregate |
|
10G* |
10G Bidirectional |
10G Bidirectional |
20G Aggregate |
|
T2* |
- |
1G Bidirectional |
2G Aggregate |
|
T3* |
- |
10G Bidirectional |
20G Aggregate |
|
Throughput = Encrypted Throughput *HSECK9 license required for compliance purposes only. |
|
|
Supported Throughput Values (default T4) |
Entitled Throughput and Throttling in >= 17.10.1a |
|
T4* |
50G Aggregate |
|
T5* |
Unthrottled |
Entitled throughput and throttling specifications in the SD-WAN controller mode
| PID |
Introductory release for PID |
Throughput without HSECK9 - bi-directional | Throughput with HSECK9 (>=17.3.2 and <17.8.1a, bi-directional) |
Throughput with HSECK9 (>17.8.1a, aggregate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C8300-1N1S-4T2X (default 250M) |
17.3.2 |
250M |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
|
C8300-2N2S-6T (default 250M) |
17.3.2 |
250M |
1G |
2G |
|
C8300-1N1S-6T (default 250M) |
17.3.2 |
250M |
1G |
2G |
|
C8300-2N2S-4T2X (default 250M) |
17.3.2 |
250M |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
|
C8200-1N-4T (default 250M) |
17.4.1a |
250M |
500M |
1G |
|
C8200L-1N-4T (default 250M) |
17.5.1a |
250M |
250M |
500M |
|
C8500-12X4QC (default unthrottled) |
17.3.2 |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
|
C8500-12X (default unthrottled) |
17.3.2 |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
|
C8500L-8S4X (default unthrottled) |
17.4.1a |
unthrott led |
unthrottled |
unthrottled |
|
C8500-20X6C (default T4) |
17.10.1a |
unthrottled |
- |
unthrottled |
Configure numeric throughput
This task shows you how to change the numeric throughput level. If you do not configure a throughput level, the platform's default throughput level is effective.
Before you begin
-
Read the sections Numeric and tier-based throughput and Numeric vs. tier-based throughput configuration.
-
Ensure that a boot level license is already configured on the device. Otherwise you will not be able to configure a throughput value. See Configure a boot level license. In the output of the show version privileged EXEC command, ensure that a license is mentioned in the
License Levelfield. -
If you're configuring throughput greater than 250 Mbps, you must install a Smart Licensing Authorization Code (SLAC) before you start with this task. To know how to do this, see Install SLAC for an HSECK9 license.
-
You can configure the
250Mvalue with or without an HSECK9 license. The difference is that aggregate throttling is effective if HSECK9 is available on the device. For more information, see Release-wise changes in throttling behavior. -
Note the throughput you are entitled to. This is indicated in the Cisco DNA license PID you purchase.
Step 1 | show platform hardware throughput level Displays the current throughput level on the device. In the accompanying example:
Example: |
Step 2 | configure terminal Enters global configuration mode. Example: |
Step 3 | platform hardware throughput crypto {100M | 10M | 15M | 1G | 2.5G | 250M | 25M | 500M | 50M} Configures the throughput level. The displayed throughput options depend on the device. Ensure that a boot level license is configured. Else, the command is not recognized as a valid one on the command line interface. In the accompanying example, 1 Gbps is the throughput that is configured, and the software version running on the device is Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.8.1a. This means that aggregate throughput throttling applies. After reload, the sum of upstream and downstream throughput will not exceed the 2 Gbps limit. Example: |
Step 4 | exit Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. Example: |
Step 5 | copy running-config startup-config Saves your entries in the configuration file. Example: |
Step 6 | reload Reloads the device. Example: |
Step 7 | show platform hardware throughput level Displays the current throughput level on the device. You can also enter the show platform hardware qfp active feature ipsec state privileged EXEC command to display the configured throughput level. Example: |
Configure tier-based throughput
This task shows you how to configure a tier-based throughput level. If you do not configure a throughput level, the platform's default throughput level is effective.
Tier-based throughput levels are supported starting with Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1a release.
Configuration of a throughput level requires a reload on physical platforms.
Before you begin
-
Read the sections Numeric and tier-based throughput and Numeric vs. tier-based throughput configuration.
-
Ensure that a boot level license is already configured on the device. Otherwise you will not be able to configure a throughput value. To know how to configure boot level license, see Configure a boot level license. In the output of the show version privileged EXEC command, ensure that a license is mentioned in the
License Levelfield. -
If you're configuring Tier 2 (T2) or a higher tier, you must install a Smart Licensing Authorization Code (SLAC) before you start with this task. To know how to do this, see Install SLAC for an HSECK9 license. T2 or higher tiers are not displayed if SLAC is not installed.
-
If you want to configure Tier 3 (T3), ensure that the boot level license is Network Advantage/ DNA Advantage, or Network Premier/DNA Premier. T3 and higher tiers are not supported with Network Essentials and DNA Essentials.
-
You can configure the
T1value with or without an HSECK9 license. The difference is that aggregate throttling is effective if HSECK9 is available on the device. For more information, see Release-wise changes in throttling behavior. -
Note the throughput you are entitled to. This is indicated in the Cisco DNA license PID you purchase.
Step 1 | show platform hardware throughput crypto Displays the current throughput level on the device. In the accompanying example, the show platform hardware throughput crypto sample output is on C8300-2N2S-4T2X. Here, the throughput is currently throttled at 250 Mbps. Example: |
Step 2 | show license authorization (Optional) Displays SLAC information on the product instance. In the accompanying example, SLAC is installed on the platform. This is so we can configure T2. Example: |
Step 3 | configure terminal Enters global configuration mode. Example: |
Step 4 | platform hardware throughput crypto {T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5} Configures a tier-based throughput. The throughput options that are displayed depend on the device. Only tiers are mentioned in the command for the sake of clarity. When you enter the command on the CLI, numeric and tier values are displayed, as shown in the accompanying example.
In the accompanying example,
Example: |
Step 5 | exit Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. Example: |
Step 6 | copy running-config startup-config Saves your entries in the configuration file. Example: |
Step 7 | reload Reloads the device. Example: |
Step 8 | show platform hardware throughput crypto Displays the current throughput level on the device. In the accompanying example, the tier value is set to T2. You can also enter the show platform hardware qfp active feature ipsec state privileged EXEC command to display the configured throughput level. Example: |
Convert a numeric throughput value to tier-based
This task shows you how to convert a numeric throughput value to a tier-based throughput value. To know how numeric throughput values are mapped to tier values, see: Tier and numeric throughput mapping .
Converting the throughput level requires a reload.
Before you begin
-
Read the Numeric vs. tier-based throughput configuration section.
-
Ensure that a SLAC is installed on the device if you're converting a numeric throughput that is equal to or greater than 250 Mbps. To know how to install SLAC, see Install SLAC for an HSECK9 license.
-
Ensure that the software version running on the device is Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1a or a later release.
Step 1 | show platform hardware throughput crypto Displays the currently running throughput on the device. Example: |
Step 2 | license throughput crypto auto-convert Converts the numeric throughput to a tier-based throughput value. The converted tier value is displayed on the CLI. Example: |
Step 3 | copy running-config startup-config Saves your entries in the configuration file. Even though the command you use to convert from numeric to tier-based throughput is a privileged EXEC command, it changes running configuration from a numeric value to a tier-based value. You must therefore save the configuration for the next reload to be displayed with a tier value. Example: |
Step 4 | reload Reloads the device. Example: |
Step 5 | show platform hardware throughput crypto Displays the currently running throughput on the device. Example: |
Step 6 | license throughput crypto auto-convert by entering the Verifies whether the conversion is complete. To cross-check whether the conversion is complete, you can also enter the conversion command again. If the numeric throughput value has already been converted, the system displays a message confirming this. Example: |
Upgrade from numeric throughput to tier-based throughput
If you're upgrading to Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1 or a later release, and the license PID is a tier-based one, you can convert throughput configuration to a tier-based value. You can also retain the numeric throughput configuration.
There is no functional impact if you have a tier-based license PID in Cisco SSM and you configure a numeric throughput value on your device.
If you want to convert to a tier-based value note the required action depending on the throughput level that is configured:
|
Throughput configuration before upgrade |
Action before upgrade |
Action after upgrade to 17.7.1 or later |
|---|---|---|
|
Lesser than 250 Mbps |
No action required. |
|
|
Equal to 250 Mbps |
Obtain an HSECK9 license and install SLAC if you want to convert to T2. | |
|
Greater than 250 Mbps |
No action required. |
Downgrade tier-based throughput to numeric throughput
If you're downgrading to a release where only numeric throughput configuration is supported, you must convert tier-based throughput configuration to a numeric throughput value before you perform the downgrade. This is applicable even if the license PID is a tier-based license PID.
If you configured a tier-based throughput value before you performed a downgrade, and the downgrade goes through, the tier-based configuration is not recognized by a pre-17.7.1 image. The configuration fails, and the throughput is not restored to the pre-downgrade level. In this scenario, you must configure a numeric throughput level after the downgrade is complete.
|
Throughput configuration before downgrade |
Action before downgrade |
Action after downgrade to a pre-17.7.1 version |
|---|---|---|
|
Numeric |
No action required. |
No action required. |
|
Tier |
No action required. |
Report license usage
After you configure your license level and throughput, you should be able to use the features associated with your license. The next step is to monitor your license usage to account for or report the licenses that you use, to Cisco. For this, you have to send a RUM report (Resource Utilization Measurement Report) to Cisco SSM to report license usage information.
To know if reporting is required, wait for a system message or refer to the policy using show commands.
-
If reporting is required, the system displays the message: %SMART_LIC-6-REPORTING_REQUIRED: A Usage report acknowledgment will be required in [dec] days. Here, [dec] is the amount of time (in days) left to meet reporting requirements.
-
If you're using show commands, refer to the output of the show license status privileged EXEC command and check the
Next ACK deadlinefield. This means a RUM report must be sent and the acknowledgment (ACK) from Cisco SSM must be installed by this date.
How you send the RUM report depends on the topology you have implemented in the Smart Licensing Using Policy environment. For more information on sending RUM reports based on your implementation, see How to Configure Smart Licensing Using Policy: Workflows by Topology.The following sections tell you how to monitor the license usage as per the license model.
Smart Licensing Using Policy
With this licensing model, you purchase the licenses you want to use, configure them on the device, and then report license usage, as required. You do not have to complete any licensing-specific operations, such as registering or generating keys before you start using the software and the licenses that are tied to it; unless you're using export-controlled and enforced licenses.
For more information, see Smart Licensing Using Policy for Cisco Enterprise Routing Platforms.
Managed Service Licensing Agreement
A Managed Service License Agreement (MSLA) is a buying program agreement, designed for Service Providers.
-
MSLA in Cisco SD-WAN controller mode
In the Cisco SD-WAN controller mode, an MSLA is supported on all products in the Cisco Catalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family. For more information, see:
Managed Service Licensing Agreement (MSLA) for Cisco SD-WAN At-a-Glance
Cisco SD-WAN Getting Started Guide → Manage Licenses for Smart Licensing Using Policy.
Cisco vManage How-Tos for Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Devices → Manage Licenses for Smart Licensing Using Policy.
-
MSLA in autonomous mode
MSLA is not supported on Cisco Catalyst 8200, 8300, and 8500 platforms in autonomous mode.