Configure Site-Cloud Support for AWS Using Branch Connect Solution
Site to Cloud Support for AWS Using Branch Connect Solution
With growing business needs there is an increased demand to extend the infrastructure without increasing costs. Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN’s Cloud OnRamp solution offers the facility to connect an SD-Routing branch to an Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud and thereby provide access to applications hosted on public clouds. The SD-Routing branch can be a data centre, branch site or campus network. This multicloud solution helps to integrate public cloud infrastructure into enterprise WAN.
This release introduces support to configure site to cloud connectivity from an SD-Routing branch to AWS using the Feature Profiles available as part of Configuration Groups. The Branch Connect solution available as part of Cloud onRamp Multicloud offering uses the Global VRF and Ethernet Interface created using Feature Profiles to establish a connection with the Transit Gateway and then automates the creation of Transit Gateway, deployment of the transit VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), and interconnection between the site and cloud.
Workflow to Configure Site to Cloud Support for AWS
This figure shows the high-level workflow of the process to configure a site to cloud connectivity for AWS.
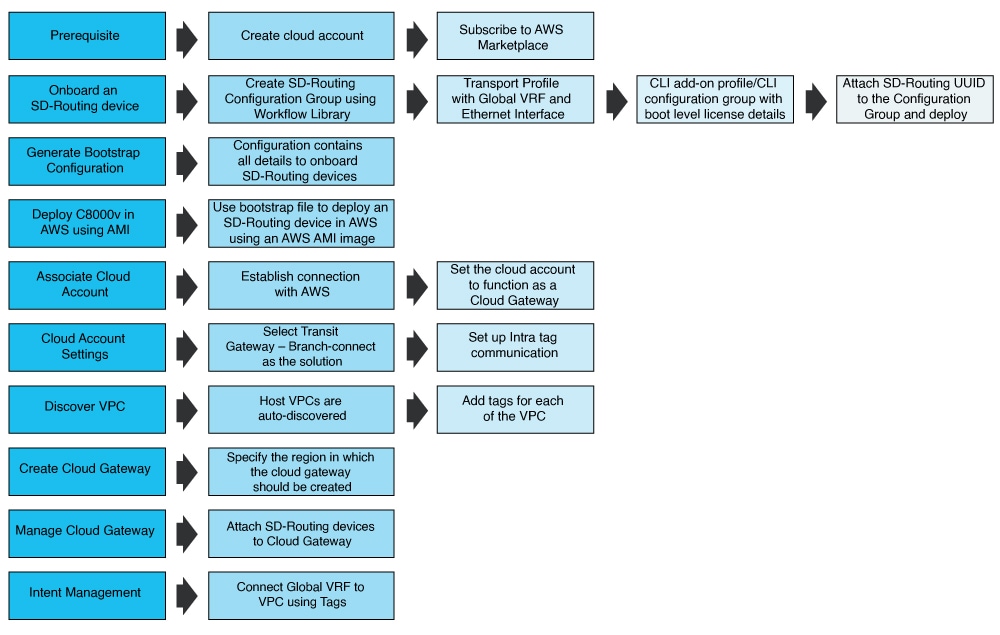
To know more about each step in the workflow, refer the following table.
|
Steps to Configure Site to Cloud Connectivity |
To Know More |
|---|---|
|
Prerequisites |
|
|
Onboard an SD-Routing Device |
|
|
Generate Bootstrap Configuration |
|
|
Deploy C8000v in AWS using AMI |
|
|
Set Up Cloud Account |
|
|
Discover VPC |
|
|
Manage |
|
|
Intent Management |
|
|
Verify |
|
|
Monitor |
Configure Site to Cloud Support for AWS Using Branch Connect Solution
This section describes the various steps involved in configuring site to cloud support for AWS using a Branch Connect solution.
Prerequisites to Configure Site to Cloud Support
Before starting the configuration to establish site to cloud connectivity for AWS, ensure that these prerequisites are met.
AWS Requirements
Set up an AWS cloud account and subscribe to AWS Marketplace using Cisco Catalyst 8000V for SD-WAN & Routing instance as an Amazon Machine Image (AMI).
For details see, Overview of Cisco Catalyst 8000v Edge Software on Amazon Web Services.
IOS XE Software Requirements
The functionality to use a Feature Profile to configure a Global VRF and Ethernet Interface is available from Cisco IOS XE 17.15.1a only. If you are on a release earlier than IOS XE 17.15.1a, you can configure VRF and Ethernet Interface using CLI Configuration Group or CLI Add-on Profile. For details, see Cloud Infrastructure on SD-Routing Devices.
Onboard an SD-Routing Device
The first step to deploying the multicloud solution is to onboard the SD-Routing device into the Cisco SD-WAN Manager. Onboarding requires that the SD-Routing device has a Configuration Group mapped to it with the following details:
-
A transport profile with a Global VRF and one or more ethernet interfaces. The SD-Routing branch can have multiple custom VRFs but currently only the global VRF is supported to connect to the Transit Gateway. For more information see Create a Global VRF in the Transport Profile.
-
A CLI-Add on profile or a CLI configuration group that includes the command to set the boot level license as Network-Advantage for the C8000v device. For more information, see Create a CLI-Add on Profile or Create a CLI Configuration Group.
Use the Workflow Library to Configure Transport Profile
The ethernet interface you set in the Transport Profile forms a connection between the SD-Routing device and the Transit Gateway.
Procedure
Step 1 | On the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager, select . Select Create SD-Routing Config to automatically create a new Configuration Group with basic settings. |
Step 2 | Specify Name and Description. Click Create SD-Routing Config. After the System Profile, Service Profile, and Transport and Management Profile are automatically created, skip adding devices to the Configuration Group. Go back to Configuration Groups listing page and select the configuration group you created. |
Step 3 | Use down arrow to expand the configuration group and select Transport and Management Profile. A global VRF is automatically created. Specify additional details if required. For details, see Global VRF. |
Step 4 | Click Save. |
Step 5 | Click + and select Ethernet Interface. Select + Add New to add an ethernet interface to the global VRF. See Ethernet Interface. Click Save. If you prefer to configure the global VRF and ethernet interface using commands, see Cloud Infrastructure on SD-Routing Devices. |
Configure Boot Level License for Catalyst C8000v Device
The Catalyst 8000V requires a mandatory Cisco DNA subscription license. A subscription license determines the features and throughput level of the Cisco C8000v device. To set a site-to-cloud connectivity, it is important to use DNA Network Advantage license so that IPsec tunnels can be set up between the SD-Routing branch and the Transit Gateway.
Create a CLI-Add on Profile to Add Bootlevel License
Procedure
Step 1 | On the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager, select the configuration group you created. Click + Add Profile. Select CLI Add-On Profile and select Create New to create a new CLI Add-On Profile. Specify name and description of the profile. |
Step 2 | In the Config Preview pane, enter the following command: license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage |
Step 3 | Click Save and Done. |
Create a CLI-Configuration Group to Add Bootlevel License
Procedure
Step 1 | On the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager, select Create Configuration Group. Specify a name and description and select the CLI Configuration Group checkbox. |
Step 2 | In the Config Preview pane, enter the following command: license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage |
Step 3 | Click Save and Done. |
Associate and Deploy the Configuration Group to an SD-Routing Device
Before you begin
Procedure
Step 1 | On Cisco SD-WAN Manager, select the Configuration Group created earlier. |
Step 2 | Click + Add and select the devices from the list. Click Save to attach the configuration group to the selected devices. |
Step 3 | To provision the configuration changes, click Deploy.
|
Generate Bootstrap Configuration
The bootstrap configuration you generate includes details such as UUID (Universally Unique Device Identifier) of the SD-Routing device, the global VRF, ethernet interface and the boot level license as well. This bootstrap configuration is used to deploy an SD-Routing device in AWS using an AWS AMI image.
Procedure
Step 1 | On Cisco SD-WAN Manager, select . |
Step 2 | Select a device, click … and select Edit. Select Bootstrap Configuration. |
Step 3 | Select Cloud-Init. Click Ok. |
Step 4 | In the MIME file pop-up window, click Download. The system downloads the file to your local system and saves it in your directory for downloads. The file name is chassis.cfg, where chassis is the device chassis ID that you uploaded in Step 1 of this task. |
Deploy C8000v Software as an AMI in AWS Console
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is an image that provides the software that is required to set up and boot an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance. This image creates a virtual machine within EC2.
When you set up an AMI in AWS the bootstrap configuration file and public IP address are used to deploy a Cisco C8000v instance and make it accessible across the internet. For more information, see Reference for Amazon EC2 instance configuration parameters.
Set Up Cloud Account
Setting up a cloud account involves setting up a connection between Catalyst SD-WAN Manager and Amazon Web Services (AWS). To form the association, the API details and Secret Key configured while setting up the Amazon Web Services account is required. Also determine if this cloud account should function as a Transit Gateway. A Transit Gateway is a software component that acts as a bridge between the branch and the AWS cloud.
Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to Workflows. Select Associate Cloud Account. | ||||||||||
Step 2 | Specify these details to perform the association between Catalyst SD-WAN Manager and AWS:
| ||||||||||
Step 3 | Click Save. |
Cloud Global Settings
After establishing a connection between Catalyst SD-WAN Manager and AWS, specify the solution you want to deploy on your Transit Gateway. The current support is only for Transit Gateway - Branch Connect. In this solution each SD-Routing device establishes two IPSec tunnels to the Transit Gateway and runs one BGP session per IPSec tunnel. In a Branch Connect solution no C8000v instances are deployed inside the Transit Gateway.
Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to Workflows. Select Cloud Global Settings. | ||||||||||||||||
Step 2 | Select the cloud provider for which you want to configure details. Click Edit. Specify details to configure the cloud setup.
| ||||||||||||||||
Step 3 | Click Update to save changes. The Transit Gateway set up is complete. |
Discover
After the Transit Gateway set up is complete, a virtual network is allocated to your AWS account based on the region in which you have created the Transit Gateway. This network is termed as a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). The integration of AWS with Catalyst SD-WAN Manager makes the process of discovering all host VPCs automatic.
Host Private Network
You can select one or more regions and use Tags to mark the VPC. Tags are metadata that you can assign to resources to easily organize, search, identify resources, and control access to resources. This is useful when you have many resources of the same type—you can quickly identify a specific resource based on the tags that you've assigned to it.
By using Tags you indicate that the VPC’s with the same tags can communicate with each other therefore establishing peering.
You can tag and untag these VPCs and use it for future connectivity. The same tag can be used to map VPCs (that is, establish connectivity between VPCs) if the Intra-Tag communication in Global settings is enabled.
Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to Workflows. Select Host Private Networks. |
Step 2 | Select one or more regions from the list. Click . |
Step 3 | Specify a tag name. These tag names are saved in the cloud account with a prefix of CiscoSdwanV2. |
Step 4 | Verify the list of regions for which tagging has to be done. Also verify the list of VPCs corresponding to each of the regions. |
Step 5 | Click Add and Save. |
Manage
After setting up the cloud account and configuring the global settings, you can create or manage a Transit Gateway by adding or removing SD-Routing branches. Additionally, you can also set up the number of tunnels for the Transit Gateway and also determine if each of these tunnels require acceleration through the AWS Global Accelerator.
Manage Cloud Gateways
A Cloud Gateway provides a path for network traffic to travel between a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and the public internet. It plays a crucial role by facilitating communication and data transfer between disparate networks, making it possible for different systems to work together seamlessly.
After setting up the cloud account and associating tags for the regions, configure a Cloud Gateway. Only one Cloud Gateway can be created per region.Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to Workflows. Select Create Cloud Gateway . | ||||||||||
Step 2 | Specify details to configure the cloud gateway.
| ||||||||||
Step 3 | Click Add to start the process of creation of a Cloud Gateway. If creation of the Cloud Gateway is successful, the status is shown as Success. |
Gateway Management
After the Transit Gateway is created, attach the onboarded SD-Routing device to the Transit Gateway.
Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to . Select Gateway Management. |
Step 2 | Select the Transit Gateway you created and click …, select Attach SD-Routing. As part of Cloud Global Settings, if you have chosen to configure this solution using Configuration Groups, the VRF and Ethernet details created are already attached to the Transit Gateway. |
Step 3 | Click Attach Sites. From the list of branches in Available Sites, select a branch you want to attach to the Transit Gateway. Click > to move the selected branch to the Selected Sites pane. Click < to remove a site from the Selected Sites pane. |
Step 4 | Click Next. Select the interface that you configured as part of the Onboarding task. This is the WAN interface associated with the Global VRF. |
Step 5 | The Public IP of the SD-Routing branch is automatically populated if the SD-Routing branch is not configured behind a NAT Gateway. In case the SD-Routing branch is set up behind a NAT Gateway, replace the local IP address with the NAT Gateway IP address. Click Next. |
Step 6 | Specify the number of tunnels you want to create for the Transit Gateway. The range is from 1 – 8 and each tunnel gives a bandwidth of 2.5 Gbps. Each tunnel automatically creates two IPSec tunnels from the SD-Routing branch to the Transit Gateway. |
Step 7 | Enable Accelerated VPN if you want the AWS Global Accelerator to optimize the performance of your applications for local and global users. Click Next. |
Step 8 | Click Next. Verify the configuration. Click Save and Exit. |
Intent Management
Ensure that you have enabled Intra Tag Communication in Global settingsbefore you start configuring intent for the VPCs .
The Intent Management workflow in Catalyst SD-WAN Manager enables connectivity between VPCs using tags created as part of Discover Host Private Network option. If two VPCs have the same tags, they can communicate with each other.
Intent is realized only if the region has a Transit Gateway connected to a branch. You can configure intent mapping without a Transit Gateway being present in different regions. The mapping intent is preserved and realized when a new Transit Gateway or mapping change is discovered.
When you deploy Transit Gateway – Branch Connect solution, only Global-VRF is supported to establish a communication channel between the Transit Gateway and branch . Any other VRFs configured for SD-Routing devices are not displayed for Intent Mapping. To establish communication between the SD-Routing branch and VPC hosts, intent mapping is required for the Global VRF. Intent Mapping can also be configured between the Global VRF and SD-WAN VPN.
Intent Management - Cloud Connectivity
Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to Workflows. Select Cloud Connectivity. |
Step 2 | Click Edit. All the tags associated with a specific branch are displayed. Each cell in the table corresponds to a region in the AWS cloud. If the region you select has a Cloud Gateway deployed, intent is realized and communication can flow between these VPCs. |
Step 3 | Click Save. |
Audit
After all the configuration is done and the Transit Gateway is connected to the branch, run a check to see if the deployment is functioning without errors.
Procedure
Step 1 | Go to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Select . Go to Workflows. Select Audit. |
Step 2 | Select AWS as the Provider. The status of the deployment is displayed. If any errors are detected in the connection between the Transit Gateway and branch the status is displayed as Out of Sync. In such cases, click Fix Sync Issues to automatically resolve any connection errors. |
Verifying Configuration Using Configuration Groups
After the site-cloud connectivity is established between the SD-Routing branch and AWS, verify that the configuration is accurate and there are no errors.
Procedure
Step 1 | On the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager, select Configuration > Configuration Groups. Select the solution type as SD-Routing. |
Step 2 | Select the configuration group created for the Global VRF and Ethernet Interface. Click down arrow to expand the Configuration Group, select the Transport and Management Profile. Click Edit to view the contents of this profile. The profile contains these auto-generated details for each SD-Routing device:
|
Verifying Configuration Using Commands
After the Transit Gateway is configured and communication is established between the site and AWS, verify the functioning using these commands.
| Use command | To |
| show ip interface brief | display all tunnels and interfaces on the device, including the status. |
| show ip route | display all propogated routes. Propagated routes, in the context of Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), are routes that a virtual private gateway (VPG) automatically adds to route tables. |
| show ip bgp all | display routes hosted under all subnets. |
Monitor MultiCloud using Catalyst SD-WAN Manager
The Multicloud dashboard helps you monitor the Transit Gateway, connected VPCs and tunnels.
On the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager, choose Monitor > Multicloud. The status of the connection between Amazon Web Service and SD-Routing branch is displayed based on these parameters:
-
Crypto sessions between IKE peers.
-
NHRP cache entries.
-
Spokes connected to NHS.