Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco Unified Computing System with EMC VNX Storage
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
About Cisco Validated Design (CVD) Program
Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco Unified Computing System with EMC VNX Storage
Oracle Siebel Customer Relationship Management Solution
Cisco Unified Computing System
Cisco UCS 2100 and 2200 Series Fabric Extenders
Design Considerations for Oracle Siebel Implementation on Cisco Unified Computing System
Scalable Architecture Using Cisco UCS Servers
EMC VNX5500 - Block and File Storage Required for Oracle Siebel
Configuring the Cisco Unified Computing System
Editing Chassis Discovery Policy
Creating Uplink Ports Channels
Creating Service Profile Templates
Creating Service Profile from the Template and associating it to a Blade
Creation of Storage Pools/RAID Groups
Creation of File System (NFS Share)
Configuring the Nexus Switches
Setting up the Nexus 5548 Switch
Enabling Nexus 5548 Switch Licensing
Configuration of Ports 29-32 as FC ports
Creating VSAN and Adding FC Interfaces
Creating VLANs and Managing Traffic
Creation and Configuration of Virtual Port Channel (VPC)
Cisco UCS Manager Service Profile update
Modifying Service Profile for Boot Policy
Understanding the Hardware and Software Prerequisites
Installation of Oracle Database
Installation of Database Client on the Oracle Siebel Gateway/Application Servers.
Preparing the Siebel File system
Downloading the Oracle Siebel Installation Archives and Running the Oracle Siebel Image Creator
Other Installation Prerequistes
Oracle HTTP Server Installation
Siebel Server/ DB Utilities Installation
Gateway Server / Enterprise Server Configuration
Creation of SWSE Logical Profile
Oracle Siebel Server Configuration
SWSE Install and Configuration
Applying the SWSE Logical profile
Lessons Learnt & Best Practices
Oracle Siebel Performance and Scalability
Business Transactions & Workload Mix
Transaction Throughput and Response Time
Best Practices & Tuning Recommendations
Application server / Oracle Siebel Enterprise
Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco Unified Computing
System with EMC VNX StorageA Cisco Validated Design for Oracle Siebel CRM 8.1.1.4 with Oracle 11g R2 Database on Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers for Workloads Scaling up to 10,000 UsersLast Updated: April 27, 2012

Building Architectures to Solve Business Problems
About the Authors
Babu Mahadevan V, Technical Marketing Engineer, Server Access Virtualization Business Unit, Cisco SystemsBabu has over 15 years of experience in large systems performance in Financial, Telecom and Retail industry verticals focusing on optimizing both custom-made applications as well commercial product deployments. Babu was a performance engineering consultant with TCS prior to Cisco and holds a Master's degree in Electronics Engineering.
Vadiraja Bhatt, Performance Architect, Server Access Virtualization Business Unit, Cisco SystemsVadiraja Bhatt is a Performance Architect at Cisco, managing the solutions and benchmarking effort on Cisco Unified Computing System Platform. Vadi has over 17 years of experience in performance and benchmarking the large enterprise systems deploying mission critical applications. Vadi specializes in optimizing and fine tuning complex hardware and software systems and has delivered many benchmark results on TPC and other industry standard benchmarks. Vadi has 6 patents to his credits in the Database (OLTP and DSS) optimization area.
Acknowledgements
For their support and contribution to the design, validation, and creation of the Cisco Validated Design, we would like to thank:
•
Deepak Adiga-Cisco
•
Radhakrishnan Manga-EMC
•
Kathy Sharp-EMC
About Cisco Validated Design (CVD) Program
The CVD program consists of systems and solutions designed, tested, and documented to facilitate faster, more reliable, and more predictable customer deployments. For more information visit www.cisco.com/go/designzone.
ALL DESIGNS, SPECIFICATIONS, STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS (COLLECTIVELY, "DESIGNS") IN THIS MANUAL ARE PRESENTED "AS IS," WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND ITS SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE. IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE DESIGNS, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
THE DESIGNS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF THE DESIGNS. THE DESIGNS DO NOT CONSTITUTE THE TECHNICAL OR OTHER PROFESSIONAL ADVICE OF CISCO, ITS SUPPLIERS OR PARTNERS. USERS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR OWN TECHNICAL ADVISORS BEFORE IMPLEMENTING THE DESIGNS. RESULTS MAY VARY DEPENDING ON FACTORS NOT TESTED BY CISCO.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0809R)
© 2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved
Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco Unified Computing System with EMC VNX Storage
Introduction
The Oracle Siebel CRM software helps organizations to differentiate their businesses to achieve maximum top-and bottom-line growth by delivering a combination of transactional, analytical, and engagement features to manage all customer-facing operations. Oracle Siebel CRM provides comprehensive CRM solutions tailored with industry needs along with pre-built integrations makes it a widely used CRM software.
Since companies compete to attract new businesses, increase customer loyalty through CRM tools, the demand can scale rapidly, forcing datacenters to expand system resources quickly to meet increasing workloads. Oracle Siebel CRM allows datacenters to scale horizontally (adding more servers at each tier as they grow), vertically (adding more powerful servers (CPUs and RAM)) or both, since it is built on Service Oriented Architecture foundation.
Oracle Siebel CRM applications, running on the Cisco Unified Computing System, can reduce the total cost of ownership at the platform, site, and organizational levels and increase IT staff productivity and business agility.
Target Audience
This document is intended to assist Solution Architects, Sales Engineers, Field Engineers and Consultants in planning, design, and deployment of Oracle Siebel CRM hosted on Cisco Unified Computing System servers. This document assumes that the reader has an architectural understanding of the Cisco UCS servers, Oracle Siebel CRM software, EMC® VNX5500™ Storage array, and related software.
Purpose of this Guide
This Cisco Validated Design demonstrates how enterprises can apply best practices for Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco Nexus family of switches and EMC VNX5500 storage array for Oracle Siebel CRM implementation.
Design validation was achieved by conducting tests for Oracle Siebel CRM workloads using HP's LoadRunner tool. Workloads were defined as small enterprise sized workloads of 600 concurrent users, medium enterprise workloads of 3000 concurrent users and large workloads of 10000 concurrent users with proportionately increased data volumes.
Business Needs
The business needs for Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco UCS servers are:
•
As companies compete to expand to new businesses and improve customer satisfaction using CRM tools such as Oracle Siebel, it can result in high system resource demands in shortest possible time.
•
Large Oracle Siebel CRM implementations require high compute, highly available system resources as optimum service levels are required to ensure business continuity.
•
Cost containment and reduced complexities when adding new system resources to meet the ever increasing Siebel CRM demands.
•
Ability of the system resources to upgrade/adopt to newer technologies such as cloud computing etc. without a significant impact on TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
To meet these business needs the Cisco Unified Computing System™ server platform provides a new data center architecture that is ideal for supporting and managing mission-critical applications. The Cisco UCS is the next-generation data center server platform that unites compute, network, storage access, and virtualization into a cohesive system designed to outperform previous server architectures, increase operational agility and flexibility while potentially dramatically reducing overall data center costs.
Testing exercises conducted at Cisco labs using a well-defined Siebel CRM workload have shown that, the Cisco UCS servers scale easily to accommodate a wide range of workloads - thus validating the Siebel CRM performance requirements can be adequately met in enterprise deployments.
Combined with EMC VNX5500 storage array, Cisco UCS servers provide a compelling proposition for Oracle Siebel CRM implementation, as VNX5500 offers unified storage (both block and file access together) along with optimal response time suiting Oracle Siebel CRM requirements. EMC VNX5500 is high-performing Unified Storage with unsurpassed simplicity and efficiency, and offers new levels of performance, protection, compliance, and ease of management.
Solution Overview
The Solution demonstrates the ease of deployment of Oracle Siebel CRM version 8.1.1.4 on a fully configured Cisco UCS system with an end to end deployment of a typical Oracle Siebel CRM implementation. The solution describes the following aspects of Siebel CRM deployment on Cisco Unified Computing System:
•
Configuring Cisco UCS for Oracle Siebel
–
Configuring Fabric Interconnect
–
Configuring Cisco UCS Blades
•
Configuring EMC VNX5500 series storage enclosures for Oracle Siebel CRM
–
Configuring the storage and creating LUNs
–
Associating LUNs with the hosts
•
Installing and configuring Oracle Siebel CRM 8.1.1.4
–
Provisioning the required server resource
–
Installing and Configuring Oracle Web Server, Siebel Gateway Server and Siebel Application Server
–
Configuring the Oracle RAC database
•
Performance characterization of Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco Unified Computing System
–
Testing and tuning Cisco UCS hardware components for Oracle Siebel CRM
–
Tuning OS level parameters
–
Tuning Oracle Siebel Components - Web server, Siebel server and Database server
•
Sizing guide for Oracle Siebel CRM applications on Cisco UCS
–
Sizing criteria and guidelines
The solution is limited to a typical, minimally customized Oracle Siebel CRM application which deals with Order Management workload. However, Oracle Siebel CRM has several modules and diverse workload characteristics which can be configured to meet the requirements of broad range of enterprise demands. Although this solution does not address all those scenarios, it provides metrics and guidelines which can be used as a baseline for extending this solution to include specific Oracle Siebel needs to deploy using Cisco Unified Computing System.
Technology Overview
Oracle Siebel Customer Relationship Management Solution
Oracle Siebel 8.1 uses a multi-tiered application framework. The Oracle Siebel environment consists of client, application, and database tiers. The client tier comprises of devices that access the application via the Web. The application tier can be broken down to two different functions, services that terminate client connections and Application Object Managers (AOM) that perform the business logic. Multiple application components can reside in the application tier providing different business functions. The database tier contains the Relational Data Base Management System (RDBMS) and shared file system. The database serves as a repository for data collections. The shared file system is for storing attachments such as Adobe Acrobat files, fax quotes, and other documents. The Oracle Siebel architecture is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Oracle Siebel Architecture
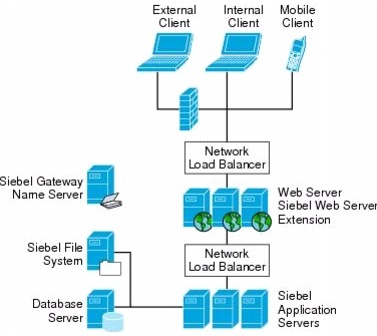
Multi-Tier Architecture
Client Tier
There are multiple client types available on the Oracle Siebel platform. The major client types are Web client, mobile client, and dedicated Web client. Wireless and handheld clients are used in specialized applications such as retail and manufacturing.
•
Oracle Siebel Web client—Oracle Siebel Web client uses a Web browser on the local PC. It connects to the Siebel Web server via http (port 80) or https (port 443). No additional software is required. The Web client is easy to maintain since it does not require any software upgrades.
•
Oracle Siebel mobile client and dedicated client—The mobile client and dedicated client require additional software installed on the PC. The additional software provides faster throughput with less data transfers for a given transaction by sending only changed data between the client and the server. For remote users, the dedicated client allows disconnected mode and synchronizes with the database when network connectivity is restored.
•
Oracle Siebel wireless client and Oracle Siebel handheld client—These two clients are specialized clients for vertical applications. The wireless client has a translator for Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), which is suitable for mobile phones. The handheld client can accommodate information on smaller screens.
Application Tier
The application tier contains two functional areas, services that terminate client connections and business logic.
The former component is called the Siebel Web Server Extension (SWSE). It is an add-on to Oracle HTTP Web server. SWSE is responsible for handling Web requests from users. It forwards user requests to the Application Object Managers (AOM) via Siebel Internet Session API (SISNAPI) protocol. Oracle Siebel provides native server load balancing for highly-available Web servers. Third party load balancers are supported as well.
There are numerous Siebel application servers that provide different business applications. Each Oracle Siebel application component can be run on a single or multiple physical servers. Application components can be load balanced at the component level across different physical server pools. Load balancing can be configured with native Siebel load balancer or a third-party load balancer.
Database Tier
The database tier provides a repository to Oracle Siebel application data. It consists of a RDBMS and a separate file system store.
•
File system—The Oracle Siebel File System (SFS) is a server with a shared directory that provides NFS access to other Oracle Siebel servers. The SFS is a shared storage area for images, reports, documents, and other data. A pointer in the database record locates the file in the SFS.
•
Database Server—The database server is the main data store for the Oracle Siebel application. The Oracle Siebel application servers connect directly to the database server. Oracle Database 11g is used in this deployment.
Gateway Name Server
Gateway name server is a repository for configuration information for each Siebel server. It has configuration information about the Siebel Enterprise.
Cisco Unified Computing System
The Cisco Unified Computing System is a next-generation data center platform that unites compute, network, and storage access. The platform, optimized for virtual environments, is designed using open industry-standard technologies and aims to reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) and increase business agility. The system integrates a low-latency; lossless 10 Gigabit Ethernet unified network fabric with enterprise-class, x86-architecture servers. It is an integrated, scalable, multi chassis platform in which all resources participate in a unified management domain.
The main components of Cisco Unified Computing System are:
•
Computing—The system is based on an entirely new class of computing system that incorporates blade servers based on Intel Xeon 5500/5600 Series Processors. Selected Cisco UCS blade servers offer the patented Cisco Extended Memory Technology to support applications with large datasets and allow more virtual machines per server.
•
Network—The system is integrated onto a low-latency, lossless, 10-Gbps unified network fabric. This network foundation consolidates LANs, SANs, and high-performance computing networks which are separate networks today. The unified fabric lowers costs by reducing the number of network adapters, switches, and cables, and by decreasing the power and cooling requirements.
•
Virtualization—The system unleashes the full potential of virtualization by enhancing the scalability, performance, and operational control of virtual environments. Cisco security, policy enforcement, and diagnostic features are now extended into virtualized environments to better support changing business and IT requirements.
•
Storage access—The system provides consolidated access to both SAN storage and Network Attached Storage (NAS) over the unified fabric. By unifying the storage access the Cisco Unified Computing System can access storage over Ethernet, Fibre Channel, Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), and iSCSI. This provides customers with choice for storage access and investment protection. In addition, the server administrators can pre-assign storage-access policies for system connectivity to storage resources, simplifying storage connectivity, and management for increased productivity.
•
Management—The system uniquely integrates all system components which enable the entire solution to be managed as a single entity by the Cisco UCS Manager. The Cisco UCS Manager has an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI), a command-line interface (CLI), and a robust application programming interface (API) to manage all system configuration and operations.
The Cisco Unified Computing System is designed to deliver:
•
A reduced Total Cost of Ownership and increased business agility.
•
Increased IT staff productivity through just-in-time provisioning and mobility support.
•
A cohesive, integrated system which unifies the technology in the data center. The system is managed, serviced and tested as a whole.
•
Scalability through a design for hundreds of discrete servers and thousands of virtual machines and the capability to scale I/O bandwidth to match demand.
•
Industry standards supported by a partner ecosystem of industry leaders.
Cisco Unified Computing System is designed from the ground up to be programmable and self integrating. A server's entire hardware stack, ranging from server firmware and settings to network profiles, is configured through model-based management. With Cisco virtual interface cards, even the number and type of I/O interfaces is programmed dynamically, making every server ready to power any workload at any time.
With model-based management, administrators manipulate a model of a desired system configuration, associate a model's service profile with the hardware components, and the system configures automatically to match the model. This automation speeds provisioning and workload migration with accurate and rapid scalability. The result is increased IT staff productivity, improved compliance, and reduced risk of failures due to inconsistent configurations.
Cisco Fabric Extender technology reduces the number of system components to purchase, configure, manage, and maintain by condensing three network layers into one. It eliminates both blade server and hypervisor-based switches by connecting fabric interconnect ports directly to individual blade servers and virtual machines. Virtual networks are now managed exactly as physical networks are, but with massive scalability. This represents a radical simplification over traditional systems, reducing capital and operating costs while increasing business agility, simplifying and speeding deployment, and improving performance. Figure 2 shows the Cisco UCS components.
Figure 2 Cisco Unified Computing System Components

Fabric Interconnect
The Cisco® UCS 6200 Series Fabric Interconnect is a core part of the Cisco Unified Computing System, providing both network connectivity and management capabilities for the system. The Cisco UCS 6200 Series offers line-rate, low-latency, lossless 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) and Fibre Channel functions.
The Cisco UCS 6200 Series provides the management and communication backbone for the Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers and Cisco UCS 5100 Series Blade Server Chassis. All chassis, and therefore all blades, attached to the Cisco UCS 6200 Series Fabric Interconnects become part of a single, highly available management domain. In addition, by supporting unified fabric, the Cisco UCS 6200 Series provides both the LAN and SAN connectivity for all blades within its domain.
From a networking perspective, the Cisco UCS 6200 Series uses a cut-through architecture, supporting deterministic, low-latency, line-rate 10 Gigabit Ethernet on all ports, 1Tb switching capacity, 160 Gbps bandwidth per chassis, independent of packet size and enabled services. The product family supports Cisco low-latency, lossless 10 Gigabit Ethernet unified network fabric capabilities, which increase the reliability, efficiency, and scalability of Ethernet networks. The Fabric Interconnect supports multiple traffic classes over a lossless Ethernet fabric from a blade server through an interconnect. Significant TCO savings come from an FCoE-optimized server design in which network interface cards (NICs), host bus adapters (HBAs), cables, and switches can be consolidated. The Cisco Fabric Interconnect is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Cisco 6200 Series Fabric interconnect

The following are the different types of Cisco Fabric Interconnects:
•
Cisco UCS 6296UP Fabric Interconnect
•
Cisco UCS 6248UP Fabric Interconnect
•
Cisco UCS U6120XP 20-Port Fabric Interconnect
•
Cisco UCS U6140XP 40-Port Fabric Interconnect
Cisco UCS 6296UP Fabric Interconnect
The Cisco UCS 6296UP 96-Port Fabric Interconnect is a 2RU 10 Gigabit Ethernet, FCoE and native Fibre Channel switch offering up to 1920-Gbps throughput and up to 96 ports. The switch has 48 1/10-Gbps fixed Ethernet, FCoE and Fiber Channel ports and three expansion slots. It doubles the switching capacity of the data center fabric to improve workload density from 960Gbps to 1.92 Tbps, reduces end-to-end latency by 40 percent to improve application performance and provides flexible unified ports to improve infrastructure agility and transition to a fully converged fabric.
Cisco UCS 6248UP Fabric Interconnect
The Cisco UCS 6248UP 48-Port Fabric Interconnect is a one-rack-unit (1RU) 10 Gigabit Ethernet, FCoE and Fiber Channel switch offering up to 960-Gbps throughput and up to 48 ports. The switch has 32 1/10-Gbps fixed Ethernet, FCoE and FC ports and one expansion slot.
Cisco UCS U6120XP 20-Port Fabric Interconnect
The Cisco UCS U6120XP 20-Port Fabric Interconnect is a 1RU, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE DCB, and FCoE interconnect providing more than 500 Gbps throughput with very low latency. It has 20 fixed 10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE DCB, and FCoE SFP+ ports.One expansion module slot can be configured to support up to six additional 10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE DCB, and FCoE SFP+ ports.
Cisco UCS U6140XP 40-Port Fabric Interconnect
The Cisco UCS U6140XP 40-Port Fabric Interconnect is a 2RU, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE DCB, and FCoE interconnect built to provide 1.04 Tbps throughput with very low latency. It has 40 fixed 10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE DCB, and FCoE SFP+ ports.
Two expansion module slots can be configured to support up to 12 additional 10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE DCB, and FCoE SFP+ ports.
Cisco UCS 2100 and 2200 Series Fabric Extenders
The Cisco UCS 2100 and 2200 Series Fabric Extenders multiplex and forward all traffic from blade servers in a chassis to a parent Cisco UCS fabric interconnect over from 10-Gbps unified fabric links. All traffic, even traffic between blades on the same chassis or virtual machines on the same blade, is forwarded to the parent interconnect, where network profiles are managed efficiently and effectively by the fabric interconnect. At the core of the Cisco UCS fabric extender are application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) processors developed by Cisco that multiplex all traffic.
Up to two fabric extenders can be placed in a blade chassis.
•
The Cisco UCS 2104XP Fabric Extender has eight 10GBASE-KR connections to the blade chassis midplane, with one connection per fabric extender for each of the chassis' eight half slots. This configuration gives each half-slot blade server access to each of two 10-Gbps unified fabric-based networks through SFP+ sockets for both throughput and redundancy. It has four ports connecting the fabric interconnect.
•
The Cisco UCS 2208XP is first product in the Cisco UCS 2200 Series. It has eight 10 Gigabit Ethernet, FCoE-capable, and Enhances Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP+) ports that connect the blade chassis to the fabric interconnect. Each Cisco UCS 2208XP has thirty-two 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports connected through the midplane to each half-width slot in the chassis. Typically configured in pairs for redundancy, two fabric extenders provide up to 160 Gbps of I/O to the chassis.
Cisco UCS Blade Chassis
The Cisco UCS 5100 Series Blade Server Chassis is a crucial building block of the Cisco Unified Computing System, delivering a scalable and flexible blade server chassis.
The Cisco UCS 5108 Blade Server Chassis, is six rack units (6RU) high and can mount in an industry-standard 19-inch rack. A single chassis can house up to eight half-width Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers and can accommodate both half-width and full-width blade form factors.
Four single-phase, hot-swappable power supplies are accessible from the front of the chassis. These power supplies are 92 percent efficient and can be configured to support non-redundant, N+ 1 redundant and grid-redundant configurations. The rear of the chassis contains eight hot-swappable fans, four power connectors (one per power supply), and two I/O bays for Cisco UCS 2104XP Fabric Extenders.
A passive mid-plane provides up to 20 Gbps of I/O bandwidth per server slot and up to 40 Gbps of I/O bandwidth for two slots. The chassis is capable of supporting future 40 Gigabit Ethernet standards. The Cisco UCS Blade Server Chassis is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Cisco Blade Server Chassis (front and back view)

Cisco UCS Manager
Cisco UCS Manager provides unified, embedded management of all software and hardware components of the Cisco Unified Computing System through an intuitive GUI, a command line interface (CLI), or an XML API. The Cisco UCS Manager provides unified management domain with centralized management capabilities and controls multiple chassis and thousands of virtual machines.
Cisco UCS Blade Server Types
The following are the different types of Cisco Blade Servers:
•
Cisco UCS B250 M2 Extended Memory Blade Server
•
Cisco UCS B230 M2 Blade Servers
•
Cisco UCS B440 M2 High-Performance Blade Servers
Cisco UCS B200 M3 Server
Delivering performance, versatility and density without compromise, the Cisco UCS B200 M3 Blade Server addresses the broadest set of workloads, from IT and Web Infrastructure through distributed database.
Building on the success of the Cisco UCS B200 M2 blade servers, the enterprise-class Cisco UCS B200 M3 server, further extends the capabilities of Cisco's Unified Computing System portfolio in a half blade form factor. The Cisco UCS B200 M3 server harnesses the power and efficiency of the Intel Xeon E5-2600 processor product family, up to 768 GB of RAM, 2 drives or SSDs and up to 2 x 20 GbE to deliver exceptional levels of performance, memory expandability and I/O throughput for nearly all applications. In addition, the Cisco UCS B200 M3 blade server offers a modern design that removes the need for redundant switching components in every chassis in favor of a simplified top of rack design, allowing more space for server resources, providing a density, power and performance advantage over previous generation servers. The Cisco UCS B200M3 Server is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Cisco UCS B200 M3 Blade Server

Cisco UCS B200 M2 Server
The Cisco UCS B200 M2 Blade Server is a half-width, two-socket blade server. The system uses two Intel Xeon 5600 Series Processors, up to 96 GB of DDR3 memory, two optional hot-swappable small form factor (SFF) serial attached SCSI (SAS) disk drives, and a single mezzanine connector for up to 20 Gbps of I/O throughput. The server balances simplicity, performance, and density for production-level virtualization and other mainstream data center workloads. The Cisco UCS B200 M2 Server is shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Cisco UCS B200 M2 Blade Server

Cisco UCS B250 M2 Extended Memory Blade Server
The Cisco UCS B250 M2 Extended Memory Blade Server is a full-width, two-socket blade server featuring Cisco Extended Memory Technology. The system supports two Intel Xeon 5600 Series Processors, up to 384 GB of DDR3 memory, two optional SFF SAS disk drives, and two mezzanine connections for up to 40 Gbps of I/O throughput. The server increases performance and capacity for demanding virtualization and large-data-set workloads with greater memory capacity and throughput. The Cisco UCS Extended Memory Blade Server is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 Cisco UCS B250 M2 Extended Memory Blade Server

Cisco UCS B230 M2 Blade Servers
The Cisco UCS B230 M2 Blade Server is a full-slot, 2-socket blade server offering the performance and reliability of the Intel Xeon processor E7-2800 product family and up to 32 DIMM slots, which support up to 512 GB of memory. The Cisco UCS B230 M2 supports two SSD drives and one CNA mezzanine slot for up to 20 Gbps of I/O throughput. The Cisco UCS B230 M2 Blade Server platform delivers outstanding performance, memory, and I/O capacity to meet the diverse needs of virtualized environments with advanced reliability and exceptional scalability for the most demanding applications.
Cisco UCS B440 M2 High-Performance Blade Servers
The Cisco UCS B440 M2 High-Performance Blade Server is a full-slot, 2-socket blade server offering the performance and reliability of the Intel Xeon processor E7-4800 product family and up to 512 GB of memory. The Cisco UCS B440 M2 supports four SFF SAS/SSD drives and two CNA mezzanine slots for up to 40 Gbps of I/O throughput. The Cisco UCS B440 M2 blade server extends Cisco UCS by offering increased levels of performance, scalability, and reliability for mission-critical workloads.
Cisco UCS Service Profiles
Programmatically Deploying Server Resources
Cisco UCS Manager provides centralized management capabilities, creates a unified management domain, and serves as the central nervous system of the Cisco UCS. Cisco UCS Manager is embedded device management software that manages the system from end-to-end as a single logical entity through an intuitive GUI, CLI, or XML API. Cisco UCS Manager implements role- and policy-based management using service profiles and templates. This construct improves IT productivity and business agility. Now infrastructure can be provisioned in minutes instead of days, shifting IT's focus from maintenance to strategic initiatives.
Dynamic Provisioning with Service Profiles
Cisco UCS resources are abstract in the sense that their identity, I/O configuration, MAC addresses and WWNs, firmware versions, BIOS boot order, and network attributes (including QoS settings, pin groups, and threshold policies) all are programmable using a just-in-time deployment model. The manager stores this identity, connectivity, and configuration information in service profiles that reside on the Cisco UCS 6100 Series Fabric Interconnect. A service profile can be applied to any blade server to provision it with the characteristics required to support a specific software stack. A service profile allows server and network definitions to move within the management domain, enabling flexibility in the use of system resources. Service profile templates allow different classes of resources to be defined and applied to a number of resources, each with its own unique identities assigned from predetermined pools.
Service Profiles and Templates
A service profile contains configuration information about the server hardware, interfaces, fabric connectivity, and server and network identity. The Cisco UCS Manager provisions servers utilizing service profiles. The Cisco UCS Manager implements a role-based and policy-based management focused on service profiles and templates. A service profile can be applied to any blade server to provision it with the characteristics required to support a specific software stack. A service profile allows server and network definitions to move within the management domain, enabling flexibility in the use of system resources.
Service profile templates are stored in the Cisco UCS 6100 Series Fabric Interconnects for reuse by server, network, and storage administrators. Service profile templates consist of server requirements and the associated LAN and SAN connectivity. Service profile templates allow different classes of resources to be defined and applied to a number of resources, each with its own unique identities assigned from predetermined pools.
The Cisco UCS Manager can deploy the service profile on any physical server at any time. When a service profile is deployed to a server, the Cisco UCS Manager automatically configures the server, adapters, Fabric Extenders, and Fabric Interconnects to match the configuration specified in the service profile. A service profile template parameterizes the UIDs that differentiate between server instances.
This automation of device configuration reduces the number of manual steps required to configure servers, Network Interface Cards (NICs), Host Bus Adapters (HBAs), and LAN and SAN switches. Figure 8 shows the Service profile which contains abstracted server state information, creating an environment to store unique information about a server.
Figure 8 Service Profile

Cisco Nexus 5548UP Switch
The Cisco Nexus 5548UP is a 1RU 1 Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet switch offering up to 960 gigabits per second throughput and scaling up to 48 ports. It offers 32 1/10 Gigabit Ethernet fixed enhanced Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP+) Ethernet/FCoE or 1/2/4/8-Gbps native FC unified ports and three expansion slots. These slots have a combination of Ethernet/FCoE and native FC ports. The Cisco Nexus 5548UP switch is shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 Cisco Nexus 5548UP switch

I/O Adapters
The Cisco UCS Blade Server has various Converged Network Adapters (CNA) options. The Cisco UCS M81KR Virtual Interface Card (VIC) option is used in this Cisco Validated Design.
This Cisco UCS M81KR VIC is unique to the Cisco UCS blade system. This mezzanine card adapter is designed around a custom ASIC that is specifically intended for VMware-based virtualized systems. It uses custom drivers for the virtualized HBA and 10-GE network interface card. As is the case with the other Cisco CNAs, the Cisco UCS M81KR VIC encapsulates fibre channel traffic within the 10-GE packets for delivery to the Fabric Extender and the Fabric Interconnect.
The Cisco UCS M81KR VIC provides the capability to create multiple VNICs (up to 128 in version 1.4) on the CNA. This allows complete I/O configurations to be provisioned in virtualized or non-virtualized environments using just-in-time provisioning, providing tremendous system flexibility and allowing consolidation of multiple physical adapters.
System security and manageability is improved by providing visibility and portability of network policies and security all the way to the virtual machines. Additional M81KR features like VN-Link technology and pass-through switching, minimize implementation overhead and complexity. The Cisco UCS M81KR VIC is as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10 Cisco UCS M81KR VIC

VIC1240
The Cisco UCS Virtual Interface Card 1240 is a 4-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)-capable modular LAN on motherboard (mLOM) designed exclusively for the M3 generation of Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers. When used in combination with an optional Port Expander, the Cisco UCS VIC 1240 capabilities can be expanded to eight ports of 10 Gigabit Ethernet. The Cisco UCS VIC 1240 enables a policy-based, stateless, agile server infrastructure that can present up to 256 PCIe standards-compliant interfaces to the host that can be dynamically configured as either network interface cards (NICs) or host bus adapters (HBAs). In addition, the Cisco UCS VIC 1240 supports Cisco Data Center Virtual Machine Fabric Extender (VM-FEX) technology, which extends the Cisco UCS fabric interconnect ports to virtual machines, simplifying server virtualization deployment.
VIC1280
The Cisco UCS Virtual Interface Card 1280 is an eight-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)-capable mezzanine card designed exclusively for Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers. The card enables a policy-based, stateless, agile server infrastructure that can present up to 256 PCIe standards-compliant interfaces to the host that can be dynamically configured as either network interface cards (NICs) or host bus adapters (HBAs). In addition, the Cisco UCS VIC 1280 supports Cisco Virtual Machine Fabric Extender (VM-FEX) technology, which extends the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect ports to virtual machines, simplifying server virtualization deployment.
EMC VNX Storage Family
The EMC® VNX™ family of storage systems represents EMC's next generation of unified storage, optimized for virtual environments, while offering a cost effective choice for deploying mission-critical enterprise applications such as Oracle Siebel. The massive virtualization and consolidation trends with servers demand a new storage technology that is dynamic and scalable. The EMC VNX series meets these requirements and offers several software and hardware features for optimally deploying enterprise applications such as Oracle Siebel. The EMC VNX family is shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11 The EMC VNX Family of Unified Storage Platforms

A key distinction of this new generation of platforms is, support for both block and file-based external storage access over a variety of access protocols, including Fibre Channel (FC), iSCSI, FCoE, NFS, and CIFS network shared file access. Furthermore, data stored in one of these systems, whether accessed as block or file-based storage objects, is managed uniformly via Unisphere, a web-based interface window. Additional information on Unisphere can be found on emc.com in the white paper titled: Introducing EMC Unisphere: A Common Midrange Element Manager, see:
http://www.emc.com/collateral/software/white-papers/h8017-unisphere-element-manager.pdf.
EMC VNX Storage Platforms
The new EMC VNX family of unified storage platforms continues the EMC tradition of providing some of the highest data reliability and availability in the industry. Apart from this they also include in their design a boost in performance and bandwidth to address the sustained data access bandwidth rates. The new system design has also placed heavy emphasis on storage efficiencies and density, as well as crucial green storage factors, such as a smaller data center footprint, lower power consumption, and improvements in power reporting. The VNX5500™ model was used in this Oracle Siebel implementation exercise. All models in EMC's new VNX storage family now support the 2.5" SAS drives in a 2U disk array enclosure (DAE) that can hold up to 25 drives, one of the densest offerings in the industry. For example, compared to the older-generation technology of storing 15 x 600 GB worth of data using the 3.5" FC drives in a 3U DAE, the new DAE which uses 25 x 600 GB drives in a 2U footprint means an increase of 2.5 times. The power efficiency of the new DAEs also makes it more cost-effective to store the increased data in this much more compact footprint without the need to increase power consumption and cooling. For more information on VNX Series, see: http://www.emc.com/collateral/hardware/data-sheets/h8520-vnx-family-ds.pdf.
Key efficiency features available with the VNX series include FAST Cache and FAST VP.
FAST Cache Technology
FAST cache is a storage performance optimization feature that provides immediate access to frequently accessed data. In traditional storage arrays, the DRAM caches are too small to maintain the hot data for a long period of time. Very few storage arrays give an option to non-disruptively expand DRAM cache, even if they support DRAM cache expansion. FAST Cache extends the available cache to customers by up to 2 TB using enterprise Flash drives. FAST Cache tracks the data temperature at 64 KB granularity and copies hot data to the Flash drives once its temperature reaches a certain threshold. After a data chunk gets copied to FAST Cache, the subsequent accesses to that chunk of data will be served at Flash latencies. Eventually, when the data temperature cools down, the data chunks get evicted from FAST Cache and will be replaced by newer hot data. FAST Cache uses a simple Least Recently Used (LRU) mechanism to evict the data chunks.
FAST Cache is built on the premise that the overall applications' latencies can improve when most frequently accessed data is maintained on a relatively smaller sized, but faster storage medium, like Flash drives. FAST Cache identifies the most frequently accessed data which is temporary and copies it to the flash drives automatically and non-disruptively. The data movement is completely transparent to applications, thereby making this technology application-agnostic and management-free. For example, FAST Cache can be enabled or disabled on any storage pool simply by selecting/clearing the "FAST Cache" storage pool property in advanced settings.
FAST Cache can be selectively enabled on a few or all storage pools within a storage array, depending on application performance requirements and SLAs.
There are several distinctions to EMC FAST Cache:
•
It can be configured in read/write mode, which allows the data to be maintained on a faster medium for longer periods, irrespective of application read-to-write mix and data re-write rate.
•
FAST Cache is created on a persistent medium like Flash drives, which can be accessed by both the storage processors. In the event of a storage processor failure, the surviving storage processor can simply reload the cache rather than repopulating it from scratch. This can be done by observing the data access patterns again, which is a differentiating factor.
•
Enabling FAST Cache is completely non-disruptive. It is as simple as selecting the Flash drives that are part of FAST Cache and does not require any array disruption or downtime.
•
Since FAST Cache is created on external Flash drives, adding FAST Cache will not consume any extra PCI-E slots inside the storage processor.
EMC FAST Cache used in this Oracle Siebel architecture is as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12 EMC FAST Cache

Additional information on EMC Fast Cache is documented in the white paper titled EMC FAST Cache - A Detailed Review which is available at:
http://www.emc.com/collateral/software/white-papers/h8046-clariion-celerra-unified-fast-cache-wp.pdf.
FAST VP
VNX FAST VP is a policy-based auto-tiering solution for enterprise applications. FAST VP operates at a granularity of 1 GB, referred to as a "slice". The goal of FAST VP is to efficiently utilize storage tiers to lower customers' TCO by tiering colder slices of data to high-capacity drives, such as NL-SAS, and to increase performance by keeping hotter slices of data on performance drives, such as Flash drives. This occurs automatically and transparently to the host environment. High locality of data is important to realize the benefits of FAST VP. When FAST VP relocates data, it will move the entire slice to the new storage tier. To successfully identify and move the correct slices, FAST VP automatically collects and analyzes statistics prior to relocating data. Customers can initiate the relocation of slices manually or automatically by using a configurable, automated scheduler that can be accessed from the Unisphere management tool. The multi-tiered storage pool allows FAST VP to fully utilize all the storage tiers: Flash, SAS, and NL-SAS. The creation of a storage pool allows for the aggregation of multiple RAID groups, using different storage tiers, into one object. The LUNs created out of the storage pool can be either thickly or thinly provisioned. These "pool LUNs" are no longer bound to a single storage tier. Instead, they can be spread across different storage tiers within the same storage pool. If you create a storage pool with one tier (Flash, SAS, or NL-SAS), then FAST VP has no impact on the performance of the system. To operate FAST VP, you need at least two tiers.
Additional information on EMC FAST VP for Unified Storage is documented in the white paper titled EMC FAST VP for Unified Storage System - A Detailed Review, see: http://www.emc.com/collateral/software/white-papers/h8058-fast-vp-unified-storage-wp.pdf.
FAST Cache and FAST VP are offered in a FAST Suite package as part of the VNX Total Efficiency Pack. This pack includes the FAST Suite which automatically optimizes for the highest system performance and lowest storage cost simultaneously. In addition, this pack includes the Security and Compliance Suite which keeps data safe from changes, deletions, and malicious activity. For additional information on this Total Efficiency Pack as well as other offerings such as the Total Protection Pack, see: http://www.emc.com/collateral/software/data-sheet/h8509-vnx-software-suites-ds.pdf
Design Considerations for Oracle Siebel Implementation on Cisco Unified Computing System
In this section, the key design considerations such as scalability, high availability, and performance are addressed for Oracle Siebel Implementation on Cisco Unified Computing System. Since most organizations use Siebel as front end application dealing with their customers/partners, the demands on non-functional aspects are very critical.
Scalable Architecture Using Cisco UCS Servers
The target workloads for the small, medium, and large enterprise were modeled based on the real world CRM implementation for this exercise is as shown in Table 1.
The classification is based on a typical deployment scenario in an enterprise, keeping in mind the load and data size requirements. These broad classifications can be taken as framework for sizing the Cisco UCS servers.
Table 1 Small/Medium/Large Siebel Enterprise
Small
600
50 GB
Medium
3000
150 GB
Large
10000
450 GB
The deployment configurations for small, medium and large Oracle Siebel enterprises are shown in Figure 13. These configurations were built by leveraging the modular architecture of Oracle Siebel as well by the choice of a range of Cisco UCS servers based on their capacity. In order to achieve high availability, redundancy at the level of the database servers, Siebel application servers, web servers with gateway servers are considered.
Figure 13 Oracle Siebel Deployment Options for Small, Medium and Large Enterprises

Figure 14 shows a deployment topology configured for a small Oracle Siebel Enterprise, which uses Cisco UCS B200/B230 servers, Cisco 6100 series Fabric Interconnects, Nexus 5000 series switches and EMC VNX5500 storage. The B200 M2 blade server is an entry level blade server which is suitable for low to moderate compute/ memory workloads such as web servers and gateway servers. However with increased CPU capacity, it can also serve as Application server in small enterprise Oracle Siebel setup.
For medium size enterprise setup, an additional blade is added at database tier to facilitate for a two node Oracle RAC (Real Application Cluster) implementation. With a typical customer scenario having 3000 concurrent users and 150 GB of database size, high availability of database is critical which is achieved using Oracle RAC. Since redundancy is essential for every critical component (such as network and I/O paths) within the database nodes, full width B250 blade server is chosen to host individual Oracle RAC nodes.
Figure 14 Small Oracle Siebel Enterprise - Topology

For large deployments, additional application servers are added as shown in Figure 15. Each of the components (Web, Application and DB server) can be scaled for increase in the workload.
Figure 15 Large Oracle Siebel Enterprise - Topology

Boot from SAN
Boot from SAN is a critical feature which helps to achieve stateless computing in which there is no static binding between a physical server and the OS / applications hosted on that server. The OS is installed on a SAN LUN and is booted using the service profile. When the service profile is moved to another server, the server policy and the PWWN of the HBAs will also move along with the service profile. The new server takes the identity of the old server and looks identical to the old server.
The following are the benefits of boot from SAN:
•
Reduce Server Footprint - Boot from SAN eliminates the need for each server to have its own direct-attached disk (internal disk) which is a potential point of failure. The following are the advantages of diskless servers:
–
Require less physical space
–
Require less power
–
Require fewer hardware components
–
Less expensive
•
Disaster and Server Failure Recovery—Boot information and production data stored on a local SAN can be replicated to another SAN at a remote disaster recovery site. When server functionality at the primary site goes down in the event of a disaster, the remote site can take over with a minimal downtime.
•
Recovery from server failures—Recovery from server failures is simplified in a SAN environment. Data can be quickly recovered with the help of server snapshots, and mirrors of a failed server in a SAN environment. This greatly reduces the time required for server recovery.
•
High Availability—A typical data center is highly redundant in nature with redundant paths, redundant disks and redundant storage controllers. The operating system images are stored on SAN disks which eliminates potential problems caused due to mechanical failure of a local disk.
•
Rapid Redeployment—Businesses that experience temporary high production workloads can take advantage of SAN technologies to clone the boot image and distribute the image to multiple servers for rapid deployment. Such servers may only need to be in production for hours or days and can be readily removed when the production need has been met. Highly efficient deployment of boot images makes temporary server usage highly cost effective.
•
Centralized Image Management—When an operating system images are stored on SAN disks, all upgrades and fixes can be managed at a centralized location. Servers can readily access changes made to disks in a storage array.
With boot from SAN, the server image resides on the SAN and the server communicates with the SAN through a Host Bus Adapter (HBA). The HBA BIOS contain instructions that enable the server to find the boot disk. After Power OnSelf Test (POST), the server hardware component fetches the designated boot device in the hardware BOIS settings. Once the hardware detects the boot device, it follows the regular boot process.
EMC VNX5500 - Block and File Storage Required for Oracle Siebel
Oracle Siebel data is traditionally stored in any of the supported RDBMS such as Oracle using block storage. In our current implementation, the EMC VNX5500 storage system is used for block storage. The EMC VNX5500's capability of storing files and block access in unified manner is leveraged in this solution. LUNs are carved out using heterogeneous storage pools (FAST Virtual Pool with Flash drives, SAS, and NL-SAS disks) to ensure meeting the Oracle Siebel CRM storage capacity and performance demands. FAST Cache is enabled for the entire array to ensure faster response times for both read and write operations.
Storing files such as PDFs, Word Documents etc., is also common requirement along with captured data. Familiar examples are adding resolution steps of Service Requests in MS word document format (or) generating an invoice document (typically a PDF) for a newly captured order. The EMC VNX5500 has datamover components which allow accessing these files using NFS/CIFS protocols and hence reduces the data management challenges.
Infrastructure Setup
This section describes the configuration and setup details for:
•
Cisco UCS with and without boot Policy
•
EMC Storage
•
Nexus Switch
Configuring the Cisco Unified Computing System
This section details the Cisco UCS configuration that is done as part of the infrastructure build for deployment of Oracle Siebel. The racking, power and installation of the chassis are described in the install guide: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/Cisco UCS/hw/chassis/install/Cisco UCS5108_install.html.
One of the important aspects of configuring a physical blade in the Cisco UCS 5108 chassis is to build a Service Profile through the Cisco UCS Manager. Service profile is an extension of the virtual machine abstraction applied to physical servers. The definition has been expanded to include elements of the environment that span the entire data center, encapsulating the server identity (LAN and SAN addressing, I/O configurations, firmware versions, boot order, network VLAN, physical port, and quality-of-service [QoS] policies) in logical service profiles that can be dynamically created and associated with any physical blade in the system within minutes as compared to the considerable time consumption in a conventional approach. The association of service profiles with the physical servers is performed as a simple, single operation. It enables migration of identities between servers in the environment without requiring any physical configuration changes and facilitates rapid Cisco UCS Server provisioning for replacements of failed servers. Service profiles can be created either from an existing template or from cloning an existing profile or from a new service profile.
Logging into the UCS Manager
To log into Cisco UCS Manager, perform the following steps:
1.
Open the Web browser with the Cisco UCS 6120 Fabric Interconnect cluster address.
2.
Click Launch to download the Cisco UCS Manager software.
3.
You might be prompted to accept security certificates; accept as necessary.
4.
In the login page, enter "admin" in username text box and the password set during the initial setup in the password text box.
5.
Click Login to access the Cisco UCS Manager software.
Verification: The Cisco UCS Manager software must show up after clicking "Login".
Editing Chassis Discovery Policy
To edit the chassis discovery policy, perform the following steps:
1.
Navigate to the Equipment tab in the right pane of the UCS Manager.
2.
In the right pane, click the Policies tab.
3.
Under Global Policies, change the Chassis Discovery Policy to 4-link.
4.
Click Save Changes in the bottom right corner.
Enabling Network Components
To enabling Fiber Channel, servers, and uplink ports, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the Equipment tab on the top left of the UCS Manager window.
2.
Select Equipment>Fabric Interconnects >Fabric Interconnect A (primary) >Fixed Module.
3.
Expand the Unconfigured Ethernet Ports section.
4.
Select ports 1-12 that are connected to the UCS chassis and right-click on them and select Configure as Server Port.
5.
Click Yes to confirm, and then click OK to continue.
6.
Select ports 17 and 19. These ports are connected to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches. Right-click on them and select Configure as Uplink Port.
7.
Click Yes to confirm, and then click OK to continue.
8.
Select Equipment > Fabric Interconnects >Fabric Interconnect A (primary) > Expansion Module 2.
9.
Ensure the FC ports 1-2 are not disabled.
10.
Click Yes to confirm, and then click OK to continue.
11.
Select Equipment > Fabric Interconnects >Fabric Interconnect A (primary).
12.
Right click, and select Set FC Switching Mode to put the Fabric Interconnect in Fiber Channel Switching Mode.
13.
Click Yes to confirm.
14.
A message displays stating that the "Fiber Channel Switching Mode has been set and the switch will reboot". Click OK to continue. Wait until the UCS Manager is available again and log back into the interface.
15.
Select Equipment > Fabric Interconnects > Fabric Interconnect B (subordinate) > Fixed Module.
16.
Expand the Unconfigured Ethernet Ports section.
17.
Select ports 1-12. These ports are connected to the UCS chassis and right-click on them and select Configure as Server Port.
18.
Click Yes to confirm and then click OK to continue.
19.
Select ports 17 and 19. These ports are connected to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches. Right-click on them, and select Configure as Uplink Port.
20.
Click Yes to confirm, and then click OK to continue.
21.
Select Equipment > Fabric Interconnects > Fabric Interconnect B (subordinate) > Expansion Module 2.
22.
Ensure the FC ports 1-2 are not disabled.
23.
Click Yes to confirm, and then click OK to save changes and exit.
Verification: Check if all configured links show their status as "up" as shown in Figure 16 for Fabric Interconnect A. This can also be verified on the Cisco Nexus switch side by running "show int status" and all the ports connected to the Cisco UCS fabric interconnects are shown as "up".
Figure 16 Configured Links Shown on Fabric Interconnect A

Creating MAC Address Pools
To create MAC Address pools, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the LAN tab on the left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.
2.
Under Pools > root.

Note
Two MAC address pools will be created, one for fabric A and one for fabric B.
3.
Right-click MAC Pools under the root organization and select Create MAC Pool to create the MAC address pool for fabric A.
4.
Enter Siebel_MAC_Pool_A for the name of the MAC pool for fabric A.
5.
Enter a description of the MAC pool in the description text box. This is optional; you can choose to omit the description.
6.
Click Next to continue.
7.
Click Add to add the MAC address pool.
8.
Specify a starting MAC address for fabric A.

Note
The default is fine, but it is recommended to change the second before last octet to be "0A" to differentiate between MAC addresses in fabric A and fabric B (00:25:85:00:0A:00).
9.
Specify the size as 32 for the MAC address pool for fabric A.
10.
Click OK.
11.
Click Finish.
12.
A pop-up message box appears, click OK to save changes.
13.
Right-click MAC Pools under the root organization and select Create MAC Pool to create the MAC address pool for fabric B.
14.
Enter Siebel_MAC_Pool_B for the name of the MAC pool for fabric B.
15.
Enter a description of the MAC pool in the description text box. This is optional; you can choose to omit the description.
16.
Click Next to continue.
17.
Click Add to add the MAC address pool.
18.
Specify a starting MAC address for fabric B.

Note
The default is fine, but it is recommended to change the second before last octet to be "0B" to differentiate between MAC addresses in fabric A and fabric B (00:25:85:00:0B:00).
19.
Specify the size as 32 for the MAC address pool for fabric B.
20.
Click OK.
21.
Click Finish.
22.
A pop-up message box appears; click OK to save changes and exit.
Verification: Select LAN tab > Pools > root. Select MAC Pools and it expands to show the MAC pools created. On the right pane, details of the MAC pools are displayed as shown in Figure 17.
Figure 17 MAC Pool Details

Creating WWPN Pools
To create WWPN pools, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the SAN at the top left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.
2.
Select WWPN Pools > root.

Note
Two WWPN pools will be created, one for fabric A and one for fabric B.
3.
Right-click WWPN Pools and select Create WWPN Pool.
4.
Enter Siebel_WWPN_Pool_A as the name for the WWPN pool for fabric A.
5.
Enter a description of the WWPN pool in the description text box. This is optional; you can choose to omit the description.
6.
Click Next.
7.
Click Add to add a block of WWPNs.
8.
Enter 20:00:00:25:B5:00:0A:00 as the starting WWPN in the block for fabric A.

Note
It is recommended to change the octet next to 25 to some number to identify the FI pair in the Datacenter (here Oracle Siebel FIs are in fifth rack hence used `B5') in order to avoid the same WWPNs get published in Nexus switch level which may be talking to multiple FI pair. Also suggested to change the second-to-last octet to be "0A" to differentiate between WWPNs in fabric A and fabric B (20:00:00:25:B5:00:0A:00).
9.
Set the size of the WWPN block to 48.
10.
Click OK to continue.
11.
Click Finish to create the WWPN pool.
12.
Click OK to save changes.
13.
Right-click WWPN Pools and select Create WWPN Pool.
14.
Enter Siebel_WWPN_Pool_B as the name for the WWPN pool for fabric B.
15.
Enter a description of the WWPN pool in the description text box. This is optional; you can choose to omit the description.
16.
Click Next.
17.
Click Add to add a block of WWPNs.
18.
Enter 20:00:00:25:B5:00:0B:00 as the starting WWPN in the block for fabric B.

Note
It is recommended to change the octet next to 25 as `B5' (from 00) and second-to-last octet to be "0B" to identify as fabric B (20:00:00:25:B5:00:0B:00).
19.
Set the size of the WWPN block to 48.
20.
Click OK to continue.
21.
Click Finish to create the WWPN pool.
22.
Click OK to save changes and exit.
Verification: The new name with the 48 block size displays in the right panel when WWPN pools is selected on the left panel. Also verify that the second-to-last octet reflects the fabric ID as shown in Figure 18.
Figure 18 WWPN Pool Details

Creating WWNN Pools
To create WWNN pools, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the SAN tab at the top left of the UCS manager window.
2.
Select Pools > root.
3.
Right-click WWNN Pools and select Create WWNN Pool.
4.
Enter Oracle Siebel_WWNN_Pool as the name of the WWNN pool.
5.
Enter a description of the WWNN pool in the description text box. This is optional; you can choose to omit the description.
6.
Click Next to continue.
7.
A pop-up window "Add WWN Blocks" appears; click Add at the bottom of the page.
8.
A pop-up window "Create WWN Blocks" appears; set the size of the WWNN block to 32.
9.
Click OK to continue.
10.
Click Finish.
11.
Click OK to save changes and exit.
Verification: The new name with the 32 block size displays in the right panel when WWNN pools is selected on the left panel as shown in Figure 19.
Figure 19 WWNN Pool Details

Creating UUID suffix pools
To create UUID suffix pools, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the Servers tab on the top left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.
2.
Select Pools > root.
3.
Right-click UUID Suffix Pools and select Create UUID Suffix Pool.
4.
Enter the name the UUID suffix pool as Siebel_UUID_Pool.
5.
Enter a description of the UUID suffix pool in the description text box. This is optional; you can choose to omit the description.
6.
Prefix is set to "derived" by default. Do not change the default setting.
7.
Click Next to continue.
8.
A pop-up window "Add UUID Blocks" appears. Click Add button at the bottom of the window to add a block of UUID suffixes.
9.
The "Form" field will be in default setting. Do not change the "From" field.
10.
Set the size of the UUID suffix pool to 32.
11.
Click OK to continue.
12.
Click Finish to create the UUID suffix pool.
13.
Click OK to save changes and exit.
Verification: Ensure that the UUID suffix pools created are displayed as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20 UUID Suffix Pool Details

Creating VLANs
To create VLANs, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the LAN tab on the left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.

Note
Three VLANs will be created for Management Traffic, Data traffic and Oracle RAC database inter-node private traffic.
2.
Right-click VLANs in the tree and click Create VLANs.
3.
Enter MGMT-VLAN for the name of the VLAN (for example, 809). This name will be used for traffic management.
4.
Keep the option "Common/Global" selected for the scope of the VLAN.
5.
Enter a VLAN ID for the management VLAN. Keep the sharing type as "none".
6.
Similarly create VLANs for Application data traffic (for example, 812) and Oracle Private traffic (192).
Verification: Select LAN tab > LAN Cloud > VLANs. Open VLANs and all of the created VLANs are displayed. The right pane gives the details of all individual VLANs as shown in Figure 21.
Figure 21 Details of Created VLANs

Creating Uplink Ports Channels
To create uplink port channels to Nexus 5548 switches, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the LAN tab on the left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.

Note
Two port channels are created, one from fabric A to both Cisco Nexus 5548 switches and one from fabric B to both Cisco Nexus 5548 switches.
2.
Expand the "Fabric A" tree.
3.
Right-click on the "Port Channels" and click Create Port Channel.
4.
Enter "13" as the unique ID of the port channel.
5.
Enter "Siebel_Po13" as the name of the port channel.
6.
Click Next.
7.
Select ports 1/17 and 1/19 to be added to the port channel.
8.
Click >> to add the ports to the Port Channel.
9.
Click Finish to create the port channel.
10.
A pop-up message box appears, click OK to continue.
11.
In the left pane, click the newly created port channel.
12.
In the right pane under "Actions", choose Enable Port Channel option.
13.
In the pop-up box, click Yes, and then click OK to save changes.
14.
Expand the "Fabric B" tree.
15.
Right-click on the "Port Channels" and click Create Port Channel.
16.
Enter "14" as the unique ID of the port channel.
17.
Enter "Siebel_Po14" as the name of the port channel.
18.
Click Next.
19.
Select ports 1/17 and 1/19 to be added to the Port Channel.
20.
Click >> to add the ports to the Port Channel.
21.
Click Finish to create the port channel.
22.
A pop-up message box appears, click OK to continue.
23.
In the left pane, click the newly created port channel.
24.
In the right pane under "Actions", choose Enable Port Channel option.
25.
In the pop-up box, click Yes, and then click OK to save changes.
Verification: Select LAN tab > LAN Cloud. On the Right Pane, select the LAN Uplinks and expand the Port channels listed as shown in the following Figure 22.

Note
In order for the Fabric Interconnect Port Channels to get enabled, the vpc needs to be configured first at Nexus 5548 Switches as described in Creation and Configuration of Virtual Port Channel (VPC).
Figure 22 Details of Port channels

Creating VSANs
To create VSANs, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the SAN tab at the top left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.
2.
Expand the SAN cloud tree.
3.
Right-click on the "VSANs" and click Create VSAN.
4.
Enter "Siebel_VSAN" as the VSAN name for Fabric A.
5.
Enter "2" as the VSAN ID.
6.
Enter "2" as the FCoE VLAN ID.
7.
Click OK to create the VSANs.
Verification: Select SAN tab >SAN Cloud >VSANs on the left panel. The right panel displays the created VSANs as shown in the following Figure 23.
Figure 23 Details of Created VSANs

Creating Boot Policies
Do not select any boot policy at this time. It must be done after creating LUNs in EMC VNX5500 storage system and establishing connectivity. To modify the Service Profile, see the section Modifying Service Profile for Boot Policy.
Creating Service Profile Templates
To create service profile templates, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the Servers tab at the top left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.
2.
Select Service Profile Templates > root. In the right window, click Create Service Profile Template under the Actions tab.
3.
The Create Service Profile Template window appears.
a.
Identify the Service Profile Template section.
–
Enter the name of the service profile template as "Cisco UCS-Oracle Siebel".
–
Select the type as "Initial Template".
–
In the UUID section, select "Siebel_UUID_Pool" as the UUID pool.
–
Click Next to continue to the next section.
b.
Storage Section
–
Select "RAID 1" for the Local Storage field for local hard disk resiliency.
–
Select the option "Expert" for the field "How would you like to configure SAN connectivity".
–
In the WWNN Assignment field, select "Siebel_WWNN_Pool".
–
Click Add button at the bottom of the window to add vHBAs to the template.

Note
We need to create four vHBAs and First pair of vHBA's will be used for SAN Boot LUN and Second pair of vHBA's will be used for Oracle Siebel Application purposes.
–
The Create vHBA window appears. Ensure that the vHBA is "vhba0".
–
In the WWPN Assignment field, select "Siebel_WWPN_Pool_A".
–
Ensure that the Fabric ID is set to "A".
–
In the "Select VSAN" field, select "Siebel_VSAN".
–
Click OK to save changes.
–
Click Add button at the bottom of the window to add vHBAs to the template.
–
The Create vHBA window appears. Ensure that the vHBA is "vhba1".
–
In the WWPN Assignment field, select "Siebel_WWPN_Pool_B".
–
Ensure that the Fabric ID is set to "B".
–
In the "Select VSAN" field, select "Siebel_VSAN".
–
Click OK to save changes.
–
Click the Add button at the bottom of the window to add vHBAs to the template.
–
Similarly create "vhba2" (with Fabric ID A) and "vhba3" (with Fabric ID B)
–
Ensure that both the vHBAs are created.
–
Click Next to continue.
c.
Network Section
–
Restore the default setting for "Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy" field.
–
Select the option "Expert" for the field "How would you like to configure LAN connectivity".
–
Click Add to add a vNIC to the template.
–
The Create vNIC window appears. Enter the name of the vNIC as "eth0".
–
Select the MAC address assignment field as "Siebel_MAC_Pool_A".
–
Select Fabric ID as "Fabric A".
–
Select appropriate VLANs (812) in the VLANs.
–
Click OK to save changes.
–
Click Add to add a vNIC to the template.
–
The Create vNIC window appears. Enter the name of the vNIC "eth1".
–
Select the MAC address assignment field as "Siebel_MAC_Pool_B".
–
Select Fabric ID as "Fabric B".
–
Select appropriate VLANs (812) in the VLANs.
–
Click OK to add the vNIC to the template.
–
Ensure that both the vHBAs are created.
–
Click Next to continue.
d.
vNIC/vHBA Placement section
–
Restore the default setting as "Let System Perform Placement" in the Select Placement field.
–
Ensure that all the vHBAs are created.
–
Click Next to continue.
e.
Server Boot Order section
–
You need not select any boot. For boot policy creation and association of service profile, see section Creating Boot Policies.
f.
Maintenance Policy, Server assignment, and operation policy Section
–
Select default settings for all these sections.
–
Custom policies can be defined for each of the three cases, for instance, in operational policy one can disable `quiet boot' in the BIOS policy
–
Click Finish to complete the creation of Service profile template.
Creating Service Profile from the Template and associating it to a Blade
To create a service profile from the template and associating it to a blade, perform the following steps:
1.
Select the Servers tab at the top left of the Cisco UCS Manager window.
2.
Select Service Profile Templates > root > Sub-Organizations > Service Template Cisco UCS-Oracle Siebel.
3.
Click Create Service Profiles From Template in the Actions tab of the right pane of the window.
4.
Enter "sb-as" in the Naming Prefix text box and the number as "1"
5.
Click OK to create service Profile
6.
Select the created Service profile Servers > Service profiles > root > sb-as-1 and go to "Change Service Profile Association"
7.
Select "Existing Server" under the option "Server Assignment" and from the list shown
8.
Select the right server based on Chassis ID/Slot number.
9.
Click OK to associate the service profile to that blade. The successful association of the service profile is as shown in Figure 24.
Figure 24 Successful Association of the Service Profile

Configuring the EMC VNX5500
Figure 25 shows the disk layout carved on the EMC VNX5500 storage which is connected to the Cisco UCS system. It leverages the FAST Cache as well as FAST Virtual Pool and Unified Storage capabilities of the VNX5500 as well the EMC best practices to carve the LUNs required for this exercise.
•
Oracle Siebel CRM data stored in Oracle database accessed randomly and requires fastest for read/write operations. For such access pattern a storage pool with SAS drives and Flash disks (SSD disks) are chosen with RAID level 5. SSD disks provide faster response time for Random access and tiered storage with SAS disks provides the necessary capacity.
•
Oracle Database Log is sequential write intensive operation, hence SAS drives with RAID level 10 is chosen.
•
For the Siebel File System where sequential writes are more than the reads (based on the workload designed in this exercise), SAS drives alone without Flash disks in the storage pool are used with RAID level 10. However based on the actual access pattern and I/O mix, appropriate drivers and RAID level can be chosen.
•
For boot LUNs, since the I/O operations are mostly sequential, SAS drives with RAID level 1 is chosen.
Local hard disk partitions are used for OS level /swap and /tmp partitions in this exercise; however it was observed that they were not used during the test executions.
For Back up LUNs, NL SAS drives are chosen since speed is not very critical with RAID level 10.
Table 2 provides Storage Pool/RAID Groups and Figure 25 shows the same.
Figure 25 Disk Layout - EMC VNX5500

Table 3 lists LUNs that were created for Oracle Siebel small setup:
Table 4 lists LUNs that were created for Oracle Siebel Medium and Large setup:
From the above table, it is clear that you need to choose an appropriate storage processor as the default owner, so that the IOs are evenly balanced.
Creation of Storage Pools/RAID Groups
To create storage pools/RAID groups, perform the following steps:
1.
Login to the EMC VNX Unisphere to create storage pools.
2.
To create Storage Pool, click Storage > Storage Configuration > storage pools > Pools tab and the click Create. The "create storage pool" pop-up window appears.
a.
Ensure that the Storage Pool type is "Pool".
b.
Enter an appropriate name for the storage pool name in the text box.
c.
Select appropriate RAID group from the drop-down list.
d.
Select the required disks from the disk selection popup window and the click OK.
3.
To create LUNs from the storage pool, right-click on the desired storage pool. A pop window "Create LUN" appears. In the General tab of Create LUN pop-up box.
a.
Click General tab of the Create LUN window. Enter the required LUN size in the LUN properties text box.
b.
Enter the name for the LUN in the "LUN Name" text box.
c.
In the Advanced tab, ensure the right SP is chosen as "Default owner" as mentioned in Table 3 and Table 4 on Oracle Siebel Small and Medium/Large setups respectively.
d.
Ensure that the Database LUNs (Oracle data) are selected as "Highest Available Tier" and Application LUNs are selected as "Lowest Available Tier" in the Tiering Policy.
4.
To associate LUNs to the host, Navigate to Hosts > Storage Group and the click Create, A pop-up window "Create Storage Group" appears.
a.
Enter an appropriate name in the "Storage Group Name" text box; click OK and then click Yes to confirm. Click LUNs tab, a pop-up window "Storage Group properties" appears.
b.
Select the LUN from the respective SPA / SPB and click Add in the "Available LUNs" to add the selected LUNs. In the "Show LUN" drop-down list, select the option "All" instead of "Not in other storage groups".

Note
The Host ID which is typically 0 for the first LUN attached to the storage group and this Host Id should match with Cisco UCS Manager Service Profile > Create Boot Policy > LUN ID for SAN boot as shown in Figure 26.
Figure 26 Selecting a Storage Group Name in EMC Unisphere

5.
To create RAID Groups, click Storage > Storage Configuration > Storage pools > RAID Groups tab and click Create. A pop-up window "create storage pool" appears.
a.
Ensure that the selected Storage Pool type is "RAID Group".
b.
Select the required disks from the "Disk Selection" popup window and click OK.
6.
To create LUNs from the storage pool, right-click on the desired storage pool. A pop window "Create LUN" appears. In the General tab of Create LUN pop-up box.
c.
Ensure that the selected Storage Pool type is "RAID Group"
d.
Enter the required LUN size in the" LUN Properties" text box.
e.
Enter the name of the LUN in the "LUN Name" text box.
f.
In the Advanced tab, ensure the right SP is chosen as "Default owner" as mentioned in Table 3 and Table 4 on Oracle Siebel Small and Medium/Large setups respectively.
Creation of File System (NFS Share)
To create Oracle Siebel File System, perform the following steps:
1.
Login to the EMC VNX Unisphere to create a Storage Pool for file system requirements for Oracle Siebel.
2.
To create the Storage Pools, click Storage > Storage Configuration > Storage pools and the click Create. A pop-up window "Create Storage Pool" appears.
a.
Ensure the option "Storage Pool" is selected in the window.
b.
Enter the name of the storage pool as "Pool 1- Siebel File System" in the Storage Pool Name text box and select RAID group as "10".
c.
Select the required disks from the "Disk selection" pop-up window and then click OK.
3.
To create LUNs from the created storage pool, right-click on storage pool. A new window "Create LUN" appears. Click the General tab in the "Create LUN" window.
a.
Enter the required LUN size in the "LUN properties" text box.
b.
Enter the name of the LUN as "SiebelFile System LUN" in the "LUN Name" text box.
c.
Click the Advanced tab, ensure that the right SP is chosen as "Default owner" as mentioned in Table 3 and Table 4 on Oracle Siebel Small and Medium/ Large setups respectively.
d.
For the Tiering Policy, select the "Auto tier" option from the drop-down list. Since the file access workload implementation is not more than 15% of total workload.
e.
The created LUN must be added to the LUN in the default File Storage Group. For this, click Hosts > Storage Groups. Select the Storage Group named " ~filestorage" and click Connect LUNs and then click OK.

Note
The Host ID (also called HLU) must be greater than or equal to 16 for the LUN, otherwise it may not show up in Volumes list.
Figure 27 shows creation of LUNs and addition of the created LUN to the default File Storage Group.
Figure 27 Connecting LUNs in Storage group Properties Window

f.
To create disk volumes, click Storage > Rescan Storage Systems. The progress of the scanning process can be observed from System > Monitoring and Alerts > Background Tasks for File. To view the disk volumes, click Storage > Storage Configuration > Volumes.
g.
To create Meta Volume, click Storage > Storage Configuration > storage pools for pool and select the "Pool 1 - Siebel File System". From the Create menu, select "Meta Volumes" for "create from" field. Enter the Pool name as "Siebel FS" and select all the volumes listed below. Select the check-box "Slice pool Volumes by Default" and click OK. Once the process is complete a new Storage pool for file (with type as user pool) is created called "Siebel FS" as shown in Figure 28.
Figure 28 Creating Siebel FS from Meta Volume

h.
To create File System, click Storage > Storage Configuration > File Systems and click Create. A pop-up window "Create File System" appears. Enter the appropriate name and size for the file system. Select "Pool 1- Siebel File System" option from the Storage Pool drop-down list. Click OK. This is shown in Figure 29.
Figure 29 Creating Siebel File System from Storage Pool

i.
You can export the created File System. To export the created File System, click Storage > Shared Folders > NFS and select the path as "/SiebelFileSystem" and click Create. A pop-up window "Create NFS Export" appears. Enter the Path name and list of Host IPs that need to access this share. Click OK. This is shown in Figure 30.
Figure 30 Exporting the Created FileSystem

This completes the file system creation on the EMC storage system.
Configuring the Nexus Switches
To configure the Nexus 5548 Switch, perform the following steps:
Setting up the Nexus 5548 Switch
To setup the Nexus 5548 switch, perform the following steps for Cisco Nexus 5548 Switch A (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A):
1.
After the initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start.
2.
Enter "yes" to enforce secure password standards.
3.
Enter the password for the admin user.
4.
Enter the password a second time to commit the password.
5.
Enter "yes" to enter the basic configuration dialog.
6.
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
7.
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
8.
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
9.
Enter the switch name as "Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A" "Enter".
10.
Continue with out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
11.
Mgmt0IPv4 address: "10.104.xxx.xxx". Enter".
12.
Mgmt0IPv4 netmask: "255.255.255.0" Enter".
13.
Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
14.
IPv4 address of the default gateway: "10.104.xxx.xxx" "Enter".
15.
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
16.
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
17.
Type of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa): rsa.
18.
Number of key bits <768-2048>: "1024" "Enter".
19.
Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
20.
Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
21.
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".

Note
Ensure to review the configuration summary before enabling it.
22.
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
23.
You may continue configuration from the console or using SSH. To use SSH, connect to Mgmt0 IP given in step 11.
24.
Log in as user "admin" with the password entered above.
To setup the Nexus 5548 switch, perform the following steps for Cisco Nexus 5548 Switch B (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B):
1.
After the initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start.
2.
Enter "yes" to enforce secure password standards.
3.
Enter the password for the admin user.
4.
Enter the password a second time to commit the password.
5.
Enter "yes" to enter the basic configuration dialog.
6.
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
7.
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
8.
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
9.
Enter the switch name: "Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B" Enter".
10.
Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
11.
Mgmt0IPv4 address: ": "10.104.xxx.xxx Enter".
12.
Mgmt0IPv4netmask: "255.255.255.0" Enter".
13.
Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
14.
IPv4 address of the default gateway: "10.104.108.xxx" Enter".
15.
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
16.
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
17.
Type of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa): rsa.
18.
Number of key bits <768-2048>: "1024 Enter".
19.
Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
20.
Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".
21.
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: "Enter".

Note
Ensure to review the configuration summary before enabling it.
22.
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: "Enter".
23.
You may continue configuration from the console or using SSH. To use SSH, connect to Mgmt0 IP given in step 11.
24.
Log in as user "admin" with the password entered above.
Enabling Nexus 5548 Switch Licensing
To enable appropriate Nexus 5548 switch licensing, perform the following steps for both Cisco Nexus 5548 A - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A), and Cisco Nexus 5548 B - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B) separately:
1.
Type "config t" to enter into the global configuration mode.
2.
Type "feature lacp".
3.
Type "feature fcoe".
4.
Type "feature npiv".
5.
Type "feature vpc".
6.
Type "feature fport-channel-trunk".

Note
FCoE feature needs to be enabled first before enabling npiv.
Verification: The command "show feature | include enabled" should list the enabled features.
Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A# sh feature | inc enabledassoc_mgr 1 enabledfcoe 1 enabledfex 1 enabledlacp 1 enabledlldp 1 enablednpiv 1 enabledsshServer 1 enabledtelnetServer 1 enabledvpc 1 enabledConfiguration of Ports 29-32 as FC ports
To configure the ports 29-32 as FC ports, perform the following steps for both Cisco Nexus 5548 A - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A), and Cisco Nexus 5548 B - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B) separately:
1.
Type "config t" to enter into the global configuration mode.
2.
Type "slot 1".
3.
Type "interface fc 1/29-32".
4.
Type "switchport mode F".
5.
Type "no shut".
Verification: The command "show interface brief" should list these interfaces as FC (Admin Mode "F").
Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A# sh interface briefInterface Vsan AdminMode AdminTrunkMode Status SFP OperMode OperSpeed(Gbps)------------------------------------------------------------------------------------fc1/29 2 F on up swl F 4fc1/30 2 F on up swl F 4fc1/31 2 F on up swl F 4fc1/32 2 F on up swl F 4Creating VSAN and Adding FC Interfaces
To create VSAN and adding FC interfaces, perform the following steps for both Cisco Nexus 5548 A - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A), and Cisco Nexus 5548 B - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B) separately:
1.
Type "config t" to enter into the global configuration mode.
2.
Type "vsan database".
3.
Type "vsan2 name UCS- Siebel".
4.
Type "vsan 2 interface fc1/29-32".
5.
Type "y" on the "Traffic on fc1/29 may be impacted. Do you want to continue? (y/n) [n]".
6.
Similarly type "y" for fc1/30, fc1/31 and fc1/32 interfaces.
Verification: The command "show vsan membership" should list fc1/29-32 under "vsan 2".
Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A# show vsan membershipvsan 2 interfaces:fc1/29 fc1/30 fc1/31 fc1/32Creating VLANs and Managing Traffic
To create necessary VLANs for example, VLAN 809 and managing data traffic for example, VLAN 812 - data traffic, perform the following steps for both Cisco Nexus 5548 A - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A), and Cisco Nexus 5548 B - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B) separately:
1.
Type "config t" to enter into the global configuration mode.
2.
From the global configuration mode, type "vlan809" and press "Enter".
3.
Type "name MGMT-VLAN" to enter a descriptive name for the VLAN.
4.
Type "exit".
5.
Type "vlan812".
6.
Type "name Data-VLAN".
7.
Type "Interface ethernet1/1-20" (make sure to choose the Ethernet interfaces where Fabric Interconnects are connected).
8.
Type "switchport mode trunk".
9.
Type "switchport trunk allowed vlan 809,812".
10.
Type "exit".
Verification: The command "show vlan" should list the vlans and interfaces assigned to it. Or, the command "show run interface <interface name> should show the configuration for a given interface or port channel.
Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A# show vlanVLAN Name Status Ports---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------809 VLAN0809 active Eth1/1,Eth1/2, Eth1/3, Eth1/4Eth1/5,Eth1/6, Eth1/7, Eth1/8Eth1/9,Eth1/10, Eth1/11, Eth1/12Eth1/13,Eth1/14, Eth1/15, Eth1/16Eth1/17,Eth1/18, Eth1/19, Eth1/20VLAN Name Status Ports---- -------------------------------- -------- ------------------812 VLAN0812 active Eth1/1, Eth1/2, Eth1/3, Eth1/4Eth1/5, Eth1/6, Eth1/7, Eth1/8Eth1/9, Eth1/10, Eth1/11, Eth1/12Eth1/13, Eth1/14, Eth1/15, Eth1/16Eth1/17,ETH1/18, Eth1/19, Eth1/20Creation and Configuration of Virtual Port Channel (VPC)
To create and configure the VPC, perform the following steps for both Cisco Nexus 5548 A - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A), and Cisco Nexus 5548 B - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B) separately:
1.
In the global configuration mode, type "vpc domain 108".
2.
Type "role priority 1000".
3.
Type "peer-keepalive destination 10.x.x.x". (This IP is the Siebel_Nexus_Switch_BMgmt IP)
4.
Type "int port-channel 108".
5.
Type "switchport mode trunk".
6.
Type "switchport trunk allowed vlan45, 809-812".
7.
Type "vpc peer-link".
8.
Type "int ethernet 1/5" (peer link port).
9.
Type "switchport mode trunk".
10.
Type "switchport trunk allowed vlan 192, 809-812".
11.
Type "channel-group 108 mode active".
12.
Type "Exit".
13.
Type "int port-channel 109".
14.
Type "switchport mode trunk".
15.
Type "switchport trunk allowed vlan 192, 809-812".
16.
Type "vpc 109".
17.
Type "Exit".
18.
Type "int ethernet 1/1".
19.
Type "channel-group 109 mode active".
20.
Type "switchport mode trunk".
21.
Type "switchport trunk allowed vlan 192, 809-812".
22.
Type "Exit".
23.
Type "int ethernet 1/1".
24.
Type "channel-group 109 mode active".
25.
Type "switchport mode trunk".
26.
Type "switchport trunk allowed vlan 192, 809-812".
27.
Type "Exit".
Verification: "show vpc" command should list the vpc properties with vpc peer-link status as "success" and Consistency status as "success"
Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A# show vpcLegend:(*) - local vPC is down, forwarding via vPC peer-linkvPC domain id : 108Peer status : peer adjacency formed okvPC keep-alive status : peer is aliveConfiguration consistency status : successPer-vlan consistency status : successType-2 consistency status : successvPC role : secondaryNumber of vPCs configured : 1Peer Gateway : DisabledDual-active excluded VLANs : -Graceful Consistency Check : EnabledvPC Peer-link status------------------------------------------------id Port Status Active vlans-- ---- ------ -----------------------------1 Po108 up 192,809-812vPC status------------------------------------------------------------------id Port Status Consistency Reason Active vlans------ ----------- ------ ----------- --------------------------109 Po109 up success success 192,809-812Creation of Zoneset and Zones
To create zoneset and zone, perform the following steps for Cisco Nexus 5548 Switch A - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A):

Note
As mentioned in Service profile template creation, the first pair of vHBAs (vHBA0 and vHBA1) are created for SAN boot process and Second pair of vHBAs (vHBA2 and vHBA3) are created for application. Hence each pair is zoned separately.
1.
From the global configuration mode, type "zoneset name UCS-Siebel vsan 2"

Note
The VSAN id should match to the VSAN Id Created in Fabric Interconnect.
2.
Type "zone name ucs-sb-med-as1-boot-a".
3.
Type "member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:05:0A:0d".

Note
This is WWPN of vHBA0 in the associated service profile of B200 blade.
4.
Type "member pwwn 50:06:01:6f:3e:a0:05:68".
5.
Type "member pwwn 50:06:01:66:3e:a0:05:68".
6.
Type "exit".
7.
Type "zone name ucs-sb-med-as1-app-a".
8.
Type "member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:05:0B:0d".

Note
This is WWPN of vHBA2 in the associated service profile of B200 blade.
9.
Type "member pwwn 50:06:01:6f:3e:a0:05:68".
10.
Type "member pwwn 50:06:01:66:3e:a0:05:68".
11.
Type "exit".
12.
Type "Zoneset activate name UCS-Siebel vsan 2".
13.
Type "copy r s".
To create zoneset and zone, perform the following steps for Cisco Nexus 5548 Switch B - (Siebel_Nexus_Switch_B):
1.
From the global configuration mode, type "zoneset name UCS- Siebel vsan 2"

Note
The VSAN id should match to the VSAN Id Created in Fabric Interconnect.
2.
Type "zone name ucs-sb-med-as1-boot-b".
3.
Type "member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:05:0A:2d".

Note
This is WWPN of vHBA0 in the associated service profile of B200 blade.
4.
Type "member pwwn 50:06:01:6e:3e:a0:05:68".
5.
Type "member pwwn 50:06:01:67:3e:a0:05:68".
6.
Type "exit".
7.
Type "zone name ucs-sb-med-as1-app-b".
8.
Type "member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:05:0B:2d".

Note
This is WWPN of vHBA2 in the associated service profile of B200 blade.
9.
Type "member pwwn50:06:01:6e:3e:a0:05:68".
10.
Type "member pwwn50:06:01:67:3e:a0:05:68".
11.
Type "exit".
12.
Type "Zoneset activate name UCS-Siebel vsan 2".
13.
Type "copy r s".
Similarly create Zones for the other blades in both Nexus switches. This can be verified by executing `
`show zoneset active vsan 2' command in the Nexus switch.
Siebel_Nexus_Switch_A# show zoneset active vsan 2zoneset name UCS-Siebel vsan 2zone name ucs-sb-med-as1-boot-a vsan 2* fcid 0x440016 [pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:05:0a:0d]* fcid 0x4405ef [pwwn 50:06:01:6f:3e:a0:05:68]* fcid 0x4403ef [pwwn 50:06:01:66:3e:a0:05:68]zone name ucs-sb-med-as1-app-a vsan 2* fcid 0x440017 [pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:05:0a:2d]* fcid 0x4405ef [pwwn 50:06:01:6f:3e:a0:05:68]* fcid 0x4403ef [pwwn 50:06:01:66:3e:a0:05:68]Figure 31 shows the zoning configuration:
Figure 31 SAN Zoning Configuration

Cisco UCS Manager Service Profile update
Since the Nexus switches are connected with the storage array and the host, you must modify the boot policy in the Service Profile to add the Storage Ports. Perform the following steps to modify the boot policy:
Modifying Service Profile for Boot Policy
In this setup, vhba0 and vhba1 are used for SAN Boot and the other two configured HBA's that is, vhba2 and vhba3 are for Oracle Siebel application server installation. Storage SAN WWPN ports will be connected in the boot policy as:
vhba0
•
Storage Port SP-B0 Primary Target - 50:06:01:6f:3e:a0:05:68
•
Storage Port SP-A0 Secondary Target - 50:06:01:66:3e:a0:05:68
vhba1
•
Storage Port SP-B1 Primary Target - 50:06:01:6e:3e:a0:05:68
•
Storage Port SP-A1 Secondary Target - 50:06:01:67:3e:a0:05:68
To modify the Service Profile for boot policy, perform the following steps:
1.
Login to the Cisco UCS Manager. Click Servers tab > Policies > Boot Policies and then click Add. A pop-up window "Create Boot Policy" appears.
2.
Enter the name as "UCS-Siebel" in the "Name" text box and in the Description text box enter "for Siebel blades" and ensure that the check box "Reboot on Boot Order Change" is checked.
3.
Add the first target as CD-ROM, as this will enable you to install Operating System through KVM Console.
4.
Click Add SAN Boot on the vHBAs section; in the "Add SAN Boot" pop-up window, type "vHBA0" and select the type as Primary and click OK. This will be the SAN Primary Target.
5.
Click Add SAN Boot Target to add a target to the SAN Boot Primary in the vHBAs window. In the "Add SAN Boot Target" pop-up window, type "0" in the "Boot Target LUN". Enter "50:06:01:6e:3e:a0:05:68" in the "Boot Target WWPN" and select the type as "Primary" and then click OK.
6.
To add another target to the SAN Boot Primary, click Add to add another SAN Boot Target in the vHBAs window; in the "Add SAN Boot Target" pop-up box, type "0" in the Boot Target LUN; type "50:06:01:67:3e:a0:05:68" in the Boot Target WWPN and ensure that the type selected is "Primary" and click OK.

Note
These WWPNs are from storage SPB0/ SPA0 ports. For more details, see: SAN Zoning Configuration, Figure 31.
7.
Similarly for the SAN Secondary Target, click "Add SAN Boot" in the vHBAs window; in the "Add SAN Boot" pop-up window, type "vHBA1" and select the type as "Secondary" and then click OK.
8.
Click Add SAN Boot Target to add a target to the SAN Boot Primary in the vHBAs window. In the "Add SAN Boot Target" pop-up window, type "0" in the "Boot Target LUN". Enter "50:06:01:6e:3e:a0:05:68" in the "Boot Target WWPN" and select the type as "Secondary" and then click OK.
9.
To add another target to the SAN Boot Primary, click Add to add another SAN Boot Target in the vHBAs window; in the "Add SAN Boot Target" pop-up box, type "0" in the Boot Target LUN; type "50:06:01:67:3e:a0:05:68" in the Boot Target WWPN and ensure that the type selected is "Secondary" and click OK.

Note
These WWPNs are from storage SPB1 / SPA1 ports. For more details, see: SAN Zoning Configuration, Figure 31.
10.
Click Save Changes to save all the settings. The Boot Policy window in Cisco UCS Manager is as shown in Figure 32.
Figure 32 Boot Policy in Service Profile

11.
To add this boot policy to the Service Profile, click Servers tab > Service Profiles > root > sb-as-1. Select the Boot Order on the right pane and click Modify Boot Policy. A pop-up window "Modify Boot Policy" appears. Select the newly created Boot Policy "UCS-Siebel" and click OK. This will reboot the blade, as "Reboot on Boot order change" is enabled in the Boot policy.
Update the other service profiles in similar way with the boot policy "UCS-Siebel" to boot from the SAN after creating necessary LUNs / Storage groups in Storage array and Zones in Nexus Switches.
Host - Storage Connectivity
To establish the Host connectivity, you need to connect the host at the EMC VNX5500 array.
Connecting Storage to the Host
Since the zones are configured in the Cisco Nexus switches with the Host HBA WWPNs, they will appear in the EMC VNX5500 Unisphere.
To connect storage to the host, perform the following steps:
1.
Login to the EMC VNX Unisphere, click Hosts> Connectivity Status under "Host management" on the right side of the window. A pop-up window "Connectivity Status" appears.
2.
Under the Host Initiators tab, the vHBA WWPNs of the associated blade is available.

Note
vHBA0 and vHBA1of the blade would appear first time before any OS install on that blade. After successful OS installation, the vHBA2 and vHBA3 will appear which is used for the application.
3.
When one of the HBA initiator is selected, click Register. A pop-up window "Register Initiator Record" appears.
4.
Select the "Initiator Type" as "CLARRiiON Open" and Failover mode as "Active/Passive mode (PNR)-failovermode 1". Define the hostname (ucsmedas1) and IP address which would be allocated to the Oracle Siebel application server.
5.
Similarly register the other vhba WWPN with the same host and IP address. Select same Failover Mode as "Active/Passive mode (PNR)-failovermode 1".
6.
To associate the LUN for this blade, associate LUN to the already created Storage group. For the Oracle Siebel application server, the storage group created is "med-sb-as1". To do this, click Hosts > Storage Groups (med-sb-as1) > Connect Hosts. In the Storage group properties pop-up box > Hosts tab, locate the "ucsmedas1" from the available hosts section and Click OK. Associating host to the Storage Groups (med-sb-as1) is shown in Figure 33.
Figure 33 Storage Group - Host Association

Storage connectivity for the other blades can be established by following the same steps as above.
RedHat Linux OS Installation
After ensuring that the Boot LUN has been made visible to the host, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) OS (version 5.4) can be installed. For the procedure to install RHEL OS, see: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/Cisco UCS/sw/b/os/linux/install/BSERIES-LINUX.pdf.

Note
Though this exercise was carried out on Red Hat Enterprise Linux OS, the same can be followed for Oracle Linux 5.4 (Red Hat compatible kernel).
EMC PowerPath Setup
EMC PowerPath is host-based software that provides automated data path management and load-balancing capabilities for heterogeneous server, network, and storage deployed in physical and virtual environments. A critical IT challenge is being able to provide predictable, consistent application availability and performance across a diverse collection of platforms. PowerPath is designed to address those challenges, helping IT meet service-level agreements and scale-out mission-critical applications.
This software supports up to 32 paths from multiple HBAs (iSCSI TCI/IP Offload Engines [TOEs] or FCoE CNAs) to multiple storage ports when the multipathing license is applied. Without the multipathing license, PowerPath will use only a single port of one adapter (PowerPath SE). In this mode, the single active port can be zoned to a maximum of two storage ports. This configuration provides storage port failover only, not host-based load balancing or host-based failover. It is supported, but not recommended, if the customer wants true I/O load balancing at the host and also HBA failover.
PowerPath balances the I/O load on a host-by-host basis. It maintains statistics on all I/O for all paths. For each I/O request, PowerPath intelligently chooses the most underutilized path available. The available underutilized path is chosen based on statistics and heuristics, and the load-balancing and failover policy in effect.
In addition to the load balancing capability, PowerPath also automates path failover and recovery for high availability. If a path fails, I/O is redirected to another viable path within the path set. This redirection is transparent to the application, which is not aware of the error on the initial path. This avoids sending I/O errors to the application. Important features of PowerPath include standardized path management, optimized load balancing, and automated I/O path failover and recovery.
For more information on PowerPath, see: http://www.emc.com/collateral/software/data-sheet/l751-powerpath-ve-multipathing-ds.pdf.
For this Oracle Siebel implementation, PowerPath Version 5.5 (Build 275) is used and following steps are used to configure the same. The Naviagent installation is done first (NaviHostAgent-Linux-64-x86-en_US-6.29.6.0.35-1.x86_64.rpm) and then PowerPath library (EMCPower.LINUX.5.5.GA.b275.tar.gz) is installed post OS installation. Similarly Naviagent / PowerPath can be installed on the other blades using the same steps.
1.After successful Red hat OS installation, Pls. ensure to add the IP address in the /etc/hosts file as NaviAgent requires this entry2.To install Naviagent, perform the following steps:[root@ucsmedas1smas emc]# rpm -ivh NaviHostAgent-Linux-64-x86-en_US-6.29.6.0.35-1.x86_64.rpmPreparing... ########################################### [100%]1:NaviHostAgent-Linux-64-########################################### [100%][root@ucsmedas1 log]# cd /opt/Navisphere/bin[root@ucsmedas1 bin]# ./naviagent startNote: Make sure to add Naviagent services to start automatically after server boot, by executing setup from OS prompt; Setup (Text mode setup Utility) ? System Services (Run tool) ? naviagent (* `selection' ) ? OK.3.PowerPath installation:[root@ucsmedas1 emc]# rpm -ivh EMCPower.LINUX-5.5.0.00.00-275.RHEL5.x86_64.rpmPreparing... ########################################### [100%]1:EMCpower.LINUX ########################################### [100%]All trademarks used herein are the property of their respective owners.NOTE:License registration is not required to manage the CLARiiON AX series array.[root@ucsmedas1emc]# emcpreg -install=========== EMC PowerPath Registration ===========Do you have a new registration key or keys to enter?[n] yEnter the registration keys(s) for your product(s),one per line, pressing Enter after each key.After typing all keys, press Enter again.Key (Enter if done): <<enter the License key >>1 key(s) successfully added.Key successfully installed.Key (Enter if done):1 key(s) successfully registered.Reboot the system.4.PowerPath Verification- Verify the /Var/log/HostIDFile.txt for the entry of ServerIP & datetime of Powerpath execution.- Execute command `powermt display dev=all' command to list the setup[root@ucsmedas1 ~]# powermt display dev=allPseudo name=emcpowerbCLARiiON ID=FNM00103100070 [Med-sb-as1]Logical device ID=600601603290290044A6B5347ED4E011 [ucsmedas1-app lun]state=alive; policy=BasicFailover; priority=0; queued-IOs=0;A, current=SP A Array failover mode: 1==============================================================================--------------- Host --------------- - Stor - -- I/O Path -- -- Stats ---### HW Path I/O Paths Interf. Mode State Q-IOs Errors==============================================================================1 fnic sda SP B6 active alive 0 01 fnic sdd SP A7 active alive 0 02 fnic sdg SP A6 active alive 0 02 fnic sdj SP B7 active alive 0 00 fnic sdm SP A6 active alive 0 00 fnic sdp SP B7 active alive 0 03 fnic sds SP A7 active alive 0 03 fnic sdv SP B6 active alive 0 0Oracle Siebel Installation
Oracle Siebel application is installed on the identified servers by following the general principles mentioned in the Oracle Siebel Bookshelf documentation:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E14004_01/books/SiebInstUNIX/SiebInstUNIXTOC.html
The key steps involved in the Oracle Siebel installation process are shown in Figure 34.
Figure 34 Oracle Siebel Installation Process

In this CVD, the Installation steps for Oracle Siebel Small Enterprise Setup is captured (which uses single instance on each layer - Single Web server, Single Gateway Server, Single Application Server and Single Database Server) and wherever appropriate, the steps required for additional servers are included for Medium / Large Enterprise setups.
Planning/Pre-Requisites
When attempting the complex task of installing and configuring Oracle Siebel CRM, it is imperative to have a considered planned approach and proper step-by-step documentation for a successful completion. This section contains the steps that articulate the planning process that was used to build the Oracle Siebel installation process for this exercise:
•
Understanding the Hardware and Software Prerequisites
•
Installation of Oracle Database
•
Installation of Database Client on the Oracle Siebel Gateway/Application Servers.
•
Preparing the Siebel File system
•
Downloading the Oracle Siebel Installation Archives and Running the Oracle Siebel Image Creator
•
Other Installation Prerequistes
Understanding the Hardware and Software Prerequisites
Please see the "Siebel System Requirements and Supported Platforms" document for latest on software/hardware prerequisites published by Oracle, see: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11886_01/V8/CORE/core_8_1.html. In this implementation, following software were used as listed in Table 5.
Hardware Sizing
In order to ensure Oracle Siebel implementation meets the required performance and availability, sizing plays a key role which depends on many factors such as: Peak Concurrent users, Expected data volumes, User access patterns and so on. The implementation exercise involved measuring performance at various loads and it is discussed in the section: Oracle Siebel Performance and Scalability.
Installation of Oracle Database
In this implementation, for Siebel Small setup, single instance of Oracle is installed (on server "ucssmdb") whereas for the Medium and Large setups, Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC) installation is considered. The Oracle Database 11gR2 (version 11.2.0.2) is downloaded from the link: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-edition/downloads/index.html and installed by following the instructions provided in the link: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/install.112/e24326/toc.htm. Table 6 lists the server specifications used for database components.
After the successful installation of the Oracle database, the Oracle Siebel Small Enterprise database appears as shown in Figure 35 in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid control.
Figure 35 Oracle Database - Siebel Small Enterprise Setup

Similarly after successful installation of Oracle 2 node RAC for Oracle Siebel Medium/ Large Enterprise, it appears as shown in Figure 36 in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid-control.
Figure 36 Oracle Database (2 Node RAC) - Siebel Medium or Large Enterprise Setup

Installation of Database Client on the Oracle Siebel Gateway/Application Servers.
Oracle database client bridges the Siebel Components communicating to each other such as Gateway server/ Siebel Servers. The installation of the Oracle database client (11gR2 32 bit client) was done following the Oracle database client Quick Installation Guide 11g Release 2(11.2) for Linux x86_64 document, see: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/install.112/e24325/toc.htm.
Preparing the Siebel File system
As described in the section Configuring the EMC VNX5500, Siebel File System is carved in EMC VNX5500 Storage array for storing documents. In the Large Enterprise setup, file attachments were inserted/ retrieved as a part of Service Request business transaction.
Downloading the Oracle Siebel Installation Archives and Running the Oracle Siebel Image Creator
Oracle Siebel Business Applications software must be installed from a network image created using Oracle Siebel Image Creator. Oracle Siebel Installation cannot be directly done from the ZIP files, JAR files, or DVDs. Perform the following steps to create images for installation.
· Download the `Oracle Siebel Business Applications Release 8.1.1.0 Media pack for Linux x86' contents by searching on Product Pack with `Oracle Siebel CRM' and Product Platform with `Linux x86-64' from edelivery.oracle.com· Copy all the jar files, Oracle Siebel.ini, media.inf, and the Linux_imagecreator executable to a common directory and execute the imagecreator utility from the common directory mentioned above, use the -console option to run in non UI mode (i.e. ./Linux_ImageCreator -console ) or use X manager manger ./Linux_ImageCreatorNote: Execute the Image Creator utility using the user login which is going to be used for Installation, in order to avoid missing any directories during installation.· The utility displays the message Welcome to the Install Shield Wizard for the Oracle Siebel Image Creator Utility. Click Next to proceed.· Specify whether you will create a new image (or add products to an existing image) or add languages to an existing image. Click Next.· Specify the DIR in which the install image will be created. Eg /solcrm/Linux/Oracle Siebel_Install_Image (must be an absolute path). Click Next.· Choose the version, the default version is derived from the presence of one of the jar files (eg 8.1.1.0). Click Next.· Choose Application Type (SBA or SIA). Click Next.· Choose the platform. Pick Linux. Click Next· Choose the Products to be included as part of the Install Image. Pick Oracle Siebel Enterprise Server and Oracle Siebel. Click Next.· Choose the language. Pick ENU. Click Next· Once all the products and languages are chosen, Image creator wizard indicates Image created successfully. Click Finish.Other Installation Prerequistes
•
Ensure non-root users created in each tier. For example, "dssys1" for web server, "siebel" for Gateway and application servers.
•
The created non-root users need write permissions on /var/adm/Oracle Siebel (this directory is created by root user).
•
Gateway Server uses Port 2320 (by default), make sure that this port is not used by any other process of the Gateway server. The port status can be verified by netstat -a | grep 2320.
•
Create tablespace Siebel_index and Siebel_data by following the steps detailed in the link: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E14004_01/books/SiebInstWIN/SiebInstCOM_RDBMS3.html#wp1809517.
•
Run grantusr.sql located at /oracle directory in the Database Server. Before executing grantusr.sql add the following command for each tablespace used:
alter user SIEBEL quota unlimited on table_space_name.
Command to execute the grantusr.sql: @/$SIEBEL_ROOT/dbsrvr/oracle/grantusr.sql
Oracle Siebel Installation
In this implementation, Oracle Siebel installation is carried out for Small Enterprise on a separate set of Cisco UCS Blades and Oracle Siebel Medium Enterprise was carried out on another set of Cisco UCS Blade Servers. The Oracle Siebel - Large Enterprise setup was expanded on the already configured Medium Enterprise setup. This section describes the installation steps for Oracle Siebel Small Enterprise with necessary comments for Medium and Large Enterprise installations.
Table 7 provides the blade names and components installed for Oracle Siebel Small Enterprise Environment.
Table 8 provides the blade names and components installed for Oracle Siebel Medium Enterprise Environment.
Table 9 provides the blade names and components that are installed/ reconfigured from Oracle Siebel Large Enterprise Environment.
Oracle HTTP Server Installation
Perform the following steps to install Oracle HTTP Server on the web server "ucssmws":
Navigate to installables directory(/solcrm/http/disk1)$./runInstaller -ignoreSysPrereqs/cdts/OHS/oracle/OraHome_1Wizard will open and follow the step by step and to complete the OHS install(Note: Make sure to run the script /cdts/OHS/oracle/OraHome_1/root.sh as "root" user)Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]: /Siebel/OHSCopying dbhome to /Siebel/OHS ...Copying oraenv to /Siebel/OHS ...Copying coraenv to /Siebel/OHS ...Database Configuration Assistant when database creation is finished run generic part of root.sh script.Now product-specific root actions will be performed.done..Connect to webserver as root user and link the libraries by executing the following commands$cd /usr/lib$ln -s libdb-4.3.so libdb-3.3.soGateway Server Installation
To install Gateway Server, Oracle Siebel server installable needs to be invoked, as Oracle Siebel maintains single installable for installing Gateway server/Oracle Siebel Server/Database Configuration Utilities or EAI connector. The steps involved in Gateway Server are listed below, which is done on "ucssmgs" server.
Log on to the Gateway server box, using the putty and navigate to the installables directory.Navigate to the directory: /solcrm/Linux/Siebel_Install_Image/Server/Siebel_Enterprise_ServerExecute the command : ./setuplinux - console (This will open up installation wizard)Select a directory to install (for example /Siebel)Select products to install - Choose `Gateway Name Server' in the list of options shown and click next (the other options are `Siebel Server' , `Database Configuration Utilities', EAI Connector)Choose the type of installation to execute as Typical and click enter( amoung Typical/Compact/Custom)Select the language or languages to be installed for your Siebel Enterprise Server and enter.(Pick enu)Click on finish to end the installation as configuration is done at later point.Siebel Server/ DB Utilities Installation
For Siebel Application Server installation, follow the same steps mentioned in Gateway Server installation, until you reach select products to install [Select "Siebel server" and "Database Configuration Utilities" (which installs all necessary database related packages)] on the "ucssmas" (Application server).
These steps need to be repeated for additional Oracle Siebel servers as we have used two application servers for Oracle Siebel Large Enterprise setup. The database configuration utilities install need to be done only once in an Enterprise setup.
Oracle Siebel Configuration
Gateway Server / Enterprise Server Configuration
The following are the configuration steps which are followed on the "ucssmgs" (gateway server):
Ensure that the Gateway Server is configured first followed by the Enterprise server, where Oracle Siebel Enterprise server is a logical collection of Oracle Siebel Servers that access the same Oracle Siebel database and File System, and managed by a single Oracle Siebel Gateway Server.
Gateway Server Configuration
To configure the Oracle Siebel Gateway Server, perform the following steps:
1. Login to the server through X manager or Putty and navigate to gtwysrvr directory2. Export SHLIB_PATH=../gtwysrvr/bin3. Run the cfgenv.sh file which would set up the paths4. Then run the below command from gtwysrvr/bin directory./ssincfgw -args LANG=language MODE=mode MODEL_FILE=SIEBEL_ROOT/gtwysrvr/admin/ enterprise_console.scmThe install wizard will open in GUI mode Or through putty execute ./ssincfgw - console which will open the install wizard in console modeYou can choose "Create New Configuration" option and enter.Select Configure a New Gateway Name Server and enterNote: For the Enterprise Server Configuration, it is required to perform all the three tasks highlighted in the wizard window.· Specify the port number this Gateway Name Server uses for connections from Siebel Server or other components. The default port number is 2320 and Click Next.· Choose Next· Choose Next· Choose Yes to Execute the Configuration.Enterprise Server Configuration
In order to configure the Oracle Siebel Enterprise server, perform the following steps:
The Oracle Siebel Configuration Wizard will execute using the following settings:Main Task Selection : Create New ConfigurationConfiguration Task Selection : Configure a New Enterprise in a Gateway Name ServerGateway Name Server Authentication User Account Name : SADMINGateway Name Server Authentication User Account Password : ********Gateway Name Server Host Name : ucssmgsGateway Name Server TCP/IP Port : 2320Oracle Siebel Enterprise Name : SBA_81Enterprise Description : SBA_81 EnterprisePrimary Oracle Siebel File System : /SiebelFileSystemRDBMS Platform : Oracle Database Enterprise EditionDatabase Table Owner : SIEBELOracle SQLNet Connect String : ucssmdbOracle Siebel Database User Account Name : SADMINOracle Siebel Database User Account Password : ********Enterprise Security Authentication Profile : Database Authentication (default)Security Adapter Name (named subsystem) : DBSecAdptPropagate Authentication Settings to the Gateway Name Server : truePress 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]1. Yes2. NoDo you want to execute configuration? [2] 1This would execute the Oracle Siebel Enterprise server configuration.Creation of SWSE Logical Profile
The following are the configuration steps for SWSE Logical profile creation on the "ucssmgs" (gateway server):
Select Create New configuration from the Siebel Configuration Wizard and Click Next.Specify the Enterprise name and the location for the Siebel Web Server Extension logical profile name.This Option is for the file compression typeChoose compression Type as None and EnterChoose Http 1.1 firewall and click nextSpecify Login Session Time as 300 and Active session Timeout value 900 secs and nextEnter Http Port as : 60001 and Https Port number as 443 or enter as appropriate and click nextDo not set the FQDN- Fully Qualified Domain Name.Specify high interactivity user and appropriate password (SADMIN and SADMIN)Do not Select the standard interactivity Password Encryption format.Specify GUESTCST and GUESTCST for the Standard Interactivity and click NextSpecify the Enterprise appropriate security token ("KEY" was used). This should not be left blank.Click NextDefault Click NextNext and Click YesThe creation of SWSE logical profile, updates the eapps.cfg present in /gtwysrvr/admin/webserver directory. This file would get propagated to all the web servers when SWSE configuration is done, see section SWSE Install and Configuration.
Database Configuration
To configure database connectivity/ tables creation execute the following steps from "ucssmas" - (application server):
ODBC Connectivity
During the Oracle Siebel Server installation, ODBC system data source name (DSN) is used to connect to the database. Before proceeding to configure the database, it is essential to verify that the ODBC DSN is configured correctly. The following steps can be used to verify the ODBC connection from Oracle Siebel server:
1.
Run the CreateDbSrvrEnvScript script (hosted in directory $SIEBSRVR_ROOT/install_script/install) to create environment setup source files dbenv.sh & dbenv.csh in the Oracle Siebel server installation directory.
2.
/CreateDbSrvrEnvScript Siebel_Root_Parent_Directory LANG DB_Platform.
3.
Execute. ./dbenv.sh to set the environment variables. Ensure that $SIEBEL_ROOT (pointing to Siebel installation directory) and LANGUAGE environment variables are correct.
4.
Verify the ODBC connection from Oracle Siebel Server by executing the below command from siebsrvr/bin directory, which should open Odbcsql prompt. odbcsql /s SBA_81_DSN /U SADMIN /P SADMIN.
Database Connectivity
Navigate to Siebel server /bin directory and run the below command to invoke the database configuration wizard:
In GUI mode./ssincfgw -args LANG=language MODEL_FILE=SIEBEL_ROOT/siebsrvr/admin/dbsrvr.scm (or)Console mode:./ssincfgw -console.Initializing InstallShield Wizard........Launching InstallShield Wizard........-------------------------------------------------------------------------------[X] 1 - Configure Product in Live Mode[ ] 2 - Configure Product for Offline Deployment[ ] 3 - Exit Configuration WizardTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Select a Configuration Task:[X] 1 - Siebel Server Configuration[ ] 2 - Database Configuration UtilitiesTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0] 2[ ] 1 - Siebel Server Configuration[X] 2 - Database Configuration UtilitiesTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Directory where the Siebel Server is installedSiebel Server Directory [/Siebel/siebsrvr]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Directory where the Siebel Database Server is installedSiebel Database Server Directory [/Oracle Siebel/dbsrvr]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Choose the appropriate database platform[ ] 1 - IBM DB2 UDB for Linux UNIX Windows[ ] 2 - IBM DB2 UDB for z/OS[X] 3 - Oracle Database Enterprise EditionTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------[X] 1 - Install Database[ ] 2 - Upgrade Database[ ] 3 - Apply Additive Schema Changes[ ] 4 - Import/Export Repository[ ] 5 - Migrate Repository[ ] 6 - Run Database UtilitiesTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------[X] 1 - Install Siebel Database[ ] 2 - Add a language to an existing Siebel DatabaseTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Please confirm that you wish to install a new Siebel database. Running thisstep against an existing Siebel database may make that database unusable.To select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------The GRANTUSR.SQL script must first be run by the database administrator (DBA)in order to create the necessary Siebel users and roles before continuing.To select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Choose whether you are installing a UNICODE or non-UNICODE Siebel Database.[X] 1 - UNICODE Database[ ] 2 - Non-UNICODE DatabaseTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Enter a valid ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) Data Source Name to access the Siebel Database connection. Default value is Siebel_DSN.ODBC Data Source Name []SBA_81_DSNPress 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Siebel Database User NameSiebel Database PasswordDatabase User Name [] SADMINDatabase Password:Database Password--(confirm):Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Siebel Database Table OwnerSiebel Database Table Owner passwordDatabase Table Owner [] SIEBELDatabase Table Owner Password:Database Table Owner Password--(confirm):Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]Please ensure you enter the correct table\\index space.-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index Table Space NameTable Space NameIndex Table Space Name [SBL_INDEX] SBL_INDX_81Table Space Name [SBL_DATA] SBL_DATA_81Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Please select whether you would like to enter a license key at this time[X] 1 - Yes I would like to enter it now[ ] 2 - No I will enter it laterTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0] 2[ ] 1 - Yes I would like to enter it now[X] 2 - No I will enter it laterTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Please indicate if the target server will use the Oracle Parallel Indexingoption:[X] 1 - Does not use the Oracle Parallel Indexing option[ ] 2 - Uses the Oracle Parallel Indexing optionTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Identifies an authorization ID designated for a group of Siebel users definedin a mainframe security packageSecurity Group ID / Grantee [SSE_ROLE]Log Output Directory [install]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Configuration is complete: your output will be saved under$SiebelRoot/siebsrvr/bin/master_<process>.ucf. To deploy the process youconfigured to the database please run the below command line:$SiebelRoot/siebsrvr/bin/srvrupgwiz /m master_<process>.ucfTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]The Siebel Configuration Wizard will execute Database Configuration Utilitiesusing the following settings:Siebel Server Directory : /Siebel/siebsrvrSiebel Database Server Directory : /Siebel/dbsrvrRDBMS Platform : Oracle Database Enterprise EditionSiebel Database Operation : Install DatabaseSelect Installation Operation : Install Siebel DatabasePlease confirm that you wish to install a new Siebel database. Running thisstep against an existing Siebel database may make that database unusable. :The GRANTUSR.SQL script must first be run by the database administrator (DBA)In order to create the necessary Siebel users and roles before continuing. :Database Encoding : UNICODE DatabaseLanguage Selection : ENUODBC Data Source Name : SBA_81_DSNDatabase User Name : SADMINDatabase Password : ********Database Table Owner : SIEBELDatabase Table Owner Password : ********Index Table Space Name : SBL_INDX_81Table Space Name : SBL_DATA_81Select License key option : No << to enter at later point>>Oracle Parallel Index : Does not use the Oracle Parallel Indexing optionPress ENTER to read the text [Type q to quit]Security Group ID / Grantee : SSE_ROLELog Output Directory : installConfiguration is complete: your output will be saved under$SiebelRoot/siebsrvr/bin/master_<process>.ucf. To deploy the process youconfigured to the database please run the below command line:$SiebelRoot/siebsrvr/bin/srvrupgwiz /m master_<process>.ucf :Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1] 11. Yes2. NoDo you want to execute configuration? [2] 1Execution Successful.Repository Import:Verified successfully.TOTAL TABLES: 328TOTAL ROWS : 3397800Cleaning up, disconnecting from the database.At the end of the configuration wizard, you can find "master_install.ucf" file, as a result of the configuration in the siebsrvr/bin directory.
The following command must be executed to apply the database configuration.
./srvrupgwiz /m master_install.ucfThe table creation process takes typically 30-40 minutes and this completes the database creation.

Note
As per Oracle Siebel 8.1 installation documentation, it is required to do the Oracle Siebel Server configuration only after completion of the database configuration.
Oracle Siebel Server Configuration
Login to Siebel application server ("ucssmas") and execute the following steps to configure Siebel Server.
Execute the file >. ./cfgenv.sh
Execute the below Script to run the Siebel Server configuration.
•
GUI mode:
./ssincfgw -args LANG=language MODE=mode MODEL_FILE=ORACLE SIEBEL_ROOT/siebsrvr/admin/Siebel_server.scm•
Console mode:
./ssincfgw -consoleInitializing InstallShield Wizard........Initializing InstallShield Wizard........Launching InstallShield Wizard........-------------------------------------------------------------------------------[X] 1 - Configure Product in Live Mode[ ] 2 - Configure Product for Offline Deployment[ ] 3 - Exit Configuration WizardTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Select a Configuration Task:[X] 1 - Database Configuration Utilities[ ] 2 - Siebel Server ConfigurationTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0] 2[ ] 1 - Database Configuration Utilities[X] 2 - Siebel Server ConfigurationTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]Welcome to the Configuration Wizard!This wizard walks you through essential tasks for configuring a Siebel Server.Please choose one of the tasks below.[ ] 1 - Create New Configuration[ ] 2 - Add Language Support for the Siebel Server[ ] 3 - Remove Existing Configuration[ ] 4 - Exit ConfigurationTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0] 1[X] 1 - Create New Configuration[ ] 2 - Add Language Support for the Siebel Server[ ] 3 - Remove Existing Configuration[ ] 4 - Exit ConfigurationTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]To select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Database Configuration InformationWarning: Before configuring the Oracle Siebel Server, make sure you have an existingSiebel Database available or have already performed the Install Database taskin the Database Configuration Wizard.To select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Gateway Name Server Authentication User Account Name:Provide the name and password for the user account used to connect to theSiebel Gateway Name Server. These values must not be left empty.Gateway Name Server Authentication User Account Name [] SADMINGateway Name Server Authentication User Account Password:Gateway Name Server Authentication User Account Password--(confirm):Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Gateway Name Server:Enter the host name for the Gateway Name Server, if it does not match thedefault. This name will be a NETBIOS-compliant machine name. If the GatewayName Server is clustered, enter the virtual host name, IP address, or virtualIP address instead.Enter the network TCP/IP port you are using with the Gateway Name Server. Thisvalue must match the configured value of the Gateway Name Server TCP/IP port.Gateway Name Server Host Name [ucssmgs]Gateway Name Server TCP/IP Port [2320]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Siebel Enterprise Name:Specify a name for the Oracle Siebel Enterprise. The name may contain alphabetic,numeric, and underscore characters and is limited to 12 characters. Specialcharacters are not supported. The name of the Enterprise must be unique whenthis Enterprise is created.Siebel Server Name:siebservrA Siebel Server name may contain alphabetic, numeric, and underscore charactersand is limited to 12 characters. Special characters are not supported. The nameof a Siebel Server must be unique in the Enterprise.Siebel Enterprise Name [SBA_81]Siebel Server Name [ucsmedas1] ucsmedas1Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Siebel Server Description:The description of the Siebel Server is used for your reference. It may be usedto identify "test" or "production" servers, for example, or identify a physicallocation. It is also useful to identify cluster members.Siebel Server Description [Siebel Server Profile ucsmedas1]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Enable Component Groups:Select the component groups to enable in this Siebel Server. For moreinformation about component groups, refer to the Siebel System AdministrationGuide.[ ] 1 - ADM[X ] 2 - Sales[ ] 3 - eChannel[ ] 4 - CallCenter[ ] 5 - CreditAsgn[ ] 6 - PIMSI[ ] 7 - FieldSvc[ ] 8 - Remote[ ] 9 - AsgnMgmt[ ] 10 - CommMgmt[ ] 11 - DandB[ ] 12 - DataQual[ ] 13 - DCommerce[X ] 14 - EAI[ ] 15 - eDocuments[ ] 16 - FcstSvc[ ] 17 - IComp[ ] 18 - ContCtr[ ] 19 - MktgOM[ ] 20 - MktgSrv[ ] 21 - RTSRemote[ ] 22 - SiebAnywhere[ ] 23 - S2S[ ] 24 - Search[ ] 25 - SAP[ ] 26 - ORCL[ ] 27 - ISS[ ] 28 - ERM[ ] 29 - HandheldSync[ ] 30 - SalesHierSvc[ ] 31 - TaskUI[ ] 32 - Wireless[X] 33 - Workflow[ ] 34 - HandheldSyncSIS[ ] 35 - eAutomotive[ ] 36 - HTIM[ ] 37 - LifeSciences[X] 38 - Communications[ ] 39 - Loyalty[ ] 40 - LoyaltyEngine[ ] 41 - Hospitality[ ] 42 - eConsumer[ ] 43 - SISME[ ] 44 - Oracle Siebel Financial Services[ ] 45 - UCM[ ] 46 - PublicSector[ ] 47 - XMLPReportTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Siebel Connection Broker Port:Enter the TCP/IP port number on which the Siebel Connection Broker componentwill receive inbound traffic for the Siebel Server. Using the default port(2321) is highly recommended, unless this port is used by other Siebelcomponents or applications co-located on this system. Possible values rangefrom 0 to 65535.Siebel Connection Broker Port [2321]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Remote Synchronization Manager Port:Specify a port number for the Siebel Remote Synchronization Manager on thisserver or server profile to listen on. This port will be used instead of thedefault port specified for the Enterprise. Make sure this port is not used byother applications. Typically, this port only needs to be changed if a port isin use by another Siebel Server on the same physical machine. (default 40400,range 0-65535)Network TCP/IP Port for Synchronization Manager [40400]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Additional Tasks for Configuring the Siebel Server:Choose any additional configuration tasks for the current Siebel Server fromthe list below.[ ] 1 - Exchange Server Synchronization[ ] 2 - Server-Specific Security Encryption Settings[ ] 3 - Server-Specific Security Authentication Profile AssignmentTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Select this option if you plan to use the Siebel Connector for OracleApplications to exchange data with your back office system, and your backoffice system stores data in an Oracle Database.[X] 1 - Register External Oracle DB ODBC DriverTo select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]To select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Final Tasks:To complete configuration of this server, verify that all of thepostinstallation tasks documented in Siebel Bookshelf are completed. Thistypically includes verifying correct setup of the environment using theEnvironment Verification Tool, which is provided in the \bin directory of theproduct installation you wish to verify.Configuration Wizard Hint: Siebel Bookshelf provides searchable documentation.For EVT command-line help run evt -? or EVT -h.To select an item enter its number, or 0 when you are finished: [0]Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]title The Siebel Configuration Wizard will execute using the following settings:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------The Siebel Configuration Wizard will execute using the following settings:Main Task Selection : Create New ConfigurationDbSrvrConfigSplash : Warning: Before configuring the Siebel Server, make sureyou have an existing Siebel Database available or have already performed theInstall Database task in the Database Configuration Wizard.Gateway Name Server Authentication User Account Name : sadminGateway Name Server Authentication User Account Password : ********Gateway Name Server Host Name : ucssmgsGateway Name Server TCP/IP Port : 2320Siebel Enterprise Name : SBA_81Siebel Server Name : apserver1Siebel Server Description : Siebel Server Profile ucssmgsSiebel Connection Broker Port : 2321Network TCP/IP Port for Synchronization Manager : 40400Register External Oracle DB ODBC Driver : trueEVTWelcome : Configuration Wizard Hint: Siebel Bookshelf provides searchabledocumentation. For EVT command-line help run evt -? or EVT -h.Press 1 for Next, 2 for Previous, 3 to Cancel or 4 to Redisplay [1]Do you want to execute configuration? [2] 1created at Wed Feb 29 02:12:00 2012, autostart: noExecution Successful.This will complete the configuration of Oracle Siebel Server.
To verify if the configuration is successful or not, perform the following steps:
1.
Verify the gateway server is started by executing
ps -ef | grep siebel
The output should list "siebsvc" process
2.
To Start the Oracle Siebel server
a.
Navigate to <Siebel_home>/siebsrvr
–
Execute. ./siebenv.sh for environment variables setup
b.
Navigate to bin directory and execute the following commands

Note
Reset_server command is to close all the stale connections/processes.
–
reset_server -e SBA_81 ucssmas
–
start_server all
Repeat the same steps for the additional servers in the Siebel Large Enterprise setup.
SWSE Install and Configuration
The SWSE enables webserver (ucssmws) to communicate with the Object Manager components running on Siebel servers. It serves as a plug-in and enables the web server to forward the incoming request URLs from the browser to the application object manager session on the Siebel server.
The installation of SWSE, sets up the Siebel directory structures and copies required files and components to the target location on the Web server.
Log on to the Web Server box, using the putty and navigate to the Directory where the Siebel installables such asNavigate to the directory /solcrm/Linux/Siebel_Install_Image/Server/Siebel_Web_Server_ExtensionExecute the command ./setuplinux (This will open up installation wizard)Pick "Install new instance of SWSE"Confirm the DIR ins which to install i.e. default it is "SIEBEL_ROOT"/sweappSelect the language for SWSE. Pick ENUClick Next to continue the configuration of the Web Server Extension or Exit the WizardExitApplying the SWSE Logical profile
The created SWSE logical profile needs to be applied on to the Oracle HTTP web server. This process updates the eapps.cfg file in addition to creating virtual directories in the web server instance. Follow the steps as mentioned below for applying the SWSE logical profile.
Log on to the web server using the account (dssys1) in whose name the webserver is installed. Navigate to the SWSE location and launch the configuration wizard after setting up the environment variable.cd /Siebel/swse/bin. ./cfgenv.shNavigate to sweapp/BIN DIR and launch the SWSE Configuration wizard using command:./ssincfgw -args LANG=ENU MODE=LIVE MODEL_FILE=../admin/swse_server.scmChoose task to apply the logical SWSE profile.Click Next. It will prompt you to pick the deployed language. Choose ENUSelect Load Balancer. In this case, Pick 'Single Siebel Server Environment'*Pick Application Server Host Name. ucssmasPick Siebel SCBroker Port Number.2321 Use the Default ValuePick VIP address. NAPick Network Port Number for Third Party Load Balancer. NAPick location where the logical SWSE Profile is storedPick location of Web Server installationLast option is to restart Web Server.This completes the Web Server configuration.In the case of multiple Application servers, in the Select Load balancer Step, choose "Siebel Native Load Balancing" so that the incoming web server requests can be divided among the application servers. This would generate lbconfig.txt in /Siebel/sweapp/admin/ directory.
Post Installation task for SWSE
Edit httpd.conf file for the following changes:
Navigate to <swse-root>/http/conf directory and open httpd.conf(with a text editor,such as vi)Modify the following two lines in the httpd.conf file:Listen:61000ServerName:10.104.xxx.xx (Web server IP)Locate the line 'Add DefaultCharset ISO-8859-1' and comment it out as internationalisation is not addressed in this exercise.Locate the line 'CustomLog /Oracle Siebel/OHS/ohs/logs/access_log common' and comment it for better performanceSet UseCanonicalName to OFF. You are required to set UseCanonicalName to OFF if you loadbalance Web servers.Set KeepAliveTimeout to 15 seconds.Set MaxKeepAliveRequests=0 for maximum performance.Verify that the SWSE process owner (such as the httpd daemon) has recursive read, write, and execute permissions for theSWSE_ROOT/public directory. This directory contains the files for the Web image publishing and file caching features.Restart the web server and this would complete the configuration of SWSE plug-in.Additional post installation tasks are:
•
Downloading the Siebel Tools and Siebel client and installing them on the desktop for necessary customizations.
•
Updating the License Keys; this can be done either using Siebel Client or Siebel Tools.
•
Taking a backup; this can be done by navigating to the /var/adm/siebel directory and taking a backup of vpd.properties file.
This completes the Oracle Siebel installation and the installed components can be verified by navigating to the Server Administration screens (navigate to Oracle Siebel Home page > Sitemap > Administration > Server Management > Enterprises) as shown in Figure 37.
Figure 37 Server Administration Window

Customizations
This section includes the following configurations:
EAI Configuration
In any typical Siebel implementation, some of the business processes are executed using EAI (Enterprise Application Interface) integrations with external systems. In this implementation the "Orders creation/update" business process is done using EAI, in which Order Creation/Update XML string is sent over HTTP and response returned with new Order number and Update Status.
To configure EAI, perform the following high level steps:
1.
Create a new workflow (name as "EAI Order Upsert") in Oracle Siebel Tools for EAI order upsert which would get invoked for an XML input and respond by a XML output.
2.
Configure a new subsystem (in HTTP service section, name as "EAI Order BS") in the eai.cfg with subsystem type as "EAITransportDataHandlingSubsys" and configure the profile parameter - "Workflow Process to Execute" as "EAI Order Upsert WF".
3.
Deploy the "EAI Order Upsert WF" workflow in the Oracle Siebel window click Sitemap > Administration Busiess process > Workflow Deployment > Active Workflow Process > Menu > Import.
4.
Similarly deploy the "EAI Order BS" business process click Sitemap > Administration Business service > Details > Menu > Import service.
Workflow Configuration
Two workflows are configured in this implementation on Service Request and Opportunity business processes.
•
After creation of a "Service request", workflow is invoked to update the priority based on its severity and insert the relevant activity.
•
After creation of an "Opportunity", workflow is invoked to insert relevant Activity and Notes based on the Opportunity channel type.
These workflows are created using Oracle Siebel Tools are as shown in the Figure 38.
Figure 38 Workflow Creation Process

The configured workflows are deployed as shown in Figure 39.
Figure 39 Configured Workflows

Lessons Learnt & Best Practices
•
Install the pre-requisites rpms (both x86 and i386 versions) to avoid server configuration issues.
compat-libstdc++-296-2.96-138.i386
compat-libgcc-296-2.96-138.i386
compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3-61.x86_64
compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3-61.i386
•
Siebel Installation completed but could not find all the directories inside the siebsrvr, gtwysrvr and dbsrvr directory.
Solution: Siebel image has to be created with the same user from which the installation is carried out. This will resolve the issue.
•
Make sure to set the following environment variables for Operating System resource limits - SIEBEL_OSD_MAXLIMITS: allows Siebel to use max OS resources which may include coredumpsize, cputime, filesize, descriptors, maxmemory, and others.
C Shell: setenv SIEBEL_OSD_MAXLIMITS 1
Korn Shell or Bourne Shell: SIEBEL_OSD_MAXLIMITS=1; export SIEBEL_OSD_MAXLIMITS
Oracle Siebel Performance and Scalability
CRM systems require customization more frequently than other business applications. Some of the common changes include adding or removing certain application modules, modifying the functions of the existing modules, and integrating the CRM application with other business applications and processes. Even though the application performance is dependent on the deployment parameters, testing the scalability of a configuration with a well-defined workload provides a useful starting point for defining appropriate configurations and sizing.
To understand the Oracle Siebel CRM performance characteristics on Cisco UCS servers, the workload is designed based on realistic Oracle Siebel implementation scenarios in order to simulate real-world usage, even though the execution is in the lab environment. The following Siebel applications are chosen for the workload simulation:
•
Siebel E-Communications—The Siebel E-communications software provides a comprehensive solution for sales and service, helping customer service and telesales representatives to provide world-class customer support, improve customer loyalty, and increase revenues through cross-selling and up-selling opportunities.
•
Siebel E-Sales—The Siebel E-sales software provides a comprehensive solution for online customers to browse product catalogs, place orders, and raise a service request for purchased products. Online payment options are also available ensuring high security and confidentiality of customers.
•
Siebel Workflow—This business process management engine automates user interaction, business processes, and integration. Administrators can add custom or pre-defined business services as well as specify logical branching, updates, inserts, and sub processes to create a workflow process tailored to specific business requirements.
•
Siebel Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)—The EAI software allows organizations to integrate legacy applications with Siebel CRM applications and to integrate Web Service support. This capability enables organizations to extend the functionality of existing applications to provide up-to-the-minute information through standard Web portals and other Web Service-enabled environments.
The combinations of these applications are chosen with the following Concurrent User mix in this exercise:
•
E-Communications (eComm) - 40% of active concurrent users
•
E-sales (eSales) - 12% of active concurrent users
•
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) - 48% of active concurrent users
Business Transactions & Workload Mix
After deciding on the Oracle Siebel Applications, the business transactions with in those applications are identified to conduct performance tests on Cisco UCS servers and Table 10 lists the business transactions and their high level descriptions. The ratio of these business transactions (workload Mix) are listed in Table 11.
Table 12 lists the navigation steps (application level transactions) with in the business transactions identified for the workload simulation.
Test Environment Setup
In order to understand the performance characteristics of Oracle Siebel CRM applications on Cisco UCS servers, three configurations are chosen as mentioned in Table 13
Table 13 Oracle Siebel Enterprise Workload
Small
600
50 GB
Medium
3000
150 GB
Large
10000
450 GB
.
This data was generated using the sample data that comes with Oracle Siebel installation. SQL scripts (to ensure unique/referential integrity constraints) and Siebel EIM (Enterprise Integration Manager) data import approaches are used recursively to create the required data volumes in the database. Care has been exercised to ensure that cardinality is ensured between the Siebel key database entities and is maintained during the data loading process.
In order to meet the workloads, three test environments are designed with the following configurations as initial setup as shown in Table 14.
Table 14 Test Environments
Small
1
1
1
Medium
1
1
2 Node (RAC)
Large
1
2
2 Node (RAC)
Tests were conducted using HP LoadRunner tool with the following settings:
•
All Virtual users login once at their start-up phase and iterate the set of navigations and logout at the end of the test - simulating call center representatives daily shift workload.
•
Virtual users are gradually ramped up and reached their steady state (20 minutes).
•
A recorded think time of 10 seconds between each step is used in the test and is varied by a random percentage of 100% - 200% with the maximum limit set to 15 seconds.
•
Pacing time (idle time between each iterations) is maintained as 30 seconds for eComms/eSales scripts and 60 seconds for EAI scripts.
Test Results
Performance tests were conducted in each setup and data was collected using performance tools (NMON), LoadRunner and Oracle AWR (Automatic Workload repository). The metrics listed were captured for each setup and subsequent pages show the findings:
•
CPU utilization (as a percentage) / Memory utilization (in GB)
•
Business transaction throughput (in number of transactions per hour)
•
Average transaction response time (in seconds)
Metrics were collected only for the Web, Application and Database servers as the resource usage and workload dependency on the gateway server is insignificant. Gateway server is a necessary component but from a sizing perspective it does not require special guidelines.
Small Enterprise
In the Siebel Small Enterprise setup as shown in Figure 40, tests with 600 concurrent users accessing 50GB database were conducted with a workload mix as described in the previous section. As expected, the resource utilization on each tier is well within acceptable limits of provisioned hardware.
Figure 40 Oracle Siebel Small Enterprise Setup

CPU / Memory Usage
Figure 41 shows the memory or CPU usage graph for Small enterprise workload.
Figure 41 Small Enterprise - CPU and Memory Usage

Table 15 provides details about business transaction on hourly basis and the system response time.
As evident from the above results, the response time of business transactions is less than 2 seconds (less than a second for Non-EAI transactions) while the CPU/RAM resource usages are optimal. This clearly shows that there is enough room for scaling the number of concurrent users and data volumes on these servers.
Medium Enterprise
In the Oracle Siebel Medium Enterprise setup as shown in Figure 42, the test is conducted simulating 3000 concurrent users accessing 150 GB database as described above. As expected, the resource utilization on each tier is well within acceptable limits as shown in Figure 43.
Figure 42 Oracle Siebel Medium Enterprise Setup

Figure 43 Medium Enterprise - CPU and Memory Usage

Table 16 provides details about the business transactions on an hourly basis and the system response time.
With the medium workload scaling up to 3000 users, CPU utilization on the application server went up moderately. On the other hand memory utilization on the RAC nodes went up significantly. This can be attributed to the increased data size and version copies of the data due to smaller database size.
The Only difference between the Medium Enterprise setup and the Large Enterprise setup is an additional node in the application server tier. Based on the resource usages seen, the Web and Database servers have room for growth beyond the 10000 users workload that is being simulated. App server CPU utilization is close to 50% which is the desirable threshold beyond which the server should not be loaded in a HA (High Available) environment with 2 servers.
Large Enterprise
In the Oracle Siebel Large Enterprise setup as shown in Figure 44, the test is conducted with 10000 concurrent users accessing a 450 GB database, with a workload mix as described in the previous section. As expected, the resource utilization on each tier is well within acceptable limits as shown in the Figure 45.
Figure 44 Oracle Siebel Large Enterprise Setup

Figure 45 Large Enterprise - CPU and Memory Usage

Table 17 provides details about the business transactions on an hourly basis and the system response time.
Transaction Throughput and Response Time
Performance and scalability are inextricably linked. For this reason, it is important to examine the throughput and response time metrics together when analyzing application performance and configuration scalability. As the application load increases, the response time must remain within acceptable bounds. As a rule of thumb, when the number of concurrent users' increase, if the increase in throughput is linear, then the increase in response times are within the acceptable limits.
In the 10000 user test, the number of users is ramped up starting from 3000 users in steps of 1000 with 20 minutes of steady state in between to observe the scalability characteristics of Siebel on Cisco UCS servers. The business transactions throughput follows near linear scaling during the entire test as shown in Figure 46.
Figure 46 Transaction Throughput

The transaction response times did not show any significant variation with the increase of concurrent users as shown in Figure 47.
Figure 47 Transaction Response Time

During the test, the resource utilizations are well within acceptable limits. The Graphs for CPU and Memory Usage for web, application and database tiers are as shown in Figure 48, Figure 49 and Figure 50 respectively.
Figure 48 CPU and Memory Usage for Web Server

Figure 49 CPU and Memory Usage for Application Server

Figure 50 CPU and Memory Usage for Database Server

As seen from these results, a combination of B200, B230, and B250 blades provide enough flexibility to accommodate broader range of requirements that is seen in a typical Oracle Siebel CRM deployment. There was no CPU bottleneck in any tier in the tests conducted in this exercise. In case of other popular additional modules such as Siebel Reporting or Siebel Communication server, Siebel EIM were to be sized, higher capacity Cisco UCS servers such as the B230 M2 (10 core per socket) can be considered for application server tier. For large database workloads Cisco UCS B440 M2 servers can form ideal choice as it offers 4 socket (10 cores each) with maximum memory of 512GB RAM. These recommendations can only form as baseline estimations and Cisco does not guarantee the actual performance and it is suggested that conducting performance tests for specific requirements before arriving at right sizing estimations.
IO Characterization
During the 10000 user test execution, the IO data access at EMC VNX5500 storage array is monitored for both block access traffic and file access traffic, since the workload is modified to include file access operations. The graphs in Figure 51 and Figure 52 show the IO block access patterns seen throughout the test on the database LUNs. In this exercise, the database servers are configured with sufficient memory and IOPS generated during the tests were not high. However in a typical Siebel deployment which is expected to have larger data sets and with workloads like reporting and EIM in the workload mix, more I/O is expected.
Figure 51 EMC VNX5500 Database - Throughput IO per Second

Figure 52 EMC VNX5500 Database - Service Time (mSec)

Figure 53 shows the IOPS traffic for the NFS (data mover) LUN during the test. As shown in Table 11 Workload Mix, only 15% of the transactions do the file operations due to which the generated IOPS is less.
Figure 53 EMC VNX5500 - NFS Traffic IO per Second

Sizing Recommendations
During the test executions, a number of tuning activities are carried out to optimize the Cisco UCS blade servers' resource utilization so that the Oracle Siebel CRM response time is well within acceptable limits. The test executed against "Large enterprise setup" (10000 concurrent user test) was designed with periodic increase in concurrent users, to learn Oracle Siebel resource demands from the sizing perspective. Based on these observations, Sizing recommendations are suggested in Table 18.
These recommendations are provided as is without warranty of any kind. It is important to note that these are to be used as guideline values, and customer workload requirements need to be factored before arriving at the actual recommendations.
The following points must be considered for Sizing estimations:
•
Siebel Gateway Server component can be installed on a minimally configured blade server as it does not consume significant resources during the normal user operations. Activities such as enterprise changes and/enterprise restarts will cause resource usage in Gateway Server and hence it should be sufficiently capable to handle the repository access load.
•
As part of installation of Small enterprise setup, database was hosted on a B230 M1 blade server (2 socket Xeon 7560, 2.26GHz, 8 cores each) and its CPU utilization was very minimal (less than 2%). Hence for the same workload, it is recommended to use B200 M2 Series blade server.
•
As part of the Database installation in Medium and Large Enterprise setups, 192 GB memory was stacked in the B250 M2 blades (refer Table 6). Based on the test results, it is recommended to have 96GB.
•
In this exercise, Oracle Siebel Applications server hosted eComm, eSales and EAI object managers and tuned to handle 5000 concurrent users each (for Large enterprise setup).
•
Sizing for High Availability requirements, in Medium and Large scale enterprises, the following sizing options can be considered.
Web-Tier—Additional web servers can be configured with help of Load balancer products such as Cisco ACE solution. The configuration details of ACE implementation for Oracle Siebel can be found at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Verticals/siebelrt.html#wp344292.
•
Sizing Recommendation—Additional blades of same type/capacity of the first web server can be added to meet the HA requirements.
Gateway-Tier—Although failure of the Gateway server does not stop Oracle Siebel Enterprise normal functioning (users can logon and existing users can continue), any enterprise level change will be restricted (for e.g: addition of Object Manager component to the enterprise) when there is a Gateway server failure. Hence redundancy at Gateway server helps in meeting the dynamic demands seamlessly. Gateway servers can be clustered in active-passive mode as described in: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/clusterware/overview/siebel-crm-protected-by-clusterware-133669.pdf.
•
Sizing Recommendation—The second instance of Gateway server can be installed on another available server which is low in resource usage.
Application-Tier—Additional Siebel servers can be seamlessly added to the Siebel Enterprise by making necessary changes to the Siebel Gateway server and SWSE profile.
•
Sizing Recommendation—The extra instances of Oracle Siebel servers can be installed on new hardware with the same capacity.
Database-Tier—Oracle Real Application Cluster solution provides the necessary redundancy at the database tier.
Best Practices & Tuning Recommendations
Several optimizations to the Oracle Siebel CRM configurations are done as part of this exercise. Summarized below, these settings and modifications that can help customers optimize performance and scalability when implementing Oracle Siebel CRM applications on Cisco UCS servers.
Web Tier
Table 19 provides the configuration details of small, medium, and large setups in web tier. Configurations are done at web server's "httpd.conf" (Oracle HTTP server configuration file) to meet the target concurrent users that are planned for each Oracle Siebel Enterprise.
Following Operating System parameters are changed for Large Enterprise (10000 users) as the workload had file operations as in Business Transactions & Workload Mix.
•
/etc/sysctl.conf added fs.file-max = 10000000
•
/etc/security/limits.conf added following entries for the `dssys1' (webserver runs on `dssys1' login)
–
dssys1 soft nofile 98304
–
dssys1 hard nofile 130880
Application server / Oracle Siebel Enterprise
Table 20 provides the configuration details of small, medium, and large setups in application tier.

Note
•
MaxTasks: Maximum number of Tasks per component per server. One thread is accounted per task.
•
MaxMTServers: An MTServer is a multi-threaded component process. This defines the maximum number of MTServers per component per server.
•
MinMTServers: This defines the minimum number of MTServers per component per server; sets the number of MTServers started on server startup.
•
SIEBEL_OSD_NLATCH controls named latches & SIEBEL_OSD_LATCH controls unnamed latches. Latches are used for communication between Siebel processes.
Database Tier
Best practices for the Oracle Database tier include setting the following initialization parameters:
•
The database version must be upgraded to Oracle Database 11gR2 version 11.2.0.2 with the patchset 10425672, as this patch fixes some of the Mutex session concurrency issues on the RAC setup.
•
Table 21 lists the parameters that are used for Small Enterprise setup.
Table 22 lists the parameters that are used for Medium/Large Enterprise Setup.
Conclusion
This CVD demonstrates how Cisco UCS servers along with the latest EMC VNX storage technologies, form a highly reliable, robust solution for Oracle Siebel CRM implementation. Typical CRM workloads have broad range of demands based on the requirements such as high number of concurrent users, increased database size, complex functionalities etc., and make it harder to implement as well to manage. However as shown in this CVD, such complexities can be easily managed by implementing on Cisco UCS servers which leverages the `Service profile' based approach and hence reduces the TCO and better ROI. Deploying Oracle Siebel CRM on Cisco UCS servers gives better control over the resource utilization and allows administrator to slice and dice the Cisco UCS components based on the need and scale. Based on the tests conducted, Cisco UCS servers provide scalable infrastructure at each tier. However these components are managed centrally using Cisco UCS Manager which is a single point management interface. Cisco UCS Manager can be further integrated with Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) Grid Control for Siebel implementations that are managed using OEM. Further resource usages can be optimized and tiers can be consolidated by implementing Virtualization technologies such as VMWare / Oracle VM, as these technologies complement Cisco UCS features like stateless computing and unified fabric architecture.
Bill of Materials
Table 23 gives details of all the hardware components used in the CVD.
Table 24 gives the details of the software used.
 Feedback
Feedback