Cisco UCS C240 M6 and M7 Solution for Microsoft Azure Local version 23H2
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback
Published: July 2024

| Date |
Change |
| July 2024 |
Original publication |
| December 2024 |
Changed Microsoft Azure Stack HCI to Microsoft Azure Local |
About the Cisco Validated Design Program
The Cisco Validated Design (CVD) program consists of systems and solutions designed, tested, and documented to facilitate faster, more reliable, and more predictable customer deployments. For more information, go to: http://www.cisco.com/go/designzone.
Cisco Validated Designs (CVDs) include systems and solutions that are designed, tested, and documented to facilitate and improve customer deployments. These designs incorporate a wide range of technologies and products into a portfolio of solutions that have been developed to address the business needs of our customers. Cisco UCS Solution for Microsoft Azure Local (formerly Microsoft Azure Stack HCI) offers highly available and scalable software-defined hyperconverged solution that is enable by the purpose-built Azure Local 23H2 Operating System. The Azure Local 23H2 Operating System is an Azure hybrid cloud designed hyperconverged solution that is based on Microsoft Windows Server 2022 and includes Storage Spaces Direct, Windows Failover Clustering, and Hyper-V.
Azure Stack is a family of three solutions that include Azure Local, Azure Stack Hub, and Azure Stack Edge. Azure Local is focused on the following use cases:
● Datacenter consolidation
● Virtual desktop Infrastructure
● Business critical infrastructure
● Storage cost reduction
● High availability and disaster recovery
● Enterprise application virtualization
● Azure Kubernetes Services
● Remote branch office system
● Arc enabled services
This document describes the architecture, topology, and deployment of Azure Local system, version 23H2 on Cisco UCS C240 M6SN, C240 M7SN and C220 M7N with Cisco Nexus 9000 series switches. Following the deployment guidance as specified in this document will result in a solution that adheres to both Cisco and Microsoft best practices.
This chapter contains the following:
● Audience
Software defined data center solutions enable IT organizations to optimize resource efficiency and improve service delivery. It combines compute virtualization, software defined storage, and virtualized networking that meets or exceeds high availability, performance, and security requirements of the most demanding deployments. The solution uses a shared-nothing architecture and takes advantage of the compute, storage, and network resources that are available within individual server. The servers are connected with external switching fabric that is provides reliable high throughput and low latency.
The audience of this document includes, but is not limited to, sales engineers, field consultants, professional services, IT managers, partner engineers, and customers who want to take advantage of an infrastructure that is built to deliver IT efficiency and enable IT innovation.
This overview and step-by-step deployment document is intended to describe in detail the procedure used to deploy the Azure Local solution on a Cisco UCS C240 M6SN, C240 M7SN and C220 M7N Rack Server with the Mellanox ConnectX-6 Dx/Lx NIC and connected to Cisco Nexus 9000 series switches. The procedure in this document should be used for deploying and evaluating this solution in a lab environment prior to deploying the solution in production. The deployment details described in this document need to be implemented as described unless stated otherwise.
This document will be periodically updated with new content. The contents will include procedures for deploying additional capabilities as well as qualified Cisco UCS firmware and drivers that must be used for deploying this solution.
This chapter contains the following:
● Cisco UCS C240 M6 Rack Server
● Cisco UCS C240 M7 Rack Server
● Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Server
● NVIDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 Dx Ethernet SmartNIC
● NVIDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 Lx Ethernet SmartNIC
● Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC)
The Cisco UCS C240 M6 Rack Server is a 2-socket, 2-Rack-Unit (2RU) rack server offering industry-leading performance and expandability. It supports a wide range of storage and I/O-intensive infrastructure workloads, from big data and analytics to collaboration. Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers can be deployed as standalone servers or as part of a Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS) managed environment to take advantage of Cisco’s standards-based unified computing innovations that help reduce customers’ Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and increase their business agility.
In response to ever-increasing computing and data-intensive real-time workloads, the enterprise-class Cisco UCS C240 M6 Rack Server extends the capabilities of the Cisco UCS portfolio in a 2RU form factor. It incorporates the 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors, supporting up to 40 cores per socket and 33 percent more memory versus the previous generation.
The Cisco UCS C240 M6 Rack Server brings many new innovations to the Cisco UCS rack server portfolio. With the introduction of PCIe Gen 4.0 expansion slots for high-speed I/O, DDR4 memory bus, and expanded storage capabilities, the server delivers significant performance and efficiency gains that will improve your application performance. Its features including the following:
● Supports third-generation Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs, with up to 40 cores per socket
● Up to 32 DDR4 DIMMs for improved performance including higher density DDR4 DIMMs (16 DIMMs per socket)
● 16x DDR4 DIMMs + 16x Intel Optane persistent memory modules for up to 12 TB of memory
● Up to 8 PCIe Gen 4.0 expansion slots plus a modular LAN-on-motherboard (mLOM) slot
● Support for Cisco UCS VIC 1400 Series adapters as well as third-party options
● Up to 28 hot-swappable Small-Form-Factor (SFF) SAS/SATA/NVMe:
◦ 28 SFF SAS/SATA (with up to 8x NVMe)
◦ 26 NVMe in all NVMe SKU (SN)
◦ 14 NVMe in all NVMe SKU (N)
◦ 16 LFF drives with options 4 rear SAS/SATA/NVMe) disk drives, or 16 Large-Form-Factor (LFF) 3.5-inch drives plus 2 rear hot-swappable SFF drives
◦ Support for a 12-Gbps SAS modular RAID controller in a dedicated slot, leaving the remaining PCIe Gen 4.0 expansion slots available for other expansion cards
◦ Option for 26 NVMe drives at PCIe Gen4 x4 (2:1 oversubscribed)
● M.2 boot options:
◦ Up to 960 GB with optional hardware RAID
● Up to five GPUs supported
● Modular LAN-on-motherboard (mLOM) slot that can be used to install a Cisco UCS Virtual Interface Card (VIC) without consuming a PCIe slot, supporting quad port 10/40 Gbps or dual port 40/100 Gbps network connectivity
● Dual embedded Intel x550 10GBASE-T LAN-on-motherboard (LOM) ports
● Modular M.2 SATA SSDs for boot
Table 1. Item and Specification Details
| Item |
Specifications |
| Form factor |
2RU rack server |
| Processors |
3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (1 or 2) |
| Memory |
32 DDR4 DIMM slots: 16, 32, 64, 128 and 256 GB and up to 3200 MHz Support for the Intel Optane DC Persistent Memory (128G, 256G, 512G) |
| PCIe expansion |
8 PCIe 4.0 slots plus 1 dedicated 12-Gbps RAID controller slot and 1 dedicated mLOM slot |
| Storage controller |
Internal controllers: Cisco 12-Gbps Modular SAS Host Bus Adapter (HBA) |
| Internal storage |
Backplane options:
● Up to 28 x 2.5-inch SAS and SATA HDDs and SSDs (up to 4 NVMe PCIe drives)
● Up to 26 x 2.5-inch NVMe PCIe SSDs (All direct attach Gen4 x4)
● Up to 16 x 3.5-inch SAS and SATA HDDs and SSDs, and optional 2 rear 2.5-inch HDDs and SSDs (up to 4 NVMe PCIe drives)
|
| Embedded Network Interface Cards (NICs) |
Dual 10GBASE-T Intel x550 Ethernet ports |
| mLOM |
Dedicated mLOM slot that can flexibly accommodate 1-, 10-, 25-, 40-, and 100-Gbps adapters |
| Power supplies |
Hot-pluggable, redundant 1050W AC, 1050W DC, 1600W AC and 2300W AC |
| Other storage |
Dedicated Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) FlexMMC for utilities (on board) Dual M.2 SATA SSDs with HW Raid support |
| Management |
|
| Rack options |
Cisco ball-bearing rail kit with optional reversible cable management farm |
| Hardware and software interoperability |
See the Cisco Hardware and Software Interoperability List for a complete listing of supported operating systems and peripheral options. |

The Cisco UCS C240 M7 Rack Server extends the capabilities of the Cisco UCS Rack Server portfolio. It incorporates the 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors with 50 percent more cores per socket advanced features like Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX), Data Streaming Accelerator (DSA), In-Memory Analytics Accelerator (IAA), and QuickAssist Technology (QAT), many applications will see significant performance improvements.
You can deploy the Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers as standalone servers or as part of the Cisco Unified Computing System managed by Cisco Intersight or Cisco UCS Manager to take advantage of Cisco standards-based unified computing innovations that can help reduce your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and increase your business agility.
The Cisco UCS C240 M7 Rack Server brings many new innovations to the Cisco UCS rack server portfolio. With the introduction of PCIe Gen 5.0 expansion slots for high-speed I/O, a DDR5 memory bus, and expanded storage capabilities, the server delivers significant performance and efficiency gains that will improve your application performance. Its features including the following:
● Supports up to two 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable CPU, with up to 60 cores per socket
● Up to 32 DDR5 DIMMs for up to 8 TB of capacity using 256 GB DIMMs (16 DIMMs per socket)
● 4800 MT/s DDR5 memory plus other speeds depending on the CPU installed
● Up to 8 PCIe 4.0 slots or up to 4 PCIe 5.0 slots, plus a hybrid modular LAN on motherboard (mLOM) /OCP 3.0 slot
● Support for Cisco UCS VIC 15000 Series adapters as well as third-party options
● Up to 28 hot-swappable Small-Form-Factor (SFF) SAS/SATA or NVMe drives (with up to 8 direct-attach NVMe drives):
◦ New tri-mode RAID controller supports SAS4 plus NVMe hardware RAID
◦ Option for 28 NVMe drives at PCIe Gen4 x2 each
● M.2 boot options:
◦ Up to two 960GB SATA M.2 drives with hardware RAID, or
◦ Up to two 960GB NVMe M.2 drives with NVMe hardware RAID
● Up to five GPUs supported
● Modular LOM / OCP 3.0:
◦ One dedicated PCIe Gen4x16 slot that can be used to add an mLOM or OCP 3.0 card for additional rear-panel connectivity
◦ mLOM slot that can be used to install a Cisco UCS Virtual Interface Card (VIC) without consuming a PCIe slot, supporting quad port 10/25/50 Gbps or dual port 40/100/200 Gbps network connectivity
◦ OCP 3.0 slot features full out-of-band management for select adapters
Table 2. Item and Specification Details
| Item |
Specifications |
| Form factor |
2RU rack server |
| Processors |
4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors (1 or 2) |
| Memory |
32 DDR5 DIMM slots: 16, 32, 64, 128 and 256 GB and up to 4800 MT/s |
| PCIe expansion |
Up to 8 PCIe 4.0 slots or up to 4 PCIe 5.0 slots plus 1 dedicated 24-Gbps RAID controller slot and 1 dedicated mLOM slot |
| RAID controllers |
Internal controllers: Cisco 12-Gbps Modular SAS Host Bus Adapter (HBA) |
| Internal storage |
Backplane options:
● Up to 28 x 2.5-inch SAS and SATA HDDs/ SSDs and NVMe SSDs (up to 8 NVMe direct attach)
● Up to 28 x 2.5-inch NVMe PCIe SSDs (all direct-attach Gen4 x2)
|
| mLOM/OCP 3.0 |
One dedicated socket (x16 PCIe lane) that can be used to add an mLOM or OCP 3.0 card for additional rear-panel connectivity. mLOM slot can flexibly accommodate 10/25/50 and 40/100/200 100-Gbps Cisco VIC adapters. OCP 3.0 slot features full out-of-band manageability that supports Intel X710 OCP Dual 10GBase-T via mLOM interposer. |
| Power supplies |
Hot-pluggable, redundant platinum and titanium options:
● Platinum: 1050W DC, and 1600W AC
●
Titanium: 1200W AC, and 2300W AC
|
| Other storage |
Dedicated Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) FlexMMC for utilities (on board) Dual M.2 SATA/NVMe SSDs with HW Raid support |
| Management |
|
| Rack options |
Cisco ball-bearing rail kit with optional reversible cable management farm |
| Hardware and software interoperability |
See the Cisco Hardware and Software Interoperability List for a complete listing of supported operating systems and peripheral options. |

The Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Server is a versatile general-purpose infrastructure and application server. This high-density, 1RU, 2-socket rack server delivers industry-leading performance and efficiency for a wide range of workloads, including virtualization, collaboration, and bare-metal applications.
The Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Server extends the capabilities of the Cisco UCS rack server portfolio. It incorporates the 4th and 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors with 50 percent more cores per socket, advanced features such as Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX), Data Streaming Accelerator (DSA), In-Memory Analytics Accelerator (IAA), and QuickAssist Technology (QAT). Many applications will see significant performance improvements.
You can deploy the Cisco UCS C-Series rack servers as standalone servers or as part of the Cisco Unified Computing System managed by Cisco Intersight or Cisco UCS Manager to take advantage of Cisco standards-based unified computing innovations that can help reduce your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and increase your business agility.
The Cisco UCS C220 M7 rack server brings many new innovations to the Cisco UCS rack server portfolio. With the introduction of PCIe Gen 5.0 for high-speed I/O, a DDR5 memory bus, and expanded storage capabilities, the server delivers significant performance and efficiency gains that will improve your application performance.
● Supports up to two 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs, with up to 60 cores per socket.
● Up to 32 DDR5 DIMMs for up to 4 TB of capacity using 128 GB DIMMs (16 DIMMs per socket).
● Up to 5600 MT/s DDR5 memory plus other speeds depending on the CPU installed.
● Up to 3 PCIe 4.0 slots or up to 2 PCIe 5.0 slots, plus a modular LAN on motherboard (mLOM) slot.
● Support for Cisco UCS VIC 15000 Series adapters as well as third-party options.
● Up to 10 SAS/SATA or NVMe disk drives:
◦ New tri-mode RAID controller supports SAS4 RAID or NVMe hardware RAID with optional up to four direct-attach NVMe drives.
◦ Option for 10 direct-attach NVMe drives at PCIe Gen4x4 each.
● M.2 boot options:
◦ Up to two 960GB SATA M.2 drives with hardware RAID.
Or
◦ Up to two 960GB NVMe M.2 drives with NVMe hardware RAID.
● Up to three GPUs supported.
● Hybrid modular LOM/OCP 3.0:
◦ One dedicated Gen 4.0 x16 slot that can be used to add an mLOM or OCP 3.0 card for additional rear-panel connectivity.
◦ mLOM allows for Cisco UCS Virtual Interface Cards (VICs) without consuming a PCIe slot, supporting quad port 10/25/50 Gbps or dual port 40/100/200 Gbps network connectivity.
◦ OCP 3.0 slot features full out-of-band management for select adapters.
Table 3. Item and Specification Details
| Item |
Specifications |
| Form factor |
1RU rack server |
| Processors |
Up to 2x 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors (1 or 2) or Up to 2x 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors (1 or 2) |
| Memory |
32 DDR5-5600 DIMM slots (16 DIMMS per CPU): 16, 32, 48, 64, 96, 128GB at up to 5600 MT/s for up to 4TB of memory with 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors or 32 DDR5-4800 DIMM slots (16 DIMMS per CPU): 16, 32, 64, 128GB at up to 4800 MT/s for up to 4TB of memory with 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors |
| PCIe expansion |
Up to 3 PCIe 4.0 slots or up to 2 PCIe 5.0slots plus 1 dedicated 24-Gbps RAID controller slot and 1 dedicated mLOM/OCP 3.0 slot |
| RAID controllers |
Internal controllers:
● Cisco 24-Gbps modular tri-mode controller supports SAS 4 or NVMe hard-ware RAID
● Cisco 12-Gbps modular RAID controller (PCIe 4.0) with 4-GB Flash-Backed Write Cache (FBWC)
or
● Cisco 12-Gbps modular SAS Host Bus Adapter (HBA)
● External controller: Cisco 12-Gbps 9500-8e SAS HBA
|
| Internal storage |
Backplane options:
● Up to 10 x 2.5-inch SAS and SATA HDDs, SSD, NVMe drives, with the option of up to 4 direct-attach NVMe drives
● Up to 10 x 2.5-inch NVMe PCIe SSDs (all direct-attach PCIe Gen4x4)
|
| mLOM/OCP 3.0 |
● One dedicated PCIe Gen4x16 slot that can be used to add an mLOM or OCP 3.0 card for additional rear-panel connectivity
● mLOM slot can flexibly accommodate 10/25/5010/25/40, and 40/100/200 100-Gbps Cisco VIC adapters
● OCP 3.0 slot features full out-of-band manageability that supports Intel X710 OCP Dual 10GBase-T via mLOM interposer
|
| Power supplies |
Hot-pluggable, redundant platinum and titanium options:
● Platinum: 770W AC, 1050W DC, and 1600W AC
● Titanium: 1200W AC, and 2300W AC
|
| Other storage |
Dedicated Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) FlexMMC for utilities (on board) Dual M.2 SATA/NVMe SSDs with HW RAID support |
| Management |
|
| Rack options |
Cisco ball-bearing rail kit with optional reversible cable management arm |
| Hardware and software interoperability |
See the Cisco Hardware and Software Interoperability List for a complete listing of supported operating systems and peripheral options. |
NVIDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 Dx Ethernet SmartNIC
NVIDIA ConnectX-6 Dx is a highly secure and advanced smart network interface card (SmartNIC) that accelerates mission-critical cloud and data center applications, including security, virtualization, SDN/NFV, big data, machine learning, and storage. ConnectX-6 Dx provides up to two ports of 100Gb/s or a single port of 200Gb/s Ethernet connectivity and is powered by 50Gb/s (PAM4) or 25/10 Gb/s (NRZ) SerDes technology.
ConnectX-6 Dx features virtual switch (vSwitch) and virtual router (vRouter) hardware accelerations delivering orders-of-magnitude higher performance than software-based solutions. ConnectX-6 Dx supports a choice of single-root I/O virtualization
(SR-IOV) and VirtIO in hardware, enabling customers to best address their application needs. By offloading cloud networking workloads, ConnectX-6 Dx frees up CPU cores for business applications while reducing total cost-of-ownership.
In an era where data privacy is key, ConnectX-6 Dx provides built-in inline encryption/decryption, stateful packet filtering, and other capabilities, bringing advanced security down to every node with unprecedented performance and scalability.
Built on the solid foundation of NVIDIA’s ConnectX line of SmartNICs, ConnectX-6 Dx offers best-in-class RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) capabilities, enabling scalable, resilient, and easy-to-deploy RoCE solutions. For data storage, ConnectX-6 Dx optimizes a suite of storage accelerations, bringing NVMe-oF target and initiator offloads.
Figure 1. NVDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 Dx
NVIDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 Lx Ethernet SmartNIC
NVIDIA ConnectX-6 Lx Ethernet network interface cards (NIC) deliver high-performance network connectivity at 25GbE speeds coupled with advanced security and the best total cost of ownership for enterprise data centers. The NICs support up to two ports of 25GbE or a single port of 50GbE networking, along with PCI Express (PCIe) Gen3 and Gen4 x8 host connectivity to meet the demands of modern workloads in the cloud, in the data center, and at the edge.
Figure 2. NVDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 Lx

Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC)
The Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC) is a baseboard management controller that provides embedded server management for Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers and Cisco UCS S-Series Storage Servers. The Cisco IMC enables system management in the data center and across distributed branch-office locations. It supports multiple management interfaces, including a Web User Interface (Web UI), a Command-Line Interface (CLI), and an XML API that is consistent with the one used by Cisco UCS Manager. IMC also supports industry-standard management protocols, including Redfish, Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMPv3), and Intelligent Platform Management Interface Version 2.0 (IPMIv2.0). The figure below shows a sample Cisco IMC screen.

Cisco Intersight is Cisco’s systems management platform that delivers intuitive computing through cloud-powered intelligence. This platform offers a more intelligent level of management that enables IT organizations to analyze, simplify, and automate their environments in ways that were not possible with prior generations of tools. This capability empowers organizations to achieve significant savings in Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and to deliver applications faster in support of new business initiatives. The advantages of the model-based management of the Cisco UCS platform plus Cisco Intersight are extended to Cisco UCS servers and Cisco HyperFlex, including Cisco HyperFlex Edge systems. Cisco HyperFlex Edge is optimized for remote sites, branch offices, and edge environments.
Endpoints supported by Cisco Intersight use model-based management to provision servers and associated storage and fabric automatically, regardless of form factor. Cisco Intersight works in conjunction with Cisco UCS Manager and the Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC). By simply associating a model-based configuration with a resource through server profiles, your IT staff can consistently align policy, server personality, and workloads. These policies can be created once and used by IT staff with minimal effort to deploy servers. The result is improved productivity and compliance and lower risk of failures due to inconsistent configuration.
Cisco Intersight will be integrated with data-center and hybrid-cloud platforms and services to securely deploy and manage infrastructure resources across data-center and edge environments. Additionally, Cisco provides integrations to third-party operations tools, starting with ServiceNow allowing you to use your existing solutions more effectively.
Cisco Intersight offers flexible deployment either as Software as a Service (SaaS) on Intersight.com or running on your premises with the Cisco Intersight virtual appliance. The virtual appliance provides users with the benefits of Cisco Intersight while allowing more flexibility for those with additional data locality and security requirements.
Cisco Intersight Features and Benefits
Table 4 lists the main features and benefits of Cisco Intersight.
Table 4. Cisco Intersight Features and Benefits
| Feature |
Benefit |
| Unified management |
Simplify Cisco UCS, Cisco HyperFlex, Pure Storage, and Cisco Network Insights management from a single management platform. Increase scale across data centers and remote locations without additional complexity. Use a single dashboard to monitor Cisco UCS and Cisco HyperFlex systems. Cisco UCS Manager, Cisco IMC software, Cisco HyperFlex Connect, and Cisco UCS Director tunneling allow access to element managers that do not have local network access. |
| Configuration, provisioning, and server profiles |
Treat Cisco UCS servers and storage as infrastructure resources that can be allocated and reallocated among application workloads for more dynamic and efficient use of server capacity. Create multiple server profiles with just a few clicks or through the available API, automating the provisioning process. Clone profiles to quickly provision Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers in standalone mode. Create, deploy, and manage your Cisco HyperFlex configurations. Help ensure consistency and eliminate configuration drift, maintaining standardization across many systems. |
| Inventory information and status |
Display and report inventory information for Cisco UCS and Cisco HyperFlex systems. Use global search to rapidly identify systems based on names, identifiers, and other information. Use tagging to associate custom attributes with systems. Monitor Cisco UCS and Cisco HyperFlex server alerts and health status across data centers and remote locations. View your Cisco HyperFlex configurations. Track and manage firmware versions across all connected Cisco UCS and Cisco HyperFlex systems. Track and manage software versions and automated patch updates for all claimed Cisco UCS Director software installations. |
| Enhanced support experience |
Get centralized alerts about failure notifications. Automate the generation, forwarding, and analysis of technical support files to the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) to accelerate the troubleshooting process. |
| Open API |
A RESTful API that supports the OpenAPI Specification (OAS) to provide full programmability and deep integrations systems. The Python and PowerShell SDKs will enable integrations with Ansible, Chef, Puppet, and other DevOps and IT Operations Management (ITOM) tools. ServiceNow integration to provide inventory and alerts to the IT Service Management platform. |
| Seamless integration and upgrades |
Upgrades are available for Cisco UCS, Cisco HyperFlex systems, and Cisco UCS Director software running supported firmware and software versions. Upgrades to Cisco Intersight are delivered automatically without requiring the resources of traditional management tool upgrades and disruption to your operations. |
Azure Local
Azure Local 23H2 is a hyper-converged Windows Server 2022 cluster that uses validated hardware to run virtualized workloads on-premises. Optionally, you can also connect to Azure services for cloud-based backup, site-recovery, and more. Azure Local solutions use Microsoft-validated hardware to ensure optimal performance and reliability, and include support for technologies such as NVMe drives, persistent memory, and remote-direct memory access (RDMA) networking.
Azure Local is a solution that combines several products:
● Hardware from an OEM partner
● Azure Local OS 23H2
● Windows Admin Center
● Azure services (optional)
Here is the link for What’s new in Azure Local, version 23H2: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/whats-new?tabs=2405releases
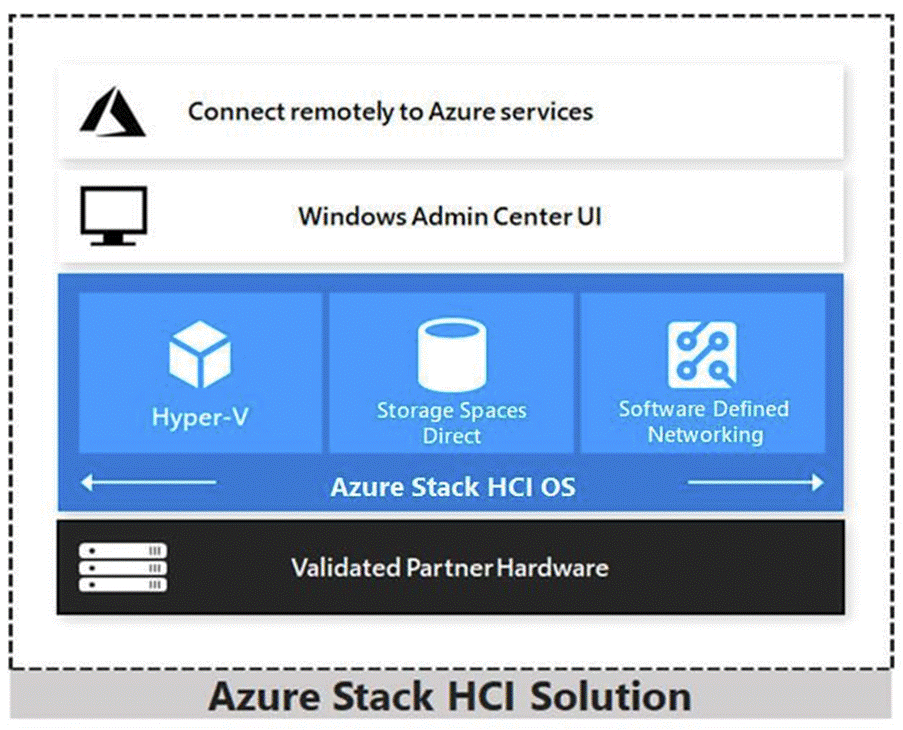
Azure Local is Microsoft’s hyperconverged solution available from a wide range of hardware partners. Consider the following scenarios for a hyperconverged solution to help you determine if Azure Local is the solution that best suits your needs:
● Refresh aging hardware. Replace older servers and storage infrastructure and run Windows and Linux virtual machines on-premises and at the edge with existing IT skills and tools.
● Consolidate virtualized workloads. Consolidate legacy apps on an efficient, hyperconverged infrastructure. Tap into the same types of cloud efficiencies used to run hyper-scale datacenters such as Microsoft Azure.
● Connect to Azure for hybrid cloud services. Streamline access to cloud management and security services in Azure, including offsite backup, site recovery, cloud-based monitoring, and more.
Hyperconverged Efficiencies
Azure Local solutions bring together highly virtualized compute, storage, and networking on industry-standard x86 servers and components. Combining resources in the same cluster makes it easier for you to deploy, manage, and scale. Manage with your choice of command-line automation or Windows Admin Center.
Achieve industry-leading virtual machine performance for your server applications with Hyper-V, the foundational hypervisor technology of the Microsoft cloud, and Storage Spaces Direct technology with built-in support for NVMe, persistent memory, and remote-direct memory access (RDMA) networking.
It helps keep apps and data secure with shielded virtual machines, network micro segmentation, and native encryption.
Hybrid Cloud Capabilities
You can take advantage of cloud and on-premises working together with a hyperconverged infrastructure platform in public cloud. Your team can start building cloud skills with built-in integration to Azure infrastructure management services:
● Azure Site Recovery for high availability and disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS).
● Azure Monitor, a centralized hub to track what’s happening across your applications, network, and infrastructure – with advanced analytics powered by AI.
● Cloud Witness, to use Azure as the lightweight tie breaker for cluster quorum.
● Azure Backup for offsite data protection and to protect against ransomware.
● Azure Update Management for update assessment and update deployments for Windows VMs running in Azure and on-premises.
● Azure Network Adapter to connect resources on-premises with your VMs in Azure via a point-to-site VPN.
● Sync your file server with the cloud, using Azure File Sync.
Management Tools
Azure Local uses the same virtualization and software-defined storage and networking software as Azure Stack Hub. However, with Azure Local you have full admin rights on the cluster and can manage any of its technologies directly:
● Hyper-V
To manage these technologies, you can use the following management tools:
● Windows Admin Center (optional)
● System Center (optional)
● Other management tools such as Server Manager, and MMC snap-ins (optional)
● Non-Microsoft tools such as 5Nine Manager (optional)
If you choose to use System Center to deploy and manage your infrastructure, you'll use System Center Virtual Machine Management (VMM) and System Center Operations Manager. With VMM, you provision and manage the resources needed to create and deploy virtual machines and services to private clouds.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V is Microsoft's hardware virtualization product. It lets you create and run a software version of a computer, called a virtual machine. Each virtual machine acts like a complete computer, running an operating system and programs. When you need computing resources, virtual machines give you more flexibility, help save time and money, and are a more efficient way to use hardware than just running one operating system on physical hardware.
Hyper-V runs each virtual machine in its own isolated space, which means you can run more than one virtual machine on the same hardware at the same time. You might want to do this to avoid problems such as a crash affecting the other workloads, or to give different people, groups, or services access to different systems.
Storage Spaces Direct
Storage Spaces Direct uses industry-standard servers with local-attached drives to create highly available, highly scalable software-defined storage at a fraction of the cost of traditional SAN or NAS arrays. The hyper-converged architecture radically simplifies procurement and deployment, while features such as caching, storage tiers, and erasure coding, together with the latest hardware innovations such as RDMA networking and NVMe drives, deliver unrivaled efficiency and performance.
One cluster for compute and storage. The hyper-converged deployment option runs Hyper-V virtual machines directly on the servers providing the storage, storing their files on the local volumes. This eliminates the need to configure file server access and permissions and reduces hardware costs for small-to-medium business or remote office/branch office deployments.

Storage Spaces Direct is the evolution of Storage Spaces, first introduced in Windows Server 2012. It leverages many of the features you know today in Windows Server, such as Failover Clustering, the Cluster Shared Volume (CSV) file system, Server Message Block (SMB) 3, and of course Storage Spaces. It also introduces new technology, most notably the Software Storage Bus.
Figure 3. Overview of the Storage Spaces Direct Stack
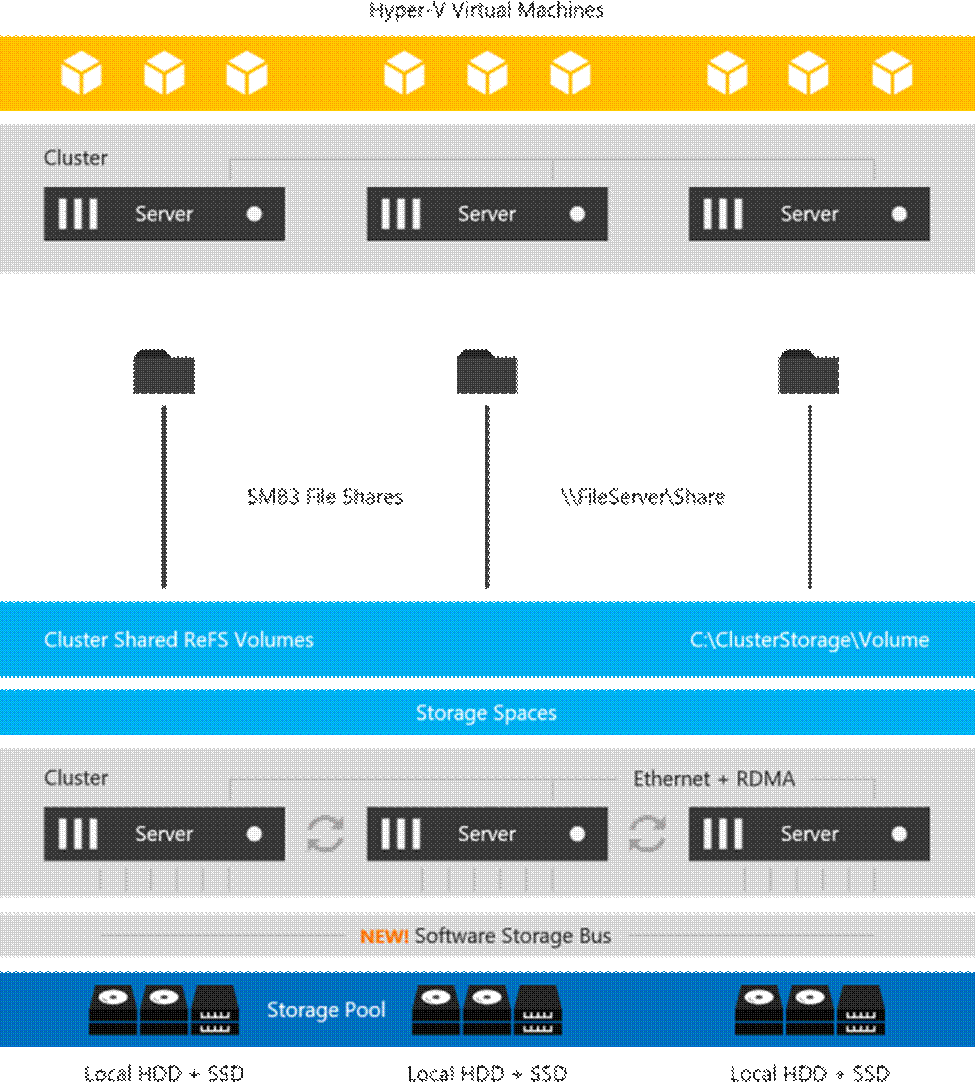
Networking Hardware. Storage Spaces Direct uses SMB3, including SMB Direct and SMB Multichannel, over Ethernet to communicate between servers. Microsoft strongly recommends 10+ GbE with remote-direct memory access (RDMA).
Storage Hardware. From 1 to 16 servers with local-attached SATA, SAS, or NVMe drives. Each server must have at least 2 solid-state drives, and at least 4 additional drives. The SATA and SAS devices should be behind a host-bus adapter (HBA) and SAS expander. We strongly recommend the meticulously engineered and extensively validated platforms from our partners (coming soon).
Failover Clustering. The built-in clustering feature of Windows Server is used to connect the servers.
Software Storage Bus. The Software Storage Bus is new in Storage Spaces Direct. It spans the cluster and establishes a software-defined storage fabric whereby all the servers can see all of each other's local drives. You can think of it as replacing costly and restrictive Fibre Channel or Shared SAS cabling.
Storage Bus Layer Cache. The Software Storage Bus dynamically binds the fastest drives present (e.g. SSD) to slower drives (e.g. HDDs) to provide server-side read/write caching that accelerates IO and boosts throughput.
Storage Pool. The collection of drives that form the basis of Storage Spaces is called the storage pool. It is automatically created, and all eligible drives are automatically discovered and added to it.
Note: We strongly recommend you use one pool per cluster, with the default settings. Read our Deep Dive into the Storage Pool to learn more.
Storage Spaces. Storage Spaces provides fault tolerance to virtual "disks" using mirroring, erasure coding, or both. You can think of it as distributed, software-defined RAID using the drives in the pool. In Storage Spaces Direct, these virtual disks typically have resiliency to two simultaneous drive or server failures (for example, 3-way mirroring, with each data copy in a different server) though chassis and rack fault tolerance is also available.
Resilient File System (ReFS). ReFS is the premier filesystem purpose-built for virtualization. It includes dramatic accelerations for .vhdx file operations such as creation, expansion, and checkpoint merging, and built-in checksums to detect and correct bit errors. It also introduces real-time tiers that rotate data between so-called "hot" and "cold" storage tiers in real-time based on usage.
Cluster Shared Volumes. The CSV file system unifies all the ReFS volumes into a single namespace accessible through any server, so that to each server, every volume looks and acts like it's mounted locally.
Failover Clustering
A failover cluster is a group of independent computers that work together to increase the availability and scalability of clustered roles (formerly called clustered applications and services). The clustered servers (called nodes) are connected by physical cables and by software. If one or more of the cluster nodes fail, other nodes begin to provide service (a process known as failover). In addition, the clustered roles are proactively monitored to verify that they are working properly. If they are not working, they are restarted or moved to another node.
Failover clusters also provide Cluster Shared Volume (CSV) functionality that provides a consistent, distributed namespace that clustered roles can use to access shared storage from all nodes. With the Failover Clustering feature, users experience a minimum of disruptions in service.
Failover Clustering has many practical applications, including:
● Highly available or continuously available file share storage for applications such as Microsoft SQL Server and Hyper-V virtual machines
● Highly available clustered roles that run on physical servers or on virtual machines that are installed on servers running Hyper-V
This chapter contains the following:
The Cisco solution for Azure Local architecture must be implemented as described in this document. Cisco provides a specific PID for ordering the configuration. The PID includes all of the required components that comprise the solution. The Azure Local cluster can be scaled from 1 to 16 servers. The architecture for the deployment of Azure Local solution consists of a storage switched configuration using two TOR switches with either fully converged or non-converged host network adapters.
The architecture has a data fabric and a management fabric. The servers connect to the data fabric using dual 100Gb connections. This data fabric is provided by the Cisco 9300 series switches which provide layer 2 connectivity and carries all the Azure Local network traffic (management, compute, and RDMA storage traffic). Server management is facilitated through an Out-of-band (OOB) management network that connects the server’s dedicated management port to an OOB management switch with 1GbE links. The servers Azure Local OS 23H2 provides a rich set of software defined services that are core to this solution.
The data center is expected to have infrastructure services such as DNS and Active Directory. WDS (Windows Deployment Service) and DHCP are also recommended to expedite deployments. These services must be accessible through the ToR (Top of Rack) or EoR (End of Row) network switches that connect the Cisco UCS C240 M6 and M7 Servers that are part of the Cisco solution for Azure Local to the datacenter infrastructure.
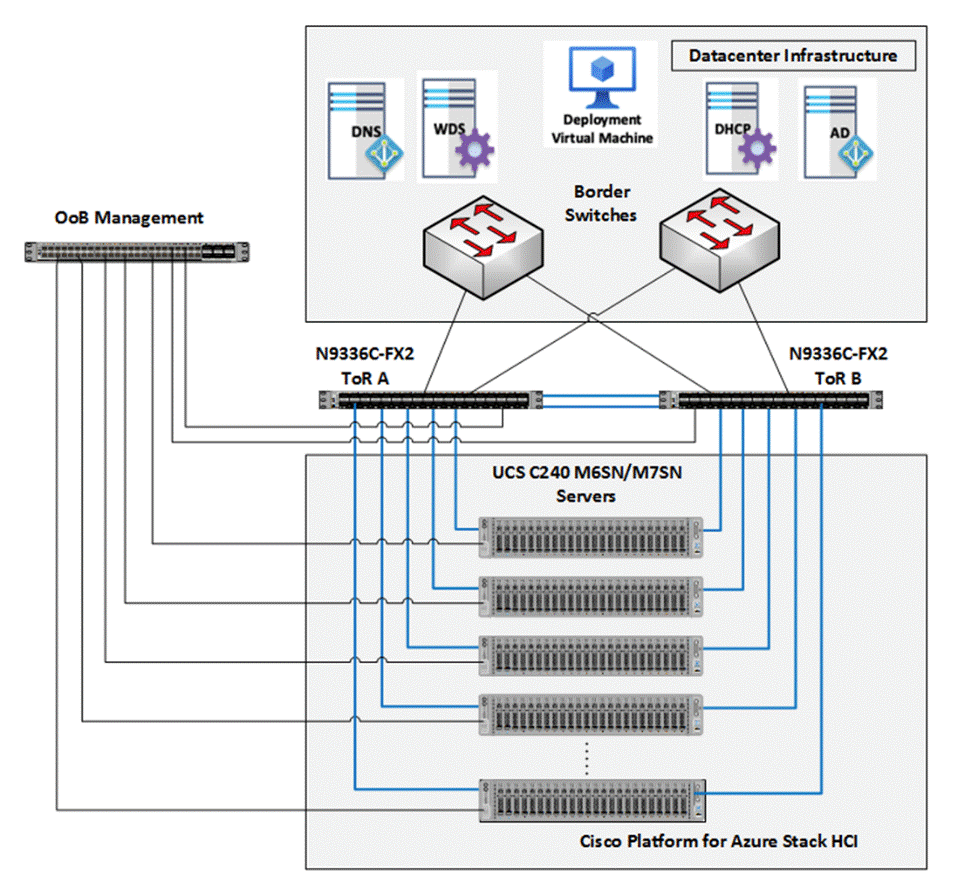
Azure Local Components
Cisco UCS C240 M6SN, C240 M7SN, or C220 M7N Servers
The Cisco UCS C240 M6SN or C240 M7SN, or C220 M7N server configuration consists of a one or two dual-port 100GbE NVDIA ConnectX-6 DX network interface cards, teamed with each port connecting to two different ToR switches and a single 1GbE dedicated management port which connects to an OOB management switch for communication with the Cisco Integrated Management Controller in each server.
The ToR switches, in this case Cisco Nexus 9300 Series Switches, carry both Azure Local cluster traffic and management network traffic to the Cisco UCS C240 M6SN or M7SN servers. The Azure Local cluster traffic flows throw 100GbE links to the NVIDIA ConnectX-6 DX network interface card/s in each server. Out-of-band management traffic is facilitated by a 1GbE connection to each of the Cisco UCS C240 M6SN, C240 M7SN, or C220 M7N severs.
The ToR (Top of Rack) switches can be any Cisco Nexus switches that have confirmed support for the Azure Local requirements. The list of supported Cisco Nexus series switches and the NX-OS version can be viewed here. The ToR switch provides layer 2 and layer 3 connectivity to the Azure Local cluster nodes. The ToR switches should include a security focused configuration that is standardized within the datacenter network. Two ToR switches in Virtual Port Channel (VPC) configuration provide high availability and redundancy for the network traffics.
The Appendix of this document has sample configurations that can be implemented in the ToR switch. These sample configurations include vPC, SVI, HSRP, and DHCP Relay.
It is expected that the datacenter has a secure OoB (Out-of-Band) management network that is used to managed network devices in the datacenter. Cisco UCS C240 M6SN and M7SN servers and the ToR switches are directly connected to the out-of-band management switches and a disjoint layer-2 configuration is used to keep the management network path separate from the data network path. The OoB network needs to have internet access in order for Cisco Intersight to be able to access the UCS C240 M6/M7 servers.
The logical topology is comprised of the following:
● Tenant/Compute Network
The Tenant network is a VLAN trunk that carries one or more VLANs that provide access to the tenant virtual machines. Those VLANs are configured on the ToR switch’s port in trunk mode. To connect VMs to these VLANs, the corresponding VLAN tags are defined on the virtual network adapter. Each tenant VLAN is expected to have an IP subnet assigned to it.
● Management Network
The management network is a VLAN that carries network traffic to the parent partition. This network is used to access the host operating system. The connectivity to the management network is provided by the management (Mgmt) vNIC in the parent partition. Fault tolerance for the management vNIC is provided by the SET switch. A bandwidth limit can be assigned to the management, as necessary.
● Storage Network
The storage network carries RoCEv2 RDMA network traffic that is used for Storage Spaces Direct, storage replication, and Live Migration network traffic. This network is also used for cluster management communication. The storage network has a Storage A and Storage B segment, each with its own IP subnet. This design keeps the east-west RDMA isolated to the ToR switches and avoids the need for the upstream switches to be configured for supporting RoCEv2 traffic.
DCB (Data Center Bridging) is required for RoCE. If DCB is used, PFC and ETS configuration is implemented properly across every network port, including network switches. RoCE-based Azure Local implementations require the configuration of three PFC traffic classes, including the default traffic class, across the fabric and all hosts.
Table 5 lists the QoS configuration used in this document. The QoS configuration should match on both – host-side networking and upstream physical network switches as well to which the nodes are connected.
| Purpose |
Cluster Traffic |
Storage (RDMA) traffic |
Default (Tenant and Management Networks) |
| Flow Control (PFC enabled) |
No |
Yes |
No |
| Traffic Class |
5 |
4 |
0 (default) |
| Bandwidth reservation |
1% for 25GbE or higher RDMA networks |
50% |
Default (no host configuration required) |
Figure 5 illustrates the east-west RDMA traffic isolation.
Figure 5. East-West RDMA Traffic Isolation
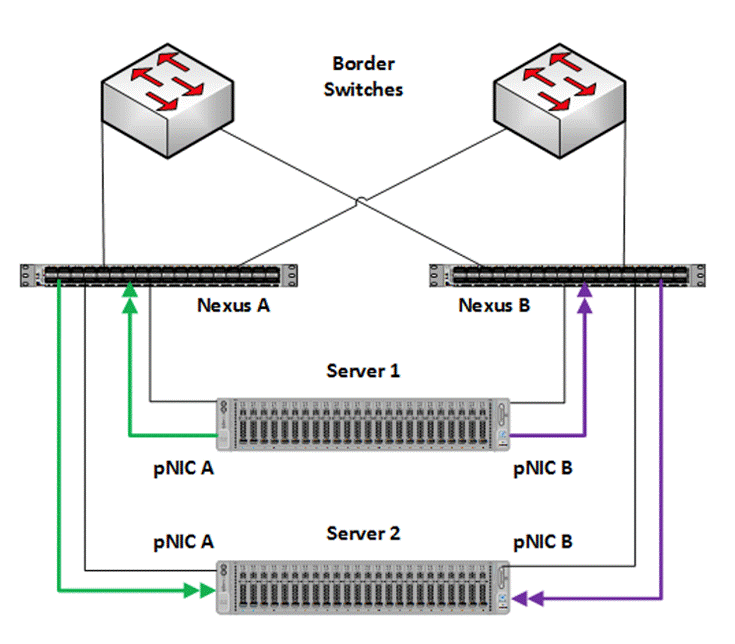
● SET Switch
This is a virtual switch with embedded teaming capabilities. The SET Switch provides teaming capabilities for network traffic that does not use SMB-Multichannel. SMB Direct (RDMA) traffic uses SMB-Multichannel for link aggregation and redundancy instead of the teaming feature in the SET switch.
MAC addresses for virtual NICs are randomly assigned to one on the physical NIC ports on the host. This MAC address assignment can be moved from one physical NIC to another at any time by the SET switch. This behavior provides load balancing and fault tolerance. A consequence of this behavior is that some of the east-west network traffic that is not storage SMB Direct (RDMA) traffic will transverse the upstream router/switch. An example of this is when virtual machine A with a virtual NIC MAC address assigned to physical NIC A communicates with virtual machine B that has virtual NIC MAC assigned to physical NIC B. Figure 6 illustrates this behavior.
Figure 6. MAC Address Assignment
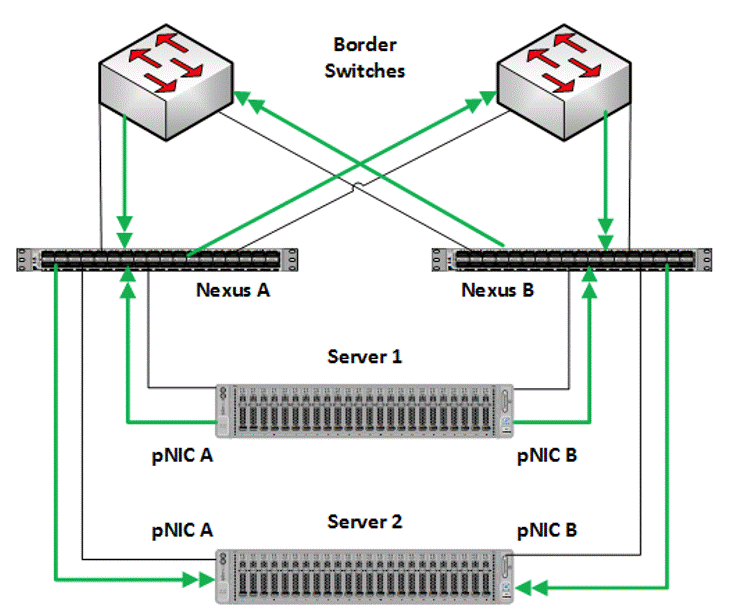
● Guest Partition
The tenant virtual machines run in the guest partition on the Hyper-V host. Each virtual machine runs in isolation from others and does not have direct access to physical hardware in the host. Network connectivity is provided to the tenant virtual machine by connecting synthetic NIC in the virtual machine to the SET switch on the host.
● Parent Partition
The parent partition is the host operating system that runs the virtualization management stack and has access to the physical server hardware. The parent partition has one management vNIC and two storage vNICs. An optional dedicated vNIC for backup operations can be added as needed.
Network ATC, a feature of Azure Local simplifies the deployment and network configuration management for Azure Local clusters. Network ATC provides an intent-based approach to host network deployment. By specifying one or more intents (management, compute, or storage) for a network adapter, you can automate the deployment of the intended configuration.
This section explains the logical topology for the below three network reference patterns:
● Storage switched, fully converged
● Storage switched, non-converged
● Storage switchless
Storage switched, fully Converged
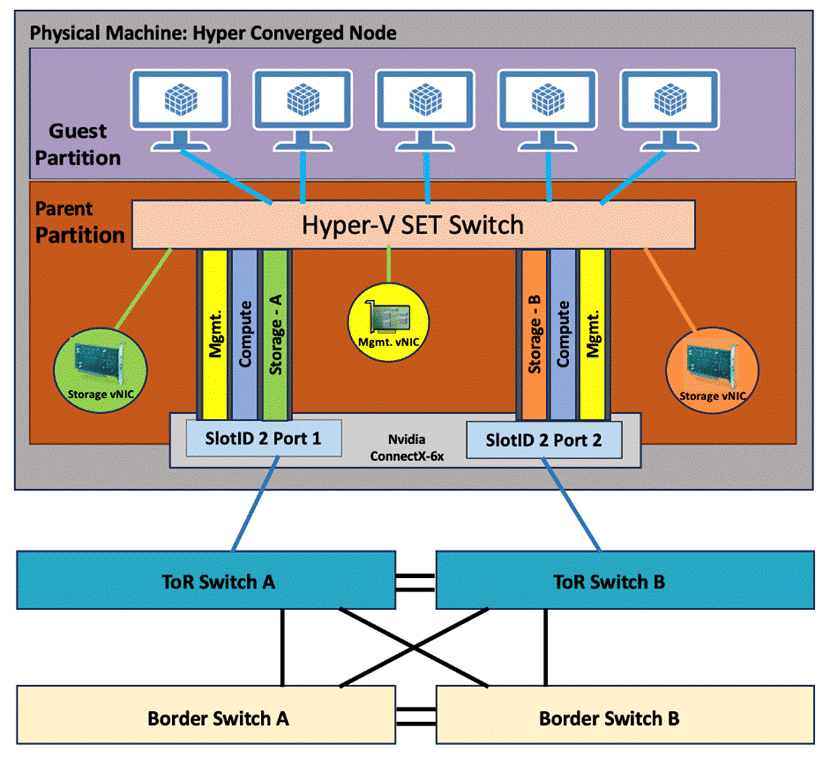
In this storage switched, fully converged network reference pattern, a single intent for compute, storage and management networks are deployed across all cluster nodes.
Consider this network reference pattern if:
● For scalable Azure Local solutions, where the storage network adapters are connected to a network switch.
● Bandwidth requirements for north-south traffic don’t require dedicated adapters.
● Physical switch ports are scare and for cost reductions.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/plan/two-node-switched-converged
As illustrated in Figure 7, storage switched fully converged network reference pattern has the following logical network components:
Figure 7. Storage switched, fully converged logical topology
Storage switched, non-converged
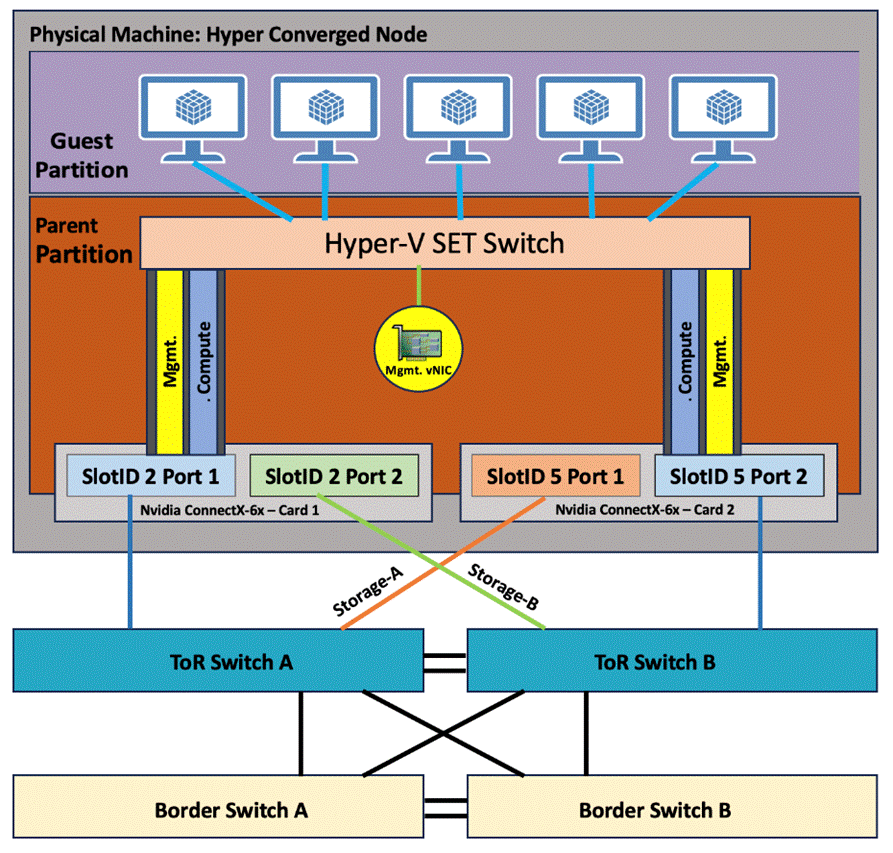
In this non-converged network pattern, two intents – one intent for compute and management networks and a separate intent for storage network are deployed across all cluster nodes.
Consider this network topology:
● For scalable Azure Local solutions, where dedicated storage network adapters are connected to a network switch.
● For enhanced network performance
● East-West storage traffic replication won’t interfere or compete with north-south traffic dedicated for management and compute
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/plan/two-node-switched-non-converged
As illustrated in Figure 8 for storage switched non-converged network reference pattern has the following logical network components:
Figure 8. Non-converged logical topology
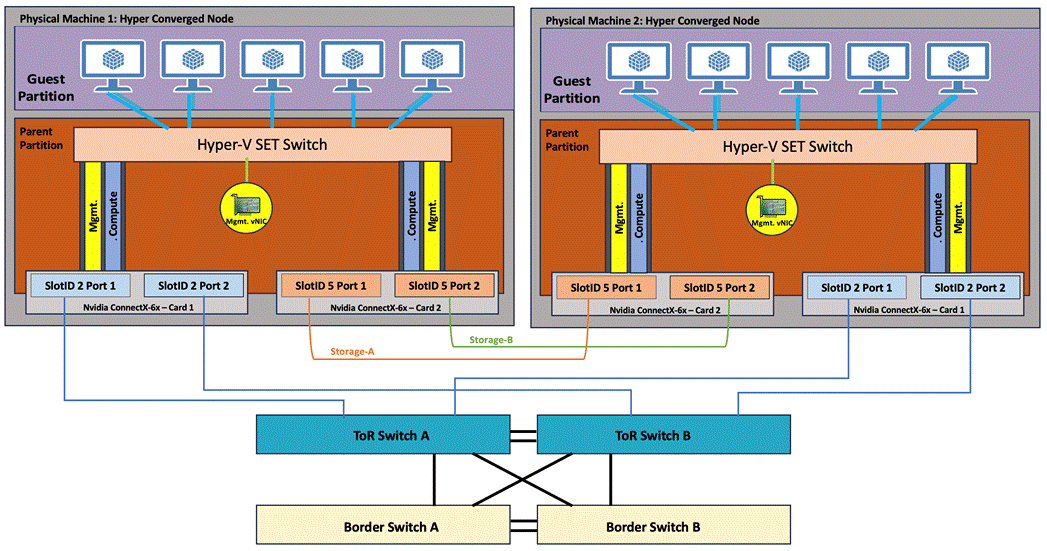
Storage Switchless
In this storage switchless network pattern, two intents – one intent for compute and management networks and a separate intent for storage network are deployed across all cluster nodes.
Consider this network topology:
● For enhanced network performance
● East-West storage traffic replication won’t interfere or compete with north-south traffic dedicated for management and compute
● Storage switchless is ideal only for smaller deployments (2 or 3-Node cluster) such as edge, ROBO, and so on.
For more information, go to: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/plan/two-node-switchless-two-switches
As illustrated in Figure 9 for storage switchless network reference pattern has the following logical network components:
Figure 9. Storage Switchless converged logical topology
Storage Network VLANs
The storage intent-based traffic in this pattern consists of two individual networks supporting RDMA traffic. Each interface is dedicated to a separate storage network, and both can use the same VLAN tag.
The storage network operates in different IP subnets. Each storage network uses the ATC predefined VLANs by default (711 and 712). However, these VLANs can be customized if necessary. If the default subnet defined by ATC is not usable, then manually assign all storage IP addresses in the cluster.
Management VLAN
All physical compute hosts require access to the management logical network. For IP address planning, each physical compute host must have at least one IP address assigned from the management logical network. A DHCP server can automatically assign IP addresses for the management network, or you can manually assign static IP addresses. When DHCP is the preferred IP assignment method, we recommend that you use DHCP reservations without expiration.
The management network supports the following VLAN configurations:
● Native VLAN – not required to supply VLAN IDs. This is required for solution-based installations.
● Tagged VLAN – supply VLAN IDs at the time of deployment.
The management network supports all traffic used for management of the cluster, including Remote Desktop, Windows Admin Center, and Active Directory.
Compute VLANs
Traditional VLANs are used to isolate your tenant workloads. Those VLANs are configured on the TOR switch’s port in trunk mode. When connecting new VMs to these VLANs, the corresponding VLAN tag is defined on the virtual network adapter.
Table 6 lists the VLANs used in this document where the default storage VLANs (711 and 712) used by Network ATC are overridden.
| VLAN Name |
VLAN ID |
| Management |
126 |
| Tenant |
100 |
| Storage-A |
107 |
| Storage-B |
207 |
Deployment Hardware and Software
This chapter contains the following:
● Customer Support Requirements
Firmware and drivers can be found on the Cisco download portal for Windows Server 2022 (Azure Local 23H2). These components will be periodically updated. Please sign up for notification at this download portal to receive notifications emails when updates are available.
The Cisco UCS C240 M6 or M7 standalone server platform for Microsoft Azure Local 23H2 firmware download portal can be accessed from the Cisco UCS C-Series Rack-Mount Standalone Server Software Download page. Also, it can be set up to notify you about the availability of the new firmware. Cisco highly recommends that you sign up for these notifications.
Table 7 lists the software components hosted on the Cisco download portal and are required for the firmware upgrade procedure.
| Component |
Description |
| ucs-c240m6-huu-4.2.3e.iso or later ucs-cxxx-drivers-windows.4.2.3e.iso or later |
Cisco UCS C240 M6 Rack Server Software Azure Local 23H2 (Win 2022) drivers for Cisco UCS C240 M6SN servers |
| ucs-c240m7-huu-4.3.2.240002.iso or later ucs-cxxx-drivers-windows.4.3.2f.iso or later ucs-c220m7-huu-4.3.2.240002.iso or later ucs-cxxx-drivers-windows.4.3.2f.iso or later |
Cisco UCS C240 M7 Rack Server Software Azure Local 23H2 (Win 2022) drivers for Cisco UCS C240 M7SN servers Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Server Software
|
The following tables list the individual component version that are part of the respective firmware bundles and driver package:
| Cisco UCS C-Series Rack-Mount Standalone Server |
||
| Component |
Firmware Version |
|
| Cisco UCS C240 M6SN |
4.2(3e) or later |
|
| Cisco UCS C240 M7SN |
4.3(2.240002) or later |
|
| Cisco UCS C220 M7N |
4.3(2.240002) or later |
|
The table below lists the component level firmware version in ucs-c240m6-huu-4.2.3e.iso file for M6 servers:
| Cisco UCS C240 M6SN Servers |
|||
| Component |
C-Series Rack-Mount |
Firmware Version |
Driver Version |
| CIMC (BMC) |
4.2(3e) |
4.2.3e |
|
| BIOS |
4.2(3e) |
C240M6.4.2.3c.0.0420230316 |
|
| Cisco-MLNX MCX623106AS-CDAT 2x100GbE QSFP56 PCIe |
4.2(3e) |
22.38.1900 |
Driver package - 3.10.51000 Driver file version - 3.10.25798.0 |
| Cisco UCS-M2-HWRAID |
4.2(3e) |
2.3.17.1014 |
|
| Boot SSD (UCS-M2-960GB) |
4.2(3e) |
D0MH077 |
10.0.17763.887 (inbox) |
| U.2 Intel P5500 NVMe |
4.2(3e) |
2CV1C033 |
10.0.20348.1547 (inbox) |
The table below lists the component level firmware version in ucs-c240m7-huu-4.3.2.240002.iso file for M7 servers:
| Cisco UCS C240 M7SN and C220 M7SN Servers |
|||
| Component |
C-Series Rack-Mount |
Firmware Version |
Driver Version |
| CIMC (BMC) |
4.3(2.240002) |
4.3(2.240002) |
|
| BIOS |
4.3(2.240002) |
C240M7.4.3.2d.0.1101232037 |
|
| Cisco-MLNX MCX623106AS-CDAT 2x100GbE QSFP56 PCIe |
4.3(2.240002 |
22.38.1900 |
Driver package - 3.10.51000 Driver file version - 3.10.25798.0 |
| Cisco UCS-M2-HWRAID |
4.3(2.240002 |
2.3.17.1014 |
|
| Boot SSD (UCS-M2-960GB) |
4.3(2.240002) |
D3MC000 |
10.0.17763.887 (inbox) |
| U.2 Intel P5520 NVMe |
4.3(2.240002) |
9CV10200 |
10.0.20348.1 (inbox) |
| Host Operating System |
|
| Host OS Version |
Azure Local OS 23H2 with current updates |
Figure10 illustrates the physical topology of an Azure Local deployment on Cisco UCS C240 M6/M7 servers with Cisco Nexus 9300 series switches. The cabling information can be found in the Appendix of this document.
Figure 10. Physical Infrastructure
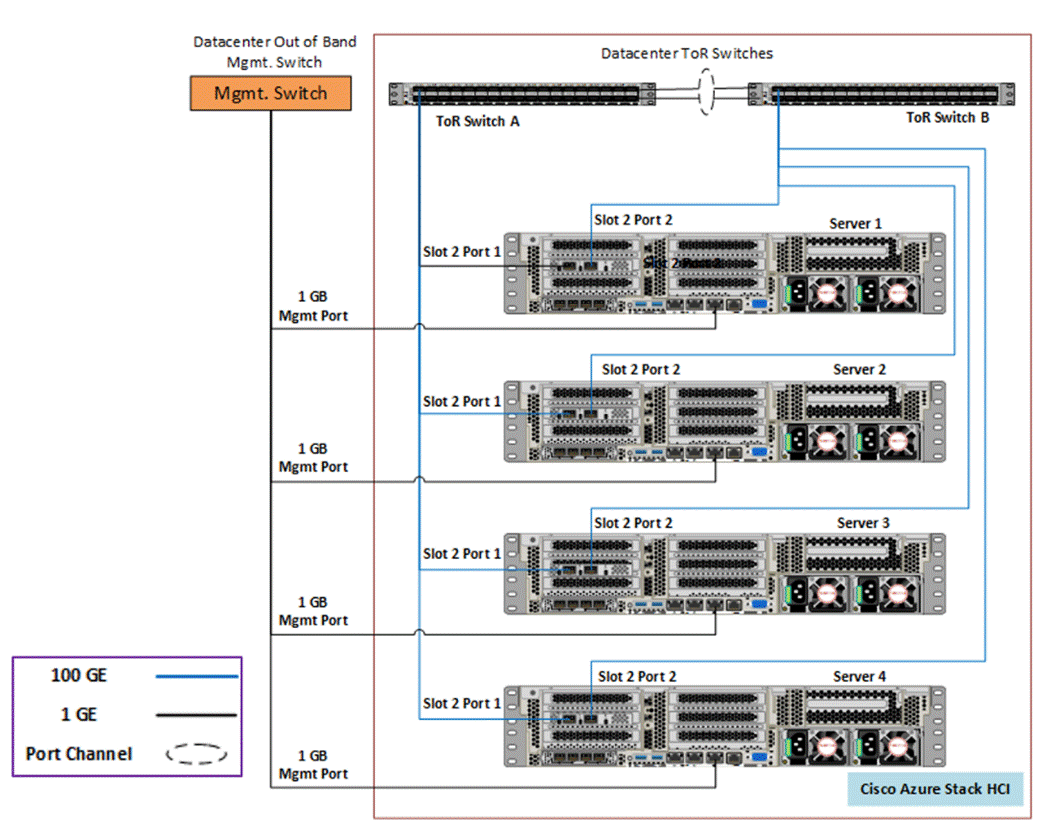
Figure 11 illustrates the data ports and management ports on the back of each server with one dual-port network adapter in a storage switched fully converged network pattern.
● In this network reference pattern, the ToR switches in redundant configuration handle northbound/southbound traffic.
● Two ports teamed on the host side handle the management, compute, and RDMA storage traffic connected to the ToR switches. Each port in the network adapter on each server is connected to a different ToR switch. SMB multichannel capability provides path aggregation and fault tolerance.
In this example, Server 1 has these two 100Gb data ports connected to ports eth1/1 port on ToR A and B switches. The single dedicated out-of-band management port is connected to an OOB management switch.
Figure 11. Storage switched, fully converged network pattern with one dual-port network adapter
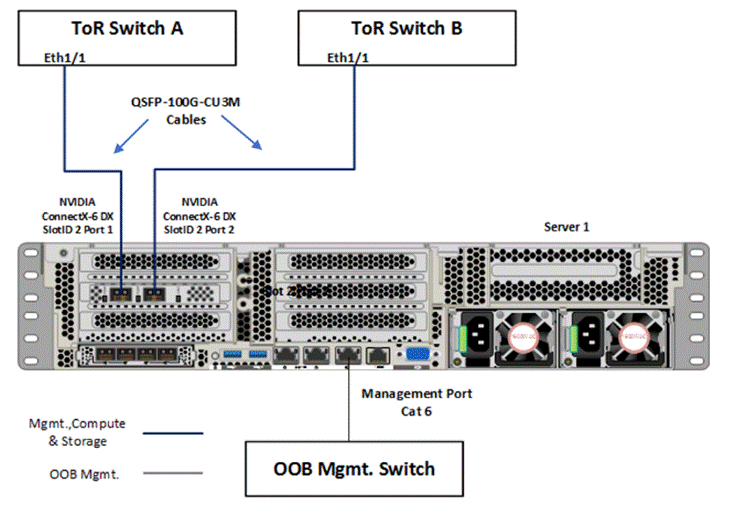
Figure 12 illustrates the data ports and management ports on the back of each server with two dual-port network adapters in a storage switched fully converged network pattern.
● In this network reference pattern, the ToR switches in redundant configuration handle northbound/southbound traffic.
● Four ports teamed on the host side handle the management, compute, and RDMA storage traffic connected to the ToR switches. Each port on the two network adapters on each server is connected to a different ToR switch. SMB multichannel capability provides path aggregation and fault tolerance.
In this example, Server 1 has two 100Gb data ports from the first network adapter connected to ports eth1/1 port on ToR A and B switches and, the other two 100Gb data ports from the second network adapter connected to ports eth1/2 port on ToR A and B switches. The single dedicated out-of-band management port is connected to an OOB management switch.
Figure 12. Storage switched, fully converged network pattern with two dual-port network adapters
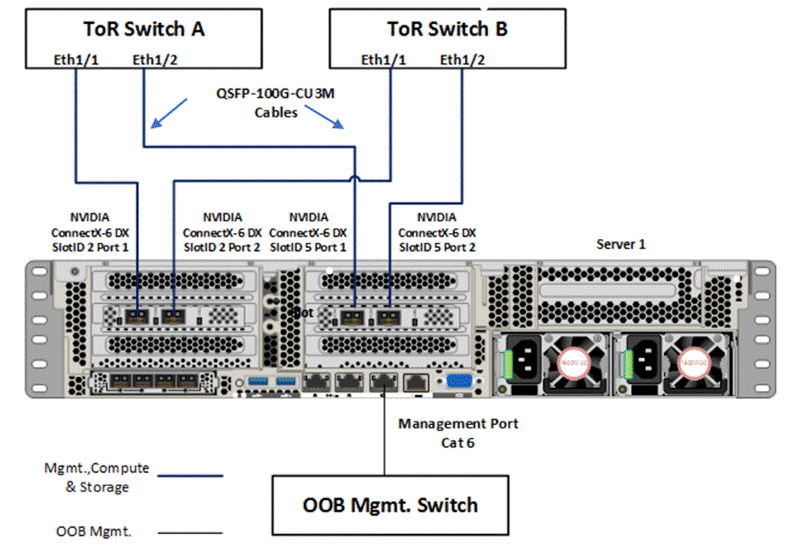
Figure 13 illustrates the data ports and management ports on the back of each server with two dual-port network adapters in a storage switched, non-converged network pattern.
● In this network reference pattern, the ToR switches in redundant configuration handle northbound/southbound traffic.
● Two ports, one from each network adapter (‘SlotID 2 Port 1’ and ‘SlotID 5 Port 2’) teamed on the host side handle the management and compute traffic connected to the ToR switches. These two ports on each server are connected to a different ToR switch.
● Two ports, one from each network adapter (‘SlotID 2 Port 2’ and ‘SlotID 5 Port 1’) in standalone configuration are used for RDMA storage traffic. These two ports on each server are connected to a different ToR switch. SMB multichannel capability provides path aggregation and fault tolerance.
In this example, Server 1 has two 100Gb data ports from the first network adapter connected to ports eth1/1 port on ToR A and B switches and, the other two 100Gb data ports from the second network adapter connected to ports eth1/2 port on ToR A and B switches. The single dedicated out-of-band management port is connected to an OOB management switch.
Figure 13. Storage switched, non-converged network pattern with two dual-port network adapters
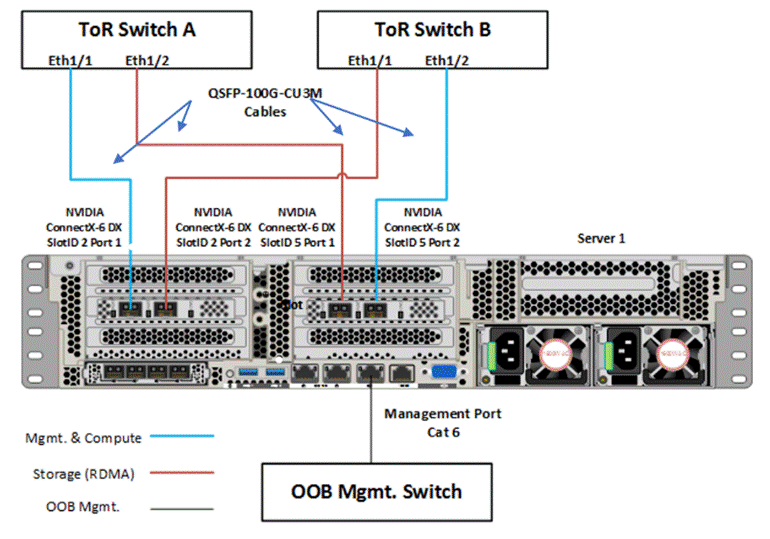
Figure 14 illustrates the data ports and management ports on the back of each server with two dual-port network adapters in a storage switchless network pattern:
● In this network reference pattern, the ToR switches in redundant configuration handle northbound/southbound traffic.
● Two ports (‘SlotID 2 Port 1’ and ‘SlotID 2 Port 2’) teamed on the host side handle the management and compute traffic connected to the ToR switches. These two ports on each server are connected to a different ToR switch.
● Two RDMA ports (‘SlotID 5 Port 1’ and ‘SlotID 5 Port 2’) in standalone configuration are used for East-West storage traffic. These two ports on each server are directly connected in a full-mesh configuration. SMB multichannel capability provides path aggregation and fault tolerance.
Figure 14. Storage Switchless network pattern with two dual-port network adapters
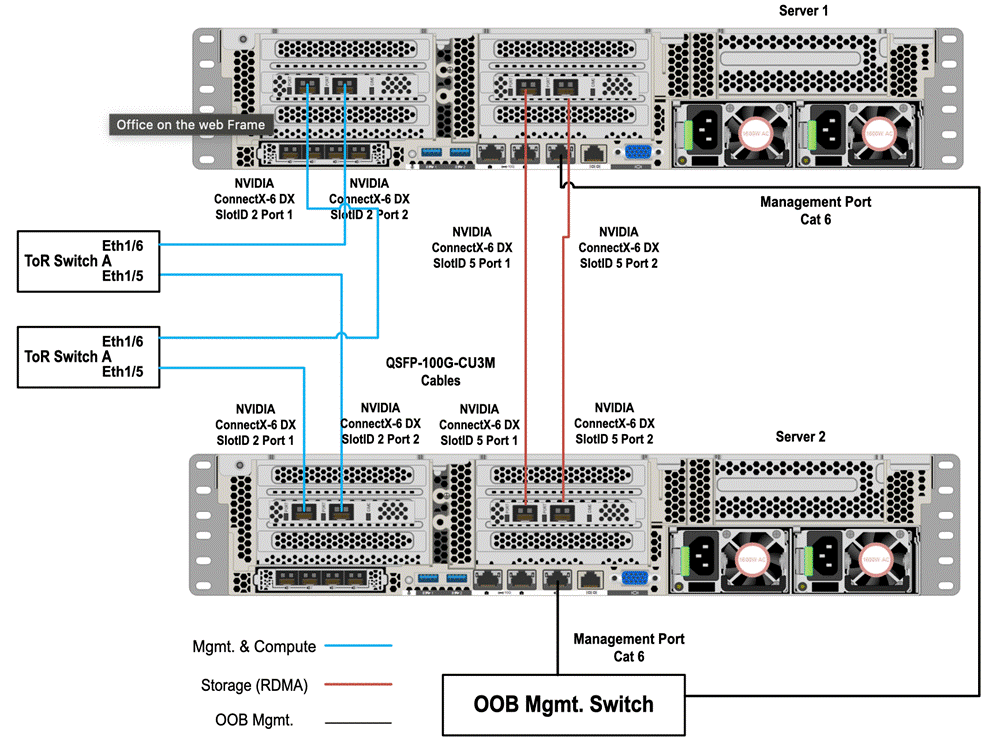
The following is the checklist for the deployment of a 4-node Azure Local cluster:
● ToR switch must support the Azure Local requirements
● ToR switch must implement L2 and L3 configuration for transporting northbound host and tenant traffic
● Out-of-Band management switch must be provided for connecting the ToR switches and Cisco UCS C240 M6 and M7 servers
● 3 IP addresses are required on the Out-of-Band Management Network for the ToR Cisco Nexus switches
● 1 IP address must be provided for each host (server) on the Out-of-Band Management Network
● VLANs
◦ 1 Management
◦ 2 Storage
◦ 1 or more tenant
● IP subnets and addresses for all endpoints for the above VLANs
● Storage VLANs and Storage subnets need to be configured on the ToR switches
● Host operating system must have access to Azure
● Datacenter infrastructure that includes Active Directory Services, DNS, and NTP
● Cluster Quorum Witness
◦ Can be Files Share or Cloud Witness
◦ Required for Cluster with fewer than 5 cluster nodes
● Recommended for clusters with 3 or greater number of nodes
● Deployment host must be provided with access to the Out-of-Band Managed network and host management network
◦ See the Remote Management Host configuration in the Appendix
● Deployment host must be running Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2022 and be domain joined to the same domain as the Azure Local hosts
● Account used to deploy Azure Local must have administrative rights on the Azure stack hosts and permissions to join the domain, add cluster securing principle to the domain, update the DNS A records for the computer joining the domain and Cluster Aware Updating services, and store Bitlocker keys in the domain
● Azure Account for registering and deploying Azure Local, version 23H2 system
● Download Azure Local OS 23H2 from the Azure portal
● Download Cisco Drivers for Azure Local 23H2 deployment from Cisco download portal (link to be added)
● Recommended Items
◦ Windows Deployment Service for PXE boot OS installation (Can be running on deployment host)
◦ DHCP server with scope for management subnet to support PXE booting. Scope is temporary and only needed during PXE boot installation phase. (Can be running on deployment host)
This solution must be purchased using the Cisco UCS product ID UCS-MAH-B00R00-M6. This product ID includes all of the required hardware to build the solution as well as the Cisco Solution Support for this solution. A sample BoM is documented in the Cisco UCS for Microsoft Azure Local Datasheet at the following link: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/data-center-virtualization/microsoft-applications-on-cisco-ucs/microsoft-azure-stack-hci.html
The solution must adhere to Cisco Guidance for deploying Azure Local on Cisco UCS product ID UCS-MAH-B00R00.
Firmware and driver version must match the versions specified in this document. This document will be update periodically with more current firmware and driver versions. Customers are required to update their systems to the latest recommended firmware and driver version for this Azure Local solution.
Note: The current firmware and drivers can be downloaded from the Cisco download portal for Azure Local. The link to the download portal is in the Firmware and Drivers section.
Note: You must obtain an Azure Local support contract from Microsoft. The following is an example of this type of support contract:
● Unified Support for Enterprise
● Premier Support for Enterprise
For support option details, go to: Get support for Azure Local - Azure Local | Microsoft Docs
This chapter contains the following:
● Requirements for Azure Local version 23H2
● Configure Cisco Integrated Management Controller for Cisco UCS C240 Servers
● Claim Cisco UCS C240 Standalone Servers in Cisco Intersight
● Configure Cisco UCS C240 Standalone Servers using Cisco Intersight
● Configure Policies to Create Server Profile
● Prepare the Active Directory
● Install the Operating System
● Configure the Operating System using SConfig
● Register Servers with Azure Arc and Assign Required Permissions for Deployment
● Deploy Azure Local using the Azure Portal
This chapter provides the instructions to deploy an Azure Local, version 23H2 system using Azure portal. You can also deploy an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template which is out of the scope of this document. To deploy from an ARM template, go to: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/deploy/deployment-azure-resource-manager-template.
Figure 15 shows the high-level deployment steps for the Azure Local version 23H2 system using the Azure portal.
Figure 15. High-level deployment steps
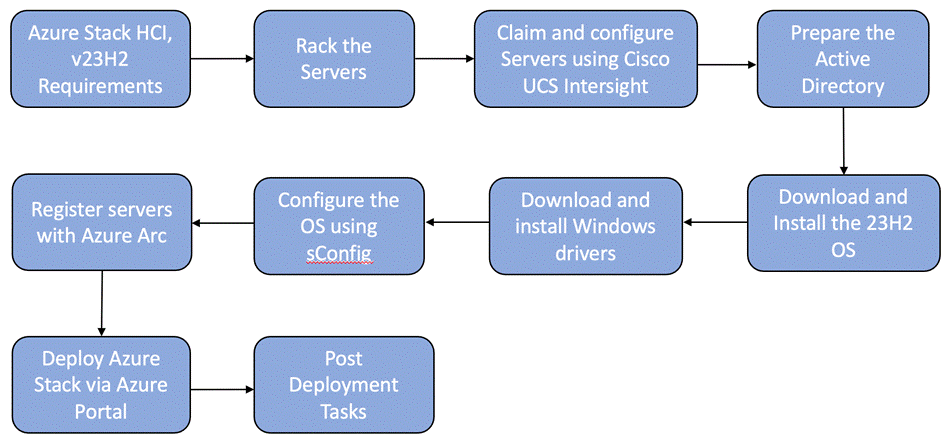
Note: Azure Local, version 23H2 is the latest GA version and doesn't support the upgrade from version 22H2. Begin the installation with a recent baseline build and then apply any update build. Strictly follow the version 23H2 deployment instructions. Don't mix steps from version 22H2 and version 23H2. For release information, go to: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/release-information-23h2
Requirements for Azure Local version 23H2
Refer to the following links to complete the requirements to deploy Azure Local version 23H2:
● Azure and System requirements: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/concepts/system-requirements-23h2
● Physical network requirements: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/concepts/physical-network-requirements?tabs=overview%2C23H2reqs
● Host network requirements: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/concepts/host-network-requirements
● Firewall requirements: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/concepts/firewall-requirements
● Network reference patterns: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/plan/network-patterns-overview
Note: A contiguous block of at least six IP addresses are required on your management network to use for Azure Local and for services such as Azure Arc, omitting addresses already used by the servers.
Configure Cisco Integrated Management Controller for Cisco UCS C240 Servers
Procedure 1. Configure Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC)
Step 1. In the BIOS POST screen, press F8 to display the CIMC configuration screen.
Step 2. A prompt displays to enter the default password and provide the user password (only first time).
Step 3. Select Dedicated NIC mode.
Step 4. Select Static or DHCP assignment.
Step 5. For Static mode, configure the IP address, Netmask and Gateway for the IPv4 setting of the CIMC.
Step 6. Select None for NIC redundancy.
Step 7. Press F10 to save the configuration and exit the utility.
Step 8. Open a web browser on a computer on the same network.
Step 9. Enter the IMC IP address of the Cisco UCS C240 M6M7 Server: http://<<var_cimc_ip_address.
Step 10. Enter the login credentials as updated in the IMC configuration.
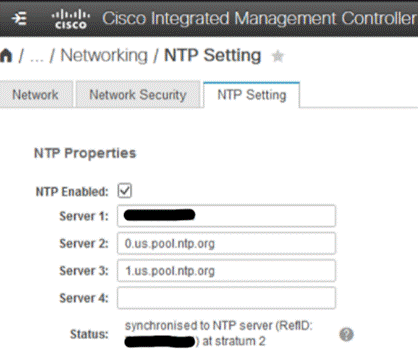
Procedure 2. Synchronize Cisco UCS C240 Servers to NTP
Note: These steps provide the details for synchronizing the Cisco UCS environment to the NTP server.
Step 1. Log back into Cisco IMC using a URL that starts with https://.
Step 2. Select the Admin at the bottom of the left window and expand.
Step 3. Click Networking > NTP Setting.
Step 4. Select NTP Enabled check box to enable and enter the NTP server addresses.
Claim Cisco UCS C240 Standalone Servers in Cisco Intersight
Procedure 1. Cisco Intersight Device Claim – Register Cisco IMC to Cisco Intersight
Step 1. From the Cisco IMC, go to Admin > Device connector.
Step 2. Click Settings.
Step 3. From Settings, go to the General tab and enable the Device connector. For the Access Mode, select Allow control and enable Tunneled vKVM.
Note: Tunneled vKVM is supported only for Cisco UCS C-Series servers with an Advantage or Premier license. Tunneled vKVM can be launched to complete OS installation from Cisco Intersight.
Step 4. Verify reachability to Cisco Intersight is updated after configuring DNS, NTP and Proxy Settings.
Step 5. Copy the Device ID and Claim Code.
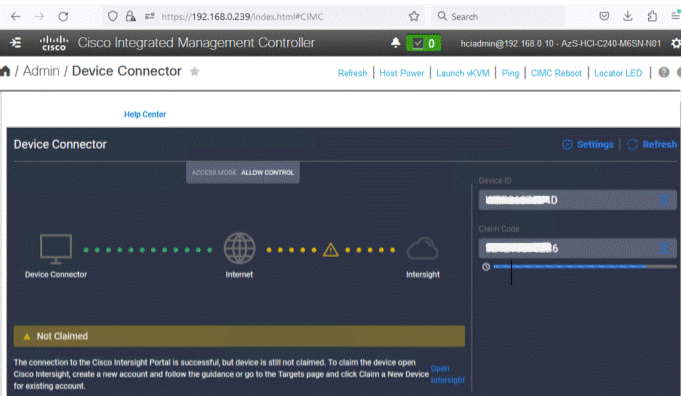
Step 6. Create a Cisco Intersight account—go to https://intersight.com/ to create your Intersight account. You must have a valid Cisco ID to create a Cisco Intersight account. If you do not have a Cisco ID, create one by clicking Sign Up.

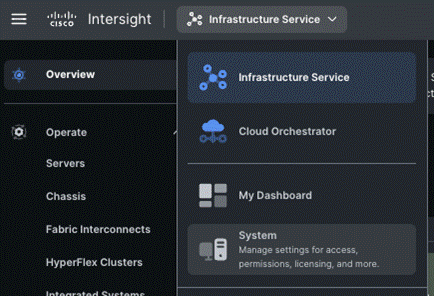
Step 7. After logging in, from the Service Selector drop-down list, select System as shown below:
Step 8. Go to ADMIN > Targets and click Claim a New Target.
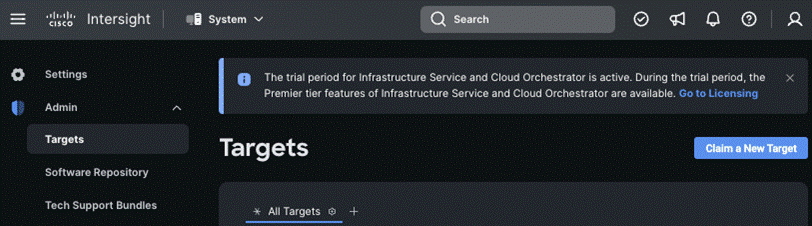
The Select Target Type window displays.
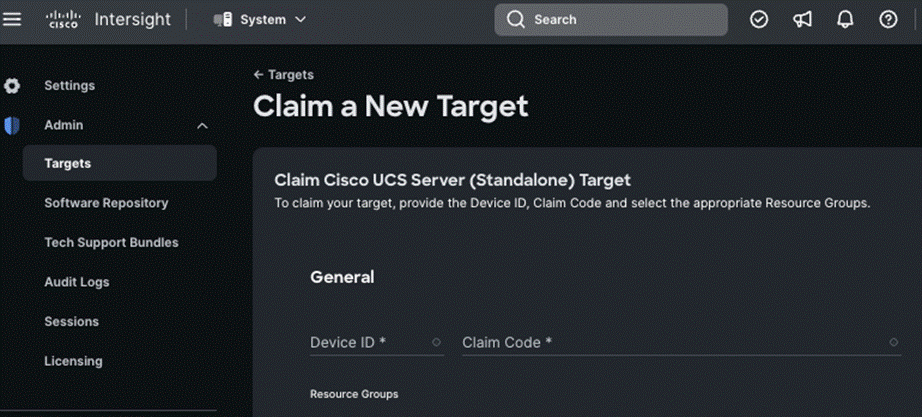
Step 9. In the filter column, select Compute / Fabric and select Cisco UCS Server (Standalone), and then click Start.
Step 10. Enter the Device ID and Claim Code obtained from Cisco IMC.
Step 11. Click Claim.
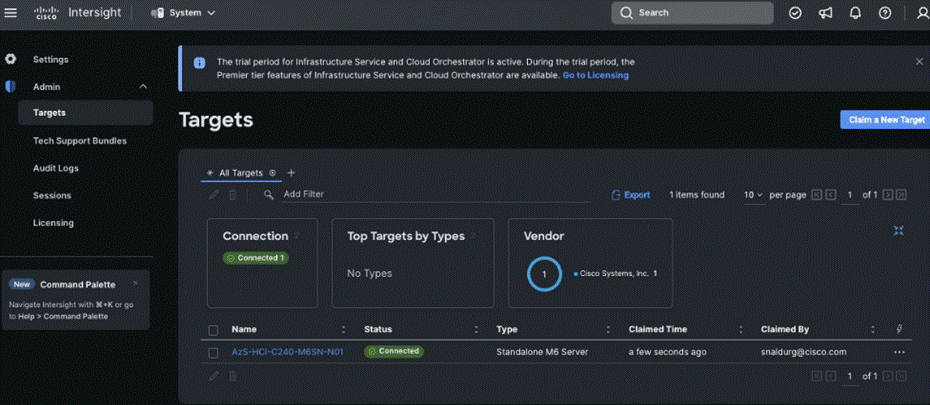
The Cisco UCS Server instance will be added to Intersight.
Step 12. Go back to Cisco IMC to confirm that the device is claimed. Click Refresh to update the status.
![]()
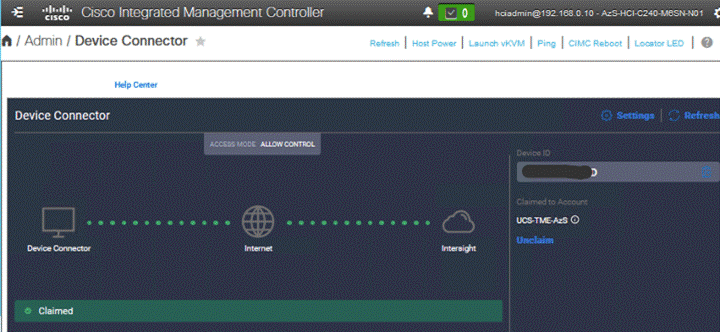
Step 13. Repeat steps 1 - 12 to claim other devices. After the targets are claimed, you can view the managed targets in the Targets table view.
Step 14. Go to Settings > Admin > Licensing and register the license to assign Essential, Advanced, or Premier license for Cisco Intersight.
For more information about the different license tiers for Cisco Intersight, go to: Cisco Intersight License Management.
Configure Cisco UCS C240 Standalone Servers using Cisco Intersight
Procedure 1. Upgrade Cisco IMC firmware for Cisco UCS C240 from Cisco Intersight
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, select Infrastructure Service.
Step 2. Go to Operate > Servers, to launch the Servers Table view and select all the servers that require CIMC firmware upgrade.
Step 3. Click the ellipses below the selected servers and click Upgrade Firmware.
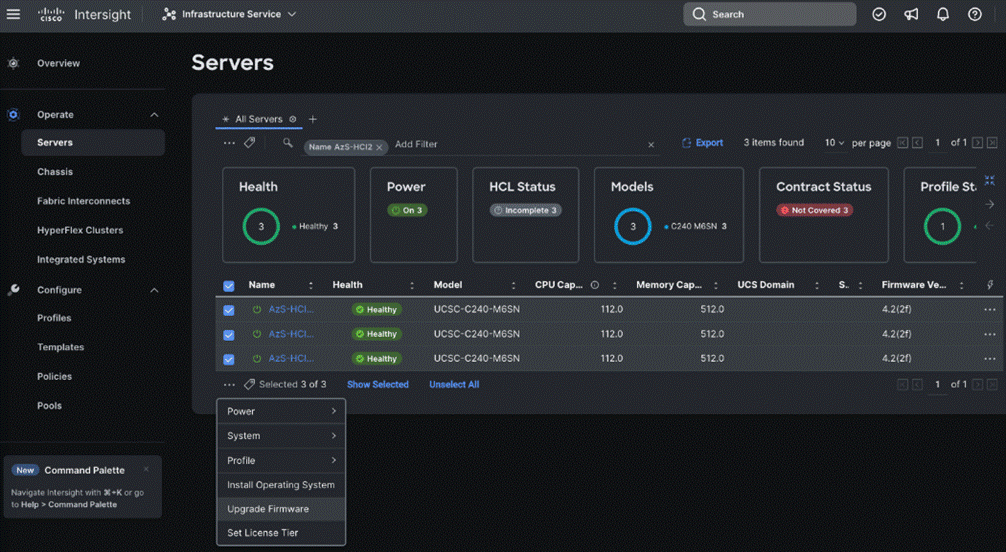
Step 4. On the Upgrade Firmware page, click Start.
Step 5. On the General page, select all the Servers and click Next.
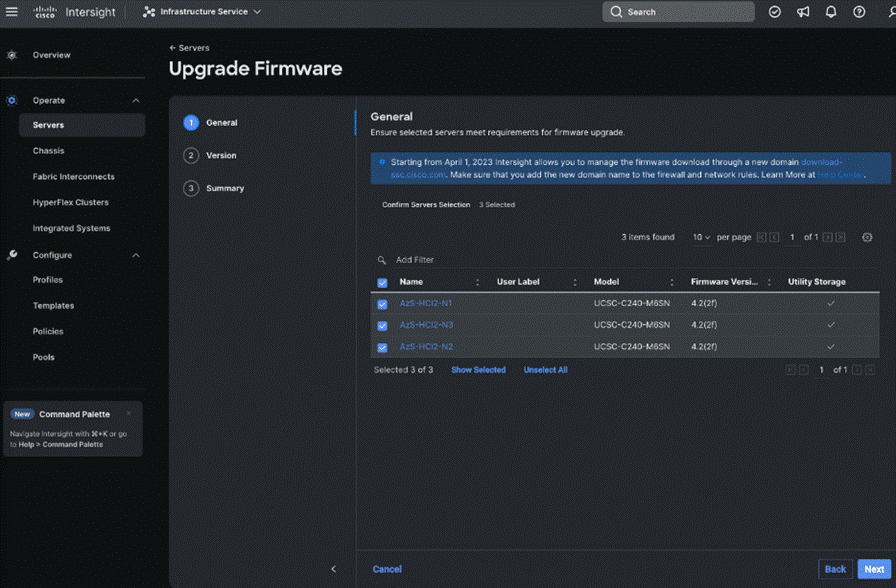
Step 6. On the Version page, enable the Advanced Mode to exclude upgrade of drives and storage controllers:
◦ Exclude Drives—Check this box to exclude upgrade of drives.
◦ Exclude Storage Controllers—Check this box to exclude upgrade of storage controllers.

Note: To exclude storage controller, ensure that the firmware version of Cisco IMC and the target upgrade firmware version is 4.1(3a) or later release.
Step 7. On the Version page under Cisco Repository, select a firmware version bundle from the list below to upgrade the servers to and click Next.
Step 8. On the Summary page, confirm the configuration and click Upgrade to initiate the upgrade.
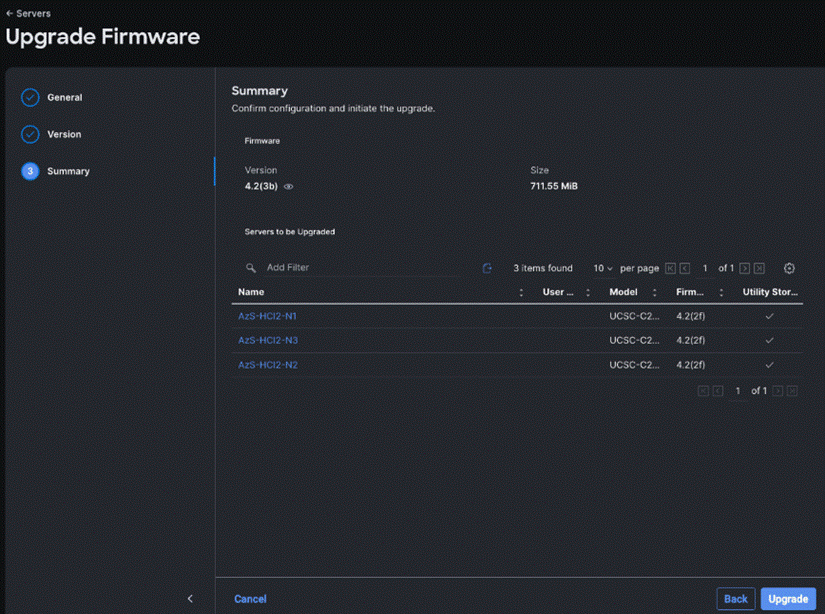
For more information on upgrading Cisco UCS C-Series Standalone Servers Firmware, go to: Before you begin.
The upgrade workflow proceeds based on the selected reboot option.
Configure Policies to Create Server Profile
Note: These steps can also be completed at the time of the Server Profile creation.
Procedure 1. Create Virtual KVM Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, select Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > Virtual KVM and click Start.
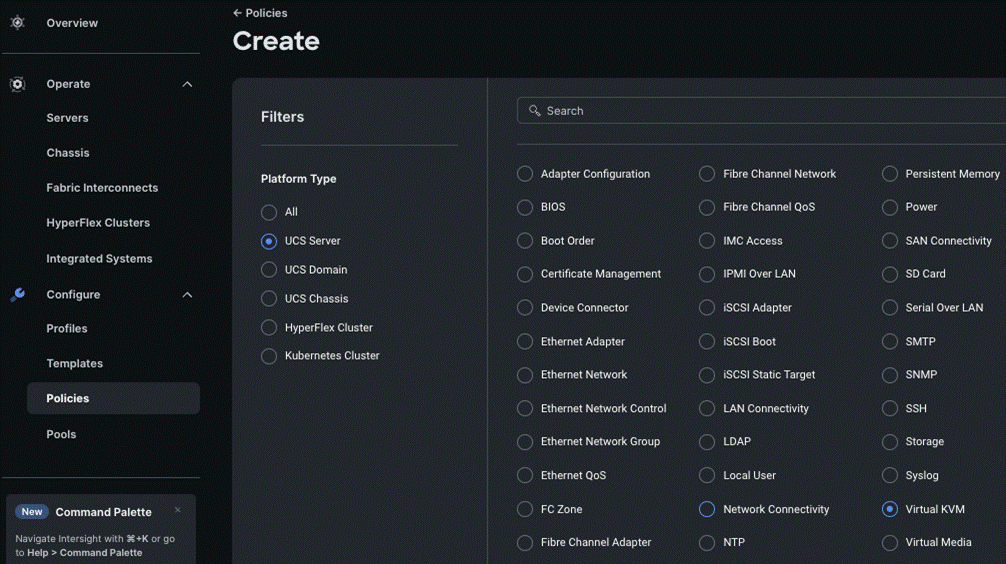
Step 3. On the Virtual KVM Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
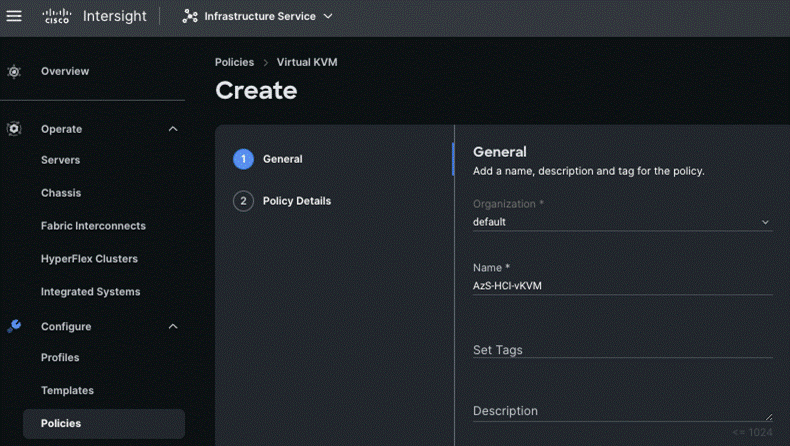
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, enable Allow Tunneled vKVM, and other options as shown below and click Create.
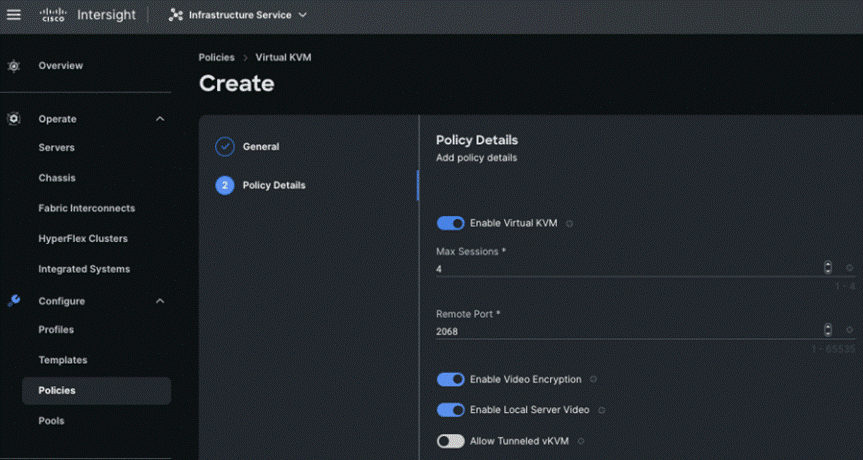
Procedure 2. Create Network Connectivity Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, select Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > Network Connectivity and click Start.
Step 3. On the Network Connectivity Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, enter the preferred IPv4 DNS server addresses and configure other options as shown below and click Create.
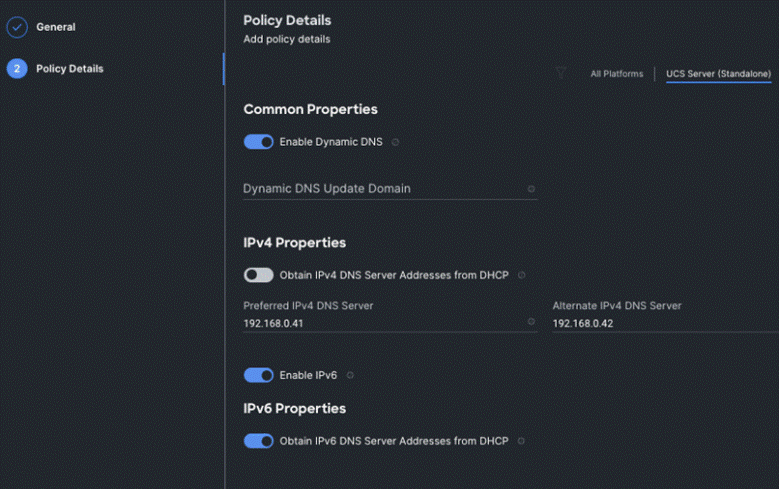
Procedure 3. Create SSH Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, select Infrastructure Services and navigate to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > SSH and click Start.
Step 3. On the SSH Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, Enable SSH and click Create.
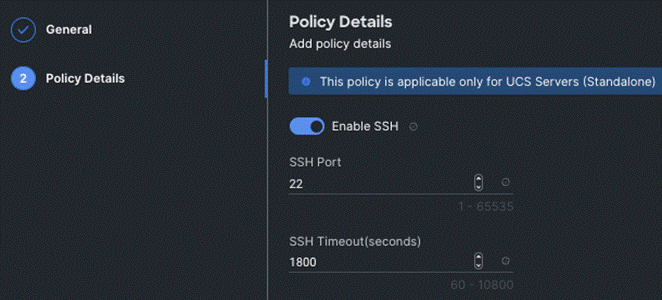
Procedure 4. Create NTP Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > NTP and click Start.
Step 3. On the NTP Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, Enable NTP, enter the NTP Server addresses and select a TimeZone. Click Create.
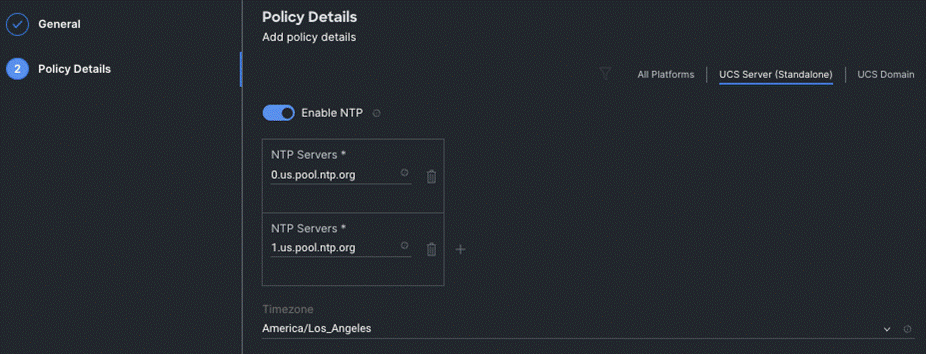
Procedure 5. Create Local User Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > Local User and click Start.
Step 3. On the Local User Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
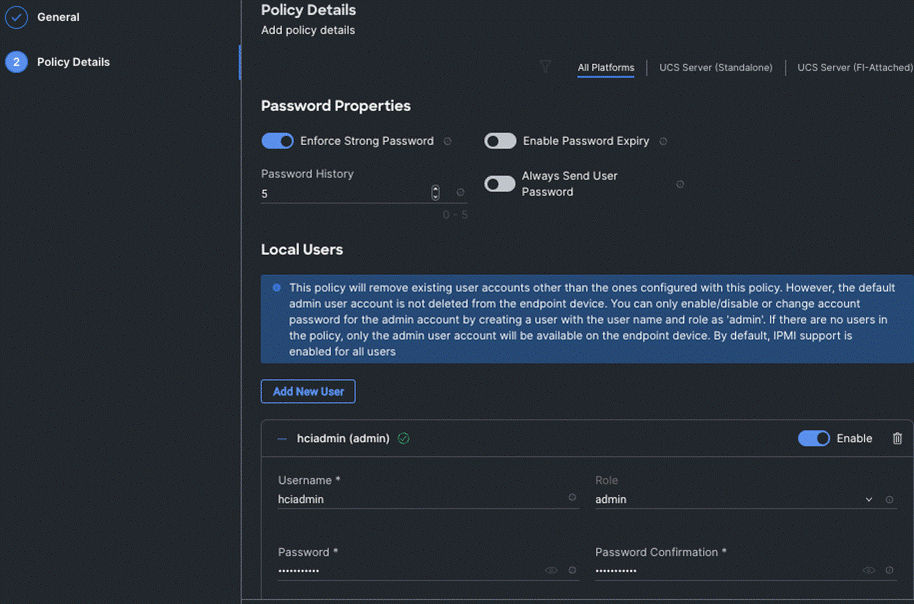
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, Configure Password Properties and Add New User. Click Create.
Procedure 6. Create Virtual Media Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > Virtual Media and click Start.
Step 3. On the Virtual Media Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
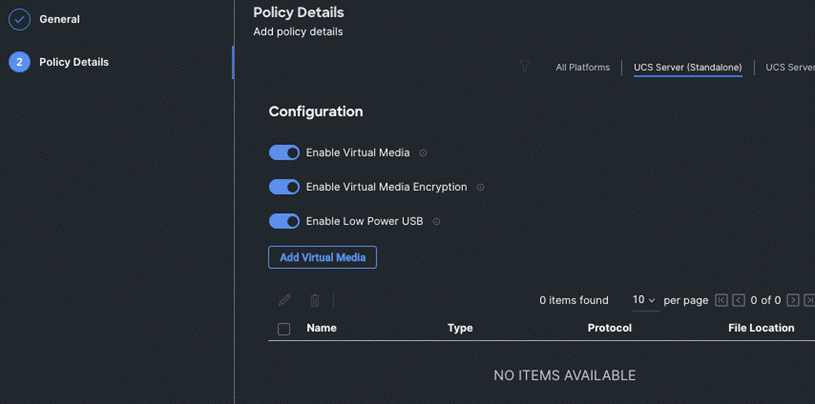
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, Enable Virtual Media and other properties if required. Click Create.
Procedure 7. Create Boot Order Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > Boot Order and click Start.
Step 3. On the Boot Order Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
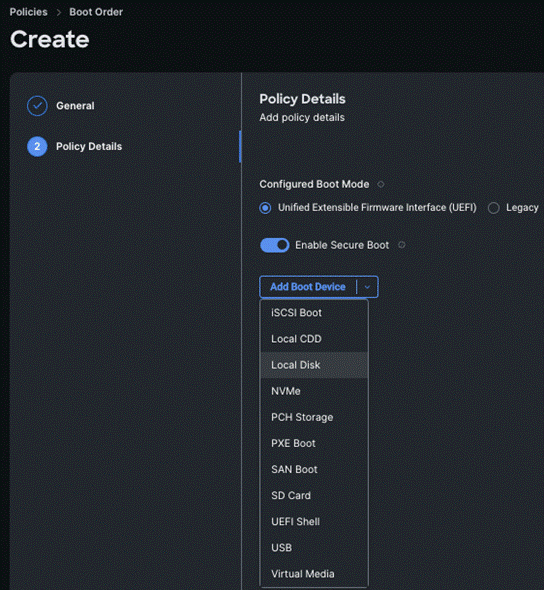
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, Enable Secure Boot and from the Add Boot Device drop-down list, select the boot devices.
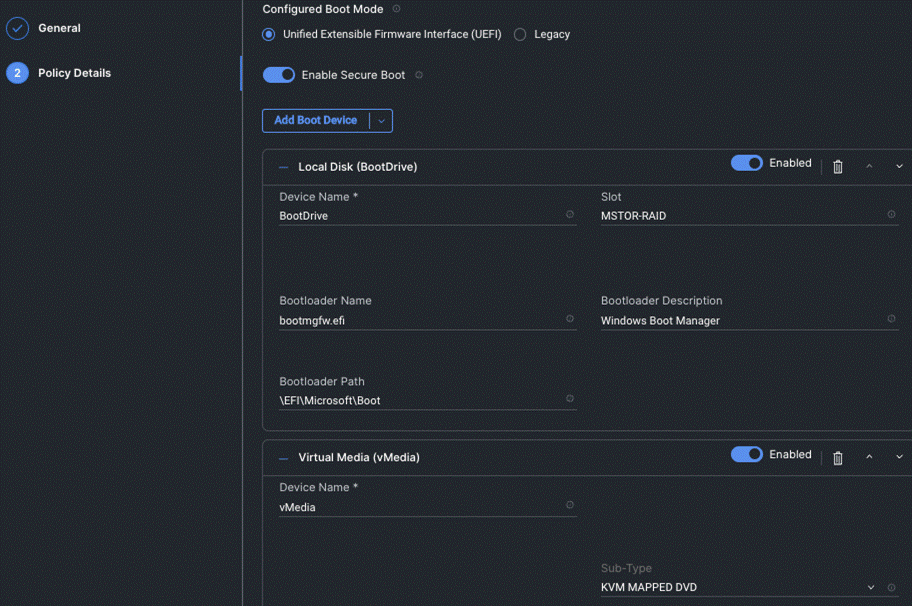
Step 5. Select Local Disk and Virtual Media and enter the details as shown in the below and click Create.
Procedure 8. Create BIOS Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > BIOS and click Start.
Step 3. On the BIOS Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, configure the tokens as shown in the following images, leaving the rest as defaults:
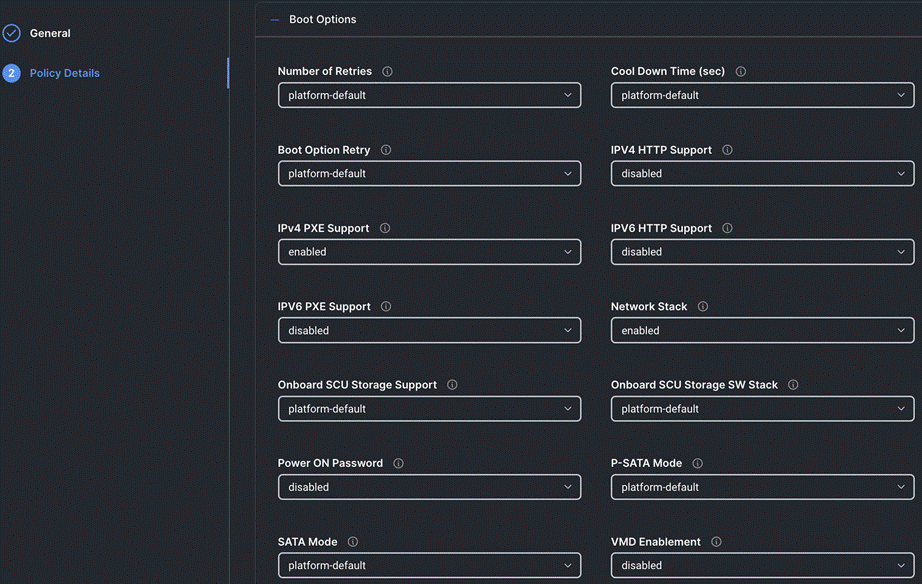
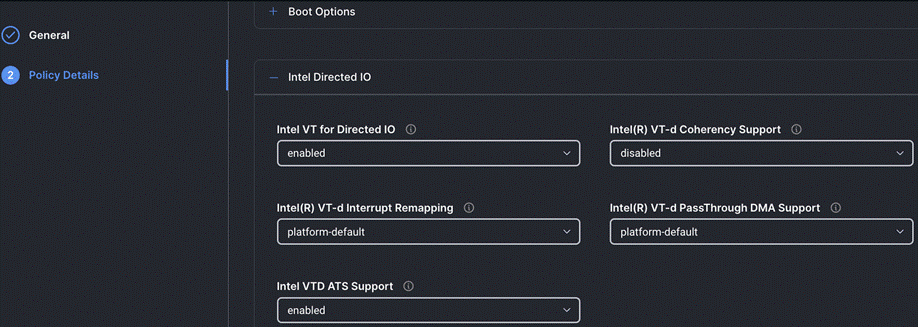
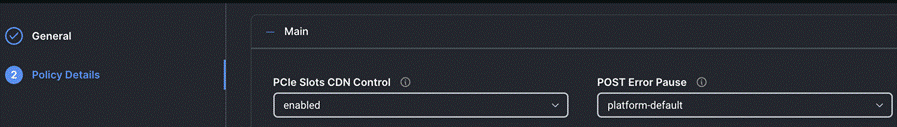


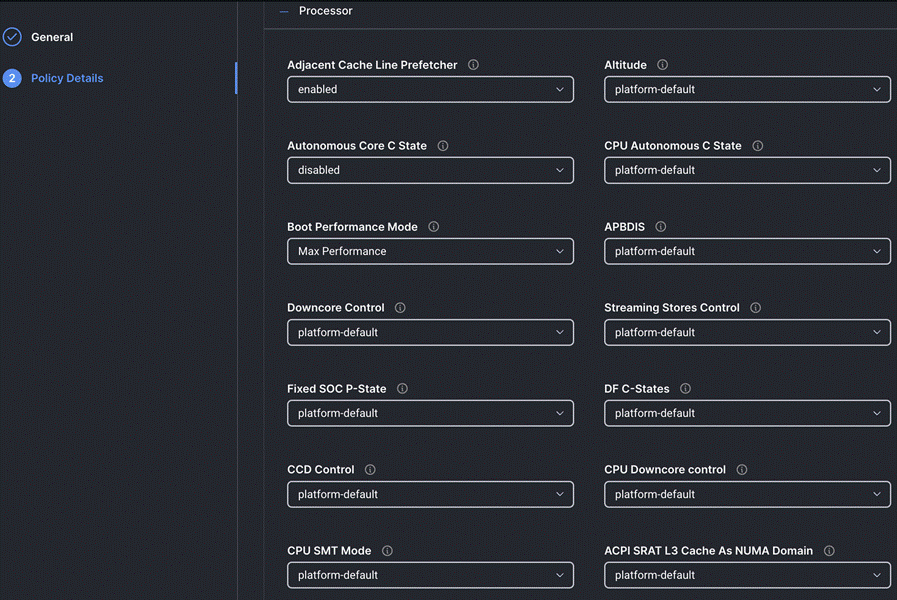
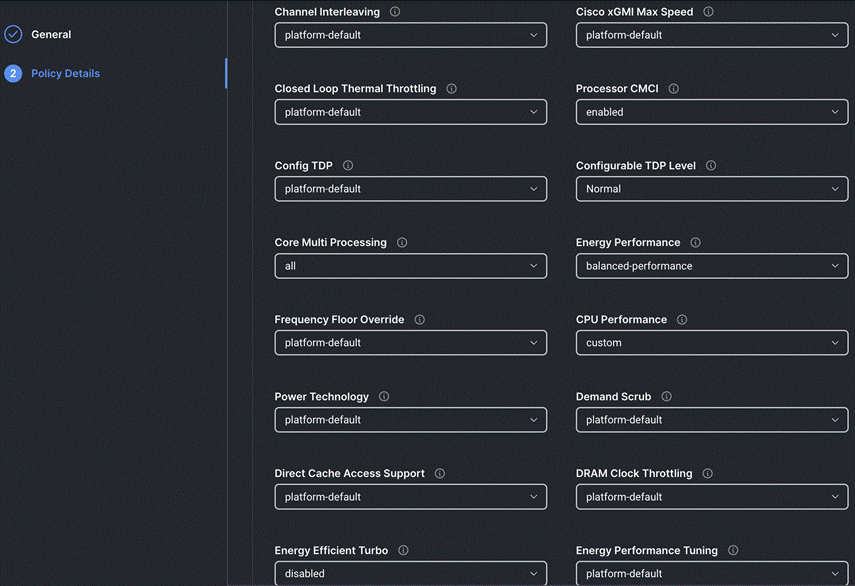
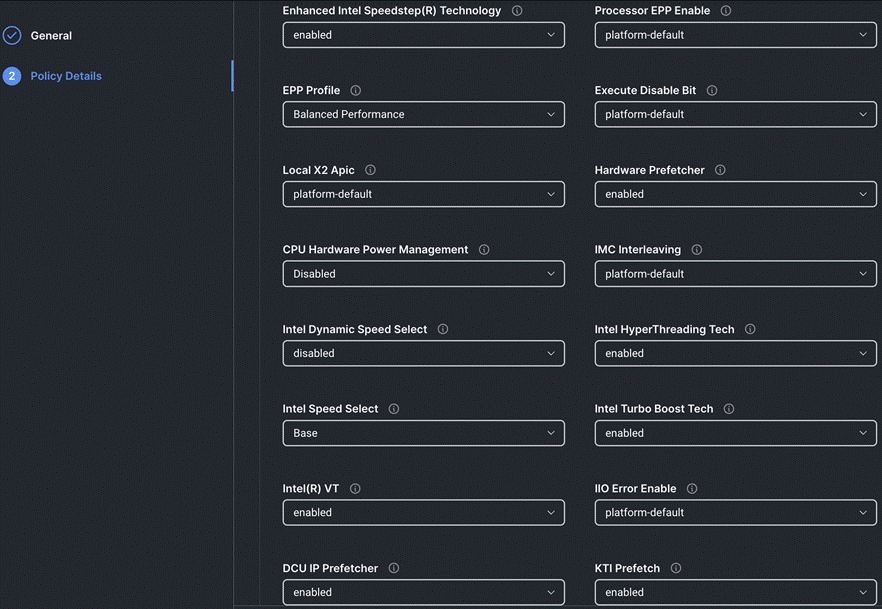
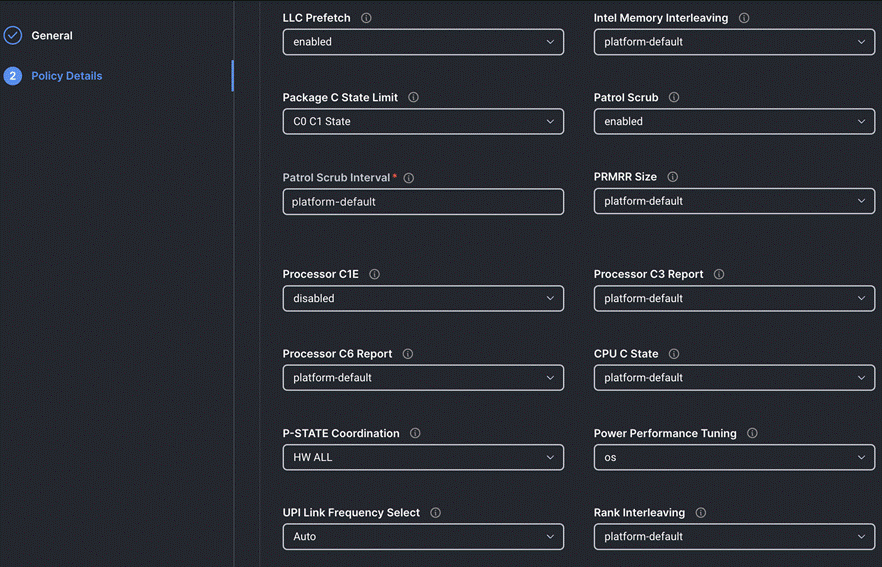
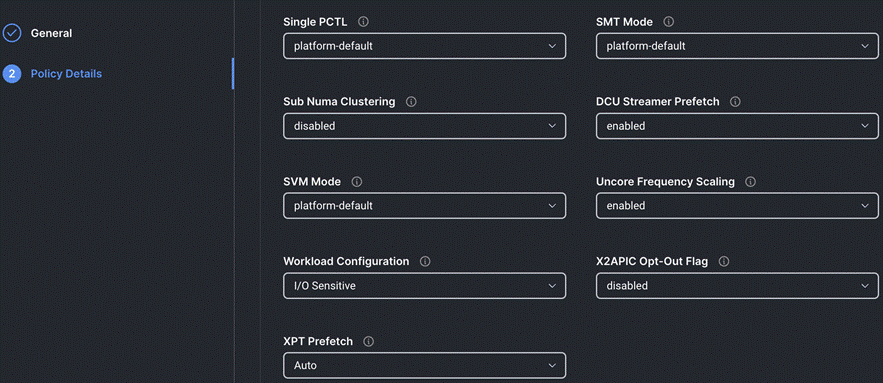
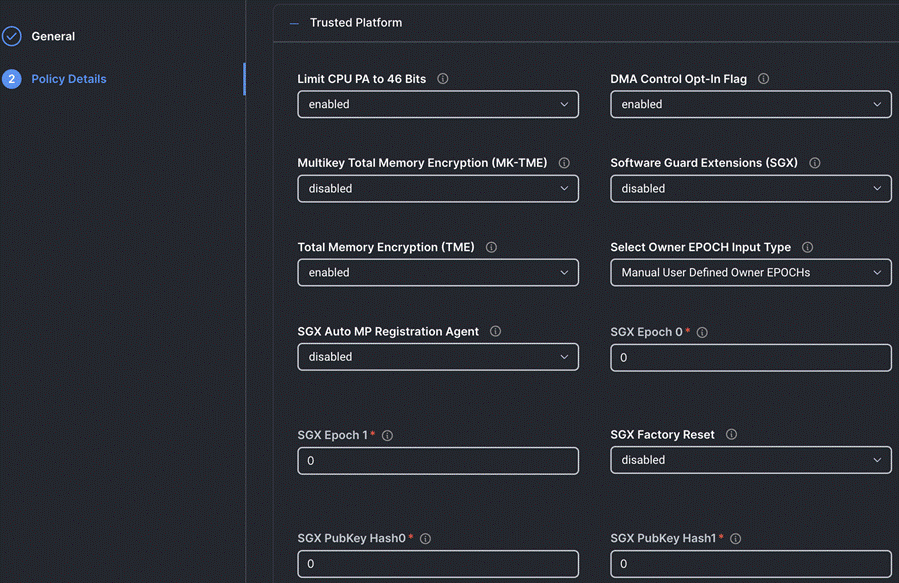

Procedure 9. Create Storage Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Server > Storage and click Start.
Step 3. On the Storage Create page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
Step 4. On the Policy Details page, Enable the M.2 RAID Configuration and select the MSTOR RAID-1 (MSTOR RAID) from the drop-down list as shown in the following figure:
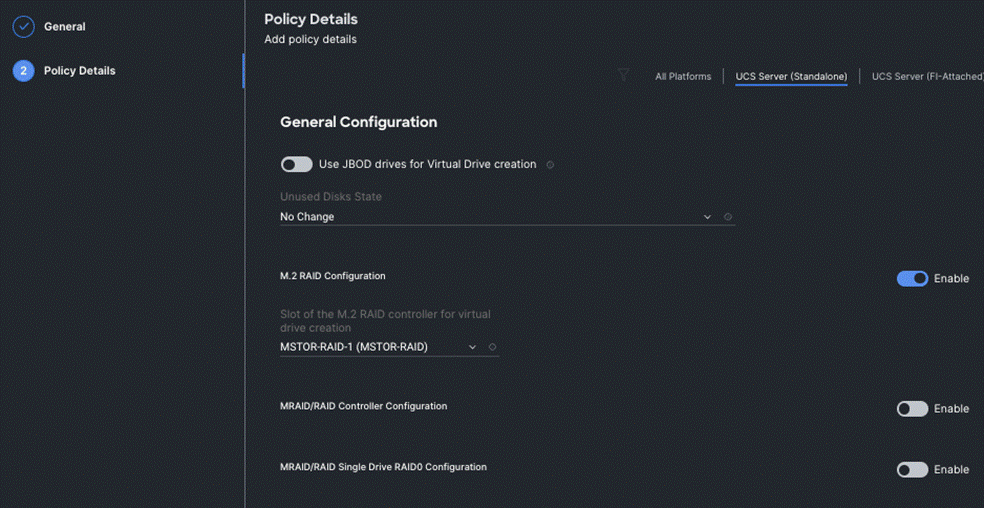
Procedure 10. Create Thermal Policy
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Policies and click Create Policy.
Step 2. On the Create page for Policies, go to UCS Chassis > Thermal and click Start.
Step 3. On the Thermal Create General page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag and click Next.
Step 4. On the Thermal Create Policy Details page, click the drop-down list under Fan Control Mode and select .
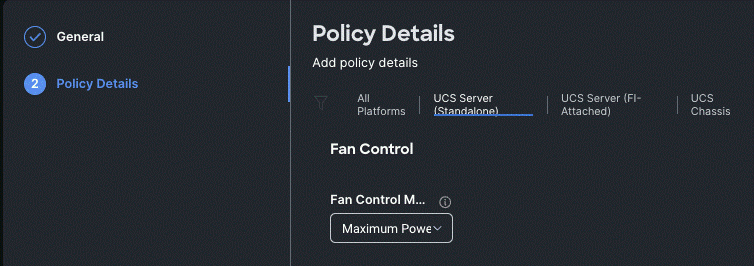
Procedure 11. Create UCS Server Profile
This procedure explains how to create a Cisco UCS server profile, clone it, and deploy servers.
Alternatively, you can create a server profile template from which multiple server profiles can be derived and deployed on servers. For more information on server profile templates, go to: https://intersight.com/help/saas/resources/cisco_intersight_managed_mode_configuration#server_profile_templates
Step 1. From the Service Selector drop-down list, click Infrastructure Services and go to Configure > Profiles and click Create UCS Server Profile.
Step 2. On the Create UCS Server Profile page, click Start.
Step 3. On the General page, enter the Organization, Name, Description and create a new tag or assign an existing tag. For Target Platform, select UCS Standalone under and click Next.
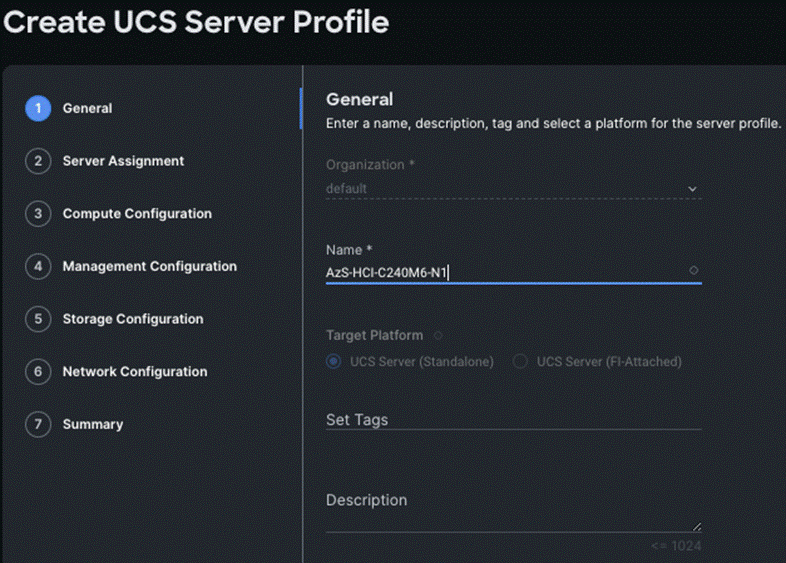
Step 4. On the Server Assignment page, click Assign Now and select a server from the list shown below:
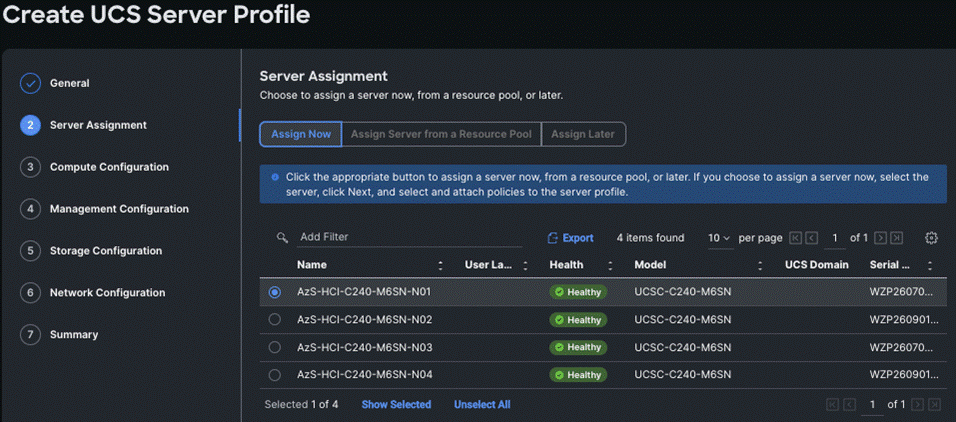
Step 5. On the Compute Configuration page, hover the mouse cursor over right-side of the row next to BIOS and click Select Policy.

Step 6. Select the policy created for BIOS in the previous section.
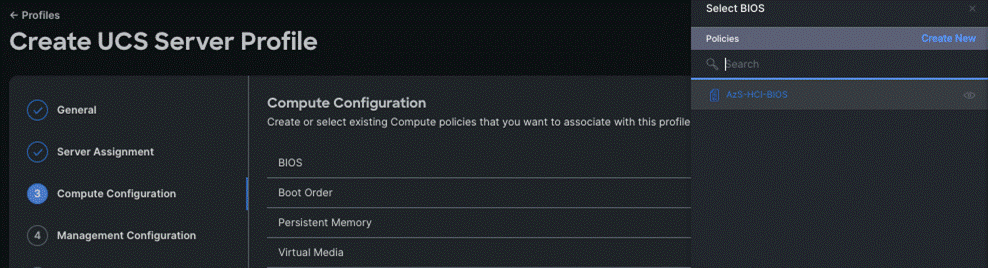
Step 7. Select the respective policies created in the previous sections for Boot Order and Virtual Media as shown below and click Next.
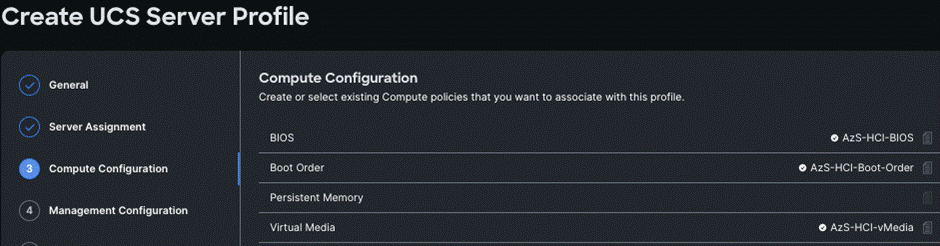
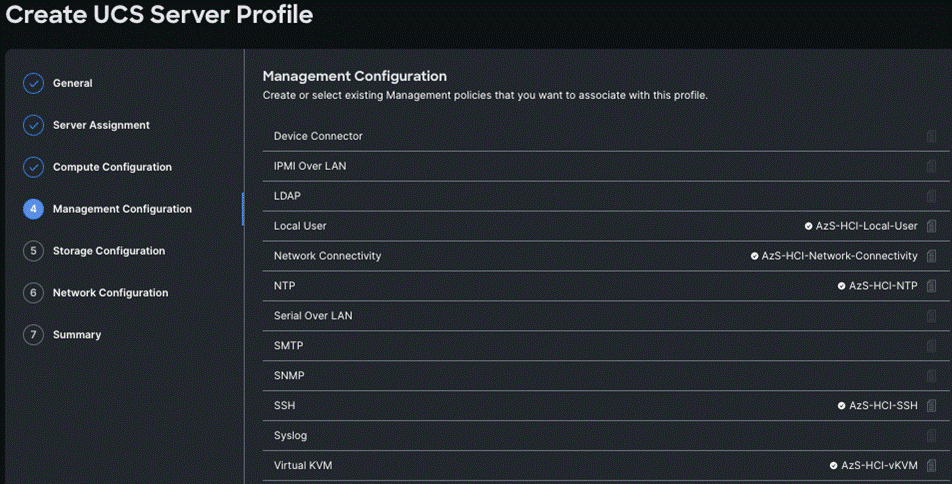
Step 8. Repeat steps 1 - 7 and complete the Management, Storage, and Network configuration and click Next.
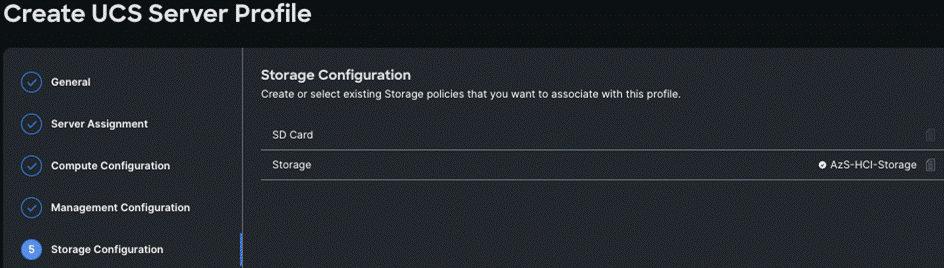
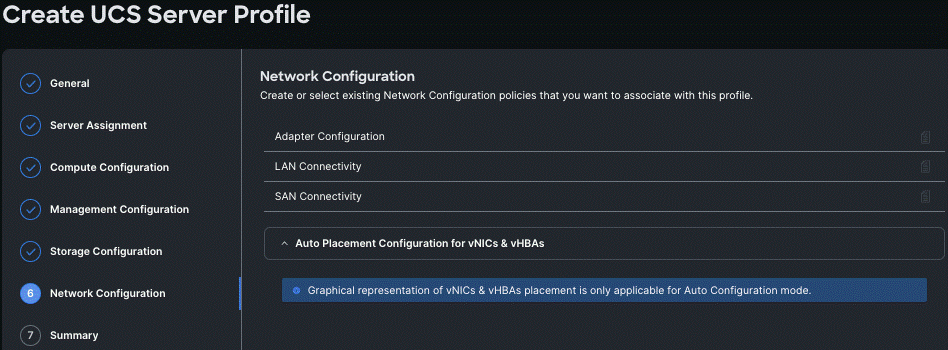
Step 9. On the Summary page, verify the configuration and click Deploy.
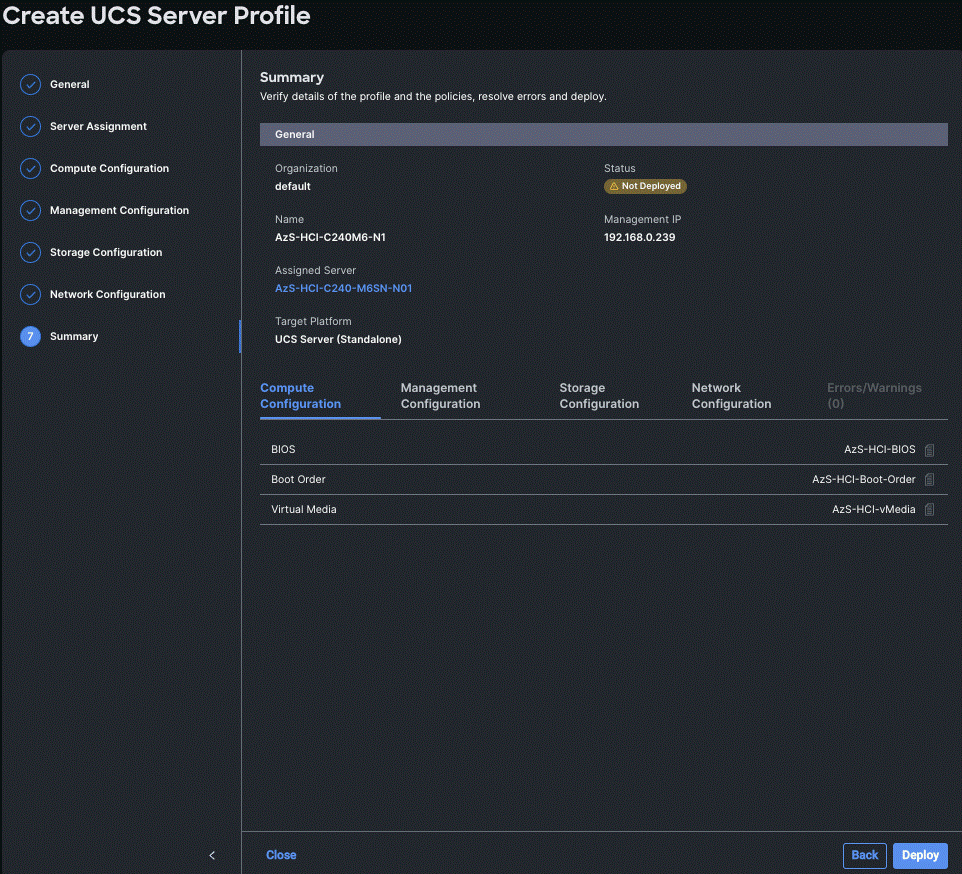
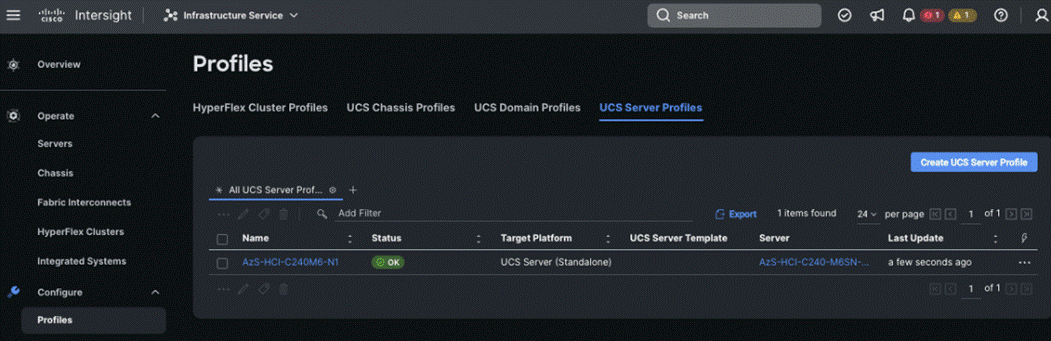
The deployment will take few minutes to complete, and the progress can be seen by clicking the Requests icon next to the Search field. The following figures show the status of the successfully deployed profile from Profile and Servers tab:
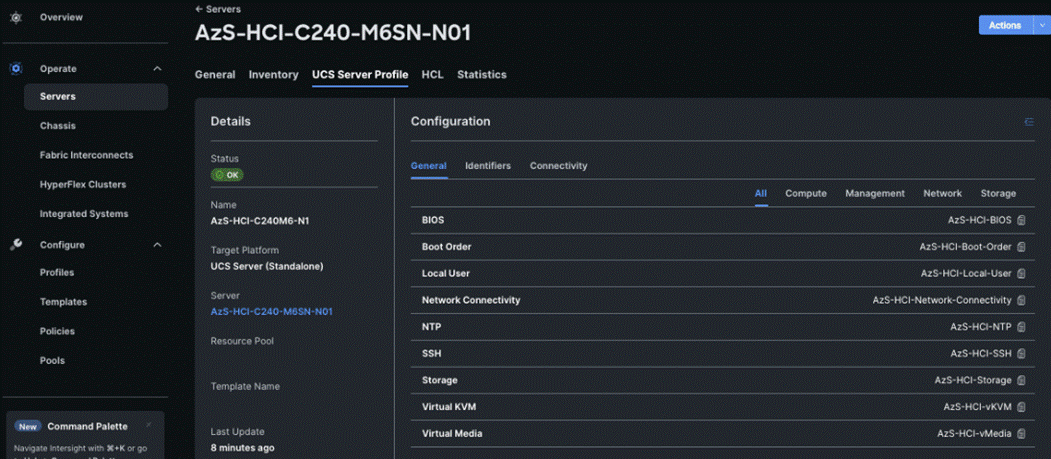
Step 10. Clone the Profile created in the previous steps, by clicking the ellipsis and selecting Clone as shown below:
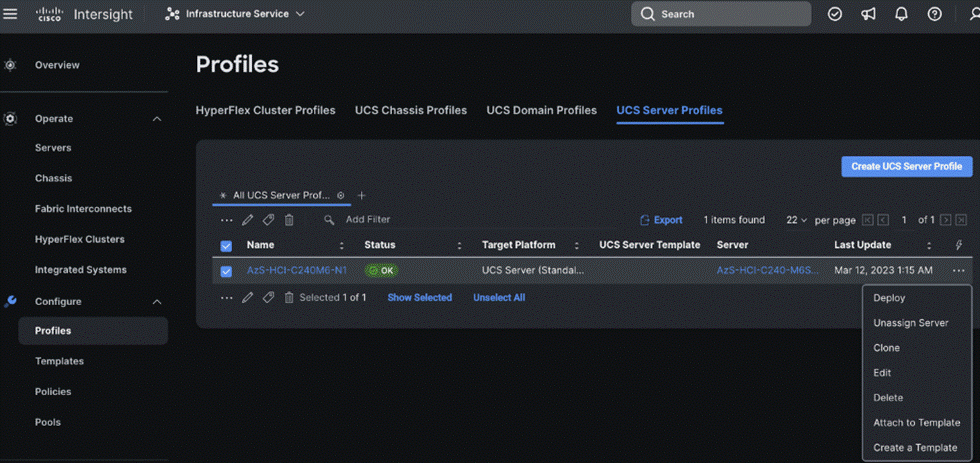
Step 11. On the General page, click Assign Now and select the remaining unassigned servers and click Next.
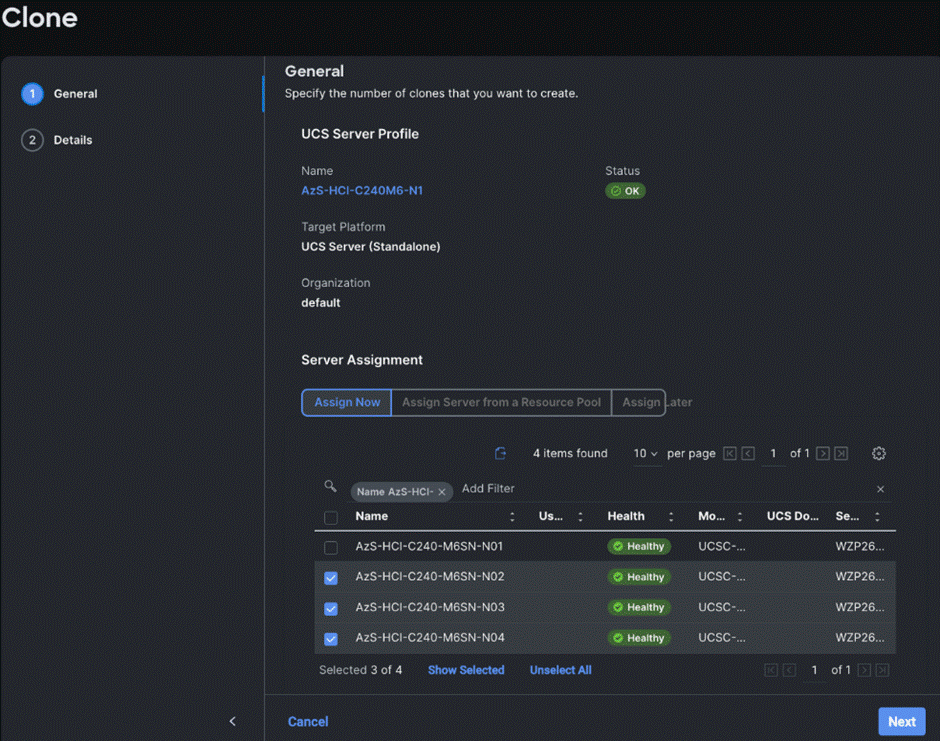
Step 12. On the Details page, edit the name under Clone Name Prefix and the number under the Start Index for Suffix as shown below and click Clone.
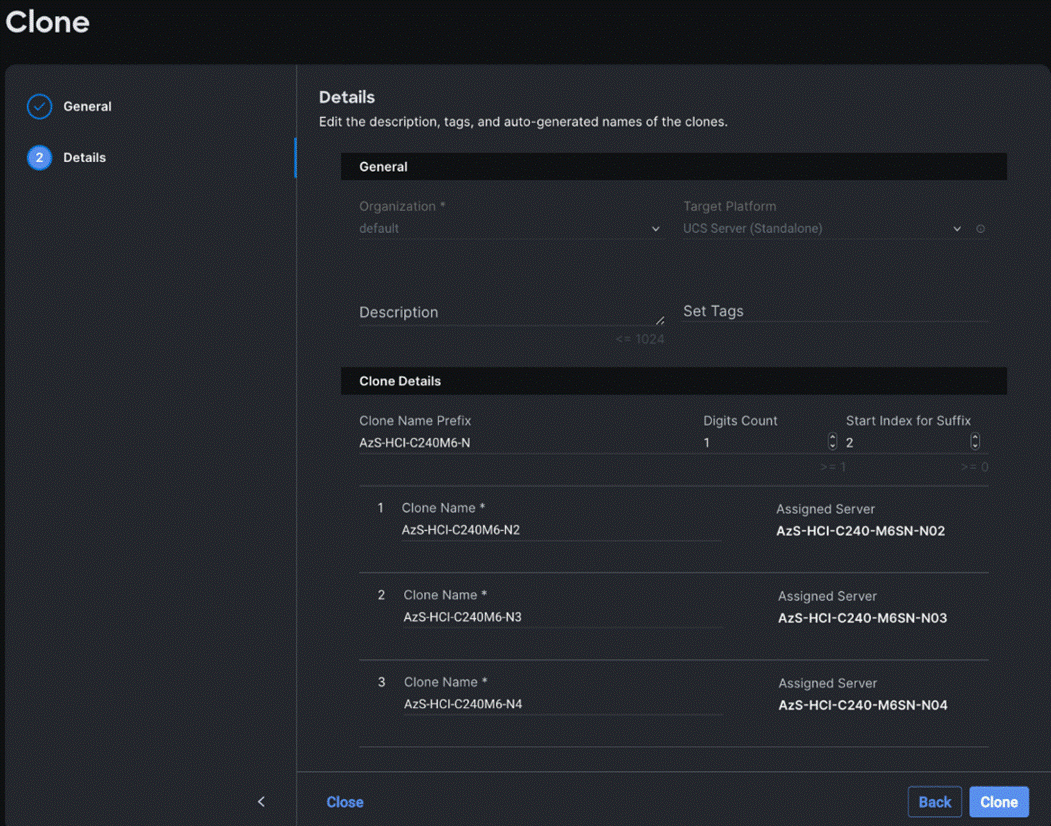
Step 13. On the Profiles page, select all the newly created profiles with Not Deployed status and click the ellipses. Click Deploy.
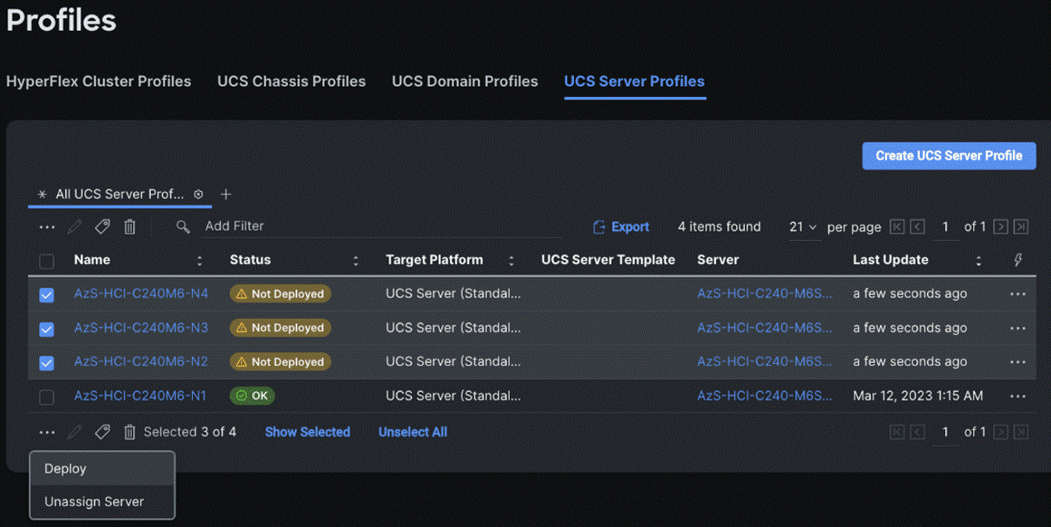
Step 14. On the Deploy pop-up page, click More Details to confirm, and click Deploy.
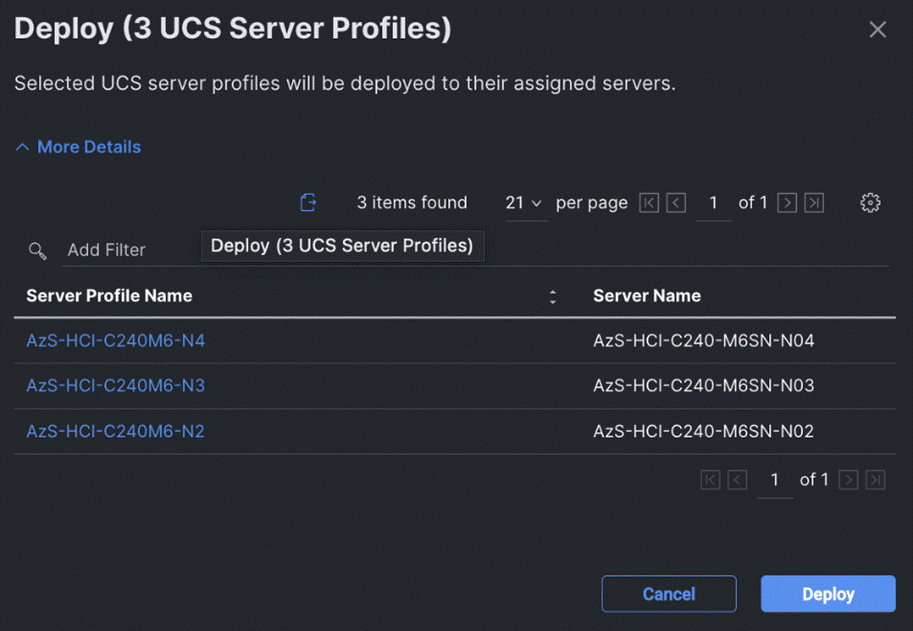
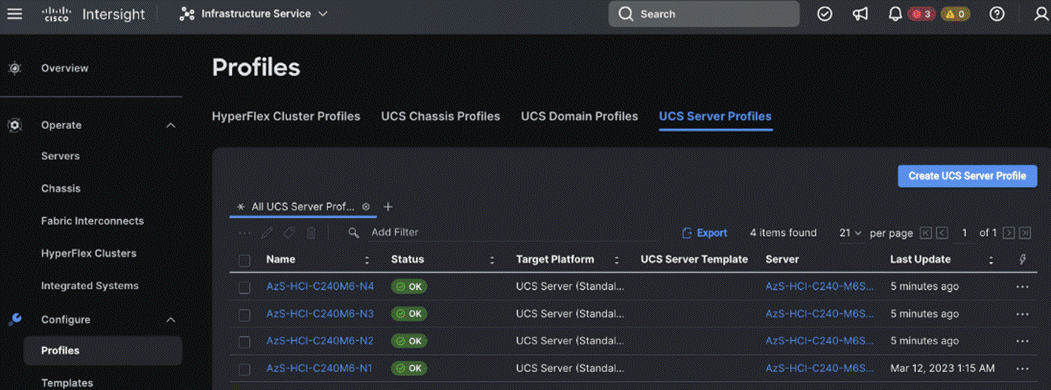
The following image shows the successfully deployed profiles on the assigned servers:
Active Directory requirements for Azure Local include:
● A dedicated Organization Unit (OU).
● Group policy inheritance that is blocked for the applicable Group Policy Object (GPO).
● A user account that has all rights to the OU in the Active Directory.
● Machines must not be joined to Active Directory before deployment.
Follow the steps in this section to prepare the Active Directory environment before deploying the Azure Local, version 23H2.
Procedure 1. Prepare the Active Directory
Step 1. Run the following command to download and install the 2402 version module from PowerShell gallery:
Install-Module AsHciADArtifactsPreCreationTool -Repository PSGallery -Force
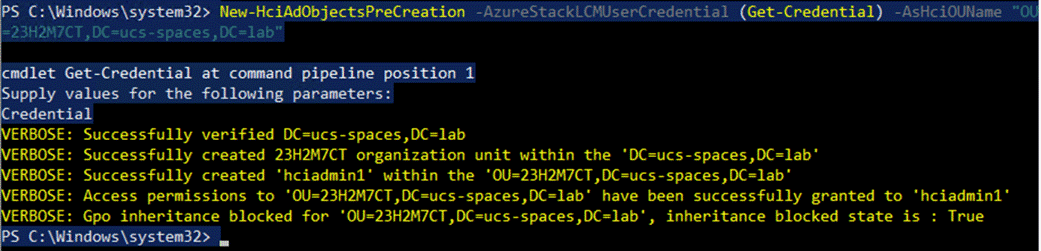
Step 2. Run the following PowerShell command to create the dedicated Organizational Unit (OU) and when prompted provide the username and password for the deployment:
Note: The password for the AzureStackLCMUser must conform to the length and complexity requirements to avoid deployment failure. Use a password that is at least 12 characters long and must also contain three out of four requirements – a lowercase character, an uppercase character, a numeral, and a special character.
New-HciAdObjectsPreCreation -AzureStackLCMUserCredential (Get-Credential) -AsHciOUName "OU=23H2M7,DC=ucs-spaces,DC=lab"
Step 3. Verify that the OU is created. If using a Windows Server client, go to Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers.
An OU with the specified name is created and within that OU, you'll see the deployment user as shown below:
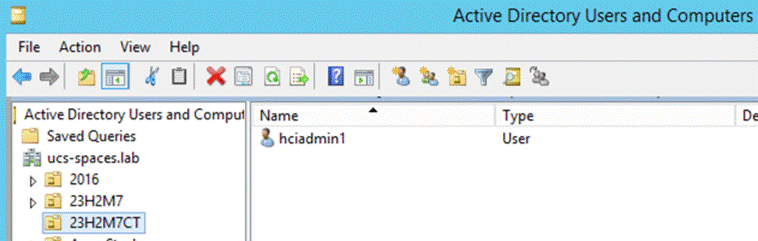
Note: Servers must not be joined to Active Directory before deployment.
Procedure 1. Download the Azure Local software from the Azure Portal
Step 1. Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account credentials.
Step 2. In the Azure portal search bar at the top, enter Azure Local and select Azure Local under the Services category.
After you select Azure Local, you're directed to the Azure Local Get started page, with the Get started tab selected by default.
Step 3. From the Get started tab, under the Download software tile, select Download Azure Local.
Step 4. From the Download Azure Local page on the right, do the following:
◦ Select the Azure Local version 23H2.
◦ Select English to download the English version of the ISO.
◦ Select the license terms and privacy notice checkbox.
◦ Click Download Azure Local . This action begins the download. Use the downloaded ISO file to install the software on each server that you want to cluster.

Note: The ISO that you download for Azure Local is OS version 25398.469. This ISO is then patched to the latest OS version during the installation process.
Procedure 1. Launch Server KVM Instance to Install the Operating System
Launch KVM to each server after the service profile association is complete. Install the Azure Local OS 23H2 using PXE boot or a vMedia mapped installation ISO. Install the Azur Stack HCI OS 23H2 using PXE boot or a vMedia mapped installation ISO. This section explains the steps to install OS using vMedia method.
Note: Installing the OS using PXE boot is out of the scope of this document.
Step 1. From the Server tab in Cisco Intersight, select Servers. From the list of options select Launch vKVM.
Step 2. From the left pane of KVM page, go to Virtual Media and select vKVM-Mapped DVD.
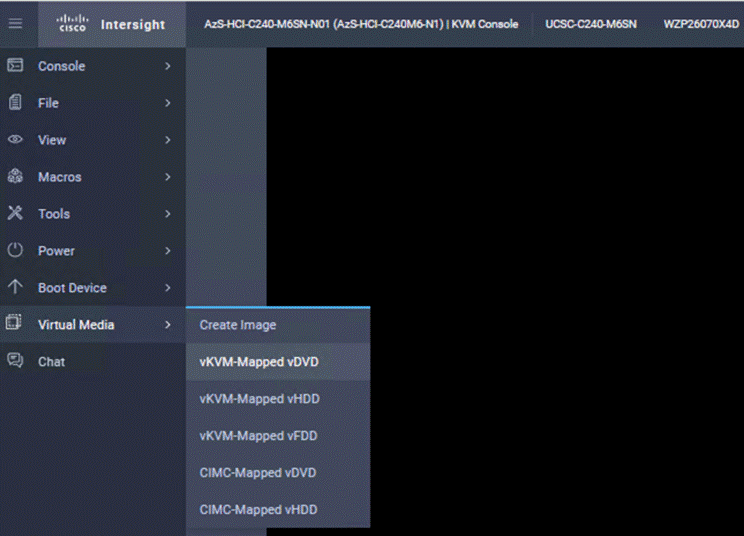
Step 3. A Map Virtual Media – CD/DVD window displays, click Browse.
Step 4. Select the downloaded Azure Local OS 23H2 and click Map Drive.
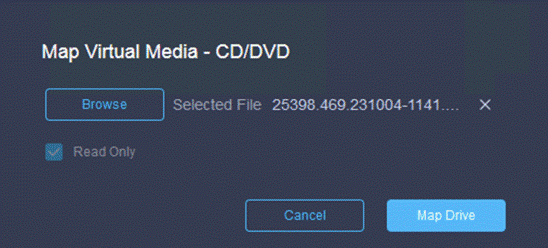
Step 5. Verify the file is selected by clicking Virtual Media.
Step 6. Go to Power and click Power Cycle System to restart the server.
Step 7. During the POST, press F6 to launch Boot Menu.
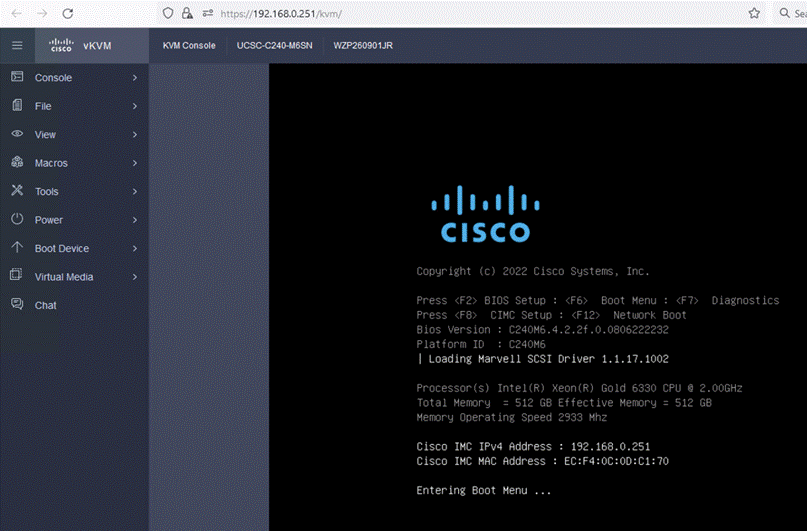
Step 8. In the Select boot device, select Cisco vKVM-Mapped vDVD and press Enter.
Step 9. Wait for Press any key to boot from CD or DVD on the screen and press any key to launch the OS installation.
Step 10. The installation wizard begins. Select the language to install or accept the default language settings, click Next and then on next page of the wizard, click Install now.
Step 11. Review the license terms on the Applicable notices and license terms page and check the box for I accept the license terms and then click Next.
Step 12. From the Type of Installation page, select Custom: Install the newer version of Azure Local only (advanced).

Step 13. Select the drive on which the operating system is installed and then click Next.
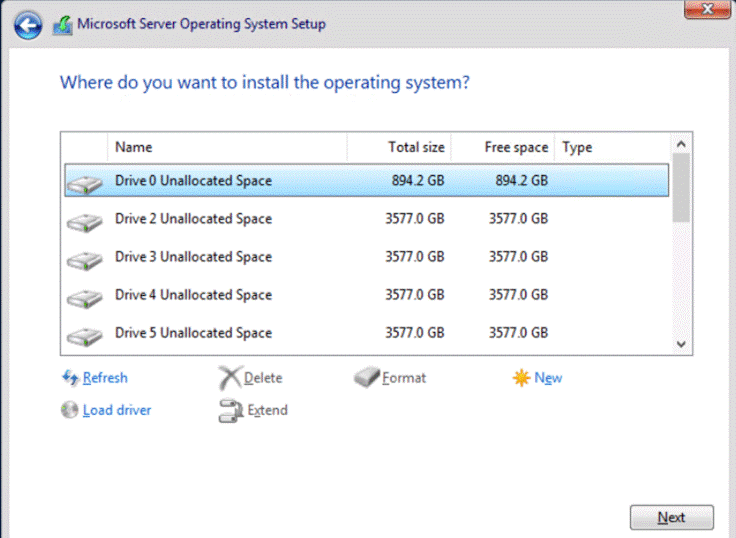
The Installing Azure Local page displays to show status on the process.

Note: The installation process restarts the operating system twice to complete the process and displays notices on starting services before opening an Administrator command prompt.
Step 14. At the Administrator command prompt, select OK to change the user's password before signing in to the operating system, then press Enter.
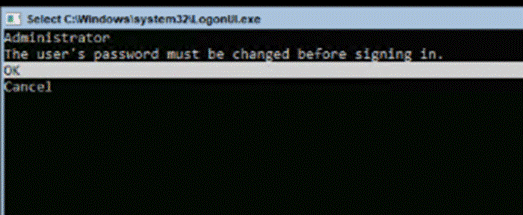
Step 15. At the Enter new credential for Administrator prompt, enter a new password.
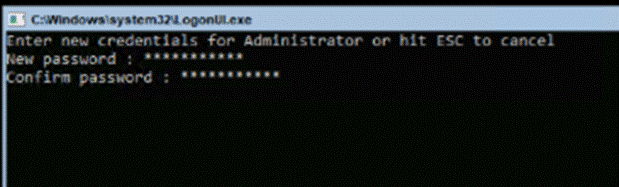
Step 16. From the Your password has been changed confirmation prompt, press Enter.
Note: Set the local administrator credentials to be identical across all servers.
Note: Make sure that the local administrator password follows Azure password length and complexity requirements to avoid deployment failure. Use a password that is at least 12 characters long and must also contain three out of four requirements – a lowercase character, an uppercase character, a numeral, and a special character.
Procedure 1. Download Windows Drivers
Post OS installation, download the relevant Windows driver image for the Cisco UCS Standalone Server software (4.2.3x for M6 servers or 4.3.x for M7 servers) from the download portal Software Download - Cisco Systems and install the drivers for Chipset, Storage, and Network.
Step 1. Mount the downloaded iso image for Windows drivers only.

Step 2. Copy the following files from the mounted drive to a separate folder. Copy this folder with drivers to all the Cisco UCS C240 M6/M7 servers:
.\ChipSet\Intel\ChipsetSoftware\x.x.x\SetupChipset.exe
.\Network\Mellanox\ConnectX4-5-6\W2K22\MLNX_WinOF2-3_0_50000_All_x64.exe
.\Storage\Intel\C600\W2K22\*.*
Procedure 2. Intel Chipset Installation
Step 1. Run the following command on all the nodes to install the chipset drivers. The system will restart automatically in couple of minutes after the chipset installation in unattended silent mode. Monitor and wait for system to restart.
SetupChipset.exe -silent
![]()
Procedure 3. NVIDIA/Mellanox ConnectX-6 DX/LX Driver Installation
Step 1. Run the following command on all the nodes to install the drivers for NVIDIA (Mellanox) in unattended mode:
Unattended install
MLNX_WinOF2-[Driver/Version]_<revision_version>_All_-Arch.exe /S /v/qn
Or Unattended install with Logs
MLNX_WinOF2-[Driver/Version]_<revision_version>_All_-Arch.exe /S /v/qn /v”/l*vx [LogFile]"

Step 2. Alternatively, run the following command to extract only the driver files and use pnputil command to install the drivers:
MLNX_WinOF2-2_0_<revision_version>_All_x64.exe /a /vMT_DRIVERS_ONLY=1
Procedure 4. Storage Drivers Install
Step 1. Run the following command to install the Intel storage (MegaSR) drivers:
pnputil.exe /add-driver C:\Deploy\C240M6-4.2.3b-Drivers\Storage\Intel\C600\W2K22\*.inf /install
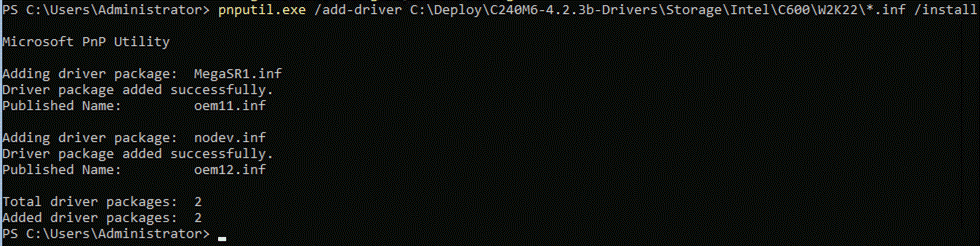
Note: All drivers can be installed using PNPUtil.exe.
The following PNPUtile.exe example can be used to install drivers:
pnputil /add-driver C:\temp\drivers \*.inf
PNPUtil.exe documentation can be found here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/devtest/pnputil
Configure the Operating System using SConfig
Procedure 1. Verify the Operating System Version
Step 1. Open a KVM session to each host and perform the following configuration to enable remote access to each host. After logging in, start PowerShell by selecting option 15 (Exit to command line (PowerShell)) in the SConfig screen.
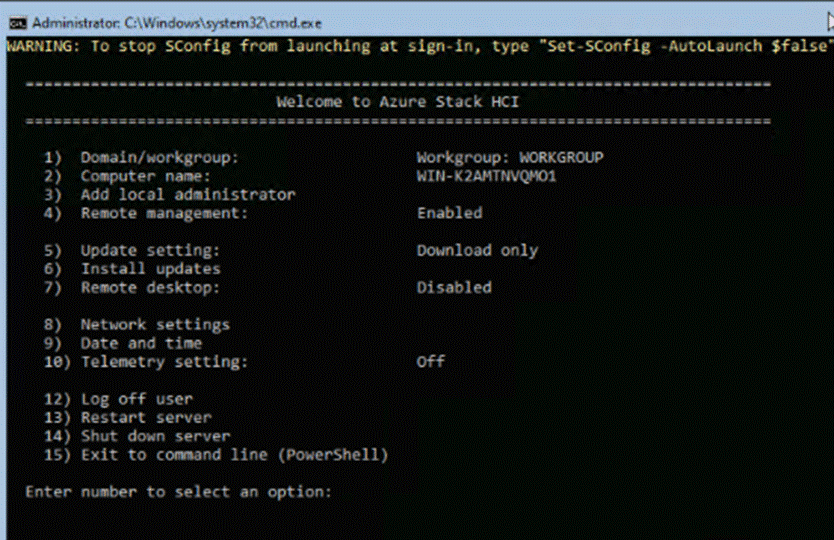
Step 2. Run the following command to verify the OS version:
Get-ComputerInfo | fl -Property OSDisplayVersion:
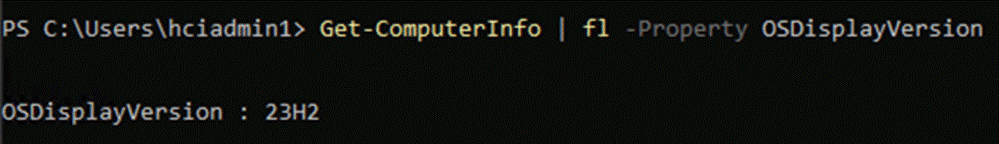
Procedure 2. Verify Available NICs Seen by the Operating System
Step 1. Run the command on each server:
Get-NetAdapter -ifDesc "Mellanox*" | ft -AutoSize:
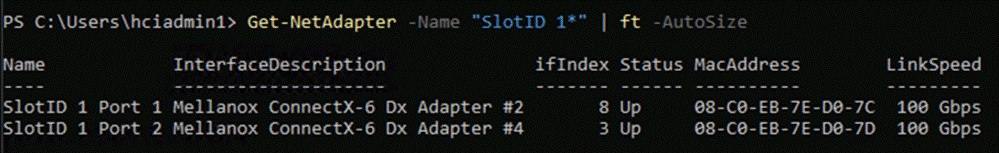
Procedure 3. Disable DHCP on Port 2 of the NIC and Verify the Setting
Step 1. Run the following commands on each server:
Set-NetIPInterface -InterfaceAlias "SlotID 1 Port 2" -Dhcp Disabled
Get-NetIPInterface -InterfaceAlias "SlotID 1 Port 2" -Dhcp Disabled -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft -AutoSize
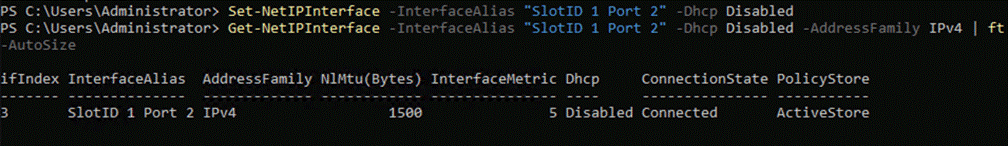
Procedure 4. Configure Static NIC IP Address for Management NIC’s
Note: Replace the IP address with the address specific to your environment.
Note: The VLAN for this subnet must be set to Native because VLAN tagging is not configured for this physical interface.
Step 1. Run the following command on each server with unique IP address:
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias "SlotID 2 Port 1" -IPAddress 192.168.126.51 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 192.168.126.1
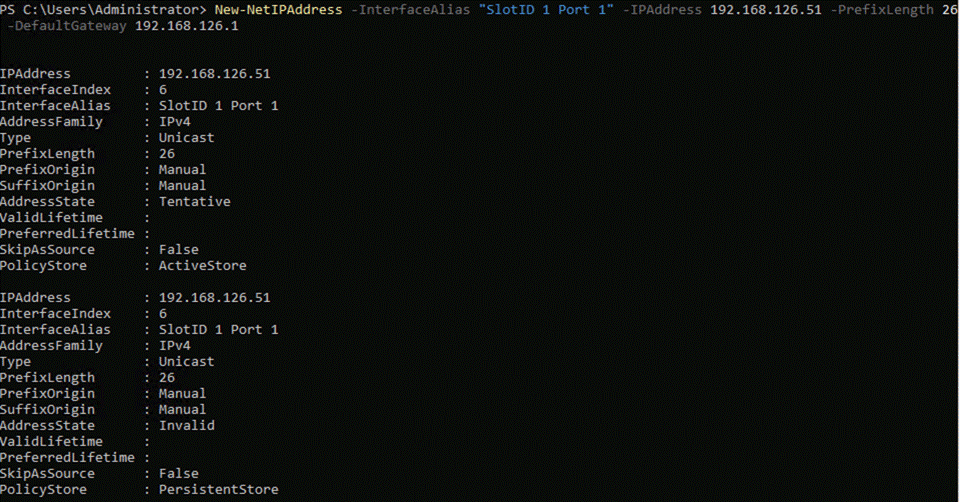
Note: Each host must have a unique host name and IP address for your environment. The following is a table of host names and IP addresses used in this deployment:
| Host Name |
IP Address |
| AzS-HCI1-N1 |
192.168.126.51 |
| AzS-HCI1-N2 |
192.168.126.52 |
| AzS-HCI1-N3 |
192.168.126.53 |
| AzS-HCI1-N4 |
192.168.126.54 |
Procedure 5. Configure DNS Client Server IP Address
Note: Replace the DNS Server IP address with the address specific to your environment.
Step 1. Run the following commands on each server:
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias "SlotID 1 Port 1" -ServerAddresses 192.168.0.41,192.168.0.42
Get-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias "SlotID 1 Port 1"
![]()
Procedure 6. Configure Proxy settings for Azure Local
If your network uses a proxy server for internet access, refer to this article about how to configure proxy settings for Azure Local, version 23H2
For information about firewall requirements for outbound endpoints and internal rules and ports for Azure Local, see Firewall requirements for Azure Local.
Procedure 7. Configure Time Zone
Time zone must have the same setting on all cluster nodes.
Step 1. Run the following command on each server to configure time zone:
Set-Timezone -Name "Pacific Standard Time"
Note: The time zone is specific to the region. The following command lists available time zones.
Get-TimeZone -ListAvailable | ft StandardName, ID
Procedure 8. Configure valid Time Server
Step 1. Run the following command on each server to validate that it is not using the local CMOS clock as a time source:
w32tm /query /status
Step 2. To configure a valid time source, run the following command on each server:
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:"dc02.ucs-spaces.lab" /syncfromflags:manual /update

Step 3. Confirm that the time is successfully synchronizing using the new time server:
w32tm /query /status

Procedure 9. Enable Remote Desktop Access on the Host Servers
Step 1. Run the following command on each server to enable RDP on all hosts:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" -Name "fDenyTSConnections" –Value 0
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Desktop"
Procedure 10. Clean Inventory Storage Drives that will be used by Storage Spaces Direct
Before you enable Storage Spaces Direct, ensure your permanent drives are empty. Run the following script to remove any old partitions and other data from the non-OS drives on all servers.
Step 1. Run the following on each server:
Update-StorageProviderCache
Get-StoragePool | ? IsPrimordial -eq $false | Set-StoragePool -IsReadOnly:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-StoragePool | ? IsPrimordial -eq $false | Get-VirtualDisk | Remove-VirtualDisk -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-StoragePool | ? IsPrimordial -eq $false | Remove-StoragePool -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-PhysicalDisk | Reset-PhysicalDisk -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-Disk | ? Number -ne $null | ? IsBoot -ne $true | ? IsSystem -ne $true | ? PartitionStyle -ne RAW | % {
$_ | Set-Disk -isoffline:$false
$_ | Set-Disk -isreadonly:$false
$_ | Clear-Disk -RemoveData -RemoveOEM -Confirm:$false
$_ | Set-Disk -isreadonly:$true
$_ | Set-Disk -isoffline:$true
}
#Inventory Storage Disks
Get-Disk | Where Number -Ne $Null | Where IsBoot -Ne $True | Where IsSystem -Ne $True | Where PartitionStyle -Eq RAW | Group -NoElement -Property FriendlyName | ft
Procedure 11. Rename Computer Name
Step 1. Run the following command:
Rename-Computer -NewName AZSHCI-M7C-N1 -Restart

The server restarts after renaming the computer.
Procedure 12. Install Required Windows Roles
Step 1. Run the following command on each server to install the Hyper-V role:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All

The server restarts after installing the role.
Register Servers with Azure Arc and Assign Required Permissions for Deployment
This section describes how to register your Azure Local servers and then set up the required permissions to deploy an Azure Local, version 23H2 cluster.
Procedure 13. Register servers with Azure Arc
Run these steps on each server that you intend to cluster.
Step 1. Install the Arc registration script from PSGallery.
#Register PSGallery as a trusted repo
Register-PSRepository -Default -InstallationPolicy Trusted
#Install required PowerShell modules in your node for registration
Install-Module Az.Accounts -RequiredVersion 2.13.2
Install-Module Az.Resources -RequiredVersion 6.12.0
Install-Module Az.ConnectedMachine -RequiredVersion 0.5.2
#Install Arc registration script from PSGallery
Install-Module AzsHCI.ARCinstaller


Step 2. Run the following to set the parameters. The script takes in the following parameters:
#Define the subscription where you want to register your server as Arc device
$Subscription = "YourSubscriptionID"
#Define the resource group where you want to register your server as Arc device
$RG = "YourResourceGroupName"
#Define the region you will use to register your server as Arc device
$Region = "eastus"
#Define the tenant you will use to register your server as Arc device
$Tenant = "YourTenantID"
Step 3. Run the following command to connect to your Azure account and set the subscription. You'll need to open browser on the client that you're using to connect to the server and open this page: https://microsoft.com/devicelogin and enter the provided code in the Azure CLI output to authenticate.
#Connect to your Azure account and Subscription
Connect-AzAccount -SubscriptionId $Subscription -TenantId $Tenant -DeviceCode
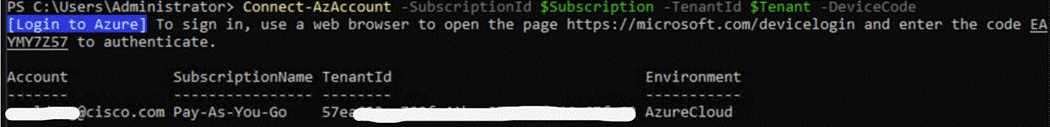
Step 4. Get the access token and account ID for the registration:
#Get the Access Token for the registration
$ARMtoken = (Get-AzAccessToken).Token
#Get the Account ID for the registration
$id = (Get-AzContext).Account.Id

Step 5. Run the Arc registration script which takes a few minutes to complete:
#Invoke the registration script. Use a supported region.
Invoke-AzStackHciArcInitialization -SubscriptionID $Subscription -ResourceGroup $RG -TenantID $Tenant -Region $Region -Cloud "AzureCloud" -ArmAccessToken $ARMtoken -AccountID $id
Note: If you're accessing the internet using a proxy server, you need to pass the -proxy parameter and provide the proxy server as http://<Proxy server FQDN or IP address>:Port when running the script.
Step 6. After the script completes successfully on all the servers, verify that your servers are registered with Arc and the mandatory Azure Local extensions are installed on your servers.
a. Go to the Azure portal and then go to the resource group associated with the registration. The servers appear within the specified resource group as Machine - Azure Arc type resources.
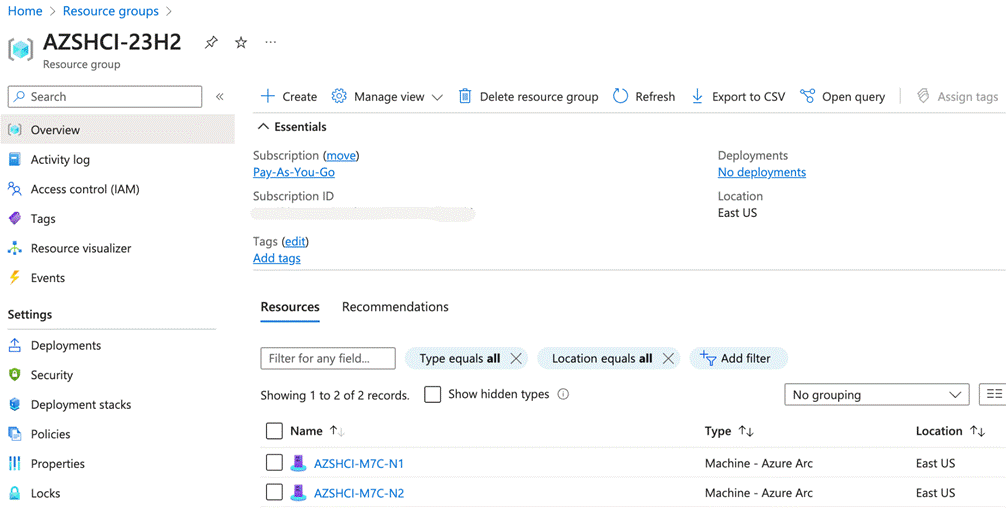
b. From the resource group, select the registered server. Go to Extensions. The mandatory extensions show up in the right pane.
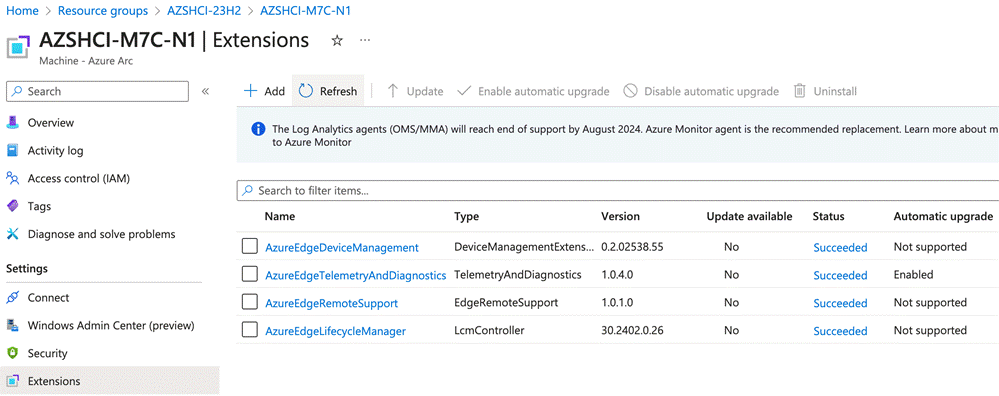
Note: If you encounter this issue – “Get-AzAccessToken failed · Issue #24963 · Azure/azure-powershell · GitHub,” follow this workaround:
Update-AzConfig -EnableLoginByWam $False
Step 7. Once the script completes, enter the following command:
Update-AzConfig -EnableLoginByWam $True
Procedure 14. Assign required permissions for deployment
Step 1. In the Azure portal, go to the subscription where the servers are registered. In the left pane, select Access control (IAM). In the right pane, click + Add and from the drop-down list, select Add role assignment.
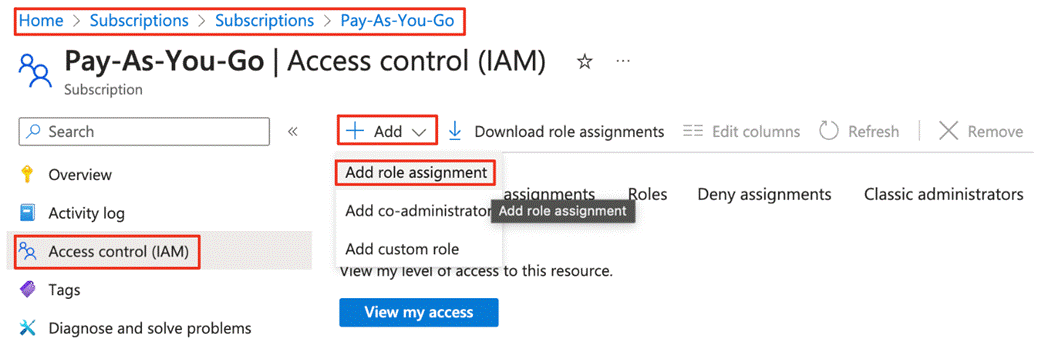
Step 2. Go through the tabs and assign the following role permissions to the user who deploys the cluster:
● Azure Local Administrator
● Reader
Step 3. In the Azure portal, go to the resource group where the servers are registered in your subscription. In the left pane, select Access control (IAM). In the right pane, select + Add and from the drop-down list, select Add role assignment.
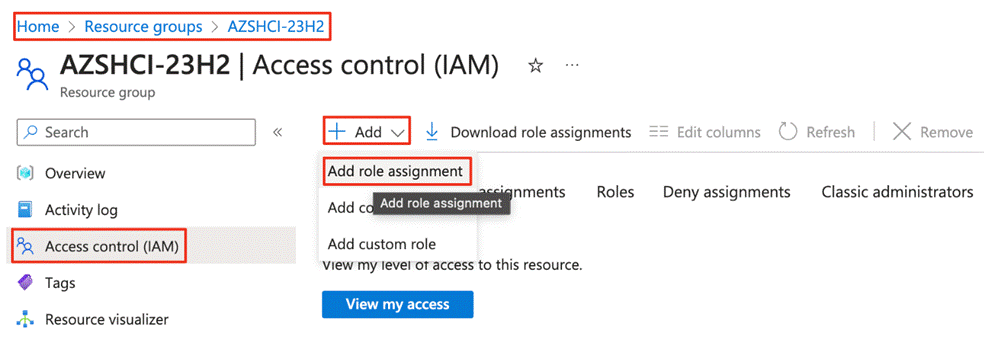
Step 4. Go through the tabs and assign the following role permissions to the user who deploys the cluster:
● Key Vault Data Access Administrator
● Key Vault Administrator
● Key Vault Secrets Officer
● Key Vault Contributor
● Storage Account Contributor
Step 5. In the right pane, click Role assignments and verify that the deployment user has all the configured roles.
Step 6. In the Azure portal, search for and select Microsoft Entra roles and administrators.

Step 7. Assign the Cloud Application Administrator role permission at the Microsoft Entra tenant level.
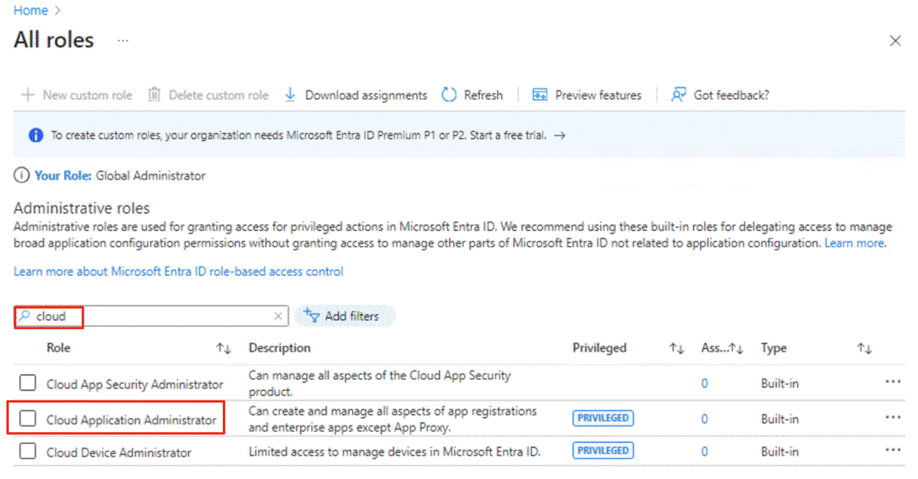
Note: The Cloud Application Administrator permission is temporarily needed to create the service principal. After deployment, this permission can be removed.
Deploy Azure Local using the Azure Portal
Follow the steps in this section to deploy an Azure Local version 23H2 system using the Azure portal.
Procedure 1. Basics setting
Step 1. In the Azure portal, search for Azure Arc. Select Azure Arc and go to Infrastructure and select Azure Local. From the Get started tab, select Deploy cluster.

Step 2. Select the Subscription and Resource group in which to store this system's resources.
Step 3. Enter the Cluster name used for this Azure Local system when Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) was prepared for this deployment.
Step 4. Select the Region.
Step 5. Create an new Key vault.
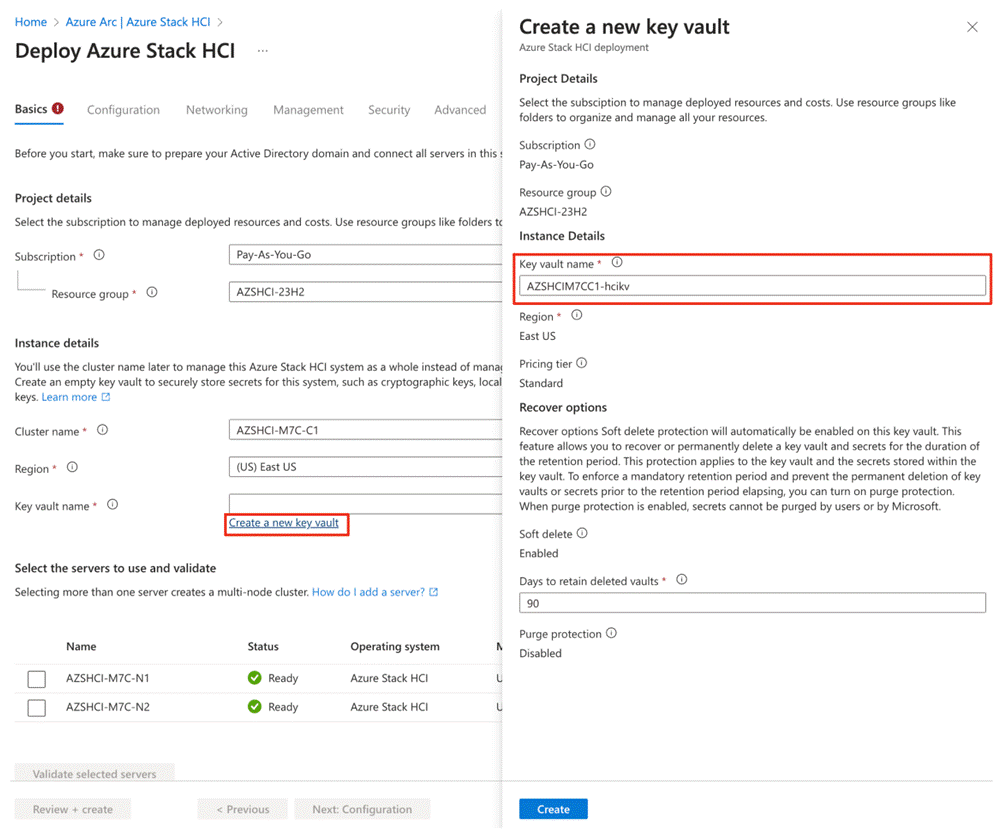
Step 6. Select the servers that make up this Azure Local system and click on Validate Selected Servers.
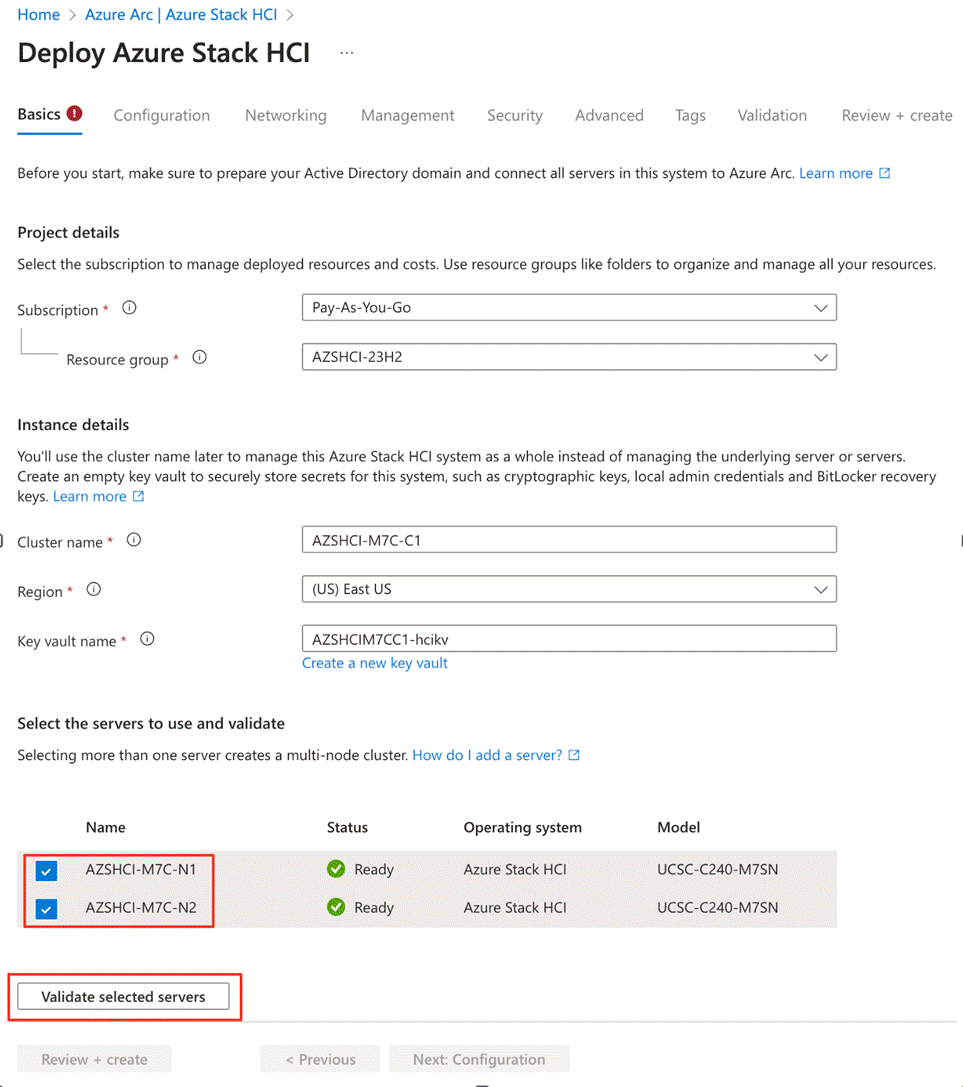
Step 7. After successful validation (a green checkbox appears), click Next: Configuration.
The validation process checks that each server is running the same exact version of the OS, has the correct Azure extensions, and has matching (symmetrical) network adapters.
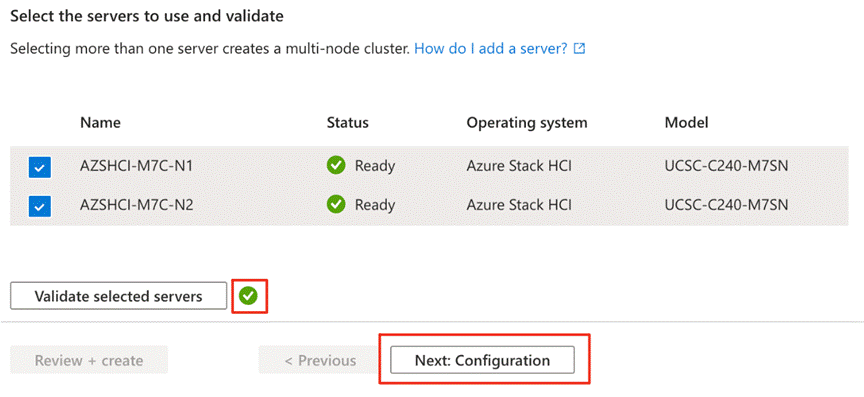
Procedure 2. Configuration settings
For this procedure, specify the deployment settings by choosing to create a new configuration or to load deployment settings from a template.
Step 1. For the source of the deployment settings, select New configuration and click Next: Networking.
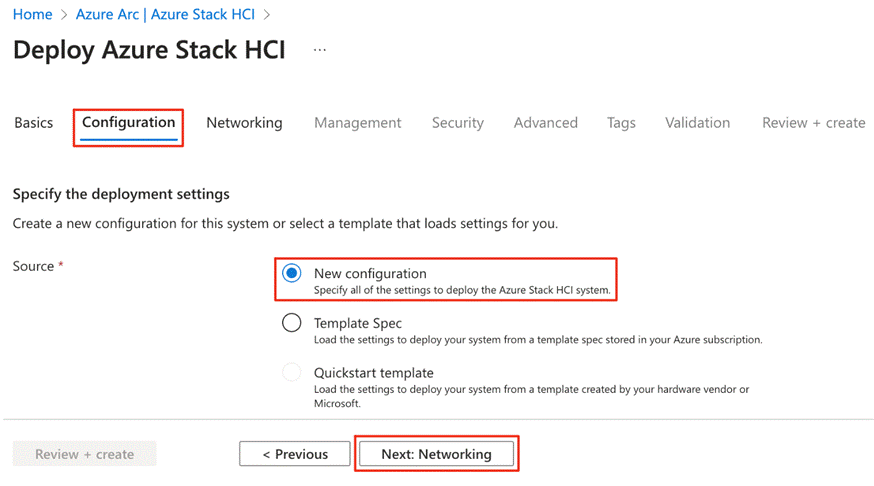
Procedure 3. Networking settings
For this procedure, specify the network settings based on the network reference pattern (as described in the earlier section) that you are planning to deploy.
Step 1. Select the Network switch for storage traffic.
● No switch for storage - For two-node clusters with storage network adapters that connect the two servers directly without going through a switch. Storage Switchless network reference pattern do not use network switch for storage.
● Network switch for storage traffic - For clusters with storage network adapters connected to a network switch. This also applies to clusters that use converged network adapters that carry all traffic types including storage. Both converged and non-converged network reference pattern use the Network switch for storage traffic.
The following steps focuses on deploying an Azure Local system using the converged network reference pattern where all the three types (Management, Compute and Storage) of traffic pass through them to a pair of upstream network switches.
Step 2. In the Group network traffic types by intent, select Group all traffic.
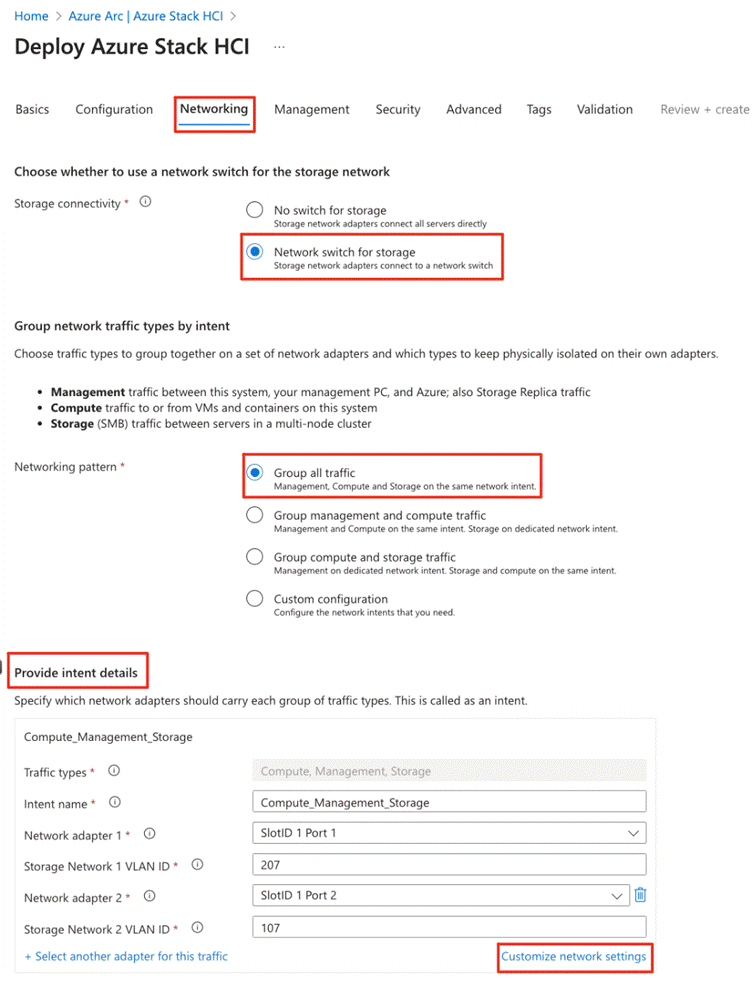
Step 3. In the Provide intent details:
● Enter an Intent name.
● From the drop-down list for Network Adapter 1, select one unused network adapter and enter the VLAN ID set on the network switches used for each storage network.
● For redundancy, click + Select another adapter for this traffic and repeat the above step for Network Adapter 2.
Step 4. Select Customize network settings and provide the following information:
● Storage traffic priority: Select 4 from the drop-down list.
● Cluster traffic priority: Select 5 from the drop-down list.
● Storage traffic bandwidth reservation: Default 50.
● Adapter properties: Select 9014 for Jumbo frame size (in bytes) and RoCEv2 for RDMA protocol from the drop-down list.
Note: Cisco recommends customizing network settings for an intent. The QoS configuration on the host side should match the QoS configuration on the network switches.
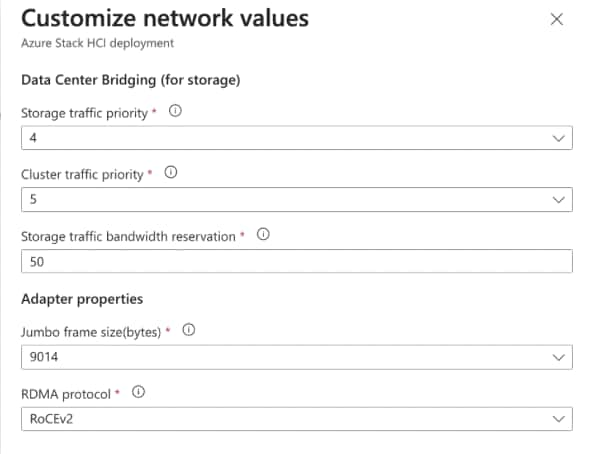
Step 5. Click Save to save the customized network values.
Step 6. From the Allocate IP addresses to the system and services, enter the required details. The block of 6 static IP addresses must be from your management network subnet. IP addresses already used by the servers should be excluded from this range.
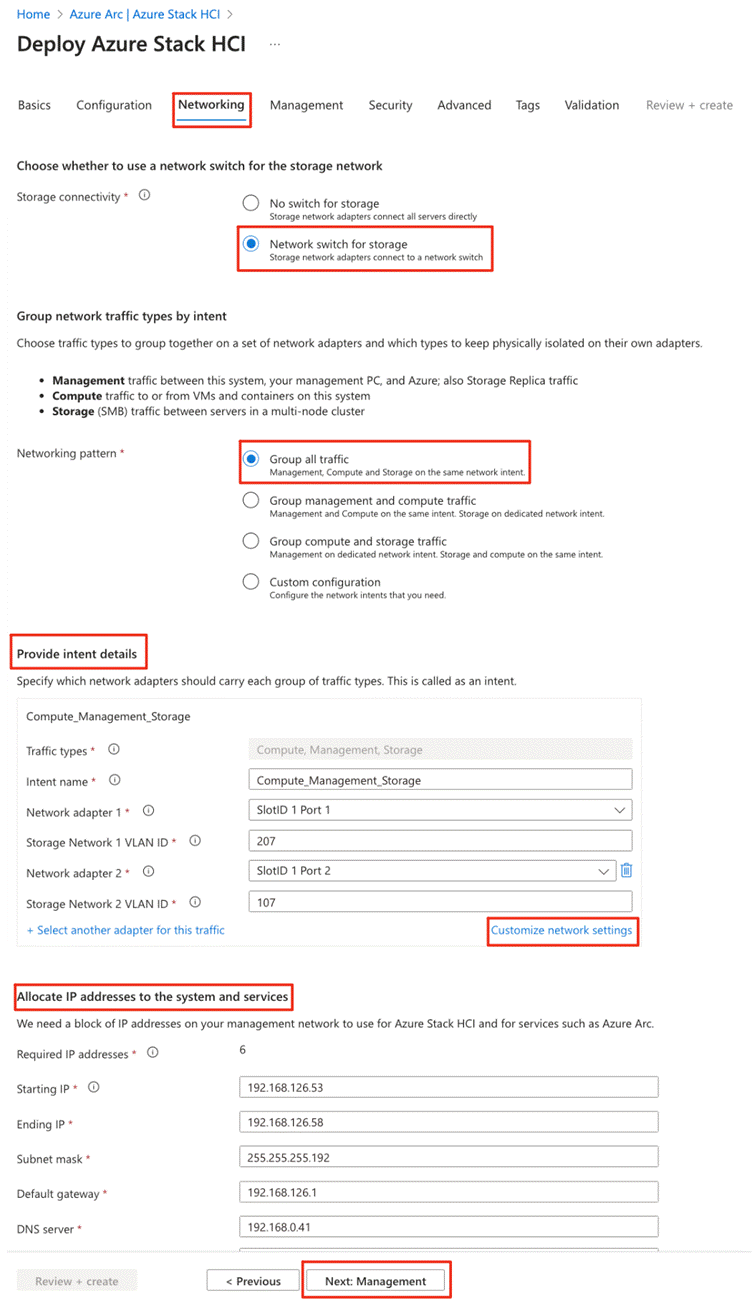
Step 7. Click Next: Management.
Procedure 4. Management settings
Step 1. In the Specify a custom location name, provide a name. This helps users identify this system when creating resources such as VMs on it.
Step 2. In the Specify cluster witness settings, select an existing Storage account or create a new Storage account to store the cluster witness file.
Step 3. Enter the FQDN name of the Active Directory Domain whose AD DS was prepared for deployment as prerequisite.
Step 4. Enter the OU created for this deployment.
Step 5. Enter the Deployment account credentials.
This domain user account was created when the domain was prepared for deployment.
Step 6. Enter the Local administrator credentials for the servers.
Note: Make sure the credentials must be identical on all servers in the system and meet the complexity requirements.
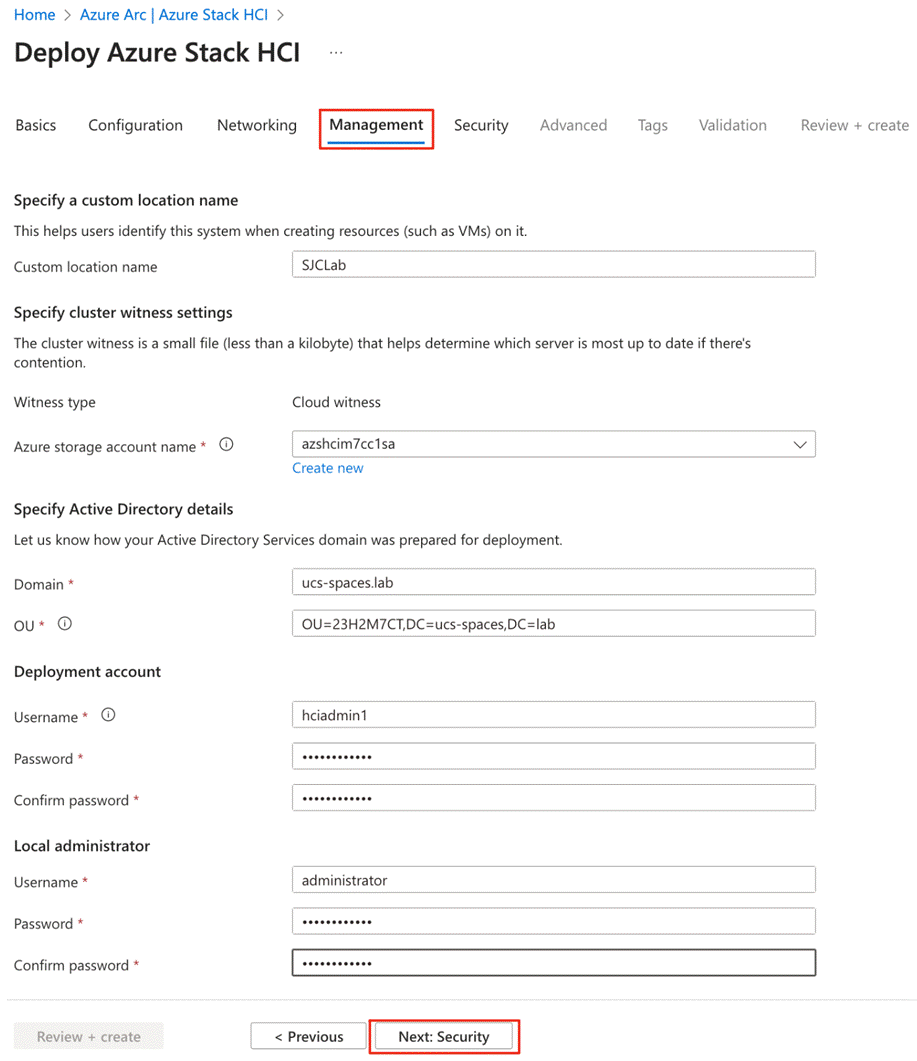
Step 7. Click Next: Security.
Procedure 5. Security settings
Step 1. Select the security level for your system's infrastructure:
● Recommended security settings – All security settings are enabled. This sets the highest security settings.
● Customized security settings – Allows you to turn on/off the security settings.
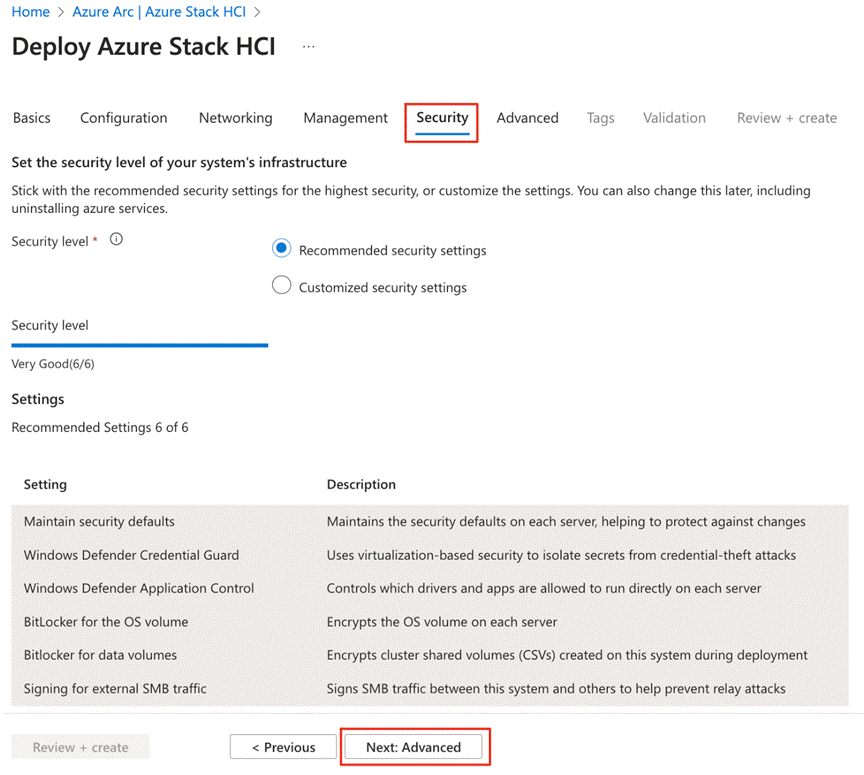
Step 2. Click Next: Advanced.
Procedure 6. Advanced and Tags settings
Optionally, follow these steps to change advanced settings and apply tags to the system.
Step 1. Select whether to create to workload and infrastructure volumes now or create just the infrastructure volume and workload volumes later. Use existing data drives is for the single servers (1-node cluster) only.
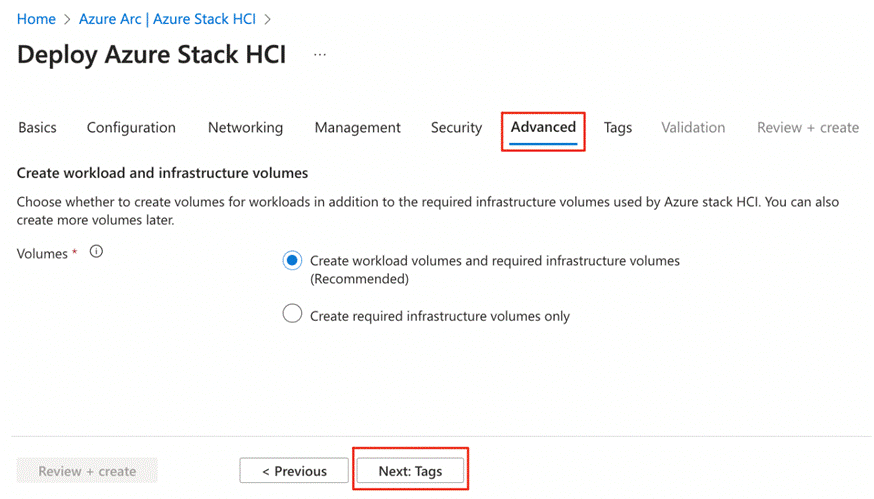
Note: Don't delete the infrastructure volumes created during deployment.
Step 2. Click Next: Tags.
Step 3. Optionally, add a tag to the resource and click Next: Validation.
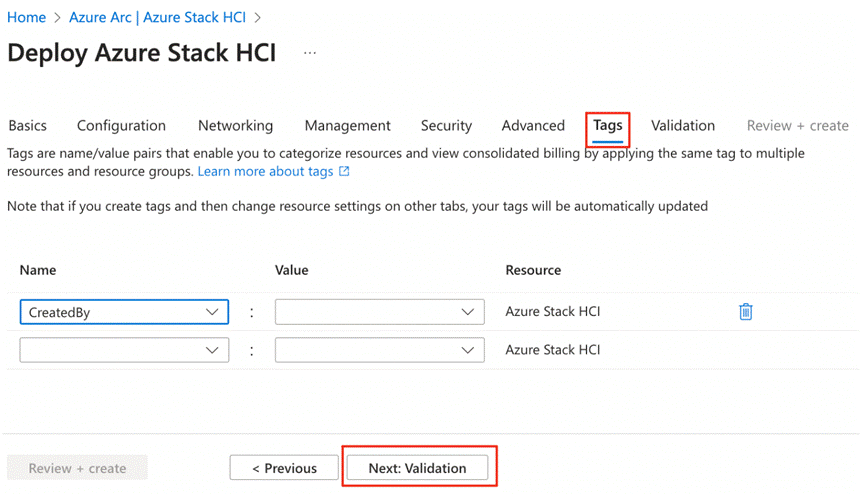
Procedure 7. Validate and deploy the system
Step 1. After successfully verifying the cluster resource object and its components are created, click Start validation.
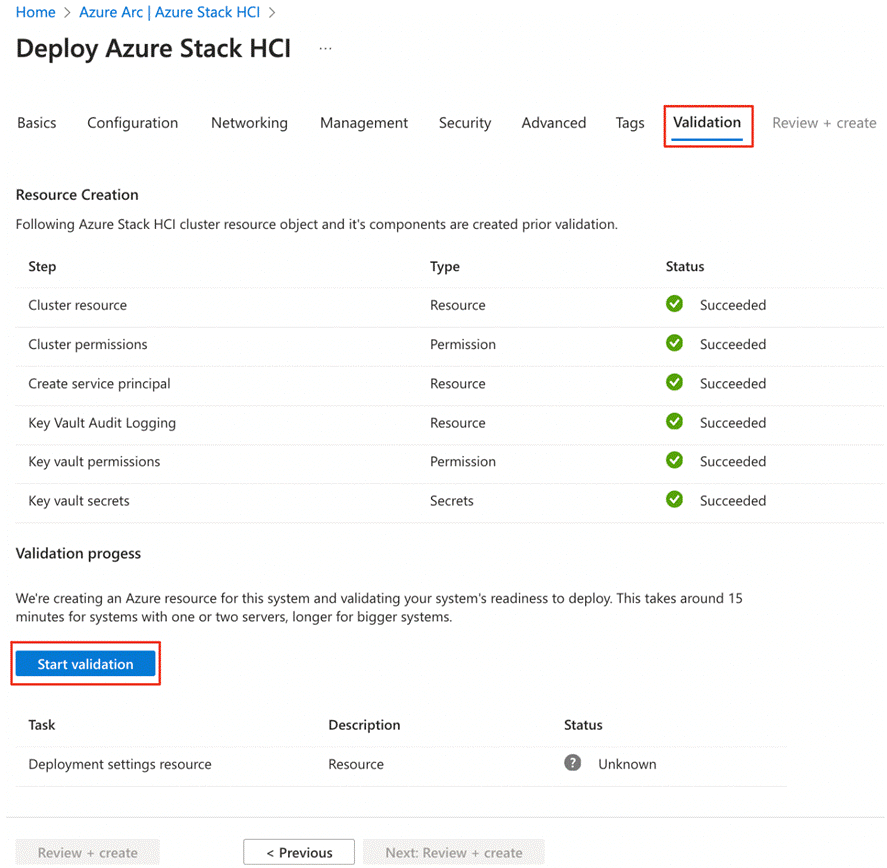
Step 2. Monitor the validation progress as they may take some time to complete depending on the number of servers in the system.
Step 3. Once the validation is completed successfully, review the results and click Next: Review + create.
Step 4. Resolve any validation errors before moving to the next step.

Step 5. Review the deployment settings and click Review + create to deploy the system.

Step 6. The deployment page will appear. Monitor the deployment progress. This may take few hours depending on the size of the system.
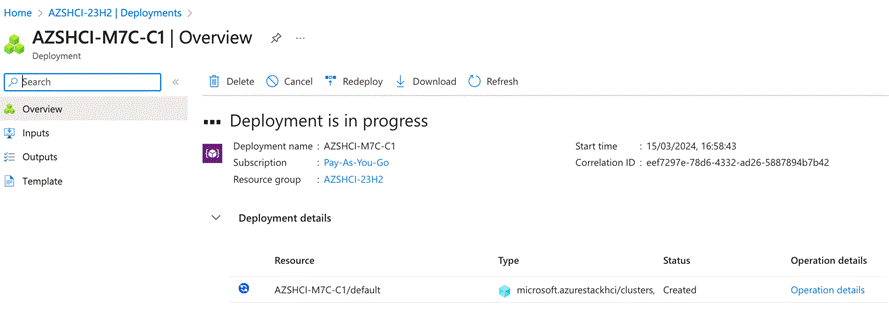
A sample of a successful deployment is shown below:
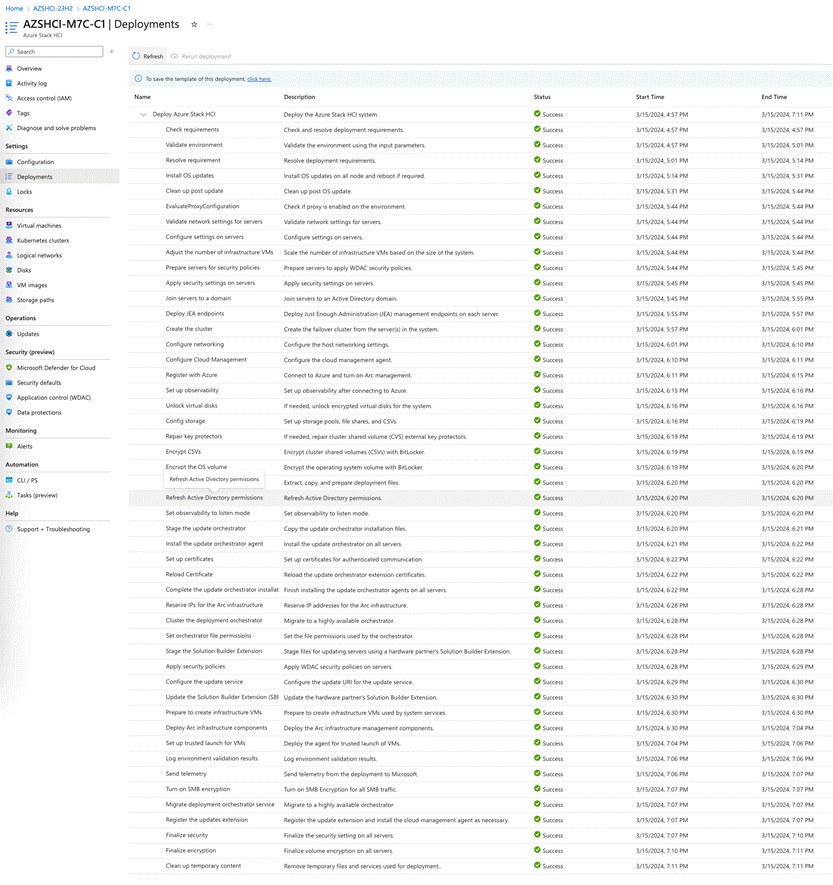
Step 7. If a deployment fails, rerun the deployment by going to Deployments and select Rerun deployment.
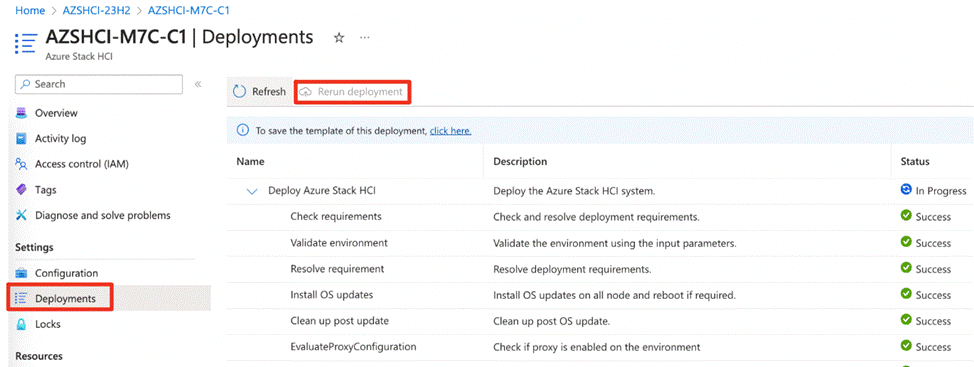
Procedure 8. Verify post deployment
Step 1. Verify a successful deployment by clicking Go to resource.
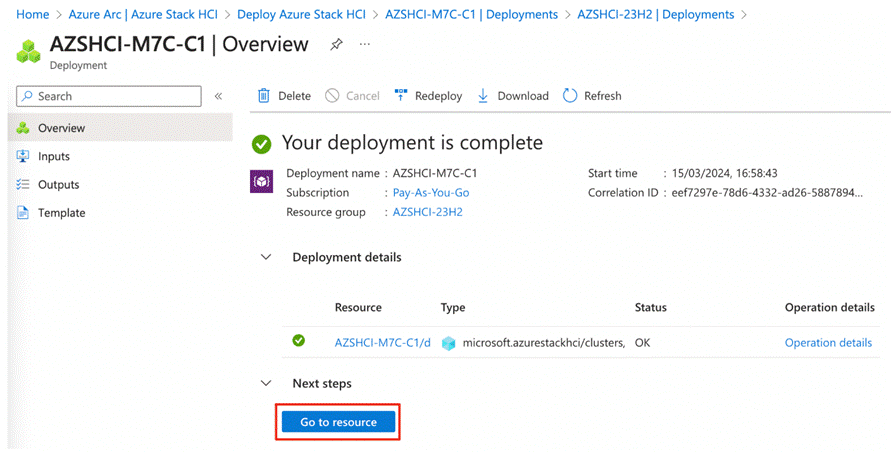
Step 2. Verify the resources created after a successful deployment. The following image shows the resources created for a 2-node Azure Local cluster:
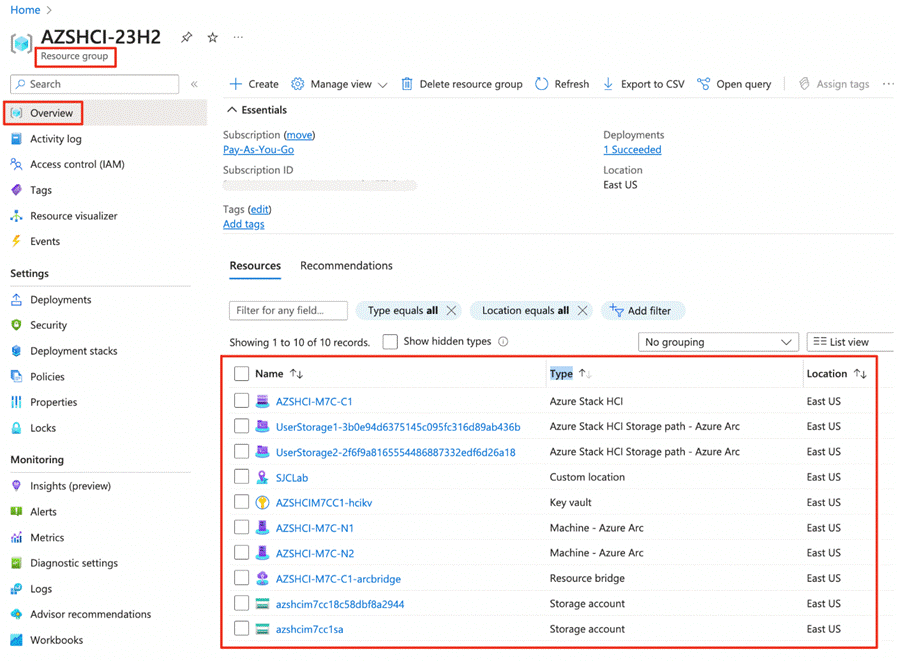
Step 3. Verify the status of storage paths. One workload volume is created per server in the system.
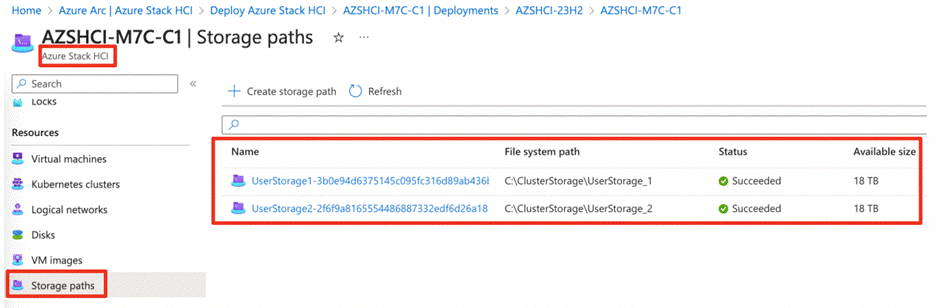
Step 4. Verify the status of Azure Arc for the nodes.
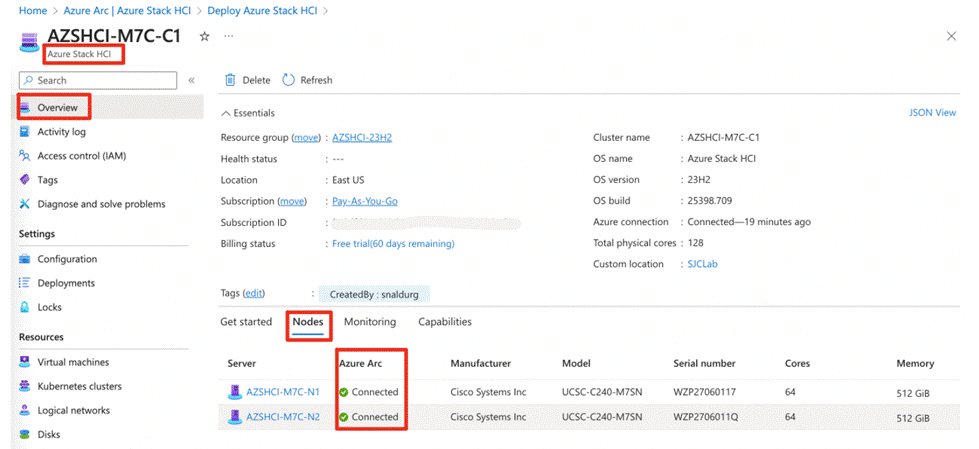
Step 5. On a cluster node, run the following command to verify the netintent status and make sure the ConfigurationStatus and ProvisioningStatus are successful and completed:
Get-NetIntentStatus | select IntentName, Host, IsComputeIntentSet, IsManagementIntentSet, IsStorageIntentSet, ConfigurationStatus, ProvisioningStatus | ft -AutoSize

Procedure 1. Post deployment tasks
Follow the steps in this procedure to enable Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) as it is disabled for security reasons after the deployment is completed.
Step 1. On your management PC, run PowerShell as an administrator.
Step 2. Run the following command to connect to your Azure Local node/server via a remote PowerShell session:
$ip="192.168.126.51"
$Creds = Get-Credential -Message "Enter Login Credentials" -User ucs-spaces\hciadmin1
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName $ip -Credential $creds

Step 3. Run the following command to enable RDP:
Enable-ASRemoteDeskTop

Procedure 2. Lock Arc Resource Bridge
Follow this procedure to configure the lock on Arc Resource Bridge to prevent it from accidental deletion.
Step 1. In the Azure portal, go to the resource group where Azure Local system is deployed.
Step 2. From the Overview > Resources tab, locate and select the Arc Resource Bridge resource to go to the resource.
Step 3. Select Locks and click Add.

Step 4. Enter the lock details and then click OK.
This appendix contains the following:
● Add Drivers and Windows Updates to a Windows Installation Image
● Create an ISO Image with Update .WIM Files
● Install and Configure DHCP Server Feature
Azure Local documentation: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/
Azure Local, version 23H2 deployment: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/deploy/deployment-introduction
Cluster-Aware Updating: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/failover-clustering/cluster-aware-updating
Active Memory Dump: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/failover-clustering/windows-server-2016-failover-cluster-troubleshooting/ba-p/372008
In this section, detailed cabling connectivity information is described for all topologies. For specific details on supported cable information, refer to the following links:
https://tmgmatrix.cisco.com/?si=Mellanox
Table 8. Cabling Map for 4-node (with 2 NICs) fully converged Azure Local cluster

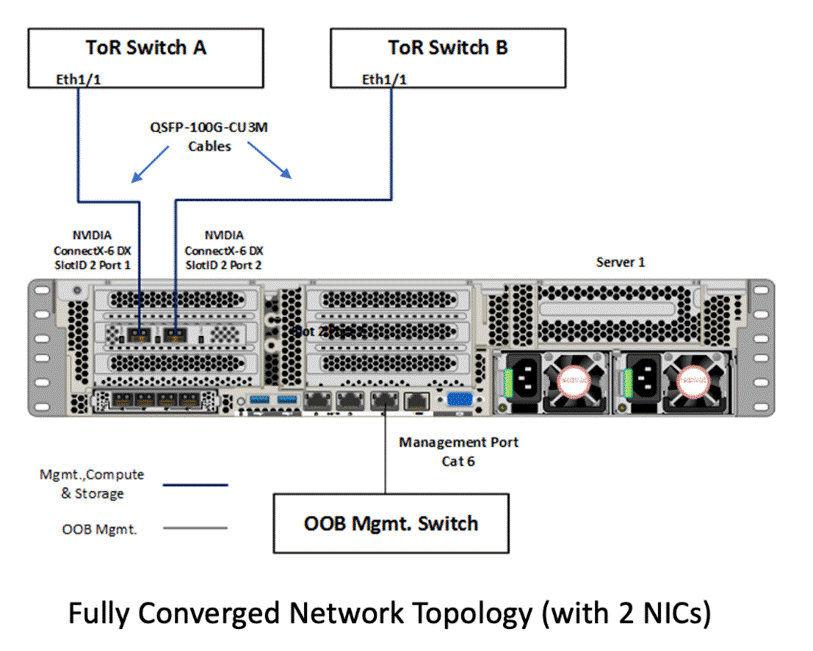
Table 9. Cabling Map for 4-node (with 4 NICs) fully converged and non-converged Azure Local cluster


Table 10. Cabling Map for 2-node (with 4 NICs) storage switchless topology for Azure Local cluster
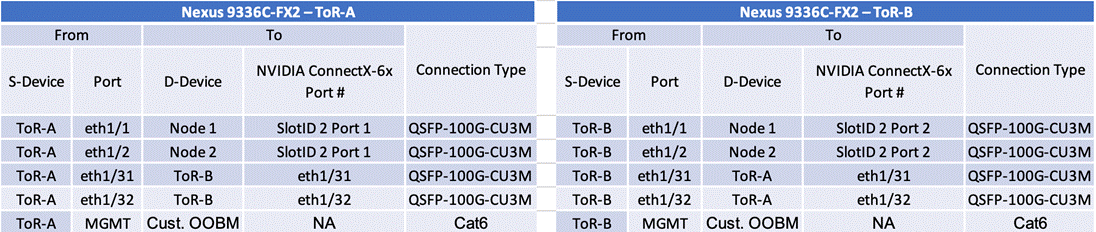


For supported cables and modules, refer to the following links:
The required Widows features are as follows:
● Clustering
● Hyper-V Management
● Group Policy Management
● Bitlocker Recovery Password Viewer
● Active Directory Management Tools
#Install required management modules
Add-WindowsFeature -Name RSAT-Hyper-V-Tools,RSAT-ADDS-Tools, RSAT-Clustering, RSAT-Clustering-MgmtRSAT-Clustering-PowerShell, RSAT-Feature-Tools-BitLocker-BdeAducExt,GPMC -IncludeManagementTools
Install-Module AZ.ConnectedMachine -force
#Update download provider modules for downloading modules from PSGallery
Set-PSRepository -Name “PSGallery” -InstallationPolicy Trusted
Install-PackageProvider -Name NuGet -Force
Install-Module -Name PowershellGet -Force -Confirm:$false
#Close and restart the PowerShell Windows before proceeding
#Configure WinRM for remote management of nodes
winrm quickconfig
#Enable sending remote management commands to the cluster nodes
$nodes = (“AzS-HCI1-N1”, “ AzS-HCI1-N2”, “ AzS-HCI1-N3”, “ AzS-HCI1-N4”)
Add Drivers and Windows Updates to a Windows Installation Image
A Windows ISO image includes boot.wim and install.wim files that are used for installation. The following are the PowerShell cmdlets to inject drivers into these .wim files.
● Get-WindowsImage: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/dism/get-windowsimage?view=win10-ps
● Mount-WindowsImage: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/dism/mount-windowsimage?view=win10-ps
● Add-WindowsDriver: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/dism/add-windowsdriver?view=win10-ps
● Dismount-WindowsImage: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/dism/dismount-windowsimage?view=win10-ps
Procedure 1. Prepare Driver Injection Computer
Step 1. Copy contents of Windows Server 2019 ISO distribution ISO, including boot.wim and install.wim, to a computer disk that will be used to inject the drivers.
Example:
Destination path = C:\temp\Source-ISO
Step 2. Copy required drivers into a subdirectory on the server. Each driver should have its own subdirectory. Each driver should include a .sys, .inf, and a .cat file at minimum. Drivers cannot be in a zip file or exe file. Chipset drivers need to be extracted prior to injection.
Example:
Destination path: C:\temp\drivers
Step 3. Create a subdirectory for mounting the target image.
Example:
md C:\temp\offline
Procedure 2. Inject Drivers into boot.wim Images
Step 1. Identify available images in the boot file (there should be two).
Example:
Get-WindowsImage -ImagePath C:\temp\Source-ISO \boot.wim
Step 2. Identify the index for the index number of the image that needs drivers.
Step 3. Mount the target image.
Example:
Mount-WindowsImage -ImagePath C:\temp\Source-ISO \boot.wim -Index 2 -Path C:\temp\offline
Step 4. Add drivers to the mounted image. You only need to add the drivers for devices that need to be accessed during the preinstallation phase and are not in the Windows distribution. This may be the boot device drivers and network drivers.
Example:
Add-WindowsDriver -Path .\offline -Driver C:\temp\drivers\[NetworkDriver]
Add-WindowsDriver -Path .\offline -Driver C:\temp\drivers\[BootDeviceDriver]
Step 5. Save and dismount the image.
Example:
Dismount-WindowsImage -Path c:\temp\offline -save
Step 6. Repeat steps 1 – 5 for the other images in the boot.wim file if necessary.
Procedure 3. Inject Drivers into install.wim images
Step 1. Identify available images in the boot file (there should be two).
Example:
Get-WindowsImage -ImagePath C:\temp\Source-ISO\install.wim
Step 2. Identify the index for the index number of the image that needs drivers.
Step 3. Mount the target image.
Example:
Mount-WindowsImage -ImagePath C:\temp\Source-ISO\install.wim -Index 4 -Path C:\temp\offline
Step 4. Add drivers to the mounted image. You only need to add all required drivers.
Example:
Add-WindowsDriver -Path C:\temp \offline -Driver C:\temp \drivers -Recurse
Step 5. Save and dismount the image.
Example:
Dismount-WindowsImage -Path c:\temp\offline -save
Step 6. Repeat steps 1 – 5 for the other images in the install.wim file if necessary.
The updated install.wim and boot.wim can be copied to and PXE server that is used for deployment. WDS (Windows Deployment Service) is an example of a PXE server that can be used to deploy the Windows operating system.
Create an ISO Image with Update .WIM Files
If a PXE server is unavailable for executing deployments, the operating system can be installed using and Windows installation ISO image. A new ISO image must be created with the updated .WIM installation files.
OSCDIMG.exe is a command line tool that can be used to create a new ISO installation image using the updated files. This tool is part of if the Automation Deployment Kit (ADK).
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/get-started/adk-install
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/manufacture/desktop/oscdimg-command-line-options
Example:
Oscdimg.exe -bC:\temp\Source-ISO\efi\microsoft\bootEfisys.bin -pEF -u1 -udfver102 C:\temp\Source-ISO C:\temp\Updated-Server2019.iso
Install and Configure DHCP Server Feature
Procedure 1. Install and Configure the DHCP Server feature
Step 1. Run the following:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name DHCP -IncludeManagementTools
netsh dhcp add securitygroups
Restart-Service dhcpserver
Add-DhcpServerv4Scope -name "HCI-Lab-P09-100.101.124.0" -StartRange 100.101.124.221 -EndRange 100.101.124.249 -SubnetMask 255.255.255.0 -State Active
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -OptionID 3 -Value 100.101.124.1 -ScopeID 100.101.124.0
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -OptionID 4 -Value 10.10.240.20 -ScopeID 100.101.124.0
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -OptionID 42 -Value 10.10.240.20 -ScopeID 100.101.124.0
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -OptionID 6 -Value 110.10.240.23 -ScopeID 100.101.124.0
Get-DhcpServerv4Scope -ScopeId 100.101.124.0
Get-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -ScopeId 100.101.124.0
#ScopeID 60 is required by WDS when DHCP is also running on the same server. ScopeID 60 is added as a DHCP a scope option when WDS is configured.
#OptionId 3 (Router)
#OptionId 4 (Time Server)
#OptionId 42 (NTP Server)
#OptionId 6 (DNS Server)
#Verify DHCP Scope
Get-DhcpServerv4Scope -ScopeId 100.101.124.0
#Verify DHCP Scope Option
Get-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -ScopeId 100.101.124.0
ToR Switch Configuration Example
This section describes the ToR (Cisco Nexus 9336C-FX2) switches example configuration used for the deployment of this Azure Local solution. The Cisco Nexus switch configuration explains the basic L2 and L3 functionality and QoS configuration for the Azure Local solution environment used in the validation environment. The gateways required for this solution are hosted by the pair of Cisco Nexus switches, but the primary routing is passed onto an existing router that is upstream of the converged infrastructure. This upstream router will need to be aware of any networks created on the Cisco Nexus switches, but configuration of an upstream router is beyond the scope of this deployment guide.
Check NXOS Version
For the Azure Local solution, the supported NXOS version is 10.3(2)F or later and the supported Cisco Nexus switches are listed here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/hci/concepts/physical-network-requirements?tabs=Cisco%2C23H2reqs
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| show version | include 'NXOS|Chassis' NXOS: version 10.3(2) [Feature Release] NXOS image file is: bootflash:///nxos64-cs.10.3.2.F.bin cisco Nexus9000 C9336C-FX2 Chassis |
show version | include 'NXOS|Chassis' NXOS: version 10.3(2) [Feature Release] NXOS image file is: bootflash:///nxos64-cs.10.3.2.F.bin cisco Nexus9000 C9336C-FX2 Chassis |
Enable Features
Some of the key NX-OS features implemented for this solution are:
● Feature interface-vlan – Allows for VLAN IP interfaces to be configured within the switch as gateways.
● Feature HSRP – Allows for Hot Standby Routing Protocol configuration for high availability.
● Feature LACP – Allows for the utilization of Link Aggregation Control Protocol (802.3ad) by the port channels configured on the switch.
● Feature vPC – Virtual Port-Channel (vPC) presents the two Nexus switches as a single “logical” port channel to the connecting upstream or downstream device.
● Feature LLDP - Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), a vendor-neutral device discovery protocol, allows the discovery of both Cisco devices and devices from other sources.
● Feature NX-API – NX-API improves the accessibility of CLI by making it available outside of the switch by using HTTP/HTTPS. This feature helps with configuring the Cisco Nexus switch remotely using the automation framework.
● Feature UDLD – Enables unidirectional link detection for various interfaces.
● Feature DHCP - Allows for the configuration of DHCP relay agent, DHCP snooping, or any of the features that depend on DHCP
● Feature scp-server - Enables the SCP (Secure Copy) server on the Cisco NX-OS device in order to copy files and from a remote device.
● Feature bgp (optional) – enables bgp to be used between ToR and aggregation router
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| feature nxapi feature scp-server cfs eth distribute feature bgp feature udld feature interface-vlan feature hsrp feature lacp feature dhcp feature vpc feature lldp |
feature nxapi feature scp-server cfs eth distribute feature bgp feature udld feature interface-vlan feature hsrp feature lacp feature dhcp feature vpc feature lldp |
Configure VLANs
The table below provides the VLANs created for different traffics used in this solution.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| vlan 2 name Reserved_Port_Ethernet vlan 101 name Tenant vlan 107 name StorageA vlan 126 name Management |
vlan 2 name Reserved_Port_Ethernet vlan 101 name Tenant vlan 207 name StorageB vlan 126 name Management |
Create Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Switched Virtual Interfaces (SVI)
These interfaces can be considered optional if the subnets of the VLANs used within the environment are managed entirely by an upstream switch, but if that is the case, all managed VLANs will need to be carried up through the vPC to the Upstream switches.
Routing between the SVIs is directly connected between them as they reside in the same Virtual Routing and Forwarding in-stance (VRF), and traffic set to enter and exit the VRF will traverse the default gateway set for the switches.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| interface Vlan2 description Unused_Ports mtu 9216 interface Vlan101 description Tenant network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.101.2/24 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 101 priority 150 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 150 ip 192.168.101.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan126 description Management Network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.126.2/26 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 126 priority 150 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 150 ip 192.168.126.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan200 description P2P_TOR1-ibgp-1_To_TOR2-ibgp-1 no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.200.45/30 no ipv6 redirects |
interface Vlan2 description Unused_Ports mtu 9216 interface Vlan101 description Tenant network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.101.3/24 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 101 priority 140 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 140 ip 192.168.101.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan126 description Management Network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.126.3/26 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 126 priority 140 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 140 ip 192.168.126.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan200 description P2P_TOR1-ibgp-1_To_TOR2-ibgp-1 no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.200.46/30 no ipv6 redirects |
Create the vPC Domain
Create a vPC domain ID with a unique number (from 1 -1000) and configure the role priority and peer-keepalive on both the switches. The vPC domain ID is same on both switches and this will handle the vPC settings specified within the switches. Note that the commands for role priority value and peer-keepalive varies slightly on both switches.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| interface mgmt0 vrf member management ip address 192.168.0.24/24
vpc domain 120 peer-switch role priority 10 peer-keepalive destination 192.168.0.25 source 192.168.0.24 delay restore 150 peer-gateway layer3 peer-router auto-recovery |
interface mgmt0 vrf member management ip address 192.168.0.25/24
vpc domain 120 peer-switch role priority 20 peer-keepalive destination 192.168.0.24 source 192.168.0.25 delay restore 150 peer-gateway layer3 peer-router auto-recovery |
On each switch, configure the Port Channel member interfaces that will be part of the vPC Peer Link and configure the vPC Peer Link:
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| interface port-channel10 description vPC Peer-Link ● switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 spanning-tree port type network service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS vpc peer-link |
interface port-channel10 description vPC Peer-Link switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 spanning-tree port type network service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS vpc peer-link |
QoS Configuration on ToR Switches (Cisco Nexus 9300 series switches)
This procedure explains the QoS configuration example for supporting RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) traffic on the ToR switches.
Using Cisco Modular Quality of Service Command Line Interface (MQC), you can define and configure QOS policies by following these steps:
1. Define a particular class of traffic.
2. After creating class-map, we put them in to a policy-map, where we mark (using bandwidth, policing, shaping, and so on) the traffic.
3. Use a service-policy command to apply that p-map to an interface in inbound or outbound direction.
Note: The QoS configuration in the host OS should match the QoS configuration performed in the Network switch (ToR) configuration
Create class-map type QoS and match based on CoS Value
In the following example, RDMA (for storage traffic) and CLUSTER-COMM (for cluster heartbeat traffic) traffic classes are defined and matched with layer 2 CoS 4 and CoS 5 respectively for classification.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| class-map type qos match-all RDMA match cos 4 class-map type qos match-all CLUSTER-COMM match cos 5 |
class-map type qos match-all RDMA match cos 4 class-map type qos match-all CLUSTER-COMM match cos 5 |
Create policy-map type QoS and Set qos-group and add/or Policing Rule
A policy-map named AzS_HCI_QoS is created and referenced to RDMA and CLUSTER-COMM class-maps and set the qos-group accordingly as shown in the following example.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| policy-map type qos AzS_HCI_QoS class RDMA set qos-group 4 class CLUSTER-COMM set qos-group 5 |
policy-map type qos AzS_HCI_QoS class RDMA set qos-group 4 class CLUSTER-COMM set qos-group 5 |
Attach policy-map type QoS as Input to an Interface
The policy-map created in the previous step is now applied to interfaces port-channel 10 and interfaces ethernet 1/1-4, where all Azure Local cluster nodes are connected.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| interface port-channel10 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/1 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/2 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/3 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/4 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS |
interface port-channel10 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/1 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/2 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/3 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS
interface Ethernet1/4 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS |
Create class-map type network-qos and match based on qos-group Value
The network QoS policy defines the characteristics of QoS properties network wide.
Two class-map type network-qos named RDMA_CL_Map_NetQoS and Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQoS are created and matched with qos-group 4 and qos-group 5, respectively.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| class-map type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 4 class-map type network-qos Cluster- Comm_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 5 |
class-map type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 4 class-map type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 5 |
Create policy-map type network-qos and Define Actions
In this example, the QoS network policy created to set Jumbo MTU for both traffic classes and no-drop (pause) to only RoCE traffic. During congestion, PFC sends a pause frame that indicates which CoS values needs to be paused This network-qos policy is then applied to the system.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| policy-map type network-qos QOS_NETWORK class type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos pause pfc-cos 4 mtu 9216 class type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos mtu 9216 class type network-qos class-default mtu 9216 system qos service-policy type network-qos QOS_NETWORK |
policy-map type network-qos QOS_NETWORK class type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos pause pfc-cos 4 mtu 9216 class type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos mtu 9216 class type network-qos class-default mtu 9216 system qos service-policy type network-qos QOS_NETWORK |
Note: For the drop and no drop configuration, you also need to enable PFC per port.
Create policy-map Type Queuing Referencing with the system-defined class-map Type Queuing and Create Actions
A policy map with minimum bandwidth percentage guarantee is specified to traffic class in periods of congestion - 50% is allocated to RDMA (storage) traffic, 49% is allocated to management and compute traffic and 1% is allocated to cluster heartbeat traffic.
Weighted random early detection (WRED) with minimum and maximum thresholds is also set to drop packets when the configured thresholds are exceeded. WRED configured with ECN (explicit congestion notification) marks packets instead of dropping them when the average queue length exceeds a specific threshold value. With WRED ECN feature, end hosts use this marking as signal that the network is congested to slow down sending packets.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| policy-map type queuing QOS_EGRESS_PORT class type queuing c-out-8q-q-default bandwidth remaining percent 49 class type queuing c-out-8q-q1 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q2 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q3 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q4 bandwidth remaining percent 50 random-detect minimum-threshold 300 kbytes maximum-threshold 300 kbytes drop-probability 100 weight 0 ecn class type queuing c-out-8q-q5 bandwidth percent 1 class type queuing c-out-8q-q6 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q7 bandwidth remaining percent 0 system qos service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT |
policy-map type queuing QOS_EGRESS_PORT class type queuing c-out-8q-q-default bandwidth remaining percent 49 class type queuing c-out-8q-q1 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q2 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q3 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q4 bandwidth remaining percent 50 random-detect minimum-threshold 300 kbytes maximum-threshold 300 kbytes drop-probability 100 weight 0 ecn class type queuing c-out-8q-q5 bandwidth percent 1 class type queuing c-out-8q-q6 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q7 bandwidth remaining percent 0 system qos service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT |
Attach policy-map Queuing to Interfaces
The example below shows policy-map queuing and priority-flow-control on are applied to ethernet 1/1-4 interfaces. Azure Local cluster nodes are connected to these interfaces.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| interface Ethernet1/1 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT
interface Ethernet1/2 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT
interface Ethernet1/3 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT
interface Ethernet1/4 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT |
interface Ethernet1/1 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT
interface Ethernet1/2 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT
interface Ethernet1/3 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT
interface Ethernet1/4 priority-flow-control mode on service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT |
The example in the following table shows the full running-configuration of both ToR switches used for this deployment in a fully converged network topology.
| ToR-A |
ToR-B |
| switchname AzS-HCI-ToR1 class-map type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 4 class-map type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 5 policy-map type network-qos QOS_NETWORK class type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos pause pfc-cos 4 mtu 9216 class type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos mtu 9216 class type network-qos class-default mtu 9216 vdc AzS-HCI-ToR1 id 1 limit-resource vlan minimum 16 maximum 4094 limit-resource vrf minimum 2 maximum 4097 limit-resource port-channel minimum 0 maximum 511 limit-resource m4route-mem minimum 58 maximum 58 limit-resource m6route-mem minimum 8 maximum 8
feature nxapi feature scp-server cfs eth distribute feature bgp feature udld feature interface-vlan feature hsrp feature lacp feature dhcp feature vpc feature lldp
mac address-table aging-time 1510
ip domain-lookup spanning-tree mode mst class-map type qos match-all RDMA match cos 4 class-map type qos match-all CLUSTER-COMM match cos 5 policy-map type qos AzS_HCI_QoS class RDMA set qos-group 4 class CLUSTER-COMM set qos-group 5 policy-map type queuing QOS_EGRESS_PORT class type queuing c-out-8q-q-default bandwidth remaining percent 49 class type queuing c-out-8q-q1 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q2 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q3 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q4 bandwidth remaining percent 50 random-detect minimum-threshold 300 kbytes maximum-threshold 300 kbytes drop-probability 100 weight 0 ecn class type queuing c-out-8q-q5 bandwidth percent 1 class type queuing c-out-8q-q6 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q7 bandwidth remaining percent 0 system qos service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT service-policy type network-qos QOS_NETWORK copp profile strict snmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0x743ead09954eb506ae83f49f45f2db95 priv des 0x743ead09954eb 506ae83f49f45f2db95 localizedkey rmon event 1 description FATAL(1) owner PMON@FATAL rmon event 2 description CRITICAL(2) owner PMON@CRITICAL rmon event 3 description ERROR(3) owner PMON@ERROR rmon event 4 description WARNING(4) owner PMON@WARNING rmon event 5 description INFORMATION(5) owner PMON@INFO ntp server 72.163.32.44 use-vrf management system default switchport
vlan 1-2,101,107,126,200,207 vlan 2 name Reserved_Port_Ethernet vlan 101 name Tenant vlan 107 name StorageA vlan 126 name Management vlan 200 name iBGP-Link vlan 207 name StorageB
spanning-tree port type edge bpduguard default spanning-tree port type edge bpdufilter default spanning-tree port type network default service dhcp ip dhcp relay ipv6 dhcp relay vrf context management ip route 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.1 congestion-control random-detect forward-nonecn vpc domain 120 peer-switch role priority 10 peer-keepalive destination 192.168.0.25 source 192.168.0.24 delay restore 150 peer-gateway layer3 peer-router auto-recovery
interface Vlan1 no ip redirects no ipv6 redirects
interface Vlan2 description Unused_Ports mtu 9216
interface Vlan101 description Tenant network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.101.2/24 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 101 priority 150 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 150 ip 192.168.101.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan126 description Management Network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.126.2/26 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 126 priority 150 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 150 ip 192.168.126.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan200 description P2P_TOR1-ibgp-1_To_TOR2-ibgp-1 no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.200.45/30 no ipv6 redirects
interface port-channel10 description vPC Peer-Link switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 spanning-tree port type network service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS vpc peer-link
interface Ethernet1/1 description AzS-HCI Fabric-A NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2 description AzS-HCI Fabric-A NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3 description AzS-HCI Fabric-A NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/4 description AzS-HCI Fabric-A NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/5
interface Ethernet1/6
interface Ethernet1/7
interface Ethernet1/8
interface Ethernet1/9
interface Ethernet1/10
interface Ethernet1/11
interface Ethernet1/12
interface Ethernet1/13
interface Ethernet1/14
interface Ethernet1/15
interface Ethernet1/16
interface Ethernet1/17
interface Ethernet1/18
interface Ethernet1/19
interface Ethernet1/20
interface Ethernet1/21
interface Ethernet1/22
interface Ethernet1/23
interface Ethernet1/24
interface Ethernet1/25
interface Ethernet1/26
interface Ethernet1/27
interface Ethernet1/28
interface Ethernet1/29
interface Ethernet1/30
interface Ethernet1/31 description VPC Peer to ToR-B:/1/31 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 channel-group 10 mode active no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/32 description VPC Peer to ToR-B:/1/32 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 channel-group 10 mode active no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/33 description P2P_Boarder1_To_ToR1 no switchport mtu 9216 ip address 192.168.200.49/30 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/34 description P2P_Boarder2_To_ToR1 no switchport mtu 9216 ip address 192.168.200.53/30 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/35
interface Ethernet1/36
interface mgmt0 vrf member management ip address 192.168.0.24/24
interface loopback0 description INFRA:Loopback_/ToR1:AzS-HCI-TOR-1:192.168.200.41 ip address 192.168.200.41/32 line console line vty boot nxos bootflash:/nxos64-cs.10.3.2.F.bin router bgp 64911 router-id 192.168.200.41 bestpath as-path multipath-relax log-neighbor-changes address-family ipv4 unicast network 192.168.101.0/24 network 192.168.126.0/26 network 192.168.200.41/32 network 192.168.200.44/30 network 192.168.200.56/30 network 192.168.200.60/30 maximum-paths 8 maximum-paths ibgp 8 template peer Border1-64821 remote-as 64821 address-family ipv4 unicast maximum-prefix 12000 warning-only template peer Border2-64821 remote-as 64821 address-family ipv4 unicast maximum-prefix 12000 warning-only template peer iBGPPeer-64911 remote-as 64911 address-family ipv4 unicast maximum-prefix 12000 warning-only neighbor 192.168.200.46 inherit peer iBGPPeer-64911 description 64811:P2P_TOR1-ibgp-1_To_TOR2-ibgp-1:192.168.200.46 neighbor 192.168.200.50 inherit peer Border1-64821 description 64821:P2P_Boarder1_To_ToR1:192.168.200.50 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-list ExternalPrefix in prefix-list ExternalPrefix out neighbor 192.168.200.54 inherit peer Border2-64821 description 64821:P2P_Boarder2_To_ToR1:192.168.200.54 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-list ExternalPrefix in prefix-list ExternalPrefix out neighbor 192.168.101.0/24 inherit peer iBGPPeer-64911 description iBGPPeer-64911-Tenant:192.168.101.0 neighbor 192.168.126.0/26 inherit peer iBGPPeer-64911 description iBGPPeer-64911-Management:192.168.126.0 |
switchname AzS-HCI-ToR2 class-map type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 4 class-map type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos match qos-group 5 policy-map type network-qos QOS_NETWORK class type network-qos RDMA_CL_Map_NetQos pause pfc-cos 4 mtu 9216 class type network-qos Cluster-Comm_CL_Map_NetQos mtu 9216 class type network-qos class-default mtu 9216 vdc AzS-HCI-ToR2 id 1 limit-resource vlan minimum 16 maximum 4094 limit-resource vrf minimum 2 maximum 4097 limit-resource port-channel minimum 0 maximum 511 limit-resource m4route-mem minimum 58 maximum 58 limit-resource m6route-mem minimum 8 maximum 8
feature nxapi feature scp-server cfs eth distribute feature bgp feature udld feature interface-vlan feature hsrp feature lacp feature dhcp feature vpc feature lldp
mac address-table aging-time 1510
ip domain-lookup spanning-tree mode mst class-map type qos match-all RDMA match cos 4 class-map type qos match-all CLUSTER-COMM match cos 5 policy-map type qos AzS_HCI_QoS class RDMA set qos-group 4 class CLUSTER-COMM set qos-group 5 policy-map type queuing QOS_EGRESS_PORT class type queuing c-out-8q-q-default bandwidth remaining percent 49 class type queuing c-out-8q-q1 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q2 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q3 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q4 bandwidth remaining percent 50 random-detect minimum-threshold 300 kbytes maximum-threshold 300 kbytes drop-probability 100 weight 0 ecn class type queuing c-out-8q-q5 bandwidth percent 1 class type queuing c-out-8q-q6 bandwidth remaining percent 0 class type queuing c-out-8q-q7 bandwidth remaining percent 0 system qos service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT service-policy type network-qos QOS_NETWORK copp profile strict snmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0x4f03854fbf75be4bec6b38ed1223a54d priv des 0x4f03854fbf75b e4bec6b38ed1223a54d localizedkey rmon event 1 description FATAL(1) owner PMON@FATAL rmon event 2 description CRITICAL(2) owner PMON@CRITICAL rmon event 3 description ERROR(3) owner PMON@ERROR rmon event 4 description WARNING(4) owner PMON@WARNING rmon event 5 description INFORMATION(5) owner PMON@INFO ntp server 72.163.32.44 use-vrf management system default switchport
vlan 1-2,101,107,126,200,207 vlan 2 name Reserved_Port_Ethernet vlan 101 name Tenant vlan 107 name StorageA vlan 126 name Management vlan 200 name iBGP-Link vlan 207 name StorageB
spanning-tree port type edge bpduguard default spanning-tree port type edge bpdufilter default spanning-tree port type network default service dhcp ip dhcp relay ipv6 dhcp relay vrf context management ip route 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.1 congestion-control random-detect forward-nonecn vpc domain 120 peer-switch role priority 20 peer-keepalive destination 192.168.0.24 source 192.168.0.25 delay restore 150 peer-gateway layer3 peer-router auto-recovery
interface Vlan1 no ip redirects no ipv6 redirects
interface Vlan2 description Unused_Ports mtu 9216
interface Vlan101 description Tenant network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.101.3/24 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 101 priority 140 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 140 ip 192.168.101.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan126 description Management Network no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.126.3/26 ip directed-broadcast no ipv6 redirects hsrp version 2 hsrp 126 priority 140 forwarding-threshold lower 1 upper 140 ip 192.168.126.1 ip dhcp relay address 192.168.0.10
interface Vlan200 description P2P_TOR1-ibgp-1_To_TOR2-ibgp-1 no shutdown mtu 9216 no ip redirects ip address 192.168.200.46/30 no ipv6 redirects
interface port-channel10 description vPC Peer-Link switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 spanning-tree port type network service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS vpc peer-link
interface Ethernet1/1 description AzS-HCI Fabric-B NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,126,207 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2 description AzS-HCI Fabric-B NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,126,207 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3 description AzS-HCI Fabric-B NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,126,207 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/4 description AzS-HCI Fabric-B NIC Port switchport mode trunk switchport trunk native vlan 126 switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,126,207 priority-flow-control mode on spanning-tree port type edge trunk mtu 9216 service-policy type qos input AzS_HCI_QoS service-policy type queuing output QOS_EGRESS_PORT no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/5
interface Ethernet1/6
interface Ethernet1/7
interface Ethernet1/8
interface Ethernet1/9
interface Ethernet1/10
interface Ethernet1/11
interface Ethernet1/12
interface Ethernet1/13
interface Ethernet1/14
interface Ethernet1/15
interface Ethernet1/16
interface Ethernet1/17
interface Ethernet1/18
interface Ethernet1/19
interface Ethernet1/20
interface Ethernet1/21
interface Ethernet1/22
interface Ethernet1/23
interface Ethernet1/24
interface Ethernet1/25
interface Ethernet1/26
interface Ethernet1/27
interface Ethernet1/28
interface Ethernet1/29
interface Ethernet1/30
interface Ethernet1/31 description VPC Peer to ToR-A:/1/31 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 channel-group 10 mode active no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/32 description VPC Peer to ToR-A:/1/32 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,107,126,200,207 channel-group 10 mode active no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/33 description P2P_Boarder1_To_ToR2 no switchport mtu 9216 ip address 192.168.200.57/30 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/34 description P2P_Boarder2_To_ToR2 no switchport mtu 9216 ip address 192.168.200.61/30 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/35
interface Ethernet1/36
interface mgmt0 vrf member management ip address 192.168.0.25/24
interface loopback0 description INFRA:Loopback_/ToR1:AzS-HCI-TOR-1:192.168.200.42 ip address 192.168.200.42/32 line console line vty boot nxos bootflash:/nxos64-cs.10.3.2.F.bin router bgp 64911 router-id 192.168.200.42 bestpath as-path multipath-relax log-neighbor-changes address-family ipv4 unicast network 192.168.101.0/24 network 192.168.126.0/26 network 192.168.200.42/32 network 192.168.200.44/30 network 192.168.200.48/30 network 192.168.200.52/30 maximum-paths 8 maximum-paths ibgp 8 template peer Border1-64821 remote-as 64821 address-family ipv4 unicast maximum-prefix 12000 warning-only template peer Border2-64821 remote-as 64821 address-family ipv4 unicast maximum-prefix 12000 warning-only template peer iBGPPeer-64911 remote-as 64911 address-family ipv4 unicast maximum-prefix 12000 warning-only neighbor 192.168.200.45 inherit peer iBGPPeer-64911 description 64811:P2P_TOR1-ibgp-1_To_TOR2-ibgp-1:192.168.200.45 neighbor 192.168.200.58 inherit peer Border1-64821 description 64821:P2P_Boarder1_To_ToR1:192.168.200.58 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-list ExternalPrefix in prefix-list ExternalPrefix out neighbor 192.168.200.62 inherit peer Border2-64821 description 64821:P2P_Boarder2_To_ToR1:192.168.200.62 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-list ExternalPrefix in prefix-list ExternalPrefix out neighbor 192.168.101.0/24 inherit peer iBGPPeer-64911 description iBGPPeer-64911-Tenant:192.168.101.0 neighbor 192.168.126.0/26 inherit peer iBGPPeer-64911 description iBGPPeer-64911-Management:192.168.126.0 |
Sanjeev Naldurgkar, Technical Leader, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Sanjeev Naldurgkar is a technical leader on the Cisco UCS Solutions Engineering and Technical Marketing team, focusing on Microsoft solutions that include Azure Stack Hub, Azure Local, and Azure. His two decades of IT experience span multiple companies including Microsoft. Sanjeev holds a bachelor’s degree in Electronics and Communications Engineering, along with leading industry certifications from Microsoft and VMware.
Acknowledgements
For their support and contribution to the design, validation, and creation of this Cisco Validated Design, we would like to thank:
● Tyson Scott, Cisco Systems, Inc.
● John McAbel, Cisco Systems, Inc.
● Babu Mahadevan, Cisco Systems, Inc.
For comments and suggestions about this guide and related guides, join the discussion on Cisco Community at https://cs.co/en-cvds.
CVD Program
ALL DESIGNS, SPECIFICATIONS, STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS (COLLECTIVELY, "DESIGNS") IN THIS MANUAL ARE PRESENTED "AS IS," WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND ITS SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE. IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE DESIGNS, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
THE DESIGNS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF THE DESIGNS. THE DESIGNS DO NOT CONSTITUTE THE TECHNICAL OR OTHER PROFESSIONAL ADVICE OF CISCO, ITS SUPPLIERS OR PARTNERS. USERS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR OWN TECHNICAL ADVISORS BEFORE IMPLE-MENTING THE DESIGNS. RESULTS MAY VARY DEPENDING ON FACTORS NOT TESTED BY CISCO.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS), Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers, Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers, Cisco UCS S-Series Storage Servers, Cisco UCS X-Series, Cisco UCS Manager, Cisco UCS Management Software, Cisco Unified Fabric, Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure, Cisco Nexus 9000 Series, Cisco Nexus 7000 Series. Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager, Cisco NX-OS Software, Cisco MDS Series, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trade-marks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries. (LDW_P1)
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0809R)
 Feedback
Feedback