Unified CCX Test Bed Description for CSR 11.0(1)
Available Languages
Cisco Unified Contact Center Express Test Bed for Collaboration Systems Release 11.0(1)
First Published: September 10, 2015
Overview
This Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (Unified CCX) test bed is used to complete testing for Cisco Collaboration Systems Release 11.0(1). The test bed is designed to simulate a medium-sized inbound and outbound contact center with local and remote agents. It uses Unified CCX for call treatment and queuing and Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified Communications Manager) for call control.
This test bed is designed to implement and test some of the design considerations and guidelines of the Cisco Collaboration Systems Release 11.x Solution Reference Network Designs (SRND), and Cisco Unified Contact Center Express SRND.
For information about how to install and configure these and other Contact Center components, see Components Installation and Configuration Guides at: Cisco Collaboration Systems for Contact Center Release 11.0(1).
More configuration information for contact center components is available at: Configuration Examples and TechNotes.
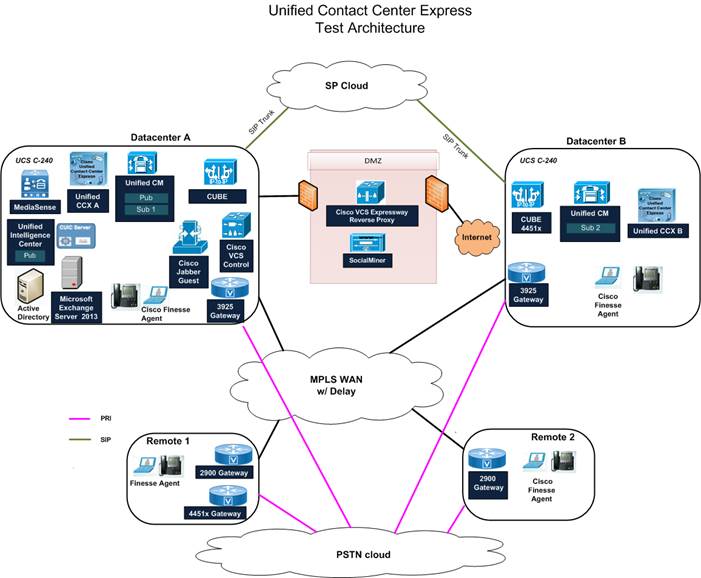
Unified CCX Test Bed and Deployment Architecture
This Unified CCX test bed is designed to replicate a 400 agent inbound and outbound contact center in multiple sites with agents located locally and in remote sites. The test bed design has two data centers separated across a WAN. There is also a standalone Cisco Unified Intelligence Center (Unified Intelligence Center) integrated with Unified CCX for web-based reporting.
The Unified CCX test bed also includes the Cisco Jabber Guest solution which allows customers to call the contact center using a browser. The call is routed through the Cisco VCS Expressway and Cisco VCS Control to the Cisco Jabber Guest server. Cisco Jabber Guest converts the call to SIP and sends it to Unified CCX for further processing.
The entire deployment uses two data centers connected through a high-speed WAN for redundancy. All solution components are designed for high availability (HA) wherever possible. The figure provides an overview of the Unified CCX Test Bed and Deployment Architecture.
For a Visio version of the test bed topology diagram, see Network Topology Diagrams for Contact Center.
Figure 1: Collaboration Systems Release 11.0(1): Unified CCX Test Architecture
General Deployment Options
Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (Unified CCX) provides a secure, highly available, and easy to deploy customer interaction management solution for up to 400 agents. This integrated solution is intended for both formal and informal contact centers.
Unified CCX provides options to address multiple functional areas such as:
■ Inbound voice
■ Outbound campaign
■ Agent email
■ Inbound web chat
■ Cisco Jabber Guest
■ Cisco MediaSense recording
Other components included are:
■ Web-based reports
■ Cisco SocialMiner user licenses for social forum activity monitoring and follow-up
■ Web-based Cisco Finesse desktops
You can deploy these options on Cisco Unified Communications on Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco Unified Communications on Cisco UCS) or any other equivalent specification-based third-party virtual servers with the supported deployment models.
The following features were tested as part of the Unified CCX deployment.
Cisco Finesse
Cisco Finesse is the next generation browser-based agent and supervisor desktop for Unified CCX. Cisco Finesse is an alternative to Cisco Agent Desktop, Cisco Supervisor Desktop, and Cisco Desktop Administrator. Cisco Finesse is available with enhanced and premium license packages and provides typical inbound voice functionality. It supports Unified Communications Manager-based silent monitoring and workflow-based recording with Cisco MediaSense (MediaSense) and Work Force Optimization (WFO).
Unified CCX Home Agent
Extend and Connect allows Unified CCX agents to work from remote locations using devices such as public switched telephone network (PSTN) phones and private branch exchange (PBX) devices. Agents are configured with a Computer Telephony Interface (CTI) remote device (instead of a physical phone). Agents’ PCs have Cisco Jabber (Jabber) installed in Extend mode. The agents can set their phone devices as the agent phone through the Jabber interface.
To reduce media setup time and enhance caller experience, a persistent connection call is placed to the agent's phone device, which the agent should not disconnect. Routed calls are delivered to the agent seamlessly over the persistent call. You can configure it so the agent hears a notification when the persistent connection call is established and a separate notification when each customer care call is delivered.
Unified CCX Multisession Web Chat
Unified CCX Premium provides the facility for users to start a chat session with the agent from a website, typically the public website of the organization. Unified CCX provides separate agent and supervisor web applications.
Unified CCX Multisession Web Chat allows a Cisco Finesse Agent to take voice calls and up to five customer chat requests.
Unified CCX Agent Email
Unified CCX allows email contacts to be routed to agents based on the email addresses to which they are sent by the customers. Finesse Agent Email feature uses skill-based routing and last-agent email routing. Cisco Finesse provides a common chat and email state, separate from voice state. Blending ensures that agents can handle voice, email, and chat contacts from the same desktop. Emails are routed only to agents that are assigned to at least one Email CSQ.
Unified CCX Predictive and Progressive Agent Outbound
The outbound feature provides outbound dialing functionality in addition to existing Unified CCX inbound capabilities. This feature allows agents who are not busy with inbound calls to handle outbound calls.
With the Outbound feature, Unified CCX places customer calls using the Unified Communications Manager.
Agent Predictive and Progressive Dialer leverages the call control and Call Progress Analysis (CPA) from SIP gateway. The SIP gateway performs call progressive analysis of the call and informs the outcome of the call to Unified CCX. All the dialed contacts, which are live voice, are connected to an agent and the remaining calls are disconnected.
Unified Communications Manager-Based MediaSense Recording in Unified CCX
The on-demand Unified CCX MediaSense recording feature allows calls to be recorded on a MediaSense server for all Unified CCX Cisco Finesse agents in a team.
Standalone Integration of Unified Intelligence Center with Unified CCX
Unified Intelligence Center is a web-based reporting application that provides historical and live data reports. You can perform the following functions:
■ Create custom queries to obtain specific data.
■ Allow different groups of people to view specific data based on their function.
■ Customize the visual presentation of the reports.
■ Customize the data that is presented in the reports.
44XX Gateway Support
The Cisco 4451x Router runs on IOS-XE Software. The Cisco IOS-XE Software is designed to provide modular packaging, feature velocity, and powerful resiliency.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation at: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html.
Subscribe to What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, as an RSS feed and deliver content directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service.
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies are considered un-Controlled copies and the original on-line version should be referred to for latest version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on the Cisco website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
© 2015 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback